The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has cleared a rail project in the Western Ghats spread across Goa and Karnataka, which can endanger its wildlife.

About the project:
- The project is the doubling the track of Hospet-Hubballi-Londa-Vasco Da Gama railway line by the Rail Vikas Nigam Ltd (RVNL).
- It involves doubling of the 353-kilometre-long railway track in Karnataka and Goa passing through the Western Ghats.
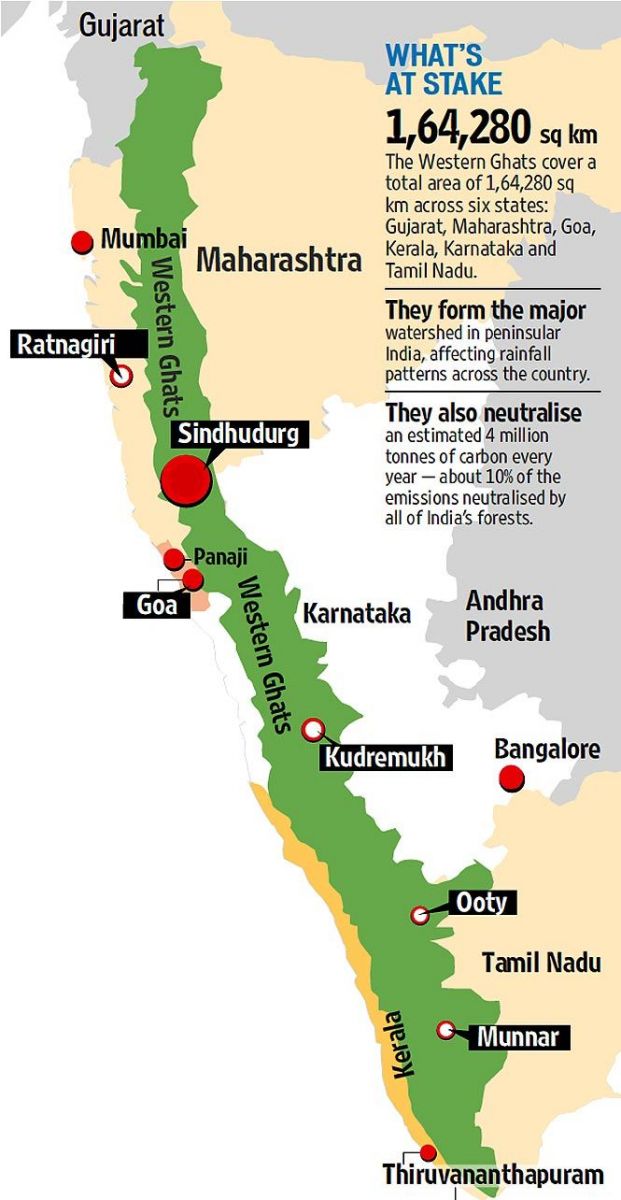
Western Ghats:
- The Western Ghats mountain range runs along the western side of India.
- The Ghats are older than the Himalayas.
- The range is known as Sahyadri in Maharashtra and Karnataka.
- It runs, about 1600 km, North to South, along the western edge of the Deccan Plateau.
- It originates near the border of Gujarat and Maharashtra, and runs through the states of Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu and Kerala, finally ending at Kanyakumari.
- These hills form the catchment area for complex riverine drainage systems that drain almost 40% of India.
- Height:
- The average elevation is about 1,200 m.
- Anaimudi (2695 m), is the highest peak of the Western Ghats, situated in Eravikulam National Park, Kerala.
- Rocks found:
- Basalt is the predominant rock found in the hills reaching a thickness of 3 km.
- Other rocks: Granite gneiss, metamorphic gneisses with detached occurrences of crystalline limestone, iron ore, dolerites and anorthosites.
- Major gaps in the range:
- Goa Gap between the Maharashtra and Karnataka sections.
- Palghat Gap on the Tamil Nadu and Kerala border between Nilgiri Hills and Anaimalai Hills.
- Recognitions:
- It is one of the eight hottest hotspots of biological diversity in the world.
- In 2012, thirty-nine places in the Western Ghats region have been declared as World Heritage Sites by the UNESCO.
- Flora and Fauna:
- There are at least 139 mammal species.
- It includes the critically endangered Malabar large-spotted civet and the endangered lion-tailed macaque.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024

