Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Sir Creek
Mains level: Disputes over Sir Creek
Former Pakistan Minister recalls plan for Sir Creek pact.
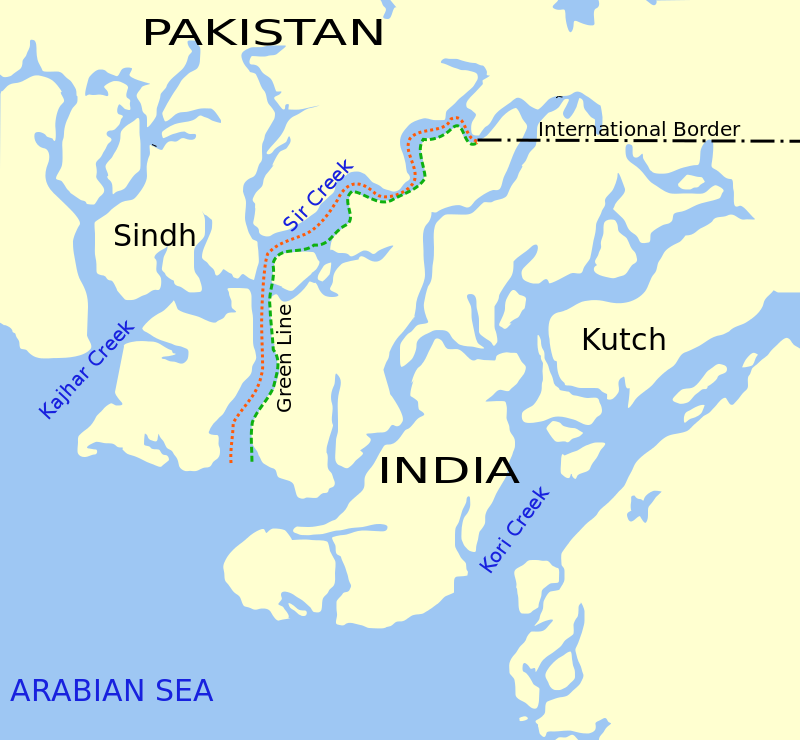
Sir Creek
- Sir Creek is a 96-km strip of water disputed between India and Pakistan in the Rann of Kutch marshlands. Originally named Ban Ganga, Sir Creek is named after a British representative.
- The Creek opens up in the Arabian Sea and roughly divides the Kutch region of Gujarat from the Sindh Province of Pakistan.
What’s the dispute?
- The dispute lies in the interpretation of the maritime boundary line between Kutch and Sindh. Before India’s independence, the provincial region was a part of the Bombay Presidency of British India.
- But after India’s independence in 1947, Sindh became a part of Pakistan while Kutch remained a part of India.
- Pakistan claims the entire creek as per paragraphs 9 and 10 of the Bombay Government Resolution of 1914 signed between then the Government of Sindh and Rao Maharaj of Kutch.
- The resolution, which demarcated the boundaries between the two territories, included the creek as part of Sindh, thus setting the boundary as the eastern flank of the creek popularly known as Green Line.
- But India claims that the boundary lies mid-channel as depicted in another map drawn in 1925, and implemented by the installation of mid-channel pillars back in 1924.
The Genesis
- The marshland of Sir Creek first became disputed in the early 20th century when the Rao of Kutch and the Chief Commissioner of Sindh Province of British India, due to different perceptions of the boundaries, laid claims over the creek.
- The case was taken up by then Government of Bombay, which conducted a survey and mandated its verdict in 1914.
- This verdict has two contradictory paragraphs, which make the India and Pakistan contenders on the same issue.
- Paragraph 9 of this verdict states that the boundary between Kutch and Sindh lies ‘to the east of the Creek,’ (Green Line) which effectively implied that the creek belonged to Sindh and, therefore, to Pakistan.
- On the other hand, Paragraph 10 states that since Sir Creek is navigable most of the year.
- According to international law and the Thalweg principle, a boundary can only be fixed in the middle of the navigable channel, which meant that it has be divided between Sindh and Kutch, and thereby India and Pakistan.
- India has used this para to consistently argue that the boundary needs to be fixed in the middle of the creek.
- Pakistan, however, claims that Sir Creek isn’t navigable but India claims that since it’s navigable in high tide, the boundary should be drawn from the mid channel.
What’s the importance of Sir Creek?
- Apart from the strategic location, Sir Creek’s core importance is fishing resources. Sir Creek is considered to be among the largest fishing grounds in Asia.
- Another vital reason for two countries locking horns over this creek is the possible presence of great oil and gas concentration under the sea, which are currently unexploited thanks to the impending deadlock on the issue.
UNCLOS supports India’s stand
- If Thalweg principle is to be upheld, Pakistan would lose a considerable portion of the territory that was historically part of the province of Sindh.
- Acceding to India’s stance would mean shifting of the land/sea terminus point several kilometres to the detriment of Pakistan, leading in turn to a loss of several thousand square kilometres of its Exclusive Economic Zone under the United Nations Convention on Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
War in 1965 and tribunal
- After the 1965 war, British Prime Minister Harold Wilson successfully persuaded both countries to end hostilities and set up a tribunal to resolve the dispute.
- The verdict of the tribunal came in 1968 which saw Pakistan getting 10% of its claim of 9,000 km (3,500 sq. miles).
- Since 1969, 12 rounds of talks have been held over the issue of Sir Creek, but both sides have denied reaching any solution.
- The region fell amid tensions in 1999 after the Pakistan Navy shot down a MiG-21 fighter plane, but the last rounds of talks were held in 2012. Since then it’s been status quo.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
