Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Evolution theories
Mains level: Darwin’s theory of evolution, exclusion form school textbooks and concerns
Central Idea
- The recent exclusion of Darwin’s theory of evolution from Indian school and college curricula has prompted concerns among scientists and educators, as it is one of the most firmly established theories in science that explains the origin of all forms of life and rescues the explanation from the belief in an intelligent designer.
What is Darwin’s theory of evolution?
Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution is one of the most influential scientific theories ever proposed. The main ideas behind Darwin’s theory of evolution include:
- Variation: Within a population, there is variation in traits among individuals.
- Inheritance: Some of these traits are passed on from parents to offspring.
- Overproduction: Most populations produce more offspring than can survive to maturity.
- Natural selection: Individuals with traits that are advantageous for survival and reproduction in their particular environment are more likely to survive and pass on their traits to their offspring, while those with less advantageous traits are less likely to survive and reproduce.
- Adaptation: Over time, the frequency of advantageous traits in a population will increase, resulting in a better match between the organisms and their environment, known as adaptation.
- Common descent: All living organisms share a common ancestor that lived in the distant past.
Facts for prelims: Scientists and theories
| Scientist | Theory | Key Points |
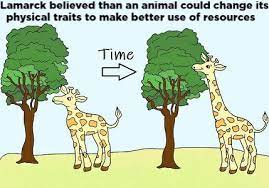
| Jean-Baptiste Lamarck | Theory of Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics | Organisms change and evolve during their lifetimes based on the environmental needs, and these changes can be passed on to their offspring. For example, giraffes developed longer necks by stretching their necks to reach higher branches, and these longer necks were passed on to their offspring. |
| Thomas Malthus | Theory of Population | Populations tend to increase faster than the food supply, leading to competition for resources. Only the individuals with advantageous traits survive, while others perish. This concept of “survival of the fittest” became an important part of Darwin’s theory. |
| Charles Darwin | Theory of Natural Selection | Organisms with advantageous traits have a greater chance of surviving and reproducing, passing on those traits to their offspring. Over time, this leads to the development of new species through the process of speciation. Darwin’s theory also emphasized the importance of variation, competition, and adaptation in the evolutionary process. |
| Alfred Russel Wallace | Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection | Similar to Darwin’s theory, Wallace’s theory emphasized the role of natural selection in the development of new species. However, Wallace also proposed that natural selection could result in the divergence of species into separate branches, which could eventually become new genera or families. |
| Hugo de Vries | Mutation Theory | Mutations, or sudden genetic changes, are the driving force behind evolution rather than gradual changes over time. De Vries also proposed the concept of “species-polymerism”, where multiple species could arise from a single ancestral species through mutations. |
| Stephen Jay Gould | Theory of Punctuated Equilibrium | Evolutionary change occurs in rapid bursts (punctuations) followed by long periods of stability (equilibrium). This theory challenges the traditional view of evolution as a slow, gradual process. Gould also emphasized the role of contingency or chance events in shaping evolutionary history. |
Why must students and teachers in school concern themselves with Darwin’s theory?
- Understanding the origin of human beings and other forms of life: Darwin’s theory of evolution is one of the most firmly established theories in science that explains the origin of human beings and all other forms of life in the world.
- Challenging the belief in an intelligent designer: Darwin’s theory rescues the explanation of the origin of life from the belief that an ‘intelligent designer’ (read: god) built them the way they are and put them in their place.
- Encouraging critical inquiry and embracing critique: The teaching of Darwin’s theory offers possibilities of confronting science’s own troubled history and requires caution alongside curiosity, creativity and imagination.
- Understanding the historical and contemporary world of science: The teaching of Darwin’s theory can help students understand that science is rarely the story of a lone man, and it is shaped by the social and cultural beliefs of its times.
- Enhancing scientific literacy: Understanding Darwin’s theory of evolution is crucial for enhancing scientific literacy, as it is an essential component of biology and a cornerstone of modern science.
Criticisms: Darwin’s theory of evolution
- Lack of transitional fossils: Some critics argue that there is a lack of transitional fossils, which are intermediate forms of species between ancestral and descendant forms. They claim that the absence of such fossils undermines the validity of the theory of evolution.
- Incomplete explanation of variation: While Darwin’s theory of natural selection explains how variation arises in a population, it does not fully explain the source of the variation. Some critics argue that the theory does not account for genetic mutations or other mechanisms that can generate variation.
- Lack of empirical evidence for macroevolution: While the theory of evolution is well-supported by empirical evidence for microevolution (small-scale changes within a species), critics argue that there is insufficient empirical evidence to support macroevolution (large-scale changes between species).
- The origin of life: Critics argue that Darwin’s theory does not explain how life originated in the first place.
- Complexity of living organisms: Critics argue that the complexity of living organisms cannot be explained solely by natural selection and that there must be some other explanation for the diversity and complexity of life.
Conclusion
- Science is a messy affair that requires caution alongside curiosity, creativity, and imagination. The teaching of Darwin’s theory must offer possibilities of confrontation without underplaying its strengths. While Darwin must remain in our textbooks, the way it is taught must change to include other influences that have shaped the theory and the consequent use of the theory by others and himself.
Mains Question
Q. What is Darwin’s theory of evolution? As the theory is being dropped from the school textbooks, discuss why must students and teachers in school concern themselves with Darwin’s theory?
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024