Why in the News?
Recent studies reveal that the Indian Plate is splitting into two, with the lower part detaching and sinking into the Earth’s mantle, a process called delamination, as published by the American Geophysical Union.
About Delamination:
- Delamination in tectonic plates refers to the process where the lower part of a continental plate, including the lower crust and/or lithospheric mantle, splits and sinks into the Asthenosphere.
- This process is driven by density differences and can lead to rapid uplift, changes in stress regimes, and altered magmatism.
- It can occur in various tectonic settings, including compressional zones, subduction zones, and intraplate regions.
- The denser lower part of the plate, including the lower crust and/or lithospheric mantle, is less buoyant than the less dense asthenosphere, leading to sinking.
- High temperatures can also weaken the lithosphere and facilitate delamination.

Indian Plate and Its Splitting:
- The Indian Plate has been colliding with the Eurasian Plate for about 60 million years, causing the formation of the Himalayas and influencing regional seismic activity.
- It is shifting northward at a rate of approximately 5 cm per year..
- The lower, denser part of the Indian Plate is detaching and sinking into the Earth’s mantle.
- This may lead to increased seismic activity due to shifts in tectonic stress.
- In regions like the Himalayan collision zone, delamination results in fractures that increase stress in the Earth’s crust, raising the likelihood of seismic events.
| [UPSC 2004] Consider the following geological phenomena:
1. Development of a fault 2. Movement along a fault 3. Impact produced by a volcanic eruption 4. Folding of rocks Which of the above cause earthquakes?
Options:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 (b) 2 and 4 (c) 1, 3 and 4 (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
Recently Google introduced its seventh-generation TPU (Tensor Processing Unit), named Ironwood.
About Ironwood
- Ironwood is Google’s seventh-generation Tensor Processing Unit (TPU), designed to accelerate AI model training and inference with improved performance and efficiency.
- It builds on previous TPUs, enhancing speed and efficiency for AI workloads.
- It has been optimized for complex AI tasks, especially those requiring high-speed data processing for neural networks and deep learning models.
- Initially used internally, Ironwood is now available via Google Cloud Platform, allowing businesses to harness its power without investing in dedicated hardware.
What is a TPU?
- A TPU is a specialized processor developed by Google to accelerate machine learning tasks, particularly those involving TensorFlow.
- TPUs are optimized for tensor operations, crucial for training deep learning models, enabling faster data processing and high efficiency.
How is TPU Different from GPU and CPU?
|
CPU |
GPU |
TPU |
| What is it? |
Central Processing Unit – General-purpose processor for various computing tasks. |
Graphics Processing Unit – Specialized for parallel processing, initially for graphics rendering. |
Tensor Processing Unit – Specialized processor designed by Google for accelerating machine learning tasks, particularly for AI and deep learning. |
| Specialization |
General-purpose tasks (sequential processing) |
Parallel processing (graphics, machine learning) |
Specialized for AI tasks (tensor computations) |
| Performance |
Slower for AI tasks due to sequential processing |
Faster than CPU for parallel tasks |
Fastest for AI tasks like matrix multiplication |
| Efficiency |
Versatile but less efficient for AI operations |
Energy-efficient for parallel tasks |
Highly energy-efficient for machine learning |
| Best for |
Running applications, managing systems |
Graphics rendering, machine learning |
Deep learning, neural network training |
| [UPSC 2020] With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following?
(1) Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units (2) Create meaningful short stories and songs (3) Disease diagnosis (4) Text-to-Speech Conversion (5) Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Options: (a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only (b) 1, 3 and 4 only (c) 2, 4 and 5 only (d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
PM recently remembered Sir Chettur Sankaran Nair, a nationalist and jurist who famously fought a courtroom battle against British officials involved in the Jallianwala Bagh massacre of 1919.
Nair’s stand in the courtroom is now a subject of a forthcoming film, Kesari Chapter 2.

About Sir Sankaran Nair:
- Born in 1857 in Mankara village, Kerala, Nair came from an aristocratic family.
- He was educated at Presidency College in Madras and pursued a law degree.
- Nair began his legal career with Sir Horatio Shepherd, Chief Justice of Madras High Court.
- In 1897, Nair became the youngest president of the Indian National Congress (Amravati (Mh) Session) and was appointed as a permanent judge of the Madras High Court in 1908.
Role in the Jallianwala Bagh Case:
- Nair challenged Michael O’Dwyer, the Lieutenant Governor of Punjab, for his role in the Jallianwala Bagh massacre (1919), accusing him of following policies that led to the massacre.
- O’Dwyer sued Nair in England for defamation. Despite biased British courts, Nair refused to apologize, even when O’Dwyer offered to forgo the £500 penalty.
- The trial highlighted the bias in the British judicial system and fuelled Indian resentment against British rule.
Other Contributions:
- Nair made progressive rulings, like supporting inter-caste and inter-religious marriages and ruling against treating converts to Hinduism as outcasts.
- He supported India’s self-government and played a key role in expanding the Montagu-Chelmsford reforms (1919).
- In 1922, Nair critiqued Gandhi‘s methods in his work “Gandhi and Anarchy”.
- He helped draft the 1919 constitutional reforms, pointing out flaws in British rule, with many of his suggestions accepted.
| [UPSC 2007] Which one of the following aroused a wave of popular indignation that led to the massacre by the British at Jallianwala Bagh?
(a) The Arms Act (b) The Public Safety Act (c) The Rowlatt Act (d) The Vernacular Press Act |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
China has suspended exports of a wide range of critical minerals and magnets after US’s tariff embargo.
What Are Rare Earth Elements (REEs) and RE Magnets?
- REEs are a group of 17 elements in the periodic table, including Lanthanum (La), Neodymium (Nd), Europium (Eu), and Ytterbium (Yb).
- Though not rare, they are found in low concentrations, making extraction challenging and costly.
-
- Light REEs (LREEs): Elements 57-63, such as La, Ce, Nd, and Sm.
- Heavy REEs (HREEs): Elements 64-71, like Gd, Tb, Dy, and Er.
- Scandium and Yttrium: Classified with HREEs due to similar chemical properties.
- Rare Earth Magnets are powerful permanent magnets made from elements like Neodymium (Nd), Samarium (Sm), and Dysprosium (Dy).
- They are far stronger and more efficient than traditional magnets, crucial for high-tech electronic applications.
Global Supply Chain of REEs:
- REEs are abundant but difficult to extract economically.
- China alone dominates, producing 70% of the global supply and controlling 80% of the refining capacity. REEs are primarily mined from China’s Bayan Obo mine.
- Australia, USA, Brazil, and Russia also contribute, though less significantly.
- Refining also is largely controlled by China, though other nations are working to build their own refining capabilities to reduce dependency.
| [UPSC 2022] Consider the following statements:
1. Monazite is a source of rare earths. 2. Monazite contains thorium. 3. Monazite occurs naturally in the entire Indian coastal sands in India. 4. In India, Government bodies only can process or export monazite.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only (b) 1, 2 and 4 only* (c) 3 and 4 only (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
PYQ Relevance:
[UPSC 2019] The long-sustained image of India as a leader of the oppressed and marginalised Nations has disappeared on account of its new found role in the emerging global order”. Elaborate.
Linkage: India’s historical role as a voice for the “Global South” and how its current global positioning might be perceived differently. This article argues for the Global South to take a leading role, which resonates with India’s past image. |
Mentor’s Comment: While current talks on delimitation focus on its effect on power-sharing between states and the Centre, another key change depends on it — the rollout of the Women’s Reservation Bill, 2023. The Bill brought gender equality to the forefront of politics. However, this widespread acceptance has, in some ways, made open and critical discussion more difficult. A compassionate, inclusive feminism recognizes both structural and interpersonal challenges women face. It avoids oversimplifying gender struggles, respects men’s societal pressures, and promotes solidarity.
Today’s editorial discusses issues related to feminism. This content will be useful for GS Paper I in the Mains exam.
_
Let’s learn!
Why in the News?
A more compassionate approach to feminism could be the right strategy right now, as it helps gain support rather than create resistance.
Why is there a caution against applying a heavy structural lens to interpersonal relationships?
- Complexity of Relationships: Interpersonal relationships are multifaceted and often not reducible to power dynamics or oppression. Eg: A husband may expect dinner but also contribute financially, which shows mutual care rather than domination.
- Risk of Oversimplification: Applying the structural lens too heavily risks oversimplifying relationships, reducing them to battles for power. Eg: A disagreement over household chores might be seen as oppressive when it could be a negotiation of responsibilities.
- Love and Care Are Often Present: Many relationships are underpinned by love, care, and mutual respect, which should not be ignored in the analysis. Eg: A father who supports his daughter’s education despite societal barriers demonstrates care beyond structural oppression.
- Men’s Experiences and Contributions: Men also face societal pressures, including financial and emotional burdens, which can reshape family dynamics. Eg: A man who works long hours in difficult conditions to support his family might experience public humiliation, while his wife remains insulated from such public pressures.
- Potential for Alienation: Focusing solely on structural analysis may alienate people, particularly those who feel embattled, like many men. Eg: Men who feel misunderstood in feminist discourse, especially those at the margins, may disengage from efforts for equality.
How can feminist discourse become more inclusive and compassionate?
- Acknowledge Multiple Forms of Suffering: Feminism should recognize the varied experiences of suffering and responsibility faced by both women and men, especially from marginalized communities. Eg: Recognizing that men, particularly in low-income families, endure public humiliation due to financial pressures, while women often carry unpaid domestic responsibilities.
- Avoid Oversimplifying Complex Dynamics: Instead of reducing all issues to power struggles, feminist discourse should appreciate the complexity of human relationships, where love, care, and duty often coexist with structural inequality. Eg: A couple might have disagreements over housework, but these can be opportunities for negotiation rather than a sign of patriarchal oppression.
- Promote Solidarity, Not Antagonism: Feminist discourse should focus on creating solidarity, especially by addressing the emotional and economic pressures that shape men’s lives, inviting them to participate in gender equity efforts. Eg: Instead of criticizing men for their limitations, feminist discourse can encourage mutual understanding and support for gender equality.
- Recognize the Interconnection of Personal and Political: Feminism should find a balance between the structural and the interpersonal, understanding that both need attention without conflating them. Eg: In rural areas, a woman may face different challenges from a financially independent urban woman, and addressing these separately helps focus on their unique struggles.
Which aspects of current feminist narratives risk alienating both men and women, especially from marginalised backgrounds?
- Oversimplification of Gender Struggles: Current feminist narratives often reduce complex interpersonal relationships to mere power struggles, ignoring the nuanced and varied experiences of individuals. This can alienate those who may not fit neatly into these narratives, particularly men from marginalized backgrounds who feel misunderstood. Eg: Depicting all men as perpetrators of patriarchy can alienate men who are struggling with their own economic and social pressures, leading to defensiveness rather than solidarity.
- Blurring of Inequities: By merging vastly different forms of inequality, such as the struggles of financially independent urban women with those of rural women fearing violence, feminist discourse risks obscuring the real, context-specific challenges faced by each group. This can alienate individuals who feel their unique struggles are being overlooked. Eg: An urban woman’s struggles with household responsibilities may be portrayed in the same light as a rural woman’s safety concerns, which can cause friction and hinder support for both groups.
- Antagonistic Tone Towards Men: A feminist narrative that is too focused on antagonism between the sexes, without acknowledging the emotional and economic pressures men face, can alienate men and prevent productive dialogue. This risks creating an “us versus them” mentality, undermining the potential for cross-gender solidarity. Eg: Men in low-income families, facing public humiliation due to financial hardship, may feel blamed for perpetuating patriarchal structures, even when they are also victims of societal pressures. This makes it harder for them to support feminist goals.
|
What has steps taken by Indian Government?
- Legislative Reforms for Women’s Safety and Empowerment: The government has enacted laws to improve women’s safety and protect their rights. Eg: The Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act (2005) was enacted to provide legal protection to women facing violence within the home. Additionally, the Criminal Law (Amendment) Act (2013) expanded the definition of sexual offenses and introduced stricter punishments for crimes like rape and acid attacks, in response to the Nirbhaya case.
- Schemes for Economic Empowerment: The government has introduced various schemes aimed at economically empowering women, especially in rural and marginalized communities. Eg: The Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (2016) provides free LPG connections to women from below-poverty-line families, reducing their dependency on traditional cooking methods that often expose them to health hazards. Similarly, schemes like Beti Bachao Beti Padhao focus on improving education and access to opportunities for girls.
- Reservation and Affirmative Action in Education and Employment: The government has implemented affirmative action measures to enhance women’s participation in education and employment. Eg: The Reservation for Women in Local Governance mandates one-third of seats in Panchayats (local governing bodies) be reserved for women, encouraging their participation in political processes and decision-making. Furthermore, policies like the Maternity Benefit Act (2017) aim to protect women’s rights in the workplace by providing paid maternity leave.
Way forward:
- Promote Intersectional Feminism: The government and society should adopt an intersectional approach to feminism, addressing the unique challenges faced by women from diverse backgrounds, including rural, urban, and marginalized communities. Eg: Tailoring policies like Beti Bachao Beti Padhao to address region-specific challenges, such as safety concerns in rural areas and educational disparities in urban areas, can create more inclusive support for all women.
- Engage Men in Gender Equality Efforts: Foster dialogue and understanding by engaging men in discussions around gender equality, recognizing their societal pressures, and encouraging shared responsibility in family and community roles. Eg: Programs like #HeForShe can be expanded to include more men, emphasizing their role in supporting gender equity at home and in the workplace, helping to bridge the gap between feminist discourse and broader societal change.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
The Right to Information (RTI) Act has clearly helped make those in power more accountable in India. However, in recent years, there have been efforts to weaken some of its important provisions, even though the Act — a major reform — was passed 20 years ago.
What is the role of Section 8(1)(j) of the RTI Act in promoting transparency?
- Balances Privacy and Public Interest: Section 8(1)(j) permits denial of personal information only if it has no relationship to public activity or interest or causes an unwarranted invasion of privacy. Eg: An officer’s medical records may be withheld, but details of their salary or qualifications can be disclosed if it serves public interest.
- Includes a Public Interest Override: Even if information is personal, it must be disclosed if larger public interest is involved. Eg: A bureaucrat’s caste certificate was disclosed in public interest when he was accused of using a fake caste certificate to secure a reserved post.
- Enhances Accountability of Public Officials: Prevents misuse of power by allowing scrutiny of officials’ actions, qualifications, and benefits. Eg: RTI queries have uncovered cases of bogus educational degrees among elected representatives and civil servants.
- Empowers Citizens to Seek Information: It strengthens democratic participation by giving citizens access to relevant information on public functionaries. Eg: Citizens have used RTI to access asset declarations of elected representatives and government officers.
- Prevents Blanket Denial of Information: Ensures that authorities cannot reject RTI requests merely by labeling the information as ‘personal’; they must justify how it affects privacy and weigh it against public interest. Eg: Information about government employees’ attendance records or transfers can be accessed to detect nepotism or irregularities.
Why does Section 44(3) of the DPDP Act, 2023 worry transparency advocates?
- Removes Public Interest Safeguard: Section 44(3) amends Section 8(1)(j) of the RTI Act by eliminating the provision that allowed disclosure of personal information in public interest. Eg: A fake caste certificate case could now be shielded from scrutiny as the information might be denied without evaluating public interest.
- Enables Blanket Denial Through Vague Definition: The term “personal information” is broad and undefined, enabling authorities to classify many types of public-relevant data as private. Eg: Details like educational qualifications or property disclosures of public servants could be denied under the label of “personal”.
- Undermines RTI as a Transparency Tool: It weakens the RTI Act’s core intent by restricting access to information that previously helped expose corruption and misconduct. Eg: RTI requests that once revealed official misconduct or nepotism in postings may now be rejected citing privacy under the DPDP Act.
How does the DPDP amendment deviate from the intent of the K.S. Puttaswamy judgment?
- Ignores the Balancing Principle of Privacy and Transparency: The K.S. Puttaswamy judgment (2017) upheld the right to privacy but emphasized that it must be balanced with other fundamental rights, including the right to information and public interest. Eg: The DPDP amendment removes the RTI Act’s public interest test, allowing personal information to be withheld even when it reveals corruption or fraud.
- Undermines Democratic Accountability: The judgment did not suggest overriding transparency laws like RTI but stressed minimum and necessary restrictions on information access. Eg: Instead of proportionate safeguards, the DPDP Act allows authorities to blanket-deny RTI requests without assessing public relevance.
- Distorts the Spirit of “Informed Citizenry”: Puttaswamy emphasized that transparency is essential for democracy, and privacy cannot be used to shield public officials from scrutiny. Eg: Information such as public officials’ property details or caste certificates may now be refused, limiting citizens’ ability to hold them accountable.
What information could now be denied under the amended RTI provisions as ‘personal’?
- Educational Qualifications and Certificates: Details about the academic background or degrees of public servants could be withheld as “personal information” under the amended provision. Eg: RTI queries that previously revealed fake degrees of elected representatives may now be denied.
- Caste and Community Certificates: Information related to caste status, often crucial in verifying eligibility for reservation benefits, may be deemed private. Eg: In cases where a public official allegedly used a fake caste certificate, such details could be denied under the privacy shield.
- Property, Assets, and Financial Disclosures: Disclosures regarding property holdings, assets, and liabilities of government employees might be refused by classifying them as personal. Eg: RTI applications that earlier exposed disproportionate assets could now be blocked.
|
Way forward:
- Restore Public Interest Safeguard: Amend the DPDP Act to reinstate the public interest clause from Section 8(1)(j) of the RTI Act, ensuring transparency is not overridden by vague privacy claims.
- Define ‘Personal Information’ Clearly: Provide a narrow and precise definition of “personal information” to prevent misuse and ensure critical public accountability data remains accessible.
Mains PYQ:
[UPSC 2020] “Recent amendments to the Right to Information Act will have profound impact on the autonomy and independence of the Information Commission”. Discuss.
Linkage: The discussion from 2020 highlights the ongoing attention on potential changes to the RTI Act. It shows that the issue of amending the RTI Act and its effects has been a concern for some time.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
A new study by researchers Sujit Raghunathrao Jagadale and Javed M. Shaikh from IIM Amritsar looks at the issue of stubble burning by examining how government policies and market systems are failing to manage the problem effectively.

Why do farmers continue stubble burning despite its harm to air quality?
- Cost-Effective Method: Stubble burning is the cheapest way for farmers to clear their fields after harvesting. Eg: Farmers burn stubble to quickly prepare their land for the next crop, especially for wheat, without incurring high labor or machinery costs.
- Lack of Affordable Alternatives: There are limited affordable and efficient alternatives to stubble burning. Eg: Farmers often do not have access to technology or subsidies for machines that can manage stubble, such as Happy Seeder or bio-decomposers.
- Government’s Focus on High-Yield Crops: The Minimum Support Price (MSP) policy incentivizes the cultivation of wheat and rice, leading to monocropping. Eg: Farmers are encouraged to grow rice continuously, which results in an abundance of stubble that needs to be disposed of quickly.
- Debt and Economic Pressure: Many farmers face financial pressures, including debt and low returns on their crops, which makes burning stubble a way to save time and money. Eg: Farmers often sell their crops to middlemen at low prices, leaving them with insufficient income to invest in sustainable farming practices.
- Lack of Strong Enforcement or Support: Although stubble burning is penalized, enforcement of laws is weak, and farmers often feel the state does not provide adequate support for eco-friendly methods. Eg: Despite penalties, farmers feel little pressure to change practices when there is insufficient governmental support or infrastructure for alternatives.
How does India’s MSP policy influence stubble burning?
- Encourages Monocropping: The MSP policy promotes the cultivation of high-yield crops like rice and wheat, leading to monocropping, which results in a large amount of stubble that must be cleared. Eg: Farmers in Punjab often grow rice followed by wheat, creating a cycle where large quantities of rice stubble need to be burned to prepare the soil for the next crop.
- Limits Crop Diversification: The MSP system prioritizes wheat and rice over other crops, making it economically unfeasible for farmers to switch to more sustainable practices or crops that would reduce stubble burning. Eg: Despite the potential for growing other crops, farmers focus on rice and wheat to benefit from MSP, leaving them with stubble that they have no economically viable option to manage.
- Financial Constraints: The MSP rates for crops like rice and wheat have remained stagnant, making it harder for farmers to invest in alternatives to stubble burning, such as machinery or composting. Eg: With wheat MSP seeing only minimal increases, farmers struggle to cover costs for labor and inputs, leading them to resort to stubble burning as the most cost-effective option to clear fields.
What has the government done in this situation?
- Implemented Subsidies for Machinery: The government has provided subsidies for the purchase of machinery like the Happy Seeder to help farmers manage stubble without burning. Eg: The Punjab government has distributed equipment like straw management machines under the Sub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanization to reduce stubble burning.
- Awareness Campaigns: The government has conducted awareness programs to educate farmers about the harmful effects of stubble burning and encourage them to adopt alternative practices. Eg: The Ministry of Agriculture and local bodies in states like Punjab and Haryana have launched campaigns to raise awareness about the environmental and health risks of stubble burning.
- Legal Measures and Penalties: Various state governments, including Punjab, have imposed fines and penalties on farmers found burning stubble, aiming to deter the practice. Eg: The Punjab government introduced a fine for stubble burning, with penalties reaching up to Rs 2,500 for each violation, although enforcement remains challenging.
|
Way forward:
- Promote Crop Diversification: Encourage farmers to shift from paddy to less water-intensive and non-stubble-generating crops through assured procurement and better MSP for alternative crops. Eg: Incentivize crops like millets and pulses to reduce stubble generation.
- Strengthen Support and Infrastructure: Scale up access to sustainable stubble management technologies and ensure timely financial and logistic support to small and marginal farmers. Eg: Expand reach of Happy Seeder and bio-decomposer solutions through local cooperatives and custom hiring centers.
Mains PYQ:
[UPSC 2015] Mumbai, Delhi and Kolkata are the three Mega cities of the country but the air pollution is much more serious probelm in Delhi as compared to the other two. Why is this so?
Linkage: Delhi’s severe air pollution, especially at certain times of the year, is caused by a combination of its location in the Indo-Gangetic Plain, nearby states burning crop stubble, and weather conditions that trap pollutants.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
The Telangana government has officially implemented the sub-categorization of Scheduled Castes (SCs) into three groups, following a Supreme Court judgment in August 2024 that upheld the constitutionality of sub-classifying SCs and Scheduled Tribes (STs) to grant separate quotas for the most marginalized groups.

About Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Their Subcategorization:
- SCs are a historically marginalized group identified in India’s Constitution to receive preferential treatment in education, employment, and political representation.
- Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 341: Empowers the President to specify castes as SCs within states or UTs.
- Article 342: Allows Parliament to include/exclude castes from the SC list.
- While grouped for reservations, disparities exist within SCs, with some groups being more disadvantaged than others.
- Subcategorization involves dividing SCs into smaller groups based on social, economic, and educational backwardness, ensuring the most marginalized receive targeted benefits.
- Sub-classification of SCs and STs for reservations is subject to judicial review to prevent misuse.
Supreme Court Verdict on Sub-categorization: State of Punjab v. Davinder Singh (2020) Case
- In its August 2024 verdict, the Supreme Court allowed states to sub-classify SCs and STs, enabling separate quotas for the most marginalized groups.
- Key Points:
- Empirical Data: Subclassification must be based on data of systemic discrimination, not political motives.
- Creamy Layer: Excludes the more advanced members of SCs/STs, applying the creamy layer principle.
- Quota Limits: No sub-categorization can exceed the overall constitutional quota ceiling.
- First-Generation Benefit: Reservations are restricted to the first generation of a family that has not benefitted from previous reservations.
|
| [UPSC 2005] Which one of the following statements is correct regarding population?
(a) Bihar has the highest percentage of Scheduled Castes in its population.
(b) The decadal growth of population of India (1991-2001) has been below 20%.
(c) Mizoram is the Indian State with the least population.
(d) Pondicherry has the highest sex ratio among the Union Territories. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
The KATRIN (Karlsruhe Tritium Neutrino Experiment) has made a groundbreaking achievement by measuring neutrino mass with a new precision.
About the KATRIN Experiment:
- The KATRIN is located at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT), specifically on its Campus North site in Karlsruhe, Germany.
- It is aimed at measuring the mass of the electron antineutrino with sub-eV precision.
- It has measured the mass of neutrinos by studying the beta decay of tritium, a radioactive form of hydrogen.
- The mass was inferred by analyzing the energy of the emitted electrons.
- Technological Setup:
- A 70-meter-long beamline with a powerful tritium source.
- A 10-meter-wide spectrometer to measure the energy of emitted electrons with high precision.
- Key Findings:
- KATRIN has set a new upper limit for neutrino mass at less than 0.45 eV/c² (8 × 10⁻³⁷ kg), nearly twice as precise as previous measurements from 2022.
- Data Collection was based on five campaigns from 2019-2021, totalling 250 days of data.
Neutrinos and Their Properties
- Neutrinos are extremely light subatomic particles that rarely interact with matter, making them difficult to detect.
- They are found in cosmic rays and solar radiation.
- Properties:
- Mass: Their small mass influences cosmic structure formation, such as galaxies and clusters.
- Weak Interaction: They interact via the weak nuclear force, allowing them to pass through vast amounts of matter.
- They are essential in particle reactions and play a key role in galaxy formation and the study of dark matter.
|
| [UPSC 2010] India-based Neutrino Observatory is included by the planning commission as a mega-science project under the 11th Five-year plan. In this context, consider the following statements:
1.Neutrinos are chargeless elementary particles that travel close to the speed of light.
2.Neutrinos are created in nuclear reactions of beta decay.
3.Neutrinos have a negligible, but non-zero mass.
4.Trillions of Neutrinos pass through the human body every second.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only (b) 1, 2 and 3 only (c) 2, 3 and 4 (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Silicon Photonics
Why in the News?
In a major breakthrough, Indian researchers have developed a new type of laser that can be placed directly onto silicon chips, a key component of modern computers.
What is Silicon Photonics?
- Silicon photonics is a technology that uses light (photons) instead of electrical signals to transmit data inside computer systems.
- Light can carry more data at higher speeds with less energy than electricity, making it a promising technology for future computing and data transfer.
- Traditional silicon chips struggle to produce light, requiring external lasers, which were inefficient and costly.
- Silicon photonics can significantly enhance data transfer speed and efficiency, benefiting industries like data centers and telecommunications.
About the Miniaturized Laser Technology
- Indian researchers have successfully integrated a laser directly onto a silicon chip, eliminating the need for separate lasers.
- The laser is made using gallium arsenide (where 20% of gallium atoms had been replaced with indium to achieve optimal light emission), which helps silicon emit light, a crucial step since silicon alone cannot produce light efficiently.
- It uses minimal power, ideal for high-performance, energy-efficient computers.
- Direct integration reduces costs, making the technology scalable for mass production.
- This innovation boosts computing power, particularly in data centers where fast data transfer is critical.
- Efforts are underway to enhance its durability, especially at higher temperatures, for broader industrial use.
| [UPSC 2008] Which one of the following laser types is used in a laser printer?
(a) Dye laser (b) Gas laser (c) Semiconductor laser (d) Excimer laser |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully tested the Mk-II(A) Laser-Directed Energy Weapon (DEW) system, marking a major achievement in the country’s defense capabilities.
About Mk-II(A) Laser-Directed Energy Weapon (DEW) System
- The Mk-II(A) Laser-DEW system, also known as Sahastra Shakti, is an indigenously developed Laser weapon with an operational range of 5km.
- It is designed to neutralize threats like drones, missiles, and remotely piloted aircraft using a 30-kilowatt laser.
- It is developed by DRDO’s Centre for High Energy Systems and Sciences (CHESS), in collaboration with other DRDO labs, academic institutions, and Indian industries.
- It focuses primarily on neutralizing aerial threats such as drones and missiles, offering a cutting-edge solution against modern warfare tactics.
How does it work?
- It utilizes radar and Electro-Optic (EO) systems for target detection.
- The laser engages the target at the speed of light, causing structural failure or significant damage.
- It delivers rapid, precise strikes with lethal impact in seconds.
- The energy used for a few seconds of firing costs as little as a couple of litres of petrol, making it cost-efficient.
- The 30-kilowatt laser ensures quick target neutralization with minimal collateral damage.
Significance of the Mk-II(A) Laser-DEW System
- Cost-Effective: Far more affordable than traditional missile systems, providing sustainable defense options.
- Reduced Ammunition Dependence: Reduces reliance on expensive ammunition, offering a long-term sustainable defence solution.
- Precision & Speed: Engages targets almost instantaneously, minimizing collateral damage and ensuring high-value targets are neutralized quickly.
- Strategic Advantage: Enhances India’s defence capabilities, providing an advanced method for protecting infrastructure and addressing evolving aerial threats.
| [UPSC 2011] With reference to Indian defence, which one of the following statements is NOT correct?
(a) With the induction of Prithvi-II, the IAF is the only air force in the world with surface-to-surface ballistic missiles under its command.
(b) Sukhoi-30 MKI jet fighters can launch air-to-air and air-to-surface precision missiles
(c) Trishul is a supersonic surface-to-air missile with a range of 30 km
(d) The indigenously built INS Prabal can launch surface-to-surface missiles |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
PYQ Relevance:
[UPSC 2018] How would the recent phenomena of protectionism and currency manipulations in world trade affect macroeconomic stability of India?
Linkage: Trump’s administration was known for implementing protectionist trade policies, primarily through tariffs, starting around that period as discussed in the article. The question asks about the impact of “protectionism” on “macroeconomic stability,” which is directly linked to concerns about a potential recession. |
Mentor’s Comment: The U.S. has been a strong supporter of free trade and a key driver of globalization since the mid-20th century. However, in a surprising shift, President Donald Trump took drastic action on April 2, calling it “Liberation Day,” by drastically changing U.S. trade policy. Until 2024, the U.S. had a low tariff rate of 2 to 3% on imports for two decades. But on April 2, Trump announced that the U.S. would now charge a minimum of 10% tariff on all imports. For imports from around 60 countries, the tariffs would be much higher, called “reciprocal” tariffs. These include a 20% tariff on the European Union (EU), 27% on India, and 46% on Vietnam.
Today’s editorial analyzes how the U.S. tariffs will affect India and the rest of the world. This topic is useful for GS Paper 2 and 3 in the UPSC Mains exam.
_
Let’s learn!
Why in the News?
On April 2, U.S. President Trump announced that the U.S. would start charging at least 10% tariffs on all imports.
What change did Trump announce on April 2 regarding U.S. tariffs?
- Introduction of a Minimum 10% Tariff on All Imports: Trump declared that the U.S. would levy a minimum 10% tariff on all imported goods, ending decades of low tariff policy. Eg: A previously tariff-free $100 imported item would now cost $110 with the new 10% tariff.
- “Reciprocal” Tariffs for Select Countries: Tariffs would be significantly higher for around 60 countries, based on what the U.S. perceives as unfair trade practices. Eg: Imports from India now face a 27% tariff, Vietnam 46%, and China a staggering 145%.
- Highest Tariffs Targeted at China: China, the largest source of U.S. imports, was hit hardest — facing 145% tariffs, as part of an aggressive move to reduce trade deficits and pressure China economically. Eg: A $100 Chinese product would now cost $245 after the new tariff.
|
How did markets respond?
- Stock Markets Nosedived: The announcement caused panic among investors, leading to sharp declines in stock markets around the world. Eg: The U.S. stock market dropped significantly, with major indices like the Dow Jones and S&P 500 seeing large declines as investors feared the impact of the tariffs.
- Increased Economic Uncertainty: The abrupt tariff increases created a sense of economic uncertainty, particularly regarding trade relations and the global supply chain. Eg: The value of the U.S. dollar fluctuated, with the dollar weakening against several currencies as concerns about a trade war heightened.
- Commodity Prices Rose: The market anticipated higher costs for goods, especially imported items, leading to a rise in the price of key commodities. Eg: Goods like electronics and consumer products became more expensive, reflecting the expected rise in tariffs and trade barriers.
What could be the chance of recession after US tariffs?
- Reduced Consumer Spending Due to Higher Prices: Higher tariffs make imported goods more expensive, which can lead to inflation and reduced purchasing power among consumers. This slowdown in consumer spending—a key driver of the U.S. economy—can drag growth. Eg: A $1,000 smartphone imported from China may now cost $2,450 due to 145% tariffs, making consumers delay or avoid big purchases.
- Strained Global Supply Chains and Business Uncertainty: Companies reliant on international supply chains may face higher input costs and uncertainty, leading to reduced investments, production delays, and job cuts.Eg: U.S. auto manufacturers sourcing parts from Asia may cut production or delay expansion due to rising costs and disrupted logistics.
- Global Retaliation and Slowing Trade: Other countries may retaliate with their own tariffs, triggering a trade war that slows global trade and weakens demand for U.S. exports, increasing the risk of a global economic downturn. Eg: If the EU or China impose counter-tariffs on U.S. agricultural or tech exports, American farmers and companies may face losses, increasing joblessness and recession risk.

|
Why is China better prepared for a trade war?
| Reason |
Why China Is Better Prepared |
Example |
| Diversified Export Markets |
Reduced reliance on U.S. by expanding trade with Asia, Europe, and Africa. |
U.S. share in China’s exports dropped from 21% (2006) to 16.2% (2022). |
| Lower Export Dependence on GDP |
Exports now form a smaller part of China’s economy, reducing vulnerability. |
Export-to-GDP fell from 35% (2012) to 19.7% (2023). |
| Focus on Tech & Innovation |
Heavy investment in AI, EVs, and domestic tech industries to cut foreign dependence. |
Made in China 2025 boosted self-reliance in high-tech sectors. |
| Manufacturing Shift to Neighbors |
Relocating production to East Asia (e.g., Vietnam) to bypass U.S. tariffs. |
Maintains supply chains while avoiding direct U.S. tariffs. |
| Strong Forex Reserves & Bond Holdings |
Large reserves used to buy U.S. treasury bonds, ensuring financial strength. |
U.S. dollar assets reduce trade/finance risks and secure China’s position. |
How will higher U.S. tariffs impact India’s exports?
- Reduced Export Earnings: Higher U.S. tariffs could decrease India’s export earnings as Indian goods would become more expensive for U.S. consumers, potentially leading to lower demand. Eg: Products like textiles and gems & jewelry, which are major export items to the U.S., might see a drop in sales due to increased tariffs.
- Impact on Key Sectors: India’s manufacturing sectors, such as automobiles and electrical machinery, might face stiffer competition due to higher tariffs, reducing their ability to compete in the U.S. market. Eg: Indian automobile exports, especially in segments like small cars, might struggle as U.S. tariffs raise the prices and reduce competitiveness.
- Diversification of Export Markets: Since the U.S. accounts for 21.8% of India’s total exports, any tariff hike could push India to explore new markets outside the U.S., reducing the impact of the tariff increase. Eg: India might increase its focus on the European Union or Southeast Asian markets, where demand for Indian goods remains strong.
- Pharmaceutical and Service Exports Unaffected: Higher tariffs on goods may not impact India’s pharmaceutical and services exports as significantly, as they are major contributors to India’s trade surplus with the U.S. Eg: Generic medicines and IT services, such as software development, will likely continue to thrive in the U.S. market despite higher tariffs on other goods.
- Pressure on Domestic Industry: Increased tariffs could also drive higher production costs in India, as it may face higher input costs for raw materials imported from the U.S. This could hurt the competitiveness of India’s export products. Eg: Sectors like steel and chemicals, which rely on U.S. exports for raw materials, may see a rise in production costs, potentially reducing profit margins.
When did the U.S. maintain low tariffs?
- Post-World War II Period (1945–1970s): After World War II, the U.S. championed free trade and maintained low tariffs to encourage global economic recovery and integrate global markets. During this period, the U.S. was seen as the chief architect of globalization. Eg: The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), established in 1947, played a crucial role in reducing global tariffs, and the U.S. led many rounds of negotiations to lower its own import duties.
- 1980s to Early 2000s: During this period, particularly under the Clinton administration, the U.S. kept tariffs low to support global trade liberalization and its dominant position in the world economy. This made the U.S. an attractive market for exports and facilitated the growth of international trade. Eg: The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) signed in 1994 between the U.S., Canada, and Mexico aimed to eliminate tariffs and increase trade between the countries, further reinforcing the U.S.’s low-tariff approach.
Why was it seen as the chief architect of globalisation during that time?
- Promotion of Free Trade Agreements: The U.S. led the establishment of various international trade agreements to reduce tariffs and promote open markets. It actively negotiated trade deals that facilitated the movement of goods, services, and capital across borders. Eg: The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), later replaced by the World Trade Organization (WTO) in 1995, was strongly influenced by the U.S. and aimed at creating a more liberalized global trade system.
- Economic Influence and Dollar Dominance: The U.S. played a dominant role in global finance, with the dollar as the primary global reserve currency. This position helped facilitate international trade and investment, as countries around the world held U.S. dollars for foreign exchange and international transactions. Eg: Countries like China and Japan invested heavily in U.S. Treasury bonds, reinforcing the U.S.’s economic influence and fostering the expansion of global markets.
- Technological and Industrial Leadership: The U.S. led technological innovation and industrial development, particularly in sectors like technology, finance, and manufacturing. This leadership helped drive global supply chains, with many countries relying on the U.S. for both innovation and as a key export market. Eg: U.S. tech giants such as Microsoft, Apple, and Google set the global stage for the digital economy, helping integrate economies worldwide into a globalized tech ecosystem.
|
Way forward:
- Diversify Export Markets: India and other countries should explore new markets outside of the U.S., especially in emerging economies and regional trade agreements, to reduce dependency on the U.S. and mitigate the effects of tariff hikes. Eg: Strengthening ties with the European Union, Southeast Asia, and Africa could help reduce reliance on the U.S. market.
- Enhance Domestic Innovation and Self-Sufficiency: Countries should focus on boosting domestic production, innovation, and technological advancements to reduce vulnerability to external trade barriers and tariffs. Eg: India could prioritize self-reliance in sectors like pharmaceuticals, electronics, and renewable energy to counter tariff pressures.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
In The State of Tamil Nadu vs. The Governor of Tamil Nadu and Another, a two-judge Bench of the Supreme Court of India, led by Justice J.B. Pardiwala and Justice R. Mahadevan, reaffirmed that Governors’ powers are limited and must follow constitutional boundaries.
What constitutional issue was addressed in the Tamil Nadu vs the Governor case?
| Aspect |
Details |
Example |
| Limits of Gubernatorial Discretion (Article 200) |
The Governor cannot withhold assent to a Bill indefinitely or act independently of the elected State Cabinet, except in constitutionally specified situations. The role is largely ceremonial. |
Governor of Tamil Nadu withheld assent to 12 Bills, including those on the appointment of Vice-Chancellors to public universities. |
| Constitutional Obligations of the Governor and State Executive |
The Governor is bound by the advice of the State Cabinet and cannot act on personal discretion unless explicitly permitted by the Constitution. This upholds representative democracy. |
Governor delayed referrals to the President without valid reasons, thereby undermining the democratic function of the State Legislature. |
| Judicial Review of Governor’s Actions |
Article 361 gives personal immunity to the Governor but does not shield official actions from judicial review. Courts can check if actions comply with the Constitution and democratic norms. |
Supreme Court held that the Governor’s inaction violated the Constitution, and invoked Article 142 to deem the Bills as assented to, resolving the legislative deadlock. |
Why was the Governor’s inaction on Tamil Nadu Bills ruled unconstitutional?
- Violation of Constitutional Duty under Article 200: The Governor is constitutionally bound to either assent to a Bill, withhold assent (and return it for reconsideration), or reserve it for the President. Indefinitely sitting on Bills without any action violates this mandate. Eg: The Governor kept 10 re-enacted Bills pending without any action or justification, undermining the role of the legislature.
- Undermining the Principles of Representative Democracy: By not acting on duly passed Bills, the Governor disregarded the advice of the elected Council of Ministers, thereby disrupting the democratic process and the legislative will of the people. Eg: Despite the Tamil Nadu Assembly passing the Bills again in a special session, the Governor forwarded them to the President without consulting the State Cabinet, showing a lack of respect for democratic norms.
When can a Governor use discretion under Article 200?
- When a Bill Affects the Powers of the High Court: The second proviso to Article 200 allows the Governor to reserve a Bill that directly affects the powers of the High Court for the President’s consideration. Eg: If a State law tries to curtail the High Court’s jurisdiction or authority, the Governor can use discretion to reserve it.
- When Presidential Assent is Constitutionally Mandatory: If a Bill falls under categories where presidential assent is specifically required (such as laws under Article 31C that seek immunity from judicial review), the Governor may reserve it. Eg: A Bill claiming protection under Article 31C, linked to Directive Principles, must be reserved for the President.
- When a Bill Fundamentally Undermines Constitutional Values: The Governor can act without ministerial advice if the Bill threatens the basic structure or core values of the Constitution. Eg: A Bill that violates secularism or federalism in an extreme manner could justify the Governor’s discretionary action.
How did the Supreme Court invoke Article 142 to resolve the constitutional deadlock in the Tamil Nadu Bills case?
- Used Article 142 to Ensure Complete Justice: The Court exercised its special power under Article 142 to deliver complete justice by deeming the 10 re-enacted Bills as having received the Governor’s assent. Eg: Instead of waiting for further assent or action from the Governor, the Court directly validated the Bills to avoid further delays in governance.
- Bypassed Unworkable Remedies Like Mandamus: Issuing a writ of mandamus (to compel the Governor to act) was seen as ineffective since the Governor is protected from personal liability under Article 361. Eg: Since the Governor cannot be punished for contempt, the Court chose Article 142 as a more enforceable solution.
- Restored the Legislative Authority of the State: By invoking Article 142, the Court reinforced the principle that the Governor cannot override the will of an elected legislature through inaction Eg: This prevented indefinite delays in implementing laws passed by the Tamil Nadu Assembly, thus preserving democratic functioning.
Why was issuing a writ of mandamus deemed inadequate?
- Governor is Immune Under Article 361: The Constitution grants the Governor personal immunity from legal proceedings while in office, making it difficult to enforce any court directive. Eg: Even if the Court issued a mandamus to compel assent or action, the Governor could not be held legally accountable for ignoring it.
- Mandamus Cannot Be Enforced Practically: Courts cannot force a Governor to exercise discretion in a particular way, only to consider doing so—making the remedy ineffective when deliberate inaction is involved. Eg: If the Governor simply delays action without giving reasons, courts have limited tools to compel a timely decision.
- Could Cause a Constitutional Standoff: Forcing the Governor through judicial direction risks undermining the separation of powers and could lead to a deadlock between constitutional authorities. Eg: If the Governor resists the court order, it could trigger a conflict between the judiciary and the executive, weakening the constitutional balance.
Way forward:
- Codify Time Limit for Assent: Amend the Constitution or enact a statutory framework to prescribe a reasonable time limit (eg: 30 days) within which the Governor must act on Bills to prevent indefinite delays.
- Enhance Legislative Oversight: Establish a mechanism for State Legislatures to seek judicial clarification or initiate review when the Governor delays action, reinforcing accountability and upholding democratic norms.
Mains PYQ:
[UPSC 2022] Discuss the essential conditions for exercise of the legislative powers by the Governor. Discuss the legality of re-promulgation of ordinances by the Governor without placing them before the Legislature.
Linkage: This question directly addresses the legislative powers of the Governor, a key aspect of their conduct. The second part specifically asks about the legality of re-promulgation of ordinances, which can be a contentious issue and often involves judicial scrutiny. This relates to the constitutional limits on the Governor’s powers, similar to the issues raised in the article.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
In March, while many urban consumers were hopeful about job opportunities, many were still negative about their income levels.

What does the gap between job optimism and income pessimism among urban consumers imply?
- Jobs Are Available, But Income Growth Is Stagnant: In March 2025, 35.5% of urban respondents reported improved job opportunities compared to a year ago, but only 23.8% reported an increase in income.
- Rising Cost of Living Without Corresponding Wage Increases: Over 90% of urban respondents indicated that commodity prices have increased over the past year, but income increases remain minimal.
- Negative Economic Outlook Despite Employment Optimism: Despite optimism regarding job opportunities, only 34.7% of urban respondents believed the overall economic situation improved compared to the previous year, the lowest share in over a year.
Why are rural respondents more pessimistic about income than urban ones?
- Dependence on Agriculture and Seasonal Employment: Rural areas heavily depend on agriculture, which is subject to seasonal fluctuations and external factors like weather conditions. Eg: A farmer in a rural area may experience low income during a poor harvest season, while urban workers with more stable jobs may not face similar income volatility.
- Limited Access to Formal and High-Paying Jobs: Urban areas offer more formal employment opportunities with better wages and benefits, while rural areas often lack access to well-paying jobs and may have higher rates of informal employment. Eg: A rural resident working as a daily wage laborer may earn less compared to an office worker in the city with a regular salary, even if both are employed.
- Lower Economic Diversification: Rural economies are less diversified compared to urban areas, which can lead to fewer job opportunities and economic growth. Eg: A rural worker may be reliant on local industries like agriculture or small-scale manufacturing, while an urban worker has access to a variety of sectors like technology, finance, and services, which tend to offer higher income prospects.
How have rising prices affected urban spending?
- Increased Spending on Essential Goods: With rising commodity prices, urban consumers are spending more on essential goods such as food, transportation, and utilities, leading to higher overall expenditures. Eg: An urban resident may see their grocery bills rise significantly due to inflation, causing them to spend more on basic food items like vegetables and grains, even if their income remains unchanged.
- Shifting Spending Priorities: As prices rise, urban consumers are prioritizing necessary expenses, often cutting back on discretionary spending like entertainment, travel, and luxury goods. Eg: A family in an urban area may reduce spending on dining out or vacations to allocate more money towards rent and daily commuting costs, adjusting their lifestyle to account for increased living expenses.
- Financial Strain Despite Employment Stability: Urban residents may continue to hold jobs, but the combination of stagnant incomes and rising costs puts financial pressure on them, leading to a higher sense of economic uncertainty. Eg: An office worker may retain their job but find it increasingly difficult to cover monthly expenses like rent and school fees for children, as inflation causes prices to rise faster than their salary increases.
What was the main factor behind the decline in positive sentiment about the economy among urban consumers in March 2025?
- Rising Commodity Prices Without Income Growth: In March 2025, over 90% of urban respondents reported that commodity prices had increased over the past year, while only 23.8% saw an increase in their income. Eg: With income levels largely stagnant and prices rising, 80% of urban respondents reported increased spending, leading to a more pessimistic view of the economy.
- Stagnant Income and Higher Spending Pressures: The survey revealed that 34.7% of urban respondents felt the overall economic situation had improved, the lowest share in over a year, indicating dissatisfaction with the broader economic outlook. Eg: An office worker might retain their job but face higher living costs (such as rent, utilities, and groceries), contributing to the sense of financial strain and a decline in positive economic sentiment, despite job availability.
Way forward:
- Focus on Wage Growth and Inflation-Linked Salary Adjustments: To address stagnant incomes, policies should ensure that wage growth keeps up with inflation, potentially through salary adjustments linked to cost-of-living indices, reducing financial strain for urban consumers.
- Boost Rural Economic Diversification and Job Creation: Improve access to diverse, high-paying jobs in rural areas through skill development programs, infrastructure improvements, and incentives for non-agricultural industries, fostering economic resilience and reducing income pessimism.
Mains PYQ:
[UPSC 2022] Economic growth in the recent past has been led by an increase in labour productivity.” Explain this statement. Suggest the growth pattern that will lead to the creation of more jobs without compromising labour productivity.
Linkage: If people in cities are worried that their incomes are not growing even though jobs are available, it shows a gap between growth driven by higher worker productivity and actual rise in people’s earnings. This is an important point discussed in this previous year’s question.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
A recent study published in Geophysical Research Letters revealed changes in both the amount and timing of rainfall using GSMaP Data between the decades 2001-2010 and 2011-2020.
About Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP)
- GSMaP is a specialized precipitation product developed through collaboration between ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation) and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency).
- It provides high-resolution precipitation data with a 0.1° x 0.1° grid and one-hour temporal resolution, focusing on the Indian subcontinent since March 2000.
- The data supports rainfall trend analysis, climate modelling, and water resource management.

Key Findings of the Study:
- Rainfall Trends:
- West-Central India: Increased daily rainfall (2 mm/day) from 2011-2020 compared to 2001-2010.
- Eastern India: A decrease of ~1 mm/day in rainfall during the same period.
- Regional Shifts: Northeastern and eastern India saw decreased rainfall, while the Indo-Gangetic Plain and southern India experienced increases.
- Vegetation & Soil Moisture:
- West-Central India saw an increase in vegetation (NDVI from 0.2 to 0.4) and soil moisture linked to increased rainfall.
- Eastern India had decreased soil moisture during the same period.
- Shifts in Peak Rainfall Timing:
- Indo-Gangetic Plain: Peak rainfall advanced by 2-4 hours.
- West-Central India: Peak rainfall delayed by 1-2 hours.
- Factors responsible for this Shift:
- Higher soil moisture supports rainfall, while reduced moisture, particularly in eastern India, decreases rainfall.
- Higher aerosol concentrations in polluted areas like the Indo-Gangetic Plain lead to earlier rainfall peaks.
- Changes in atmospheric circulation, topography, and coastal influences also affect rainfall distribution and timing.
| [UPSC 2012] Consider the following statements:
1. The duration of the monsoon decreases from southern India to northern India.
2. The amount of annual rainfall in the northern plains of India decreases from east to west.
Which of the statements given above is / are correct?
(a) 1 Only (b) 2 Only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
Researchers from Thiruvananthapuram have developed a cost-effective Real-Time LAMP (rt-LAMP) Assay for early Tuberculosis (TB) diagnosis.
About the rt-LAMP Assay
- The rt-LAMP assay (real-time Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification) is a molecular diagnostic test designed to detect TB DNA with high precision.
- It can detect TB DNA at concentrations as low as 10 copy numbers per microlitre, ensuring early detection even with low bacterial loads.
- Developed by SCTIMST, Thiruvananthapuram, the rt-LAMP assay uses Syto 16, a fluorescent dye, to monitor DNA amplification in real time, addressing the limitations of traditional LAMP tests.
- Working Principle:
- It uses six primers for DNA amplification (compared to two in RT-PCR), enhancing amplification speed.
- It operates at a single temperature, unlike RT-PCR, making it simpler and more cost-effective.
- It monitors the amplification process continuously, providing faster results.
Advantages Offered:
- High Sensitivity and Specificity: Ensures accurate detection of TB DNA due to the use of six primers.
- Cost-Effective: Uses affordable fluorescent dyes and primers, reducing diagnostic costs.
- Speed: Produces results in just 10-20 minutes, faster than traditional tests.
- Ease of Use: Compatible with existing RT-PCR machines, reducing the need for new infrastructure.
- High Throughput: Can process 96-384 tests in one run, making it ideal for high-volume settings.
| [UPSC 2007] Which of the following types is used by computed tomography employed for visualization of the internal structure of the human body?
(a) X-rays (b) Sound Waves (c) Magnetic Resonance (d) Radioisotopes |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
India and Italy have decided to enhance cooperation in trade, defence, clean energy, and high technology while working jointly on the India-Middle-East-Europe-Economic Corridor (IMEEC).
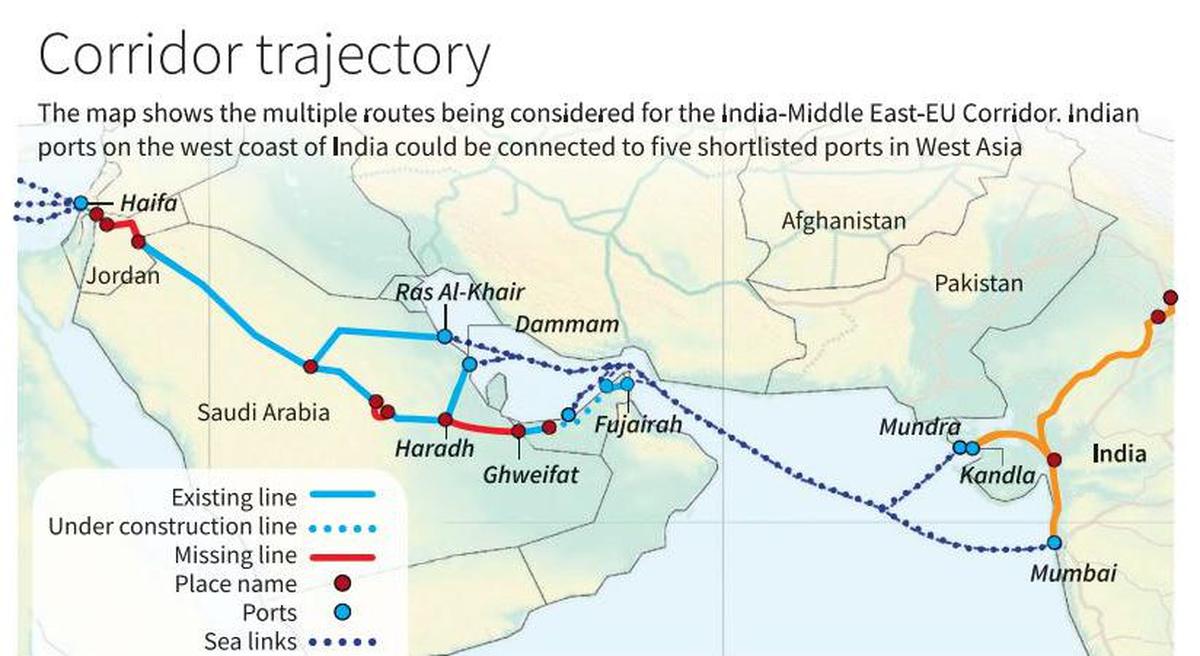
About IMEEC Project:
- IMEEC is a key initiative under the Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII), aimed at infrastructure development in developing regions.
- It was formally endorsed on September 10, 2023, during the 2023 G20 New Delhi summit.
- Signatories include: India, United States, UAE, Saudi Arabia, France, Germany, Italy, and the European Union.
- Objective: To integrate Asia, Europe, and the Middle East to boost economic cooperation, trade, and regional connectivity.
- IMEEC consists of two main corridors:
- East Corridor: Connecting India to the Arabian Gulf.
- Northern Corridor: Connecting the Gulf region to Europe.
- Key Ports to be Connected:
- India: Mundra, Kandla, Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust (Mumbai).
- Middle East: Fujairah (UAE), Jebel Ali (Dubai), Dammam (Saudi Arabia).
- Israel: Haifa Port.
- Europe: Piraeus (Greece), Messina (Italy), Marseille (France).
Significance of the Project:
- IMEEC will create a cost-efficient ship-to-rail transit network, enhancing existing transport links.
- The project will transform regional trade dynamics and foster sustainable economic growth.
| [UPSC 2023] With reference to India’s projects on connectivity, consider the following statements:
1. East-West Corridor under Golden Quadrilateral Project connects Dibrugarh and Surat.
2. Trilateral Highway connects Moreh in Manipur and Chiang Mai in Thailand via Myanmar.
3. Bangladesh-China -India -Myanmar Economic Corridor connects Varanasi in Uttar Pradesh with Kunming in China.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
Earlier this month, severe weather in the United States, including heavy rainfall, strong winds, and thunderstorms, was caused by an Atmospheric River.
What is an Atmospheric River?
- An atmospheric river is a narrow, fast-moving band of moisture and wind that transports large amounts of water vapor across vast distances.
- They form when large-scale weather patterns align, creating channels of moisture transport from tropical oceans, guided by low-level jet streams toward the coast.
- They typically span 402-606 km in width and can extend over 1600 km in length.
- The most powerful atmospheric rivers transport moisture equivalent to the Mississippi River’s flow.
- Example: The Pineapple Express, a well-known atmospheric river, transports moisture from Hawaii to the West Coasts of the U.S. and Canada.
- The intense rainfall from atmospheric rivers leads to flooding, mudslides, and infrastructure damage, with wind speeds comparable to hurricanes.

Impact and Climate Change:
- Rising global temperatures cause more water to evaporate, and warmer air can hold more moisture.
- For every 1°C increase, the atmosphere can hold 7% more moisture, leading to stronger storms.
- Research indicates such events will likely grow longer and more intense.
| [UPSC 2023] With reference to the Earth’s atmosphere, which one of the following statements is correct?
(a) The total amount of insolation received at the equator is roughly about 10 times of that received at the poles.
(b) Infrared waves are largely absorbed by carbon dioxide that is concentrated in the upper atmosphere.
(c) Infrared waves are largely absorbed by water vapour that is concentrated in the lower atmosphere.
(d) Ultraviolet rays are absorbed by the ozone layer lying in the ionosphere. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
PYQ Relevance:
[UPSC 2019] What are the continued challenges for women in India against time and space?
Linkage: The challenges that women still face are a major concern under the Beijing Platform for Action and are likely to be reviewed in the Beijing India Report. Pointing out these ongoing issues shows how much more needs to be done to reach the goals of the Beijing Declaration. |
Mentor’s Comment: It’s been 30 years since the Beijing Declaration set a global plan for gender equality across areas like education, health, and politics. In India, it led to key laws like the Domestic Violence Act and the POSH Act, and encouraged women’s economic empowerment. However, poor implementation still creates a gap between legal rights and the real experiences of women.
Today’s editorial discusses how gender inequality and climate change are interconnected. This topic is relevant for GS Paper 1 (Women’s Issues), GS Paper 2 (Policy Making), and GS Paper 3 (Impact of Climate Change). It highlights the challenges women face due to climate change and the need for better policies to address these issues.
_
Let’s learn!
Why in the News?
The report lacks a strong link between climate and gender, and this needs to be fixed through policy improvements and changes at the grassroots level.
Why does this report lack a strong link between climate and gender?
- Limited Focus on Gender-Specific Impacts: The report fails to adequately highlight how climate change specifically affects women, especially in rural areas. Eg: It doesn’t emphasize the extra burden women face in collecting water or gathering fuel during droughts, which worsens due to climate change.
- Insufficient Data on Gendered Vulnerabilities: The report lacks comprehensive data on the gendered impacts of climate change, leaving out how women are disproportionately affected by disasters and resource scarcity. Eg: It overlooks how climate-induced migration increases women’s vulnerability to gender-based violence.
- Absence of Gender-Responsive Climate Policies: The report doesn’t propose clear actions for integrating gender into climate policies, limiting women’s participation in climate adaptation and decision-making. Eg: There are no specific recommendations for promoting women’s leadership in local climate action plans or agricultural adaptation strategies.
|
What challenges do rural women face due to gender inequality and climate change?
| Challenge |
Impact on Rural Women |
Example/Evidence |
| Education Disruption |
Climate-induced migration and household burdens force girls to drop out of school. |
In Dhanelikanhar village, Chhattisgarh, girls are leaving school due to displacement caused by climate stress and migration. |
| Unpaid Care Work |
Resource scarcity increases women’s burden of water, fuel collection, and caregiving, limiting their economic opportunities. |
Arsht-Rock report: Rural Indian women work over 8 hours daily, with 71% of their labor unpaid, deepening gender inequality. |
| Health Vulnerability |
Malnutrition, anaemia, and reproductive health issues rise due to food insecurity and lack of healthcare access. |
Over 50% of pregnant women in India are anaemic; food-insecure women are 1.6x more likely to suffer from anaemia. |
| Livelihood Loss |
Extreme weather reduces agricultural output and affects non-farm livelihoods where women are largely employed. |
Climate change causes up to 33% income loss in rural areas, with women in non-farm sectors most affected. |
| Exposure to Violence and Safety Risks |
Climate stress and resource conflicts heighten risks of intimate partner violence and general insecurity. |
A study shows every 1°C rise in temperature leads to 8% more physical violence and 7.3% more sexual violence against women in India. |
Why is a gender-climate lens vital for India’s sustainable future, as per the Beijing India Report 2024?
- Inclusive Policy Design: A gender-climate lens ensures that women’s specific vulnerabilities are addressed in climate policies. Eg: Only 6% of climate policies globally mention women, leading to gender-blind strategies in India’s rural development.
- Strengthening Resilience: Recognizing women’s roles in natural resource management and agriculture strengthens community resilience to climate shocks. Eg: Rural and tribal women preserve climate-resilient seeds, essential for adaptive farming during droughts and floods.
- Reducing Inequality: Targeted climate budgeting and gender audits help close gaps in access to resources, services, and decision-making power. Eg: Women’s unpaid work, like water and fuel collection, could rise to 8.3 hours/day by 2050 without gender-responsive policies.
- Boosting Food Security: Closing the gender gap in agricultural resources increases productivity and national food security. Eg: Empowering women farmers can raise farm yields by 20%-30%, feeding up to 150 million more people.
- Empowering Local Leadership: Women-led climate initiatives promote local innovation, disaster preparedness, and sustainability. Eg: Women’s self-help groups in climate-vulnerable areas act as first responders during disasters and promote eco-friendly practices.

What are the steps taken by the Indian government?
- Inclusion in National Climate Frameworks: The government has integrated gender concerns into major climate policies like the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) and State Action Plans (SAPCCs). Eg: Some SAPCCs include women’s role in sustainable agriculture and water management initiatives.
- Legislative and Policy Support for Women’s Empowerment: Laws like the Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act and POSH Act strengthen the overall gender rights framework, which intersects with climate resilience. Eg: These laws provide safety nets that support women’s participation in community and environmental activities.
- Promotion of Women-Led Livelihoods in Rural Missions: Schemes like the National Rural Livelihoods Mission (NRLM) support women’s Self-Help Groups (SHGs) to engage in sustainable practices. Eg: Women SHGs in Odisha and Chhattisgarh are trained in climate-resilient farming and forest produce collection.
|
Where should policies and budgets focus to support gender-responsive climate action? (Way forward)
- Gender-Responsive Climate Budgeting: Policies must ensure budgets address the specific climate vulnerabilities of women and prevent greenwashing. Eg: Creating separate budget lines for women’s disaster relief and climate-resilient livelihood schemes in rural areas.
- Climate Education and Skill Building: Invest in capacity building for women to participate in climate action and green jobs. Eg: Training rural women in solar panel installation or eco-friendly farming techniques.
- Support Hubs and Safety Services: Establish community hubs that offer healthcare, disaster relief, and protection from gender-based violence. Eg: Setting up women-centric climate support centers in flood-prone regions of Assam.
- Non-Farm Livelihood Diversification: Promote alternative income sources for women affected by climate-related agricultural losses. Eg: Funding mushroom farming or tailoring units for women in drought-hit Bundelkhand.
- Inclusion in Local Governance and Decision-Making: Ensure women’s representation in local climate planning and governance bodies. Eg: Mandating women’s participation in State and District Climate Action Committees in Madhya Pradesh.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the news?
The National Education Policy aims to transform India’s separate higher education system by creating large institutions that offer education across multiple fields.
What distinguishes multidisciplinary, cross-disciplinary, and interdisciplinary approaches in higher education?
| Approach |
Description |
Example (Eg) |
| Multidisciplinary |
Involves multiple disciplines working together, but each maintains its own methods and boundaries. |
Eg: A team of economists, biologists, and engineers working on a project about climate change, but each discipline works separately within their own domain. |
| Cross-disciplinary |
Encourages collaboration between disciplines but without integrating their knowledge. |
Eg: An educationist and an economist working together on a project, but they maintain their individual disciplinary perspectives without merging them. |
| Interdisciplinary |
Integrates concepts, methods, and frameworks from different disciplines to create a unified approach. |
Eg: A course titled “Environmental Economics” combining economics, environmental science, and sociology to address climate change through an integrated perspective. |
Why must single-stream institutions be phased out under the National Education Policy?
- Encouraging Cross-Disciplinary Collaboration: Single-stream institutions focus only on one discipline, limiting students’ exposure to other fields. Phasing them out encourages the integration of various disciplines, fostering collaboration. Eg: A single-stream commerce college could partner with a neighboring arts college, allowing students to explore subjects like economics and sociology alongside their commerce studies.
- Expanding Knowledge and Skill Sets: Multidisciplinary institutions allow students to develop a broader skill set by learning from multiple disciplines, enhancing their adaptability and problem-solving abilities. Eg: A student in a multidisciplinary university could take courses in both computer science and environmental studies, enabling them to work on tech-driven solutions for environmental issues.
- Meeting Global Educational Standards: Single-stream institutions limit the scope of education, whereas multidisciplinary campuses are more aligned with global trends in higher education that emphasize holistic, well-rounded learning. Eg: In top global universities, students often have the flexibility to take courses from diverse fields, making them more versatile and better prepared for complex, real-world challenges.
How can Indian universities promote cross-disciplinary learning and collaboration?
- Encouraging Joint Courses and Programs: Indian universities can create joint courses and programs that combine subjects from different disciplines, allowing students to explore connections between fields and work on collaborative projects. Eg: A course titled “Sustainability in Urban Planning” could combine inputs from urban studies, environmental science, and economics, encouraging students to approach problems from multiple perspectives.
- Fostering Collaborative Research Projects: Universities should establish research centers and projects that bring together faculty and students from different disciplines to work on solving real-world challenges, promoting cross-disciplinary collaboration. Eg: A research project focused on public health could involve faculty from medicine, economics, sociology, and environmental science to address issues like the spread of infectious diseases in urban areas.
Who plays a crucial role in fostering interdisciplinary thinking?
- Faculty Members: Professors and researchers play a crucial role in fostering interdisciplinary thinking by encouraging students to approach problems from multiple disciplinary angles and by designing courses and projects that integrate knowledge from different fields. Eg: A professor from the economics department might collaborate with faculty from environmental science and sociology to create a course on “Environmental Economics,” encouraging students to consider both economic policies and environmental impacts in solving global challenges.
- University Administration: University leaders and administrators can support interdisciplinary thinking by creating structures that promote cross-department collaboration, offering funding for interdisciplinary research, and ensuring that the curriculum encourages interaction across disciplines. Eg: A university may establish an “Interdisciplinary Research Fund” to support projects that involve multiple departments.
What challenges do they face in current academic structures?
- Rigid Departmental Boundaries: Traditional departments often have defined areas of focus, making collaboration difficult across disciplines. Eg: A physics department may not easily partner with a social sciences department on a project related to climate change impacts.
- Lack of Incentives for Interdisciplinary Work: Faculty members are primarily rewarded for publishing in their specific discipline, not for interdisciplinary research. Eg: A researcher in environmental science might find it hard to get recognition for a joint paper with a computer science expert on climate modeling.
- Limited Interdisciplinary Training for Faculty: Many professors are trained and specialize in a single discipline, which hinders their ability to teach or engage in interdisciplinary approaches. Eg: An economics professor may not have the skills to incorporate concepts from sociology or political science into their curriculum.
Way forward:
- Integrating Interdisciplinary Curriculum: Universities should design flexible curricula that allow students and faculty to take courses and engage in research across disciplines, breaking traditional academic silos.
- Incentivizing Interdisciplinary Research and Collaboration: Establish funding programs and academic recognition for interdisciplinary research to motivate faculty and students to work across departmental boundaries.
Mains PYQ:
[UPSC 2020] National Education Policy 2020 is in conformity with the Sustainable Development Goal-4 (2030). It intends to restructure and reorient education system in India. Critically examine the statement.
Linkage: Multidisciplinary universities need to be established to reach the goal by 2030, aligning with the timeframe of SDG-4. This question directly talk about the NEP 2020’s intent to restructure and reorient the education system, which is central to the idea of shaping the university of the future.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now










