Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: About CITES;
Mains level: The Kaza Summit and its objectives;
Why in the news?
At the KAZA 2024 Summit in Livingstone, Zambia, delegates reiterated the urge for member states to withdraw from CITES because they seek approval to trade their plentiful ivory and wildlife items.
About the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES):
|
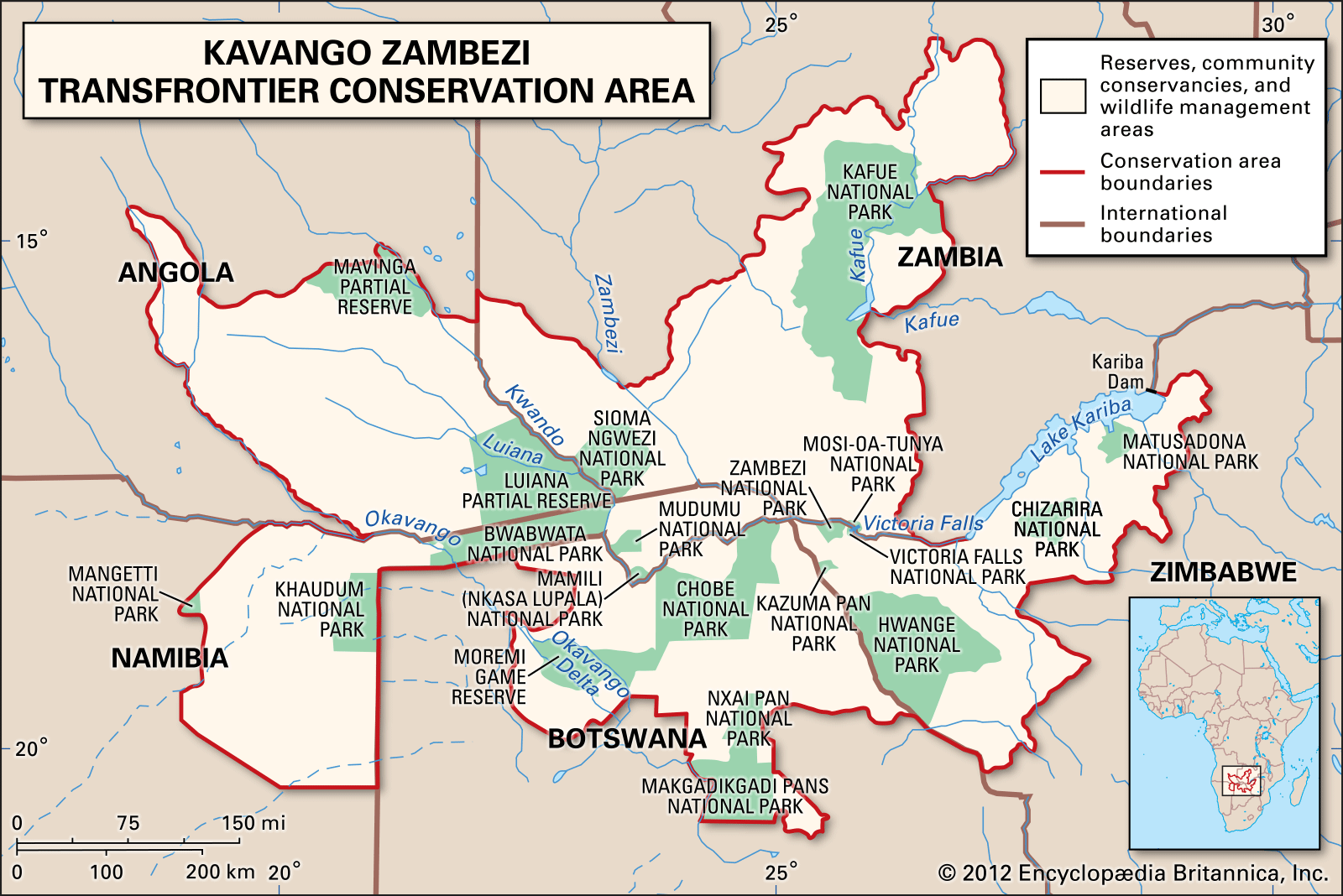
What is Kavango-Zambezi Trans-Frontier Conservation Area (KAZA-TFCA)?
- The Kavango-Zambezi Trans-Frontier Conservation Area (KAZA-TFCA) spans 520,000 square kilometers. It covers parts of five southern African nations. These nations are Angola, Botswana, Namibia, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
- The area is centered around the Okavango and Zambezi river basins. The combined elephant population in these nations represents over two-thirds of Africa’s total, estimated at around 450,000.
- Botswana has the largest elephant population within the region, with 132,000 elephants. Zimbabwe follows with 100,000 elephants.
Key Objectives of KAZA 2024 Summit :
- Conservation: Promote the sustainable management and conservation of wildlife across the five member states: Angola, Botswana, Namibia, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
- Economic Benefit: To explore ways to monetize abundant wildlife resources, particularly elephants, to fund conservation efforts and benefit local economies.
Dominant Issues:
- At the 19th meeting of the CITES conference in Panama in 2022, KAZA states and five other southern African countries advocated for opening up trade in ivory and elephant products.
- Southern African countries, including those in the KAZA region, argue that their large elephant populations contribute to habitat loss and human-wildlife conflict.
- Despite repeated requests, CITES delegates rejected the proposal, leading to frustration among African countries.
- Ten countries, including KAZA states and others like Eswatini, Lesotho, Mozambique, South Africa, and Tanzania, declared a dispute with CITES. They criticized CITES for straying from its founding principles and adopting ideologies over science-based conservation strategies.
Way forward:
- Lobbying for Change: Advocacy for a more equitable and science-based approach to wildlife trade regulations within international frameworks like CITES.
- Regional Cooperation: Enhance collaboration among member states to develop joint conservation strategies and share best practices for managing human-wildlife conflicts.
- Diversification of Revenue Streams: Explore alternative sources of funding for conservation efforts, such as ecotourism, carbon credits, and sustainable agriculture.
Mains PYQ:
Q How does biodiversity vary in India? How is the Biological Diversity Act, 2002 helpful in the conservation of flora and fauna? (250 Words, 15 Marks) (UPSC IAS/2018)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
