Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Maternal Mortality , key trends
Mains level: Institutional birth in India
Kerala has yet again emerged on top when it comes to maternal and child health, with the State recording the lowest Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) of 30 (per one lakh live births) in the country.
What is Maternal Mortality?
- Maternal mortality refers to deaths due to complications from pregnancy or childbirth.
- The maternal mortality ratio (MMR) is defined as the number of maternal deaths during a given time period per 100,000 live births during the same time period.
- It depicts the risk of maternal death relative to the number of live births and essentially captures the risk of death in a single pregnancy or a single live birth.
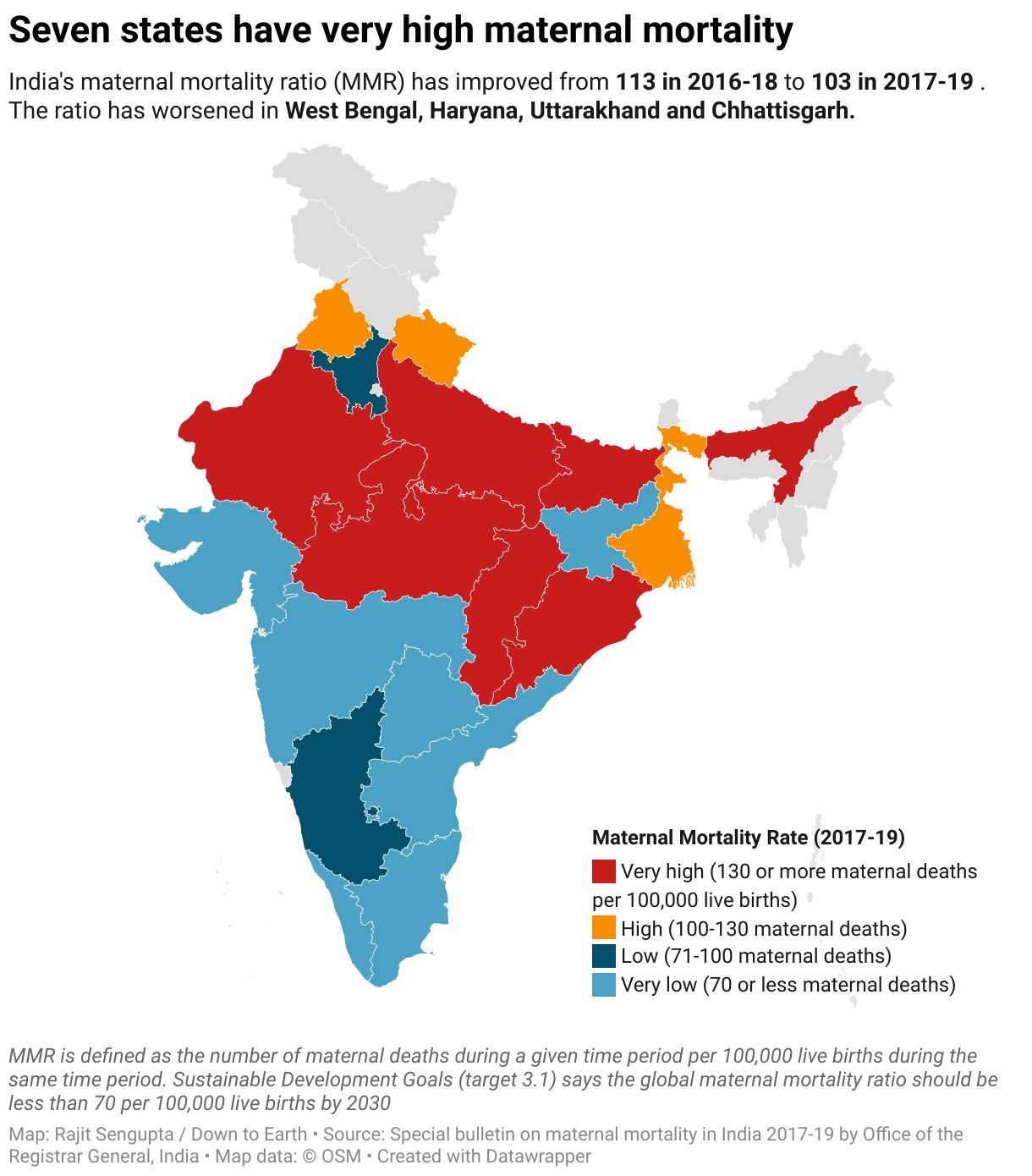
Trends in India
- India’s maternal mortality ratio (MMR) has improved to 103 in 2017-19, from 113 in 2016-18.
- Seven Indian states have very high maternal mortality. These are Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Bihar, Odisha and Assam.
- The MMR is ‘high’ in Punjab, Uttarakhand and West Bengal. This means 100-130 maternal deaths per 100,000 live births.
- It is ‘low’ in Haryana and Karnataka.
- The states of Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan and Bihar have seen the most drop in MMR.
- West Bengal, Haryana, Uttarakhand and Chhattisgarh have recorded an increase in MMR over the last survey.
Various determinants of maternal health in India

UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
