Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Methane emission
Why in the News?
The European Union introduced a new regulation in May 2024 requiring fossil fuel companies to routinely measure, report, and reduce methane emissions.
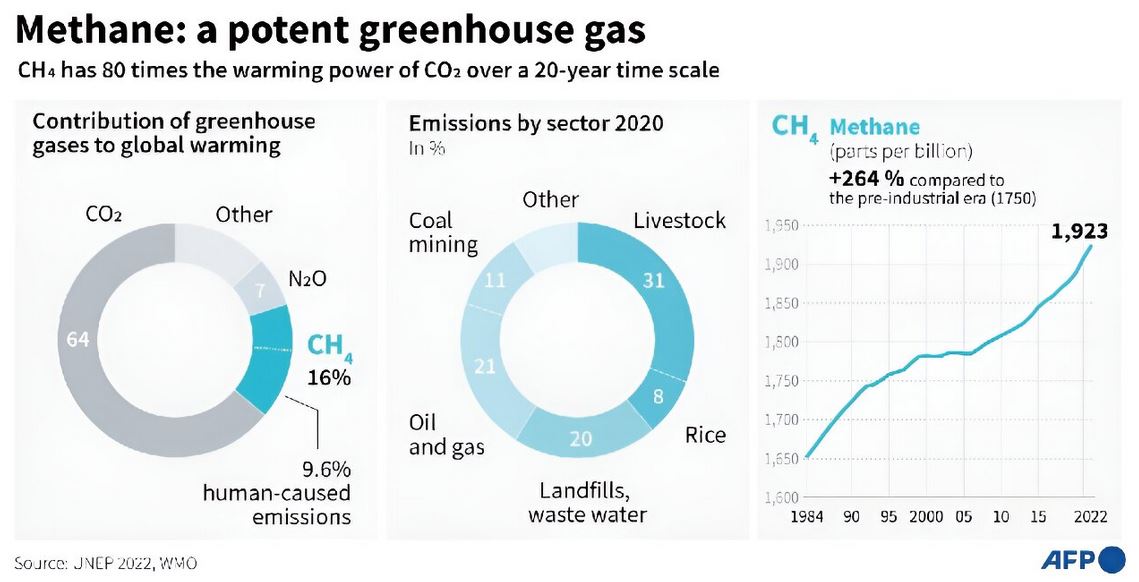
About Methane Emissions:
| Details | |
| Nature | Colorless, Odourless.
Considered a short-lived climate pollutant due to its shorter atmospheric lifetime compared to CO2. |
| Global Warming Potential (GWP) | 80 times more potent than carbon dioxide over a short term. GWP100: 28 (over 100 years)Accounts for approximately 30% of global warming. |
| Atmospheric Lifetime | Breaks down in about 12 years; shorter-lived compared to CO2. |
| Major Sources | – Cattle farming: 32% of human-caused methane emissions (includes manure and enteric fermentation) – Landfills: Approximately 20% – Wastewater treatment: Around 8% – Rice cultivation: About 10% – Industrial processes: Varied but significant |
| Natural Non-Human Sources | Includes wetlands and permafrost, which release methane through natural processes. |
| Impact Compared to CO2 | Traps 84 times as much heat as CO2 over a 20-year period. CO2 has a longer-term warming effect but is less potent. |
| Key Initiatives | Global Methane Pledge: Launched at UN COP26, signed by over 90 countries, led by the US and EU.
India did not sign. |
PYQ:[2019] Consider the following:
Which of the above are released into atmosphere due to the burning of crop/biomass residue? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2, 3 and 4 only (c) 1 and 4 only (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
