From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
Mains level: safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products
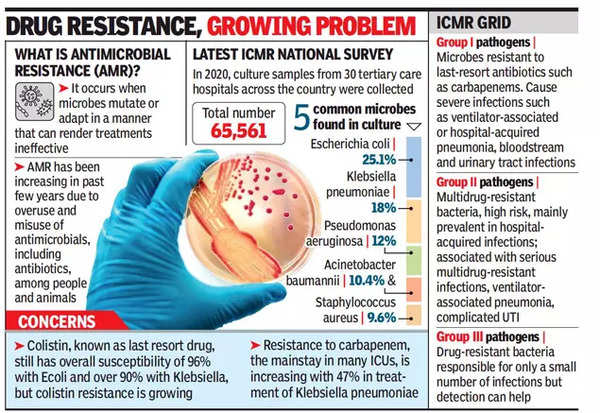
Central idea
The study reveals a startling prevalence of unapproved and banned Fixed Dose Combinations (FDCs) of antibiotics in India, posing risks of antimicrobial resistance. The pharmaceutical industry’s exploitation of FDCs to evade regulations, coupled with regulatory inefficiencies, calls for urgent interventions to safeguard public health
Key Highlights:
- Alarming Prevalence: In 2020, 60.5% of antibiotics in India were unapproved FDCs, with an additional 9.9% banned, raising concerns about antimicrobial resistance.
- Patient Compliance vs. Risks: FDCs, aimed at improving patient adherence, pose risks due to potential interactions between combined drugs, necessitating a stringent approval process.
- Pharmaceutical Industry’s Strategy: Exploitation of FDCs allows the industry to evade drug price regulations, contributing to the proliferation of irrational combinations.
Key Challenges:
- Regulatory Framework Inefficiency: Continued sale of unapproved FDCs highlights regulatory inefficiency, allowing non-compliance despite existing legal provisions.
- Reactive Regulatory Measures: Reliance on Section 26A orders reveals a reactive rather than proactive regulatory approach, indicating systemic challenges.
Key Terms:
- Fixed Dose Combination (FDC): Combinations of multiple drugs in a single dosage form, potentially affecting drug interactions and therapeutic efficacy.
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): The ability of microorganisms to resist the effects of medications, posing a global health threat.
Key Phrases:
- Pharmaceutical Industry’s Exploitation: The strategic use of FDCs to avoid regulatory scrutiny undermines the integrity of drug pricing and quality.
- Ineffectiveness of Regulatory Measures: Despite legal provisions, the regulatory system relies on reactive prohibitions rather than proactive prevention.
Key Quotes:
- “Unapproved FDCs may contribute to the AMR problem in India.”
- “The pharmaceutical industry gets to provide its own standards for government testing of FDCs.”
Key Statements:
- Extent of the Issue: The study underscores the alarming prevalence of unapproved and banned FDCs in India, emphasizing the urgent need for regulatory intervention.
- Industry Motives: The article critically examines the pharmaceutical industry’s profit-driven motives, exposing the imbalance between pseudo-innovation for profit and genuine drug development.
- Regulatory Challenges: Scrutiny of regulatory challenges and legal inconsistencies indicates a systemic failure in ensuring the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products.
Key Examples and References:
- Academic Study: Reference to the academic study published in the Journal of Pharmaceutical Policy and Practice (2023) highlighting the extent of unapproved FDCs.
- Historical Context: Tracing the issue back to 1978 and subsequent regulatory amendments provides context to the ongoing challenges.
Critical Analysis:
- Industry Practices: The article critically examines the pharmaceutical industry’s motives, highlighting the imbalance between pseudo-innovation for profit and genuine drug development.
- Regulatory Challenges: Scrutiny of regulatory challenges and legal inconsistencies indicates a systemic failure in ensuring the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products.
Way Forward:
- Urgent Regulatory Actions: Emphasizes the need for regulatory actions to address the menace of unapproved and banned FDCs, preventing potential contributions to antimicrobial resistance.
- Proactive Regulatory Framework: Calls for a proactive regulatory framework that prioritizes public health over industry interests and plugs existing legal loopholes.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
