Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Unicorns
Mains level: Paper 3- Start-ups in India
Context
As per the Economic Survey 2021-22, India has become the third-largest startup ecosystem in the world after the US and China.
Start-up ecosystem in India
- India attracted huge investment in startups in 2021: Private equity investment was $77 billion, of which $42 billion went to early-stage ventures.
- Every startup where salaries are paid by investors rather than customers is breathlessly rethinking business plans.
How do startups benefit society?
1] Innovation, productivity and job creation:
- The high failure rate of startups is not a problem per se — society only needs a few successes to harness the gains of innovation, productivity and job creation.
- A new book, The Power Law makes the case that startup investing is unlike public market investing.
- He suggests public markets follow a “normal” distribution like human height — most people cluster around the average with a few exceptionally low or high.
- But venture investments follow a “power law” of distribution, that is, most go to zero but the tiny number that succeeds more than compensate for the losses or mediocrity of the many.
2] Losses caused by startups are not passed on to society
- Startups don’t socialise their losses, Corporate bank loans expanded from Rs 18 lakh crore in 2008 to Rs 54 lakh crore in 2014.
- Such high corporate bank loans created bad loans that needed many lakh crores of government money to recapitalise nationalised banks.
- This money was diverted from government spending on healthcare, education and defence.
- The current venture capital binge will also create many write-offs but this cost will fall on consenting adults with broad shoulders — foreign institutions, angel investors and entrepreneurs with successful previous exits.
3] Startups will solve real problems for Indians:
- Ending our poverty needs higher productivity regions, cities, sectors, firms and individuals.
- A modern state is a welfare state that does less commercially so it can do more socially.
- It needs allies in reimagining financial inclusion, supply chains, distribution logistics, employability, retail, transport, media, healthcare, agriculture and much else.
- Many of our startups shall redeem their pledge to solve these problems “not wholly or in full measure, but very substantially”.
Three issues related to startups
- 1] Fiscal and monetary policy normalisation: The global capital supply fuelling startup funding faces challenges from fiscal and monetary policy normalisation: The rate-sensitive two-year US government bond recently touched a 1.6 per cent yield after being at 0.4 per cent as recently as November — because the risk-free return cannot be return-free-risk forever.
- Investors are returning to weighing financial sustainability and capital efficiency along with addressable markets.
- 2] Excesses: This explosive startup funding has created excesses.
- 3] A different approach of public markets: Private markets are not only delaying IPOs — Amazon went public within three years of starting with less than half the value of a unicorn — but unicorn IPOs’ underperformance suggests that public markets have a different calibration.
Conclusion
The few startups that survive will raise India’s soft power and prosperity by using improbable ideas to solve impossible problems. What we need is to ensure the policy environment for the startups to boom.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Global Environmental Change (GEC) programme
Mains level: Paper 2- Water management
Context
The Global Water System Project, which was launched in 2003 as a joint initiative of the Earth System Science Partnership (ESSP) and Global Environmental Change (GEC) programme, epitomises global concern about the human-induced transformation of fresh water and its impact on the earth system and society.
Valuation of water
- It is globally estimated that the gap between demand for and supply of fresh water may reach up to 40% by 2030 if present practices continue.
- SDG 6: The formation of the 2030 Water Resource Group in 2008, at the instance of the World Economic Forum, and the World Bank’s promotion of the group’s activity since 2018, is in recognition of this problem and to help achieve the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) on water availability and sanitation for all by 2030 (SDG 6).
- The latest UN World Water Development Report, 2021, titled ‘Valuing Water’, has laid stress on the proper valuation of water by considering five interrelated perspectives: water sources; water infrastructure; water services; water as an input to production and socio-economic development, and socio-cultural values of water.
Need for hydro-social cycle approach
- Designing a comprehensive mix of divergent views about water along with ecological and environmental issues held by stakeholder groups is necessary.
- In this context, a hydro-social cycle approach provides an appropriate framework.
- It repositions the natural hydrological cycle in a human-nature interactive structure and considers water and society as part of a historical and relational-dialectical process.
- The anthropogenic factors directly influencing a freshwater system are the engineering of river channels, irrigation and other consumptive use of water, widespread land use/land cover change, change in an aquatic habitat, and point and non-point source pollution affecting water quality.
The intra- and inter-basin transfer (IBT) of water
- IBT is a major hydrological intervention to rectify the imbalance in water availability due to naturally prevailing unequal distribution of water resources within a given territory.
- There are several IBT initiatives across the world.
- The National River Linking Project of India is one of those under construction.
- Based on a multi-country case study analysis, the World Wildlife Fund/World Wide Fund for Nature (2009) has suggested a cautious approach and the necessity to adhere to sustainability principles set out by the World Commission on Dams while taking up IBT projects.
Issues with assumptions, use and management of freshwater resources in India
1] Contestation on concept of the surplus and deficit basin
- The basic premise of IBT is to export water from the surplus basin to a deficit basin.
- However, there is contestation on the concept of the surplus and deficit basin itself as the exercise is substantially hydrological.
- Besides this, rainfall in many surplus basins has been reported as declining.
- The status of the surplus basin may alter if these issues are considered.
2] Low capacity utilisation
- There is concern about the present capacity utilisation of water resources created in the country.
- By 2016, India created an irrigation potential for 112 million hectares, but the gross irrigated area was 93 million hectares.
- There is a 19% gap, which is more in the case of canal irrigation.
- In 1950-51, canal irrigation used to contribute 40% of net irrigated area, but by 2014-15, the net irrigated area under canal irrigation came down to less than 24%.
- Groundwater irrigation now covers 62.8% of net irrigated area.
- Low efficiency of irrigation projects: The average water use efficiency of irrigation projects in India is only 38% against 50%-60% in the case of developed countries.
- More water consumption for crops: Even at the crop level we consume more water than the global average.
- Rice and wheat, the two principal crops accounting for more than 75% of agricultural production use 2,850 m 3/tonnes and 1,654 m 3/tonnes of water, respectively, against the global average of 2,291m 3/tonnes and 1,334m 3/ tonnes in the same order.
- The agriculture sector uses a little over 90% of total water use in India.
- And in industrial plants, consumption is 2 times to 3.5 times higher per unit of production of similar plants in other countries.
- Similarly, the domestic sector experiences a 30% to 40% loss of water due to leakage.
3] Low use of greywater
- Grey water is hardly used in our country.
- It is estimated that 55% to 75% of domestic water use turns into greywater depending on its nature of use, people’s habits, climatic conditions, etc.
- At present, the average water consumption in the domestic sector in urban areas is 135 litres to 196 litres a head a day.
- If grey water production in the rural areas is considered it will be a huge amount.
- The discharge of untreated grey water and industrial effluents into freshwater bodies is cause for concern.
- The situation will be further complicated if groundwater is affected.
4] Other issues
- Apart from the inefficient use of water in all sectors, there is also a reduction in natural storage capacity and deterioration in catchment efficiency.
Way forward
- The issues are source sustainability, renovation and maintenance of traditional water harvesting structures, grey water management infrastructure, groundwater recharge, increasing water use efficiency, and reuse of water.
- The axiom that today’s water system is co-evolving and the challenges are mainly management and governance has been globally well accepted.
- It is important to include less predictable variables, revise binary ways of thinking of ‘either or’, and involve non-state actors in decision-making processes.
Conclusion
A hybrid water management system is necessary, where along with professionals and policy makers the individual, a community and society have definite roles in the value chain. The challenge is not to be techno-centric but anthropogenic.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Inland Waterways
Mains level: Innlad water transit and its significance
- Month after setting sail on the Ganga from Patna, a vessel carrying 200 metric tonnes of food grains for the Food Corporation of India (FCI), docked at Guwahati’s Pandu port on the southern bank of the Brahmaputra.
- The occasion is believed to have taken inland water transport, on two of India’s largest river systems, to the future.
Why is a Ganga-Brahmaputra cargo vessel in focus?
- There is nothing unusual about a cargo vessel setting sail from or docking at any river port.
- This has rekindled hope for the inland water transport system which the landlocked northeast depended on heavily before India’s independence in 1947.
Inland water service: A necessity for the NE
- Seamless cargo transportation has been a necessity for the northeast.
- Around Independence, Assam’s per capita income was the highest in the country.
- This was primarily because of access for its tea, timber, coal and oil industries to seaports on the Bay of Bengal via the Brahmaputra and the Barak River (southern Assam) systems.
- Ferry services continued sporadically after 1947 but stopped after the 1965 war with Pakistan, as Bangladesh used to be East Pakistan then.
- The scenario changed after the river routes were cut off and rail and road through the “Chicken’s Neck”, a narrow strip in West Bengal, became costlier alternatives.
- The start of cargo movement through the Indo-Bangladesh Protocol (IBP) route is going to provide the business community a viable, economic and ecological alternative.
How did the water cargo service through Bangladesh come about?
- The resumption of cargo transport service through the waterways in Bangladesh has come at a cost since the Protocol on Inland Water Transit and Trade was signed between the two countries.
- India has invested 80% of ₹305.84 crore to improve the navigability of the two stretches of the IBP (Indo-Bangladesh Protocol) routes — Sirajganj-Daikhowa and Ashuganj-Zakiganj in Bangladesh.
- The seven-year dredging project on these two stretches till 2026 is expected to yield seamless navigation to the north-eastern region.
- With this, the distance between NW1 and NW2 will reduce by almost 1,000 km once the IBP routes are cleared for navigation.
Policy boosts to IWs
- The Government has undertaken the Jal Marg Vikas project with an investment of ₹4,600-crore to augment the capacity of NW1 for sustainable movement of vessels weighing up to 2,000 tonnes.
- Sailors who made the cargo trips possible have had difficulties steering clear of fishing nets and angry fishermen in Bangladesh.
- These hiccups will get sorted out with time.
Why go for IWT?
- Inland Water Transport (IWT) is a fuel-efficient, environment friendly and cost effective mode of transport having potential to supplement the over-burdened rail and congested roads.
- It is a boon where road transport is least feasible.
Back2Basics: Inland Waterways

UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: UPI123Pay
Mains level: UPI payments through feature phones
The Reserve Bank of India has launched a new Unified Payments Interface (UPI) payments solution for feature phone users dubbed ‘UPI123Pay’.
What is UPI?
- UPI is an instant real-time payment system developed by NPCI facilitating inter-bank transactions.
- The interface is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India and works by instantly transferring funds between two bank accounts on a mobile platform.
What is UPI123Pay?
- UPI ‘123PAY’ is a three-step method to initiate and execute services for users which will work on simple phones.
- It will allow customers to use feature phones for almost all transactions except scan and pay.
- It doesn’t need an internet connection for transactions. Customers have to link their bank account with feature phones to use this facility.
- Feature phone users will now be able to undertake a host of transactions based on four technology alternatives.
- They include calling an IVR (interactive voice response) number, app functionality in feature phones, missed call-based approach and also proximity sound-based payments, the RBI said.
- Such users can initiate payments to friends and family, pay utility bills, recharge the FAST Tags of their vehicles, pay mobile bills and also allow users to check account balances.
- Customers will also be able to link bank accounts, set or change UPI PINs.
Others: ‘Digisaathi’
- A 24×7 helpline for digital payments has also been set up by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI).
- The helpline christened ‘Digisaathi’ will assist the callers/users with all their queries on digital payments via website and chatbot.
- Users can visit www.digisaathi.info or call on 14431 and 1800 891 3333 from their phones for their queries on digital payments and grievances.
Why UPI123Pay was created?
- UPI, which was introduced in 2016, has become one of the most used digital payments platforms in the country.
- The volume of UPI transactions has already reached ₹76 lakh crore in the current year, compared to ₹41 lakh crore in FY21.
- However, at present, efficient access to UPI is available largely via smartphones.
How will users make payments without internet?
The new UPI payments system offers users four options to make payments without internet connectivity:
- Interactive Voice Response (IVR): Users would be required to initiate a secured call from their feature phones to a predetermined IVR number and complete UPI on-boarding formalities to be able to start making financial transactions like money transfer, mobile recharge, EMI repayment, balance check, among others.
- App-based functionality: One could also install an app on feature phone through which several UPI functions, available on smartphones, will be available on their feature phone, except scan and pay feature which is currently not available.
- Missed call facility: The missed call facility will allow users to access their bank account and perform routine transactions such as receiving, transferring funds, regular purchases, bill payments, etc., by giving a missed call on the number displayed at the merchant outlet. The customer will receive an incoming call to authenticate the transaction by entering UPI PIN.
- Proximity sound-based payments: One could utilise the proximity sound-based payments option, which uses sound waves to enable contactless, offline, and proximity data communication on any device.
How do UPI payments through sound work?
- UPI payments using sound isn’t new. When Google Pay was first launched in 2017 as Tez, the app had a sound-based system of payments built in.
- Google called this ‘Cash Mode’ in which phones would emit ultrasonic sounds that could be used by other Tez users to accept and receive money.
- It’s somewhat like Bluetooth but instead of using radio waves, it uses sound waves to transfer data from one device to the next.
- A company called ToneTag also produces audio-based point-of-sale machines.
Is payment through sound secure?
- Sound wave-based payments are meant to be contactless, but occur within a certain proximity only.
- Ultrasonic waves are outside the usual human hearing range, but such payment systems can also use audible sounds, something that US-based startup Chirp showcased back in 2011.
- Devices using such systems are encrypted, and only the devices involved can recognize the emitted waves.
- The sound waves being emitted are encrypted, meaning the receiving device will need to have decryption codes to complete the transaction.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Land Monetisation Corporation (NLMC)
Mains level: Asset Monetization

The Union Cabinet has approved the setting up of a new government-owned firm National Land Monetisation Corporation (NLMC) for pooling and monetizing sovereign and public sector land assets.
What is NLMC?
- The National Land Monetisation Corporation (NLMC) is being formed with an initial authorised share capital of ₹5,000 crore and paid-up capital of ₹150 crore.
- The government will appoint a chairman to head the NLMC through a “merit-based selection process” and hire private sector professionals with expertise.
- The NLMC will undertake monetization of surplus land and building assets of Central public sector enterprises (CPSEs) as well as government agencies.
How will it function?
- NLMC will own, hold, manage and monetise surplus land and building assets of CPSEs under closure and surplus non-core land assets of Government-owned CPSEs under strategic disinvestment.
- This will speed up the closure process of CPSEs and smoothen the strategic disinvestment process of Government-owned CPSEs, the statement said.
- NLMC will undertake surplus land asset monetisation as an agency function, and assist and provide technical advice to the Centre in this regard.
- The NLMC board will comprise senior Government officers and eminent experts, while its chairman and non-Government directors will be appointed through a merit-based selection process, the statement said.
- The Corporation will have minimal full-time staff, hired directly from the market on a contract basis.
Stipulated tasks
- CPSEs have referred around 3,400 acres of land and other non-core assets to the Department of Investment and Public Asset Management (DIPAM) for monetisation.
- Monetisation of non-core assets of MTNL, BSNL, BPCL, BEML, HMT, is currently at various stages of the transaction, as per latest data in the Economic Survey 2021-22.
Significance of NLMC
- The government would be able to generate substantial revenues by monetizing unused and under-used assets.
- The new corporation will also help carry out monetization of assets belonging to public sector firms that have closed or are lined up for a strategic sale.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Article 19
Mains level: Paper 2- Issues with the sealed cover jurisprudence
Context
A Division Bench of the Kerala High Court has dismissed the appeal filed by a television channel. The trouble emanating from the judgment is that the state need not even show that its security is threatened. It can conveniently choose the ‘sealed cover’ route.
Background of the case
- The Ministry had said that the licence could not be renewed for reasons related to national security.
- The stand of the Government was endorsed by both the Single and Division Benches of the High Court.
- In the judgment of March 2, the Division Bench said: “It is true that the nature, impact, gravity and depth of the issue is not discernible from the files.
- Still, the Bench chose to dismiss the appeals by bluntly saying that “there are clear and significant indications impacting the public order and security of the state”.
- All that is necessary to ban a news broadcaster are these ‘indications’ — which are never revealed to the broadcaster.
Issues with the judgement
1] Violation of the fundamental rights
- A whole set of rights are directly hit by the ban. The first is the right to freedom of speech and expression of the television channel.
- The rights to association, occupation and business are also impacted.
- Moreover, the viewers also have a right to receive ideas and information.
- All these rights are altogether suspended by the executive. The only contingency in which these rights under Article 19(1) can be interfered with are reasonable restrictions under Article 19(2).
- The judgment creates a situation that endorses the breach of fundamental rights on the one hand, and blocks remedy for the victim through a court of law and a process known to law on the other hand.
2] Takes away the power of judicial review
- India’s Constitution does not give a free hand to the executive to pass arbitrary orders violating such rights.
- Basic feature of the Constitution: The Supreme Court of India has repeatedly held that judicial review of executive action is the basic feature of the Constitution.
- The decisions in Minerva Mills vs Union of India (1980) and L. Chandra Kumar vs Union of India (1997) reiterated this fundamental principle.
- Test of reasonable restriction: If the executive wishes to limit rights — in this case, censor or restrict speech — it must show that the test of reasonable restrictions is satisfied.
- The ‘sealed cover’ practice inverses this position.
3] Lack of examination of national security ground
- There was no examination of the national security plea based on the proportionality analysis, well established in our recent jurisprudence.
- Also, when a three-judge Bench in the Pegasus case ( Manohar Lal Sharma vs Union of India, 2021) has categorically held that the state does not get a “free pass every time the spectre of ‘national security’ is raised”.
Proportionality analysis
- In Modern Dental College vs State of Madhya Pradesh (2016), the top court adopted the proportionality test “a limitation of a constitutional right will be constitutionally permissible if:
- (i) it is designated for a proper purpose
- (ii) the measures undertaken to effectuate such a limitation are rationally connected to the fulfillment of that purpose;
- (iii) the measures undertaken are necessary in that there are no alternative measures that may similarly achieve that same purpose with a lesser degree of limitation; and finally
- (iv) there needs to be a proper relation (‘proportionality stricto sensu’ or ‘balancing’) between the importance of achieving the proper purpose and the social importance of preventing the limitation on the constitutional right”.
- This was reiterated in K.S. Puttaswamy vs Union of India (2017).
Conclusion
The MediaOne case might create a real problem area that needs resolution by the Supreme Court.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: GST Council
Mains level: Paper 2- Use of taxation to discourage tobacco use
Context
Tobacco is a silent killer in our midst that kills an estimated 1.35 million Indians every year.
The harm caused by tobacco
- It is the use of tobacco as a result of which more than 3,500 Indians die every single day, as estimated by scientific studies.
- It also comes at a heavy cost: an annual economic burden of ₹1,77,340 crore to the country or more than 1% of India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
How price and taxation of tobacco matters
- Research from many countries around the world including India shows that a price increase induces people to quit or reduce tobacco use as well as discourages non-users from getting into the habit of tobacco use.
- There is overwhelming consensus within the research community that taxation is one of the most cost-effective measures to reduce demand for tobacco products.
- There has been no significant tax increase on any tobacco product for four years in a row.
- This is quite unlike the pre-GST years where the Union government and many State governments used to effect regular tax increases on tobacco products.
- As peer-reviewed studies show, the lack of tax increase over these years has made all tobacco products increasingly more affordable.
- The absence of a tax increase on tobacco has the potential to reverse the reduction in tobacco use prevalence that India saw during the last decade and now push more people into harm’s way.
- It would also mean foregone tax revenues for the Government.
Way forward
- The Union Budget exercise is not the only opportunity to initiate a tax increase on tobacco products.
- The Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council could well raise either the GST rate or the compensation cess levied on tobacco products especially when the Government is looking to rationalise GST rates and increase them for certain items.
- For example, there is absolutely no public health rationale why a very harmful product such as the bidi does not have a cess levied on it under the GST while all other tobacco products attract a cess.
- GST Council meetings must strive to keep public health ahead of the interests of the tobacco industry and significantly increase either the GST rates or the GST compensation cess rates applied on all tobacco products.
Conclusion
The aim should be to arrest the increasing affordability of tobacco products in India and also rationalise tobacco taxation under the GST.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Small Savings Schemes
Mains level: Paper 3- Managing economic uncertainties due to crisis
Context
Amid Ukraine crisis and high oil prices, the larger concern is how the government and the RBI will navigate this period at a time of record government borrowings, and prevent domestic interest rates from hardening.
The Triffin paradox in current context
- It is ironic that even as emerging economies running current account deficits are getting punished by a depreciating currency and a hardening of interest rates, we are witnessing the US dollar appreciating and US treasuries strengthening.
- The most common argument for such a macroeconomic paradox is named after the economist Robert Triffin (the Triffin Paradox).
- It postulates that the US current account deficit is purely a reflection of the US supplying large amounts of dollars to fulfil the world’s demand.
- In other words, central banks across the world must build up claims on the US to back their domestic money growth.
Dollar’s dominance
- Former US Federal Reserve Chairman Bernanke even extended this argument in 2005 to the “saving glut” proposition by espousing that emerging economies were accumulating foreign exchange reserves in dollars, and diverting domestic savings to buy US treasuries.
- There are several counter arguments to this view that effectively state that the dominance of the US dollar is inevitable in the global financial architecture, and it is purely a fault of emerging market economies.
Need for the unconventional tools to avoid the disruption by government borrowing
This can be done in the following ways
1] Spread the borrowing over four quarters after taking real-time view of disruption
- Every year, the government front-loads its large borrowing programme by completing 60 per cent of the borrowings in the first half of the year.
- This time, the RBI and the government may take a real-time view of disruptions and spread the borrowings over four quarters, keeping the initial two quarters light.
- The borrowing programme can also be announced as per a quarterly schedule and there could be even two auctions during the week.
- These steps could smoothen out the non-disruptive elements in government borrowings.
2] Reconfigure the borrowing program
- For example, as rates move up, banks tend to prefer short-term investments while insurance companies, provident funds and others prefer longer-term investments.
- Given this, the borrowing schedule can be reconfigured with a higher proportion of short-and medium-tenor securities being offered in the initial months, while pushing back the longer tenor securities to the second half of the year.
3] Push Small Savings Schemes
- Third, small savings collections have significantly exceeded budget estimates.
- The government could think of giving a push to small savings schemes such as the Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY).
- The SSY has witnessed the registration of 2.82 crore girl children in the seven years since its inception in 2015, leaving enough room for further mop-up.
- The newly opened accounts may even be given an enhanced savings limit in the first year to catch up for the years lost for these new additions.
4] Listing of LIC
- LIC currently holds around Rs 23.5 trillion worth of government bonds, higher than even than the RBI.
- LIC’s G-sec holding is around 19 per cent, while in comparison the banking system’s ownership stands at around 38 per cent.
- Thus LIC’s listing should augur well for the bond market as the insurance behemoth may have to deploy a greater share of inflows in safer avenues domestically.
- This is a plausible option as banks may have to readjust their deposits into credit as the economic recovery gains momentum.
Conclusion
Rising oil prices have placed policymakers in an unenviable position. If higher oil prices are fully passed through, it will result in higher inflation and hence higher rates as a consequence. In such a scenario it is best to follow the first option by using unconventional policy measures.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: MVA, BBIN
Mains level: BBIN and its significance
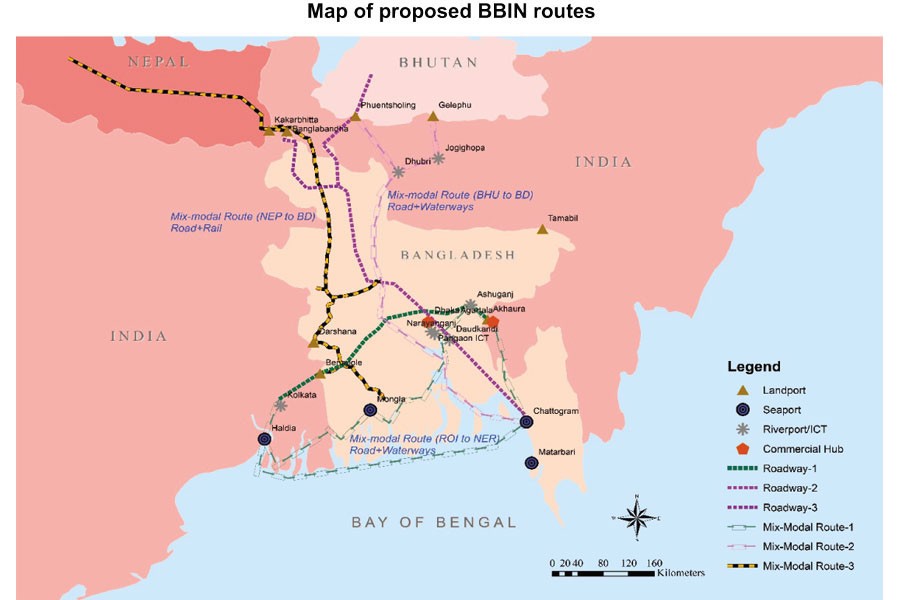
With Bhutan continuing to sit out the Motor Vehicles Agreement (MVA) of the sub-regional Bangladesh-Bhutan-India-Nepal (BBIN) grouping, a meeting of the other three countries was held to discuss the next steps in operationalizing the agreement for the free flow of goods and people between them.
What is Motor Vehicles Agreement (MVA)?
- India, Nepal, Bhutan and Bangladesh signed a Motor Vehicles Agreement (MVA) for the Regulation of Passenger, Personal and Cargo Vehicular Traffic among the four South Asian neighbours.
- It was signed on 15 June 2015 at the BBIN transport ministers meeting in Thimpu, Bhutan.
- The act will facilitate a way for a seamless movement of people and goods across their borders for the benefit and integration of the region and its economic development.
Key terms of the Agreement
- Trans-shipment of goods: Cargo vehicles will be able to enter any of the four nations without the need for trans-shipment of goods from one country’s truck to another’s at the border.
- Free transport: The agreement would permit the member states to ply their vehicles in each other’s territory for transportation of cargo and passengers, including third-country transport and personal vehicles.
- Electronic permit: As per the agreement each vehicle would require an electronic permit to enter another country’s territory, and border security arrangements between nations’ borders will also remain.
- Ultra-security: Vehicles are fitted with an electronic seal that alerts regulators every time the container door is opened.
Implementation status of the agreement
- The agreement will enter into force after it is ratified by all four member nations.
- The agreement has been ratified by Bangladesh, India and Nepal.
- The lower house of the Bhutanese parliament approved the agreement in early 2016, but it was rejected by the upper house in November 2016.
- Bhutan has requested for a cap to be fixed on the number of vehicles entering its territory
What next?
- India remains “hopeful” that Bhutan could change its position on the project, it was decided at a meeting in November 2021 to go ahead for now, given that there are no new signals from Thimphu on the project.
- Progress on the seven-year-old project has been slow, despite several trial runs being held along the Bangladesh-India-Nepal road route for passenger buses and cargo trucks.
- There are still some agreements holding up the final protocols.
Back2Basics: Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal (BBIN)
- BBIN Initiative is a sub-regional architecture of countries in Eastern South Asia, a sub-region of South Asia.
- The group meets through the official representation of member states to formulate, implement and review quadrilateral agreements across areas such as water resources management, connectivity of power, transport, and infrastructure.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: TPD
Mains level: Refugee crisis of Ukranians
Responding to the crisis, EU Member States made the unprecedented decision to activate a major European Union’s Council Directive, known as the Temporary Protection Directive (TPD).
What is Temporary Protection?
- The EU Commission describes “temporary protection” under the TPD as an “exceptional measure to provide immediate and temporary protection to displaced persons from non-EU countries and those unable to return to their country of origin”.
- The directive applies when there is a risk that the standard asylum system is struggling to cope with demand stemming from a mass influx risking a negative impact on the processing of claims.
Objectives of this protection
- To both establish minimum standards for giving temporary protection to displaced persons
- To promote a balance of effort between Member States in receiving and bearing the consequences of receiving such persons
Why establish standards?
The Commission gives two reasons for doing so:
- It reduces disparities between the policies of EU States on the reception and treatment of displaced persons in a situation of mass influx.
- It promotes solidarity and burden-sharing among EU States with respect to receiving large numbers of potential refugees at one time.”
What obligations does the TPD place upon EU states?
According to the European Commission, the TPD “foresees harmonised rights for the beneficiaries of temporary protection”, which include:
- Residence permit for the duration of the protection (which can last from 1-3 years),
- Appropriate information on temporary protection,
- Access to employment,
- Access to accommodation or housing,
- Access to social welfare or means of subsistence,
- Access to medical treatment,
- Access to education for minors,
- Opportunities for families to reunite in certain circumstances, and
- Guarantees for access to the normal asylum procedure
The TPD also contains provisions for the return of displaced persons to their country of origin, unless they have committed serious crimes or they “pose a threat to security from the benefit of temporary protection”.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Karewa
Mains level: Land degradation

Kashmir’s highly fertile alluvial soil deposits called ‘karewas’ are being destroyed in the name of development, much to the peril of local people
What are Karewas?
- The Kashmir valley is an oval-shaped basin, 140 km long and 40 km wide, trending in the NNW–SSE direction.
- It is an intermountain valley fill, comprising of unconsolidated gravel and mud.
- A succession of plateaus is present above the Plains of Jhelum and its tributaries.
- These plateau-like terraces are called ‘Karewas’ or ‘Vudr’ in the local language.
- These plateaus are 13,000-18,000 metre-thick deposits of alluvial soil and sediments like sandstone and mudstone.
- This makes them ideal for cultivation of saffron, almonds, apples and several other cash crops.
Significance of Karewas
- Today, the karewa sediments not only hold fossils and remnants of many human civilisations and habitations, but are also the most fertile spots in the valley.
- Kashmir saffron, which received a Geographical Indication (GI) tag in 2020 for its longer and thicker stigmas, deep-red colour, high aroma and bitter flavour, is grown on these karewas.
How are they formed?
- The fertility of these patches is believed to be the result of their long history of formation.
- When formed during the Pleistocene period (2.6 million years to 11,700 years ago), the Pir Panjal range blocked the natural drainage in the region and formed a lake spanning 5,000 sq km.
- Over the next few centuries, the water receded, making way for the valley and the formation of the karewas between the mountains.
Threats to Karewas
- Despite its agricultural and archaeological importance, karewas are now being excavated to be used in construction.
- Between 1995 and 2005, massive portions of karewas in Pulwama, Budgam and Baramulla districts were razed to the ground for clay for the 125-km-long Qazigund-Baramulla rail line.
- The Srinagar airport is built on the Damodar karewa in Budgam.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Pal-Dadhvav Massacre
Mains level: Major tribal uprisings in freedom struggle
The Gujarat government has marked 100 years of the Pal-Dadhvav killings, calling it a massacre “bigger than the Jallianwala Bagh”.
Pal-Dadhvav Massacre
- The massacre took place on March 7, 1922, in the Pal-Chitariya and Dadhvaav villages of Sabarkantha district, then part of Idar state.
- The day was Amalki Ekadashi, which falls just before Holi, a major festival for tribals.
- Villagers from Pal, Dadhvav, and Chitariya had gathered on the banks of river Heir as part of the ‘Eki movement’, led by one Motilal Tejawat.
- The movement was to protest against the land revenue tax (lagaan) imposed on the peasants by the British and feudal lords.
- Tejawat, who belonged to Koliyari village in the Mewad region of Rajasthan, had also mobilised Bhils from Kotda Chhavni, Sirohi, and Danta to participate.
The fateful day
- Tejawat had been outlawed by the Udaipur state, which had announced a Rs-500 reward on his head.
- The Mewad Bhil Corps (MBC), a paramilitary force raised by the British that was on the lookout for Tejawat, heard of this gathering and reached the spot.
- On a command from Tejawat, nearly 2000 Bhils raised their bows and arrows and shouted in unison- ‘We will not pay the tax’.
- The MBC commanding officer, HG Sutton, ordered his men to fire upon them creating a huge stampede.
- Nearly 1,000 tribals (Bhils) fell to bullets. While the British claimed some 22 people were killed, the Bhils believe 1,200-1,500 of them died.
Must read:
Important Rebellions and Peasant Movements
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Param Ganga, Petaflops
Mains level: National Supercomputing Mission

The National Supercomputing Mission (NSM) has now deployed “PARAM Ganga”, a supercomputer at IIT Roorkee, with a supercomputing capacity of 1.66 Petaflops.
What is a Supercomputer?
- A supercomputer is a computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer.
- The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) instead of million instructions per second (MIPS).
- Since 2017, there are supercomputers which can perform over a hundred quadrillion FLOPS (peta FLOPS).
- Since November 2017, all of the world’s fastest 500 supercomputers run Linux-based operating systems.
PARAM Ganga
- PARAM Ganga is designed and commissioned by C-DAC under Phase 2 of the build approach of the NSM.
- It is based on a heterogeneous and hybrid configuration of Intel Xeon Cascade lake processors, and NVIDIA Tesla V100.
- There are 312 (CPU+GPU+HM) nodes with a total peak computing capacity of 1.67 (CPU+GPU+HM) PFLOPS performance.
- The cluster consists of compute nodes connected with the Mellanox (HDR) InfiniBand interconnect network.
- The system uses the Lustre parallel file system and operating system is CentOS 7.x.
Back2Basics: National Supercomputing Mission (NSM)
- NSM is a proposed plan by GoI to create a cluster of seventy supercomputers connecting various academic and research institutions across India.
- In April 2015 the government approved the NSM with a total outlay of Rs.4500 crore for a period of 7 years.
- The mission was set up to provide the country with supercomputing infrastructure to meet the increasing computational demands of academia, researchers, MSMEs, and startups by creating the capability design, manufacturing, of supercomputers indigenously in India.
- Currently there are four supercomputers from India in Top 500 list of supercomputers in the world.
Aims and objectives
- The target of the mission was set to establish a network of supercomputers ranging from a few Tera Flops (TF) to Hundreds of Tera Flops (TF) and three systems with greater than or equal to 3 Peta Flops (PF) in academic and research institutions of National importance across the country by 2022.
- This network of Supercomputers envisaging a total of 15-20 PF was approved in 2015 and was later revised to a total of 45 PF (45000 TFs), a jump of 6 times more compute power within the same cost and capable of solving large and complex computational problems.
When did India initiate its efforts to build supercomputers?
- India’s supercomputer program was initiated in the late 1980s, when the United States ceased the export of a Cray Supercomputer due to technology embargos.
- This resulted in India setting up C-DAC in 1988, which in 1991, unveiled the prototype of PARAM 800, benchmarked at 5 Gflops. This supercomputer was the second-fastest in the world at that time.
- Since June 2018, the USA’s Summit is the fastest supercomputer in the world, taking away this position from China.
- As of January 2018, Pratyush and Mihir are the fastest supercomputers in India with a maximum speed of Peta Flops.
What are the phases of the National Supercomputing Mission?
Phase I:
- In the first phase of the NSM, parts of the supercomputers are imported and assembled in India.
- A total of 6 supercomputers are to be installed in this phase.
- The first supercomputer that was assembled indigenously is called Param Shivay. It was installed in IIT (BHU) located in Varanasi.
- Similar systems, Param Shakti (IIT Kharagpur) and Param Brahma (IISER, Pune) were also later installed within the country.
- The rest will be installed at IIT Kanpur, IIT Hyderabad and Jawaharlal Nehru Institute of Advanced Studies (JNIAS).
Phase II:
- The supercomputers that are installed so far are about 60% indigenous.
- The 11 systems that are going to be installed in the next phase will have processors designed by the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) and will have a cumulative capacity of 10 petaflops.
- These new systems are to be constructed more cost-effectively than the previous ones.
- One of the 11 proposed supercomputers will be installed
- at C-DAC exclusively for small and medium enterprises so that they can train employees as well as work on supercomputers at a very low cost.
Phase III:
- The third phase aims to build fully indigenous supercomputers.
- The government had also approved a project to develop a cryogenic cooling system that rapidly dispels the heat generated by a computing chip. This will be jointly built together by IIT-Bombay and C-DAC.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Maternal mortality rate
Mains level: Paper 2- Women's representation in politics
Context
For a proper appraisal of the relations between gender and democracy, we ought to examine the links between violence, representation, and the political participation of women.
Role of women in South Asian democracy
- Historically, one of the peculiar paradoxes of South Asian democracy has been the continued presence of strong women leaders at the executive centre coupled with a generally appalling condition of women in society at large.
- South Asia has had the largest number of women heads of state — including Sirimavo Bandaranaike, Chandrika Kumaratunga, Indira Gandhi, Khaleda Zia, Sheikh Hasina, and Benazir Bhutto — of any region in the world till recently.
- Under-represented: While women have played very visible and important roles at the higher echelons of power and at the grassroots level in social movements, they have been under-represented in political parties as officials and as members of key decision-making bodies.
Electoral representation of women in India
- In India, women currently make up 14.6 per cent of MPs (78 MPs) in the Lok Sabha, which is a historic high.
- Although the percentage is modest, it is remarkable because women barely made up 9 per cent of the overall candidates in 2019.
- In electoral representation, has fallen several places in the Inter-Parliamentary Union’s global ranking of women’s parliamentary presence, from 117 after the 2014 election to 143 as of January 2020.
- In terms of electoral quotas, there were two outstanding exceptions in the 2019 general elections.
- Voluntary parliamentary quota: West Bengal under Mamata Banerjee and Odisha under Naveen Patnaik opted for voluntary parliamentary quotas, fielding 40 per cent and 33 per cent women candidates, respectively.
Growing turnout of women voters and its implications
- Assertion of citizenship rights: In 1962, the male voter turnout in India was 16 percentage points higher than for women. Six decades later, in the 2019 Lok Sabha elections, women’s participation exceeded that of men for the first time.
- This suggests an increasing assertion of citizenship rights among women.
- The growing turnout of women voters could influence political parties’ programmatic priorities and improve their responsiveness to women voters’ interests, preferences, and concerns, including sexual harassment and gender-based violence.
- Women-centric schemes: The state government in Bengal ran and highlighted many women-centric schemes that potentially played a central role in their victory.
- The central government must be commended for its achievements in two areas in particular: Its DBT schemes such as the Pradhan Mantri Vaya Vandana Yojana and the Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyan.
- As a result, maternal mortality rate has reduced from 167 (2011-13) to 113 (2016-18).
- The Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Bill, 2017 is another landmark achievement that extended the paid maternal leave to 26 weeks from the existing 12 weeks.
Way forward
- Government must use its parliamentary majority to finally pass the Women’s Reservation Bill, as was promised in their 2014 election manifesto.
- Until that happens, the initiative taken by the governments of Banerjee and Patnaik to increase women’s parliamentary presence must serve as an inspiration to other Indian states.
Conclusion
The extent to which parties represent women and take up their interests is closely tied to the health and vitality of democratic processes.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Paper 2- Russia-Ukraine war
Context
Russian President Vladimir Putin’s nuclear sabre-rattling in Ukraine, has triggered a far more consequential debate on the importance of atomic weapons in deterring Chinese expansionism.
Background
- Ukraine agreed in 1994 to give up the nuclear weapons that it inherited from the Soviet Union in return for guarantees on Kyiv’s sovereignty and territorial integrity.
- Clearly, those legal guarantees were no substitute for nuclear weapons.
Changing stand on nuclear weapons
- Debate in Japan: In an important statement last week, the former prime minister of Japan, Shinzo Abe, called for a national debate on hosting American nuclear weapons on Japanese soil.
- One element of the debate is the fact that nuclear weapons remain the greatest deterrent, especially against a vastly superior adversary.
- Korea strengthening nuclear deterrence: In South Korea, which is electing its president this week, front-runner Yoon Suk-yeol has talked of strengthening Seoul’s nuclear deterrence against both Pyongyang and Beijing.
- Taiwan and Australia developing nuclear submarine: Taiwan, is reportedly developing a nuclear-powered submarine that could offer some deterrence against a Chinese invading force.
- Australia, which is working with the UK and the US to build nuclear-powered submarines, is accelerating the project after the Ukraine invasion.
Threat of escalation to nuclear war
- The threat of escalation to the nuclear level was very much in the mind of NATO’s military planners when the alliance refused to be drawn into a firefight with Russia in Ukraine.
- Moscow is also conscious of the fact that there are two nuclear weapon powers in Europe — Britain and France.
- Nuclear sharing arrangement: Russia is also aware of the “nuclear sharing” arrangements between the US and some European allies — Belgium, Germany, Italy, and the Netherlands.
- Under this framework, European allies host US nuclear weapons on their soil and authorise their armed forces to deliver American nuclear weapons on Russia.
- Nuclear sharing also involves continuous consultations on nuclear doctrine and the planning of nuclear operations.
- The US and its allies are also pursuing a “hybrid war” that boosts Ukrainian resistance against Russian armed forces and raises military, economic, and political costs of Moscow’s aggression.
Threat of China invading Taiwan
- Taiwan is far more important for Asian (and global) security than Ukraine is for Europe.
- Taiwan sits at the heart of the Western Pacific and straddles the sea line of communication in the world’s most dynamic economic arena.
- It is the main source of silicon chips for the world.
- When China conquers Taiwan it will dramatically transform the geopolitics of Asia.
- As Putin becomes more dependent on China, Russia is bound to back Xi Jinping’s ambitions in Asia.
- This is the context in which China’s eastern neighbours are taking a fresh look at the nuclear option.
- Nuclear sharing arrangement: On the nuclear front, the debate in Japan and South Korea is about potential nuclear sharing arrangements with the US.
- In Taiwan and Australia, the emphasis is on developing nuclear-powered submarines.
- Deployment of strategic weapons: The US too is debating the deployment of new strategic weapon systems in Asia that might encourage China to pause before trying to emulate Russia’s Ukraine adventure.
Consider the question ” Russia’s invasion of Ukraine is going to transform the nuclear landscape of Asia. Comment.”
Conclusion
One way or another, Russia’s war in Ukraine is bound to transform the Asian nuclear landscape.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Economic implications of Russia-Ukraine War

The economic sanctions imposed by the US, UK, and the EU on Russia for going to war against Ukraine could prove to be detrimental to the country.
What do economic sanctions mean?
- Economic sanctions are penalties or bans that are levied against a country to push it to modify its strategic decisions.
- They include withdrawal of customary trade and financial relations for security and foreign policy purposes.
- Sanctions could result in cutting economic ties in every respect such as terms of trade, financial assistance, transit support, travel bans, asset freezes, and trade restrictions.
- The curbs could also be targeted, thus restricting transactions with certain businesses, groups, or individuals.
- Amid increased global and economic interdependence, they could prove to be detrimental for the targeted country.
How do sanctions impact an economy?
- No country can afford to be a closed economy.
- The affected country’s supply chain gets disrupted in terms of the inflow of goods and services and for reaching out to the export markets.
- In the former, there is a risk of the internal economy being crippled, especially if it depends on imports of critical raw materials.
- The domestic economy could also be deprived of external market support.
- The risk element is high especially in case of economic curbs being imposed collectively, such as by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) or the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO).
What are the economic sanctions against Russia?
- Major Russian banks have been banned from the SWIFT financial messaging service and their assets have been frozen.
- Sanctions have been levied on the Russian Direct Investment Fund and against some of Russia’s wealthiest people.
- Access to air-space has been denied and export controls introduced.
- The countries imposing curbs on Russia account for 34% of world GDP.
What is the cost of such restrictions?
- This depends on the economic strength of the country being targeted.
- Russia cannot be brushed aside as an ordinary economy.
- The country is important to the global economy because of its oil reserves and access to nuclear power.
- Russia is also a supplier of sophisticated defence products and is an important supplier of crucial defence products to India.
- Given the long-term strategic nature of the relationship, India is abstaining from voting on resolutions to condemn Russia.
How did India manage curbs after Pokhran-II?
- India’s dependence on external assistance was more than $100 billion.
- The government appealed to non-resident Indians (NRIs) whose annual savings were more than $400 billion.
- NRIs’ subscription to government bonds was more than double the annual foreign assistance.
- India could also showcase its scientific strength as none of the scientists involved were trained abroad.
- This helped India display confidence, especially to investors.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: No-Fly Zone
Mains level: Read the attached story

The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) Secretary General stated that the organisation would not designate the Ukrainian airspace as a ‘No Fly Zone’ which he said would lead to a full-fledged war in Europe, involving many more countries and resulting in greater human suffering.
What is a No-Fly Zone ?
- In simple terms, a No-Fly Zone refers to a particular airspace wherein aircraft, excluding those permitted by an enforcement agency, are barred from flying.
- Articles under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter dealing with Action with Respect to Threats to the Peace, Breaches of the Peace, and Acts of Aggression’ are invoked to authorise a potential no-fly zone.
- Article 39 dictates the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) to determine the probable existence of any threat to peace or an act of aggression.
- It suggests further measures, if required, are to be carded out in accordance to Article 41 and 42 to restore international peace and security.
- No fly zones have been implemented without UN mandate too.
Cases of implementation
- In 1991 after the first Gulf War, U.S. and its coalition partners imposed two no fly zones over Iraq to prevent Saddam Hussain born attacking ethnic groups.
- In non-combat situations, No fly zones can be imposed permanently and temporarily over sensitive installations or for high profile events like Olympics.
What is the feasibility of ‘No fly zone over Ukraine?
- No-fly zone declarations are essentially a compromise in situations demanding a response to ongoing violence, but full military intervention is politically untenable.
- NATO has previously imposed No-Fly Zones in non-member states like Libya and Bosnia. With Russia it fears a full-fledged war in Europe.
- It has been demanding that NATO scale back to the pre-1997 arrangements. Both Russia and Ukraine are not members of NATO.
- Due to this the idea of imposing a no fly zone’ over Ukraine has been rejected outright.
- If implemented, it means NATO deploying aircraft and assets which would result in a direct confrontation with Russia.
What are the broad contours in a No-Fly Zone?
- The UNSC had banned all flights in the Libyan airspace post adoption of Resolution 1973 in 2011 in response to the Libyan Civil War.
- Member slates were asked to deny permission to any Libyan registered aircraft to use the territory without requisite approval.
- Further, the member states could bar any entity from flying if they found reasonable grounds to believe the aircraft is ferrying lethal or non-lethal military equipment.
- Member states were permitted to allow flights whose sole purpose was humanitarian, such as delivery of medical supplies and food, chauffer humanitarian workers and related assistance, or evacuating foreign nationals from the territory.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ‘Donate a Pension’ Scheme
Mains level: Not Much
The Union Labour and Employment Ministry has launched the “donate a pension” scheme.
‘Donate a Pension’ Scheme
- This scheme allows any citizen to pay the premium amount on behalf of an unorganized worker under the Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Maan-Dhan
- Maan-Dhan scheme is a government scheme meant for old age protection and social security of unorganized workers.
Eligibility criteria and benefits
- The scheme was launched in 2019, allows unorganized sector workers between 18 and 40 years who earn up to ₹15,000 a month to enroll by paying a premium amount between ₹55 and ₹200, depending on the age, that would be matched by the government.
- On reaching the age of 60, the beneficiaries would get a ₹3,000 monthly pension.
Features of the scheme
- The scheme allows a citizen to “donate the premium contribution of their immediate support staff such as domestic workers, drivers, helpers, caregivers, nurses in their household or establishment.
- The donor can pay the contribution for a minimum of one year, with the amount ranging from ₹660 to ₹2,400 a year depending on the age of the beneficiary, by paying through maandhan.in or visiting a Common Service Centre.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Stagflation
Mains level: Economic impact of Russian invasion
Reports suggest that crude oil prices soared and touched almost $140 per barrel mark amid Russian invasion of Ukraine. This has posed a risk of causing Stagflation in India.
What is Stagflation?
- Stagflation is a stagnant growth and persistently high inflation. It, thus, describes a rather rare and curious condition of an economy.
- Iain Macleod, a Conservative Party MP in the United Kingdom, is known to have coined the phrase during his speech on the UK economy in November 1965.
- Typically, rising inflation happens when an economy is booming — people are earning lots of money, demanding lots of goods and services and as a result, prices keep going up.
- When the demand is down and the economy is in the doldrums, by the reverse logic, prices tend to stagnate (or even fall).
- But stagflation is a condition where an economy experiences the worst of both worlds — the growth rate is largely stagnant (along with rising unemployment) and inflation is not only high but persistently so.
How does one get into Stagflation?
- The best-known case of stagflation is what happened in the early and mid-1970s.
- The OPEC (Organisation of Petroleum Exporting Countries), which works like a cartel, decided to cut crude oil supply.
- This sent oil prices soaring across the world; they were up by almost 70%.
- This sudden oil price shock not only raised inflation everywhere, especially in the western economies but also constrained their ability to produce, thus hampering their economic growth.
- High inflation and stalled growth (and the resulting unemployment) created stagflation.
Is India facing stagflation?
- In the recent past, this question has gained prominence since late 2019, when retail inflation spiked due to unseasonal rains causing a spike in food inflation.
- In December 2019, it was also becoming difficult for the government to deny that India’s growth rate was witnessing a secular deceleration.
- As revised estimates, released in January end, now show, India’s GDP growth rate decelerated from over 8% in 2016-17 to just 3.7% in 2019-20.
- However, the answer to this question in December 2019 was a clear no.
- For one, in absolute terms, India’s GDP was still growing, albeit at a progressively slower rate.
Why this is a cause of concern?
- Russia is the world’s second-largest oil producer and, as such, if its oil is kept out of the market because of sanctions, it will not only lead to prices spiking, but also mean they will stay that way for long.
- While India is not directly involved in the conflict, it will be badly affected if oil prices move higher and stay that way.
- India imports more than 84% of its total oil demand. At one level, that puts into perspective all the talk of being Atmanirbhar (or self-reliant).
- Without these imports, India’s economy would come to a sudden halt — both metaphorically as well as actually.
Expected impact on Indian Economy
- Higher inflation would rob Indians of their purchasing power, thus bringing down their overall demand.
- In other words, people are not demanding enough for the economy to grow fast.
- Private consumer demand is the biggest driver of growth in India.
- Such aggregate demand — the monetary sum of all the soaps, phones, cars, refrigerators, holidays etc. that we all spend on in our personal capacity — accounts for more than 55% of India’s total GDP.
- Higher prices will reduce this demand, which is already struggling to come back up to the pre-Covid level.
- Fewer goods and services being demanded will then disincentivise businesses from investing in new capacities, which, in turn, will exacerbate the unemployment crisis and lead to even lower incomes.
Back2Basics: Inflation and its impact
- Depression: It is Economic depression is a sustained, long-term downturn in economic
- Deflation: It is the general fall in the price level over a period of time.
- Disinflation: It is the fall in the rate of inflation or a slower rate of inflation. Example: a fall in the inflation rate from 8% to 6%.
- Reflation: It is the act of stimulating the economy by increasing the money supply or by reducing taxes, seeking to bring the economy back up to the long-term trend, following a dip in the business cycle. It is the opposite of disinflation.
- Skewflation: It is the skewed rise in the price of some items while remaining item prices remain the same. E.g. Seasonal rise in the price of onions.
- Stagflation: The situation of rising prices along with falling growth and employment, is called stagflation. Inflation accompanied by an economic recession.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Jyotiba Phule
Mains level: NA

Maharashtra Governor has recently received flak for his remarks on the social reformist couple Jyotirao and Savitribai Phule.
Who were the Phules?
- Mahatma Jyotirao and Savitribai Phule stand out as an extraordinary couple in the social and educational history of India.
- They spearheaded path-breaking work towards female education and empowerment, and towards ending caste- and gender-based discrimination.
- In 1840, at a time when child marriages were common, Savitri at the age of ten was married to Jyotirao, who was thirteen years old at the time.
- The couple later in life strove to oppose child marriage and also organised widow remarriages.
The Phules’ endeavors and legacy
- Education: Jyotirao, the revolutionary that he was, observed the lack of opportunities for education for young girls and women.
- Leaders of the masses: He started to educate his wife at home and trained her to become a teacher. Together, by 1848, the Phules started a school for girls, Shudras and Ati-Shudras in Poona.
- Widow shelter: The historic work was started by Jyotirao when he was just 21 years old, ably supported by his 18-year-old wife. In 1853, Jyotirao-Savitribai opened a care centre for pregnant widows to have safe deliveries and to end the practice of infanticide owing to social norms.
- Prevention of infanticide: The Balhatya Pratibandhak Griha (Home for the Prevention of Infanticide) started in their own house at 395, Ganj Peth, Pune.
The Satyashodhak Samaj:
- Literally meaning ‘The Truth-Seeker’s Society’ was established on September 24, 1873 by Jyotirao-Savitribai and other like-minded people.
- The Samaj advocated for social changes that went against prevalent traditions, including economical weddings, inter-caste marriages, eradication of child marriages, and widow remarriage.
- The Phules also had far-sighted goals — popularising female education, establishing an institutional structure of schools in India, and to have a society where women worked in tandem with men.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now








