The James Webb Space Telescope, NASA’s largest space science telescope ever constructed, is scheduled to be sent into orbit in December.
James Webb Space Telescope (JWST)
- It is a space telescope being jointly developed by NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA).
- It has taken 30 years and $10bn to develop, and is being described as one of the grand scientific endeavors of the 21st Century.
What is the goal of this telescope?
- The telescope will be able to see just about anything in the sky.
- However, it has one overriding objective – to see the light coming from the very first stars to shine in the Universe.
- These pioneer stars are thought to have switched on about 100-200 million years after the Big Bang, or a little over 13.5 billion years ago.
- Webb will be picking out groupings of these stars.
- They are so far away their light – even though it moves at 300,000km per second – will have taken billions of years to travel the cosmos.
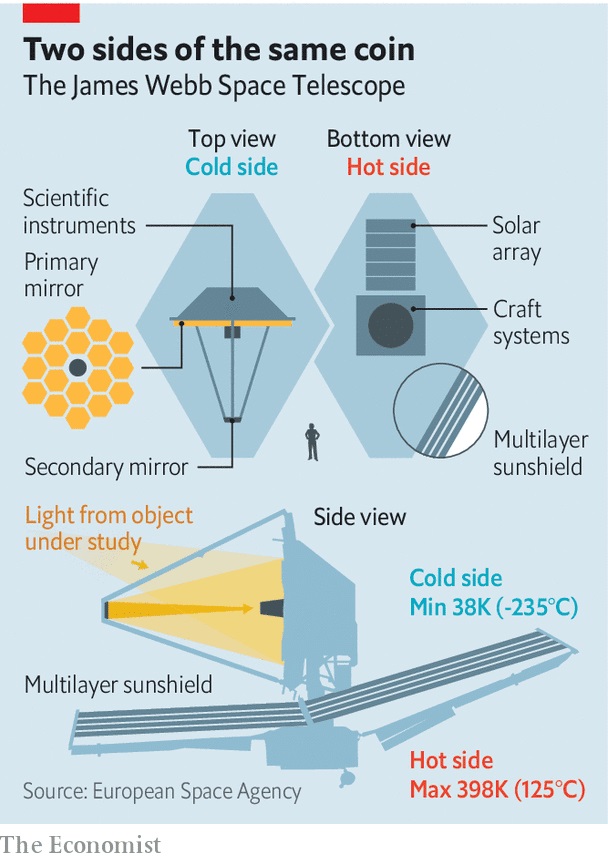
JWST mirror

- One of the most important objects it will carry is a large mirror which will help collect light from the objects being observed.
- The primary mirror is made of 18 hexagonal-shaped mirror segments — each 1.32 metre in diameter — stitched together in a honeycomb pattern.
- The primary mirror is a technological marvel.
- The lightweight mirrors, coatings, actuators and mechanisms, electronics, and thermal blankets when fully deployed form a single precise mirror that is truly remarkable.
- Each mirror segment weighs approximately 20 kilograms and is made from beryllium.
Why beryllium?
- NASA explains that beryllium was used as it is both strong and light.
- Beryllium is very strong for its weight and is good at holding its shape across a range of temperatures. Beryllium is a good conductor of electricity and heat and is not magnetic.
- Because it is light and strong, beryllium is often used to build parts for supersonic airplanes and the Space Shuttle.
- It added that special care was taken when working with beryllium because it is unhealthy to breathe in or swallow beryllium dust.
So, it does not have gold?
- After the beryllium mirror segments were polished a thin coating of gold was applied to it. Gold helps improve the mirror’s reflection of infrared light.
- The gold was coated using a technique called vacuum vapour deposition.
- The mirrors are kept inside a vacuum chamber and a small quantity of gold is vapourised and deposited on the mirror.
- The thickness of the gold is just 100 nanometers. So less than 50 grams of gold was used for the entire mirror.
- A thin layer of glass was also deposited on top of the gold layer to protect it from scratches.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
