From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: TFR, Demographic Dividends
Mains level: Population explosion in India
When this century ends, India may no longer be a country of a billion, says a projection that appears in the online edition of the Lancet. The reference forecasts for China and India peaked before 2050 and both countries thereafter had steep declining trajectories.
Try this question from CSP 2011:
Q.India is regarded as a country with ‘Demographic Dividend’. This is due to
(a) Its high population in the age group below 15 years
(b) Its high population in the age group of 15-64 years
(c) Its high population in the age group above 65 years
(d) Its high total population
World to see the peak
- A new analysis published in The Lancet has projected that the world population will peak much earlier than previously estimated.
- It projects the peak at 9.73 billion in 2064, which is 36 years earlier than the 11 billion peaks projected for 2100 by last year’s UN report World Population Prospects.
- For 2100, the new report projects a decline to 8.79 billion from the 2064 peak.
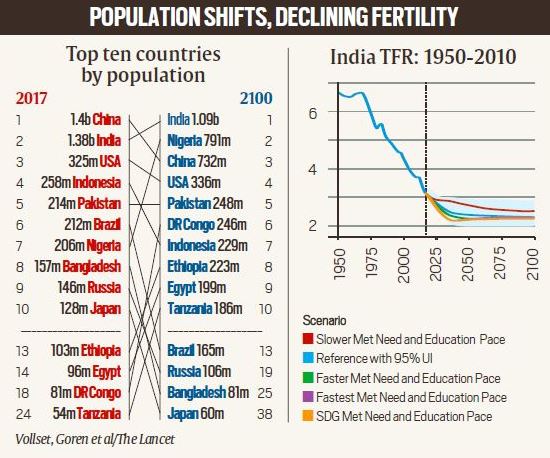
5 most populated countries
- The five largest countries in 2100 are projected to be India, Nigeria, China, the U.S. and Pakistan.
- However, these forecasts showed different future trajectories between countries.
- Nigeria is forecast to have continued population growth through 2100 and was expected to be the second-most populous country by then.
Predictions on India’s population
- For India, the report projects a peak population of 1.6 billion in 2048, up from 1.38 billion in 2017.
- By 2100, the population is projected to decline by 32% to 1.09 billion.
- However, meeting UN Sustainable Goal Development targets, the peak would be earlier and see a population decline to 929 million.
- Conventional wisdom is that though a decline in population is expected, it is expected to begin only around 2046.
- The fall according to the latest 2019 assessment by the UNDP calculation, is expected to see India’s population settle at a little over 1.4 billion.
Reasons for fall
- The sharper fall is due to the assumption that all women globally will have much higher access to contraception and education.
- This scenario will lead to a sharper reduction in the Total Fertility Rate, a metric that shows on average how many children a woman must have to keep replenishing the population.
- A TFR is lower than 2.1leads to a decline in a country’s population.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024


?