Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: What is Ballast Water?
Mains level: Serious concern due to Ballast Water;
Why in the News?
The TN Water Resources Department (WRD) has informed the National Green Tribunal that it has requested ₹160 crore from Kamarajar Port in Ennore, Tamil Nadu, to address the removal of invasive mussels along the coast near the port.
- The WRD has accused Kamarajar Port of being primarily responsible for the spread of this invasive species due to its failure to regulate ballast water from ships.
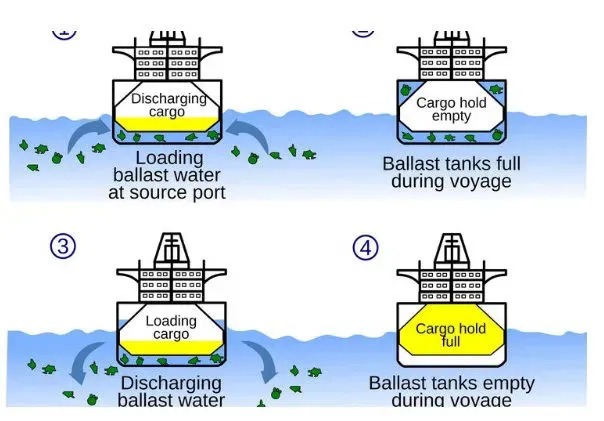
What is Ballast Water?
- Ballast water is fresh or saltwater held in the ballast tanks of ships. It is used to provide stability and maneuverability during a voyage, especially when a ship is not carrying enough cargo or when additional stability is required due to rough seas.
- Ballast water can carry a variety of biological materials, including bacteria, microbes, and small invertebrates. When discharged at a new location, this water can introduce non-native species into local ecosystems, potentially leading to ecological imbalances.
How Serious is the Problem?
- Invasive Species in India: Scientists have recorded nearly 30 invasive species entering Indian waters through ship ballast water, with the charru mussel (Mytella strigata) being one of the most harmful. This species has replaced native species in critical habitats like Pulicat Lake in Tamil Nadu.
- Ecological Impact: The introduction of invasive species can disrupt local ecosystems, outcompete native organisms, and significantly affect biodiversity. The charru mussel has a high survival rate and prolific reproduction, exacerbating its impact on marine environments.
- Economic Consequences: The proliferation of invasive species can hinder fishing activities and affect the livelihoods of local communities dependent on marine resources.
What are Global Regulations?
- Ballast Water Management (BWM) Convention: The International Maritime Organization (IMO) adopted the BWM Convention, which came into force in 2017. This convention aims to prevent the spread of harmful aquatic organisms and pathogens through ballast water.
- Under the BWM Convention, ships must manage their ballast water to ensure that aquatic organisms and pathogens are removed or rendered harmless before discharge.
- Compliance: Countries like Australia and New Zealand have stringent regulations to prevent ballast water from damaging their marine ecosystems, including rigorous checks of ballast water management systems.
What is India’s Position?
- As of July 2023, India has not signed the BWM Convention, meaning there are no obligations for ships calling at Indian ports to comply with its regulations. This lack of participation raises concerns about the unchecked discharge of ballast water.
- While other maritime regulations apply in Indian ports but the discharge of ballast water is not subject to checks or regulations, leading to potential ecological risks.
Way forward:
- Adopt and Implement the BWM Convention: India should consider ratifying the Ballast Water Management (BWM) Convention to align with international standards.
- Strengthen Domestic Regulations and Awareness: Even before ratifying the BWM Convention, India can introduce national legislation to regulate ballast water discharge in its ports.
Mains PYQ:
Q How does biodiversity vary in India? How is the Biological Diversity Act,2002 helpful in conservation of flora and fauna? (2018)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024