Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ART, Key features of the Bill
Mains level: ART regulation in India
The Lok Sabha has passed the Assisted Reproductive Technology- ART (Regulation) Bill,, 2020 that proposes the establishment of a national registry and registration authority for all clinics and medical professionals serving in the field.
Key highlights of the Bill:
Definition of ART
- The Bill defines ART to include all techniques that seek to obtain a pregnancy by handling the sperm or the oocyte (immature egg cell) outside the human body and transferring the gamete or the embryo into the reproductive system of a woman.
- Examples of ART services include gamete (sperm or oocyte) donation, in-vitro-fertilisation (fertilising an egg in the lab), and gestational surrogacy (the child is not biologically related to surrogate mother).
- ART services will be provided through: (i) ART clinics, which offer ART related treatments and procedures, and (ii) ART banks, which store and supply gametes.
Regulation of ART clinics and banks
- The bill provides that every ART clinic and bank must be registered under the National Registry of Banks and Clinics of India.
- It will act as a central database with details of all ART clinics and banks in the country.
- State governments will appoint registration authorities for facilitating the registration process.
- Clinics and banks will be registered only if they adhere to certain standards (specialised manpower, physical infrastructure, and diagnostic facilities).
- The registration will be valid for five years and can be renewed for a further five years.
Conditions for gamete donation and supply
- Screening of gamete donors, collection and storage of semen, and provision of oocyte donor can only be done by a registered ART bank.
- A bank can obtain semen from males between 21 and 55 years of age, and oocytes from females between 23 and 35 years of age.
- An oocyte donor should be an ever-married woman having at least one alive child of her own (minimum three years of age).
- The woman can donate oocyte only once in her life and not more than seven oocytes can be retrieved from her.
- A bank cannot supply gamete of a single donor to more than one commissioning couple (couple seeking services).
Conditions for offering ART services:
- ART procedures can only be carried out with the written informed consent of both the party seeking ART services as well as the donor.
- The party seeking ART services will be required to provide insurance coverage in the favour of the oocyte donor (for any loss, damage, or death of the donor).
- The Bill also requires checking for genetic diseases before the embryo implantation.
Rights of a child born through ART
- A child born through ART will be deemed to be a biological child of the commissioning couple and will be entitled to the rights and privileges available to a natural child of the commissioning couple.
- A donor will not have any parental rights over the child.
National and State Boards:
- The Bill provides that the National and State Boards for Surrogacy constituted and will for the regulation of ART services.
- Key powers and functions of the National Board include:
- Advising the central government on ART related policy matters
- Reviewing and monitoring the implementation of the Bill
- Formulating code of conduct and standards for ART clinics and banks
- Overseeing various bodies to be constituted under the Bill
- State Boards will coordinate enforcement of the policies and guidelines for ART as per the recommendations, policies, and regulations of the National Board
Offences and penalties
Offences under the Bill include:
- Abandoning, or exploiting children born through ART,
- Selling, purchasing, trading, or importing human embryos or gametes,
- Using intermediates to obtain donors,
- Exploiting commissioning couple, woman, or the gamete donor in any form, and
- Transferring the human embryo into a male or an animal
- These offences will be punishable with a fine between 5 and 10 lakh rupees for the first contravention.
- For subsequent contraventions, these offences will be punishable with imprisonment for a term between eight and 12 years, and a fine between 10 and 20 lakh rupees.
- Any clinic or bank advertising or offering sex-selective ART will be punishable with imprisonment between five and ten years, or fine between Rs 10 lakh and Rs 25 lakh, or both.
- No court will take cognisance of offences under the Bill, except on a complaint made by the National or State Board or any officer authorised by the Boards.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NJIC
Mains level: Judicial Infrastructure in India

The Supreme Court orally said that courts cannot wait on the whims and fancies of the Government, but need a proper mechanism for funding the development of judicial infrastructure.
National Judicial Infrastructure Corporation (NJIC)
- The idea for such NJIC was first proposed by CJI Ramana in March this year, even before he took office.
- It mooted the idea of an “umbrella national organization” that would take care of the need for judicial infrastructure.
- Such a corporation would bring the uniformity and standardization required to revolutionize judicial infrastructure, said CJI.
- Soon after he was sworn in, the CJI commenced work on the NJIC and a survey of 6,000 trial courts in various states was undertaken as part of this exercise.
CJI recommends the composition of NJIC
- The CJI has said that the Judiciary is least interested in retaining control of the council.
- The composition can be of the Union Minister for Law and Justice, the Secretary, Finance, etc.
- The States can also be represented.
- The benefit of having a senior judge or Chief Justice on it would be that they are in the know of things.
Why need NJIC?
- No central agency: Presently, there is no agency to ensure use of funds allocated to augment judicial infrastructure
- Infrastructure gap: There is a substantial gap in infrastructure and availability of basic amenities in the lower judiciary.
- Lack of basic amenities: There is a lack of court halls, residential accommodation, and waiting room for litigants in trial courts, especially in smaller towns and rural areas.
- Budgetary lapses: Experience shows that budgetary allocation for state judiciary often lapses since there is no independent body to supervise and execute works.
NJIC is expected to fill this vacuum and overcome problems related to infrastructure.
Significance of NJIC
- The modernization of judicial infrastructure did not mean building more courts or filling up vacancies or ploughing through vacancies.
- An efficient “judicial infrastructure” means providing equal and free access to justice.
- This could be realized through a barrier-free and citizen-friendly environment.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Features of the Dam Safety Bill
Mains level: Dame Safety

The Dam Safety Bill 2021 was moved in the Rajya Sabha but the debate could not be held because of disruptions from the Opposition parties.
Dam Safety Bill, 2021
- The Bill provides for surveillance, inspection, operation and maintenance of dams to prevent disasters, and institutional mechanisms to ensure safety.
- It applies to over 5,000 dams across the country, many of which are currently in poor conditions.
- It has been met with significant opposition, particularly from several states that claim the bill oversteps the Centre’s mandate.
Which dams are covered?
- All dams in India with a height above 15 metres come under the purview of the bill.
- Dams between 10 to 15 metres of height are also covered but only if they meet certain other specifications in terms of design and structural conditions.
National Committee on Dam Safety
- The Bill provides for the constitution of a National Committee on Dam Safety (NCDS) which is to be chaired by the Central Water Commissioner (CWC).
- The other members of the NCDS will be nominated by the Centre and will include up to 10 representatives of the Centre, 7 state government representatives, and 3 experts on dam safety.
- The NCDS is to formulate policies for dam safety and to prevent dam failures.
- In the event of a dam failure, the NCDS will analyse why the failure occurred, and suggest changes in dam safety practices to ensure there aren’t any repetitions.
National Dam Safety Authority (NDSA)
- The bill provides for the formation of a NDSA which will be responsible for implementing the policies of the NCDS, and will resolve issues between State Dam Safety Organisations (or SDSOs) and dam owners.
- The NDSA will also specify regulations for the inspection of dams and will provide accreditation to the various agencies working on the structure of dams and their alteration.
State Dam Safety Organisations (SDSOs)
- The bill will also result in the establishment of SDSOs, and State Committees on Dam Safety (SCDSs).
- The jurisdiction of the SDSOs will extend to all dams in that specific state.
Cross jurisdictions
- The NDSA will, in some cases, possess this jurisdiction, for example, if a dam owned by one state is situated in another or crosses multiple states, or if a dam is owned by a central public sector undertaking.
- SDSOs will be in charge of scrutinizing dams under their jurisdiction and maintaining a database of the same.
- The SCDS will review the work of the SDSO, and will also have to assess the impact of dam-related projects on upstream and downstream states.
- The bill gives the Central government the power to amend the functions of any of the above bodies through a notification, whenever it is deemed necessary to do so.
How does Bill change the functioning of dams?
- If the bill is made into a law, then dam owners will have to provide a dam safety unit in each dam.
- The dam safety unit will be required to inspect the dam before and after the monsoon session, and also during and after natural disasters such as earthquakes and floods.
- The bill requires dam owners to prepare emergency action plans. Risk-assessment studies will also have to be undertaken by owners, regularly.
- At specified, regular intervals, and in the event of either a modification to the dam’s structure or a natural event that may impact the structure, dam owners will have to produce a comprehensive safety evaluation by experts.
Do you know?
The point of contention are four dams — Mullaperiyar, Parambikulam, Thunakkadavu and Peruvaripallam — located in Kerala but owned, operated and maintained by the Tamil Nadu Government.
Issues with bill
- The primary objection to the bill is that is unconstitutional, as water is one of the items on the State List.
- Tamil Nadu, which currently possesses four dams situated in Kerala, is opposed to the Bill as it would result in the four dams falling under the NDSA.
- This will be doing away with Tamil Nadu’s rights over the maintenance of the dam.
- The Bill states that the NCDS will be chaired by the Central Water Commissioner.
- However the Supreme Court has ruled in the past that such a scenario is prohibited, as it involves the CWC, an advisor, functioning both as a regulator and the head of the NCDS.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: G20, G7 and its members
Mains level: Not Much
India has joined the G20 ‘Troika’with Indonesia and Italy.
G20 Troika
- Troika refers to the top grouping within the G20 that consists of the current, previous and incoming presidencies — Indonesia, Italy and India.
- With this move, India has started the procedure for taking over the G20 presidency.
Significance of the move
- India will assume the G20 presidency on December 1, 2022 from Indonesia, and will convene the G20 Leaders’ Summit for the first time in India in 2023.
- Indonesia took over the G20 presidency this year.
Do you know?
A Sherpa is the personal representative of a head of state or head of government who prepares an international summit, such as the annual G7 and G20 summits.
About G20 Countries

- Formed in 1999, the G20 is an international forum of the governments and central bank governors from 20 major economies.
- Collectively, the G20 economies account for around 85 percent of the Gross World Product (GWP), 80 percent of world trade.
- The members of the G20 consist of 19 individual countries plus the European Union (EU).
- The 19 member countries of the forum are Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, South Korea, Turkey, United Kingdom and the United States.
- The European Union is represented by the European Commission and by the European Central Bank.
- India has been a member of the G20 since its inception in 1999.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Global Gateway Project
Mains level: Countering projects against Chinese BRI

The European Union has unveiled a project called ”Global Gateway” that is worth 300 billion euros ($340 billion). The project is being seen as a response to China’s Belt and Road strategy.
Global Gateway Project
- It is the initiative Build Back Better World and the European Global Gateway that are reinforcing each other.
- The bloc will mobilize the financial aid in public and private infrastructure investment around the world.
- It is an offshoot of a plan by G7 countries to offer developing countries an alternative to Belt and Road.
- The project will probably extend the remit of the European Fund for Strategic Investment, or create a similar institution, which can act as a guarantor for riskier investments in the ‘Global South’.
- The EU has indicated it especially wants to compete for infrastructure development projects in Africa.
About Belt and Road Initiative
- The Belt and Road is a flagship project of Chinese President Xi Jinping that was launched in 2013.
- Beijing has invested $139.8 billion in the project which is the centerpiece of Chinese foreign policy.
- BRI aims to develop land and sea infrastructure to better connect China to Asia, Europe and Africa for trade and development, and it has found many partners around the world.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC), WHO
Mains level: Not Much
The World Health Assembly (WHA) took the historic decision to form a global treaty to “strengthen pandemic prevention, preparedness and response”.
Significance of the launch
- The launch of putting together this accord is the second such initiative taken under Article 19.
- The first initiative was the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC), which came into effect in 2005.
About FCTC
- The Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC) is the world’s first modern-day global public health treaty.
- It is also the first treaty negotiated under the auspices of the World Health Organization (WHO).
- The treaty entered into force in February 2005.
- It was signed by 168 of the 192 WHO member states and more than 180 WHO member states have become parties to the convention.
Highlights of the FCTC
The FCTC provides an internationally coordinated response to combating the tobacco epidemic and sets out specific steps for governments addressing tobacco use, including:
- Adopting tax and price measures to reduce tobacco consumption
- Banning tobacco advertising, promotion and sponsorship
- Creating smoke-free work and public spaces
- Putting prominent health warnings on tobacco packages
- Combating illicit trade in tobacco products
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: TFR and replacement rate
Mains level: Paper 2- Regional demographic variation and its implications for federalism in India
Context
Recent results from National Family Health Survey-5 (NFHS-5) suggest that we are entering an era where we will have to tackle these challenges.
A milestone in India’s demographic history: TFR at 2.0
- NFHS-5 places the total fertility rate (TFR) at 2.0.
- With two parents having two children, we have reached a replacement level of fertility.
- Due to many young people, the population will continue to grow, but the replacement level fertility is a significant milestone in India’s demographic history.
- This decline is spread evenly across the country, with 29 states and UTs having a TFR of 1.9 or less, with seven below 1.6.
- All southern states have a TFR of 1.7-1.8, similar to that of Sweden.
- Even states that have not reached replacement fertility — Bihar and Uttar Pradesh — seem to be headed in that direction.
- Part of the original coterie of lagging states, Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan both have achieved TFRs of 2.0.
Challenge: Supporting the ageing population
- Supporting ageing population: As fertility declines, the proportion of the older population grows, and societies face the challenge of supporting an ageing population with a shrinking workforce.
- This challenge is greater for leaders at the beginning of the demographic transition — Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
- Interestingly, these are also among the more prosperous states in India, whose economic activities increasingly rely on migrant labour from other states.
- Many industries such as auto parts manufacturing and construction in southern states rely on semi-skilled migrants, often transported under contractual arrangements, from northern and eastern states, particularly Bihar, Uttar Pradesh and Odisha.
Rethinking the critical dimension of Indian federalism
- Dependence on migrat workforce: Many industries such as auto parts manufacturing and construction in southern states rely on semi-skilled migrants, often transported under contractual arrangements, from northern and eastern states, particularly Bihar, Uttar Pradesh and Odisha.
- Allocation of political power: While the Indian constitution mandates allocation of Lok Sabha seats across states in proportion to their population via the Delimitation Commission, the Emergency-era 42nd amendment froze seat allocation to the population share of states in the 1971 Census.
- Equity consideration in central allocation to states: The division of central allocation to states is another area where population concerns have dominated equity considerations.
- Much of the Centre-state revenue sharing occurs through recommendations of various Finance Commissions.
- The sixth to fourteenth Finance Commissions allocated resources between states using the 1971 population shares of various states.
- The Fifteenth Finance commission used Census data from 2011, but it also added the criteria of demographic performance, rewarding states with lower TFR.
Type of demographic policy India needs to pursue
- Pursue policy followed by China? Does India want to pursue China’s route of sharply lower fertility, with a large number of families stopping at one child, or are we content with moderately below replacement fertility of about 1.7-1.8?
- If the latter, we are well-positioned to head in this direction.
- Issues faced by China: while very low fertility provides a temporary demographic dividend with a reduced number of dependents to workers, the increased burden of caring for the elderly may become overwhelming over the long term.
- Advantage of Regional demographic variation in India: India is fortunate that its demographic dividend may be smaller, but is likely to last for a more extended period due to regional variation in the onset of the fertility decline.
- As southern states struggle with the growing burden of supporting the elderly, northern states will supply the workforce needed for economic growth.
- Economic expansion: The increasing pace of migration may help shore up economic expansion in the south with its shrinking workforce augmented by workers from other states.
Consider the question “Examine the influence of regional demographic variation on the fedaralism in India? How such variation can help India?”
Conclusion
The Sixteenth Finance Commission and the next Delimitation Commission must be freed from the burden of managing the demographic transition, focused on carrying out their tasks in the best interests of Indian federalism.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: AUKUS
Mains level: Paper 2- Implications of China's aggressive policies for geopolitics
Context
One of the many consequences of China’s assertive posture in Asia has been the emergence of geopolitical coalitions to limit the prospects for Beijing’s regional dominance.
Two new coalitions forcing China rethink
- Quad and AUKUS: Two new coalitions that have got a lot of political attention are the Quadrilateral framework involving Australia, India, Japan and the US, and the AUKUS, which brings together Australia, the United Kingdom and the United States.
- Until recently, China was quite contemptuous of the new political formations.
- It had compared the Quad to “seafoam” that is here now but gone in a second.
- China’s dismissive attitude has now yielded place to denunciation.
US’s policy forcing China to rethink
- Two big factors are behind China’s rethinking.
- Consensus in the US on Challenging China: One was the surprising emergence of American domestic political consensus on challenging China.
- Beijing believed that Donald Trump was an exception to the longstanding US policy of deeper economic integration with China and sustained political engagement. But Biden has simply reinforced Trump’s strategy.
- US making alliances critical element of China policy: Trump thought that alliances are a burden on US taxpayers.
- Biden, in contrast, has made alliances a critical element of his China strategy.
- The idea was to create “situations of strength” vis-a-vis China by rebuilding US alliances and developing new coalitions.
- In Asia, the Biden administration moved quickly to strengthen the traditional security ties with its allies in northeast Asia — Japan and South Korea.
- Elevating the Quad to leaders-level: It also elevated the Quad to the leaders-level within weeks after Biden took charge and had a physical summit in Washington six months later.
- AUKUS: It also announced the AUKUS.
- Biden travelled to Europe in June this year to revitalise the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation.
- Summit with Russia: Biden also decided on an early summit with Russian President Vladimir Putin that took place in Geneva at the end of his European tour.
- Rebalancing relations: Biden’s team believed that the greatest strength of the US was its wide network of allies and partners.
- And that mobilising them was the key to rebalancing relations with China.
How China is making alliances and partnerships?
- While China’s economic reach is now global and deep, political and military alliances have not been part of Beijing’s tradition.
- Relations with Russia at peak: Beijing’s ties with Moscow have never been as close as they are.
- Relations with N. Korea and Pakistan: China also has strong alliance-like relations with North Korea and Pakistan.
- But there can be little comparison though between the kind of strengths that American allies bring to the table with those of China’s partners.
Is Asian geopolitical structure turning in China’s favour?
- Beijing was betting on the proposition that the Asian geopolitical structure was turning, irretrievably, in China’s favour.
- This is based on a number of propositions.
- Location of the US: America, located far from Asia, will have trouble overcoming the tyranny of geography in a conflict with China.
- The economic and military power of China: China’s hard power — both economic and military — relative to the US is growing rapidly and shifting the local balance of power in its favour.
- Location of China: The proximity of China and Asian regional integration have made Beijing the most important economic partner for the whole region.
- Beijing believed that few Asian nations would want to spoil their commercial relations with China and align with Washington.
- Power imbalance: The vast imbalance in military power between Beijing and its neighbours it presumed would dissuade most Asian states from considering armed confrontations with China
- Breaking up coalition: China counted on the fact that it is easier to break up coalitions than build them.
Implications of China’s aggressive policies
- Making the US unfriendly prematurely: Chinese policies have driven the US towards an unanticipated internal consensus on containing Beijing.
- Making a friendly America into an enemy prematurely could go down as one of Xi Jinping’s egregious strategic errors.
- Driving regional countries towards the US: China’s aggressive regional policies are driving many countries like Australia, India, Japan, the Philippines and Vietnam, towards the US.
- Neighbouring countries pursuing stronger national military capacities: While the military balance of power in Asia has certainly turned in China’s favour, it has not cowed down its neighbours.
- Many are pursuing stronger national military capabilities to limit some of the threats from China.
- Stoked nationalism: China, which never stops to emphasise its own nationalism, appears to have underestimated the depth of similar sentiment in other Asian states.
- Today, it is driving many of China’s neighbours into the US camp.
- It is America and not China that today talks about the sovereignty and territorial integrity of Asian nations.
Consider the question “One of the many consequences of China’s assertive posture in Asia has been the emergence of geopolitical coalitions to limit Beijing’s regional dominance. Critically analyse.”
Conclusion
It has been quite fashionable in the West as well as in the East, to proclaim that China’s hegemony is inevitable, American decline is terminal, and Asian coalitions are unsustainable. Those conclusions are premature at best. For Xi Jinping has squandered many of China’s natural geopolitical advantages.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Citizenship of India
Mains level: Read the attached story
More than six lakh Indians renounced citizenship in the past five years, the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) informed the Lok Sabha.
Citizenship in India
- Citizenship is in the Union List under the Constitution and thus under the exclusive jurisdiction of Parliament.
- The Constitution does not define the term ‘citizen’ but gives, in Articles 5 to 11, details of various categories of persons who are entitled to citizenship.
- Unlike other provisions of the Constitution, which came into being on January 26, 1950, these articles were enforced on November 26, 1949 itself, when the Constitution was adopted.
Various provisions for Indian Citizenship
Article 5
- It provided for citizenship on the commencement of the Constitution.
- All those domiciled and born in India were given citizenship.
- Even those who were domiciled but not born in India, but either of whose parents was born in India, were considered citizens.
- Anyone who had been an ordinary resident for more than five years, too, was entitled to apply for citizenship.
Article 6
- Since Independence was preceded by Partition and migration, Article 6 laid down that anyone who migrated to India before July 19, 1949, would automatically become an Indian citizen if either of his parents or grandparents was born in India.
- But those who entered India after this date needed to register themselves.
Article 7
- Even those who had migrated to Pakistan after March 1, 1947 but subsequently returned on resettlement permits were included within the citizenship net.
- The law was more sympathetic to those who migrated from Pakistan and called them refugees than to those who, in a state of confusion, were stranded in Pakistan or went there but decided to return soon.
Article 8
- Any Person of Indian Origin residing outside India who, or either of whose parents or grandparents, was born in India could register himself or herself as an Indian citizen with Indian Diplomatic Mission.
Various Amendments for Citizenships
- According to Article 11, Parliament can go against the citizenship provisions of the Constitution.
- The Citizenship Act, 1955 was passed and has been amended four times — in 1986, 2003, 2005, and 2015.
- The Act empowers the government to determine the citizenship of persons in whose case it is in doubt.
- However, over the decades, Parliament has narrowed down the wider and universal principles of citizenship based on the fact of birth.
- Moreover, the Foreigners Act places a heavy burden on the individual to prove that he is not a foreigner.
(1) 1986 amendment
- The constitutional provision and the original Citizenship Act gave citizenship on the principle of jus soli to everyone born in India.
- However, the 1986 amendment to Section 3 was less inclusive as it added the condition that those who were born in India on or after January 26, 1950 but before July 1, 1987, shall be an Indian citizen.
- Those born after July 1, 1987 and before December 4, 2003, in addition to one’s own birth in India, can get citizenship only if either of his parents was an Indian citizen at the time of birth.
(2) 2003 amendment
- The then government made the above condition more stringent, keeping in view infiltration from Bangladesh.
- Now the law requires that for those born on or after December 4, 2004, in addition to the fact of their own birth, both parents should be Indian citizens or one parent must be Indian citizen and other should not be an illegal migrant.
- With these restrictive amendments, India has almost moved towards the narrow principle of jus sanguinis or blood relationship.
- This lay down that an illegal migrant cannot claim citizenship by naturalization or registration even if he has been a resident of India for seven years.
(3) Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019
- The amendment proposes to permit members of six communities — Hindus, Sikhs, Buddhists, Jains, Parsis and Christians from Pakistan, Bangladesh and Afghanistan — to continue to live in India if they entered India before December 14, 2014.
- It also reduces the requirement for citizenship from 11 years out of the preceding 14 years, to just 6 years.
- Two notifications also exempted these migrants from the Passport Act and Foreigner Act.
- A large number of organisations in Assam protested against this Bill as it may grant citizenship to Bangladeshi Hindu illegal migrants.
Losing of Indian Citizenship
- The Citizenship Act, 1955 also lays down the three modes by which an Indian citizen may lose his/her citizenship.
- It may happen in any of the three ways: renunciation, termination and deprivation.
(1) Renunciation
- An Indian Citizen of full age and capacity can renounce his Indian citizenship by making a declaration to that effect and having it registered.
- But if such a declaration is made during any war in which India is engaged, the registration shall be withheld until the Central Government otherwise directs.
- When a male person renounces his citizenship, every minor child of him ceases to be an Indian citizen.
- Such a child may, however, resume Indian citizenship if he makes a declaration to that effect within a year of his attaining full age, i.e. 18 years.
(2) Termination
- If a citizen of India voluntarily acquires the citizenship of another country, he shall cease to be a citizen of India.
- During the war period, this provision does not apply to a citizen of India, who acquires the citizenship of another country in which India may be engaged voluntarily.
(3) Deprivation
- Deprivation is a compulsory termination of citizenship of India.
- A citizen of India by naturalization, registration, domicile and residence, may be deprived of his citizenship by an order of the Central Government if it is satisfied that the Citizen has:
- Obtained the citizenship by means of fraud, false representation or concealment of any material fact
- Shown disloyalty to the Constitution of India
- Unlawfully traded or communicated with the enemy during a war
- Within five years after registration or neutralization, been imprisoned in any country for two years
- Ordinarily resident out of India for seven years continuously
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Nuclear Projects in India
Mains level: Carbo feasibility of Nuclear Energy

Supporters of the Nuclear Energy source say that it is a climate-friendly way to generate electricity. However, this is subjected to various considerations often not discussed.
Why focus on Nuclear Energy?
- The main factors for its choice were reliability and security of supply.
- The latest figures on global carbon dioxide emissions call into question the world’s efforts to tackle the climate crisis.
Soaring CO2 emissions
- CO2 emissions are set to soar 4.9% in 2021, compared with the previous year, according to a study published earlier this month by the Global Carbon Project (GCP), a group of scientists that track emissions.
- In 2020, emissions dropped 5.4% due to the COVID-19 pandemic and associated lockdowns.
- The energy sector continues to be the largest emitter of greenhouse gases, with a share of 40% — and rising.
Is nuclear power a zero-emissions energy source?
No. Nuclear energy is also responsible for greenhouse gas emissions.
- Uranium mining: Uranium extraction, transport and processing produces emissions.
- Construction of power plants: The long and complex construction process of nuclear power plants also releases CO2, as does the demolition of decommissioned sites.
- Nuclear waste and its transportation: This also has to be transported and stored under strict conditions — here, too, emissions must be taken into account.
- Water consumption: Power plants depend on nearby water sources to cool their reactors, and with many rivers drying up, those sources of water are no longer guaranteed.

How much CO2 does nuclear power produce?
- Results vary significantly, depending on whether we only consider the process of electricity generation, or take into account the entire life cycle of a nuclear power plant.
- A report released in 2014 by the IPCC estimated a range of 3.7 to 110 grams of CO2 equivalent per kilowatt-hour (kWh).
- It’s long been assumed that nuclear plants generate an average of 66 grams of CO2/kWh.
How climate-friendly is nuclear compared to other energies?
- If the entire life cycle, nuclear energy certainly comes out ahead of fossil fuels like coal or natural gas.
- But the picture is drastically different when compared with renewable energy.
- Nuclear power releases 3.5 times more CO2 per kilowatt-hour than photovoltaic solar panel systems.
- Compared with onshore wind power, that figure jumps to 13 times more CO2.
- When up against electricity from hydropower installations, nuclear generates 29 times more carbon.
Can we rely on nuclear energy to help stop global warming?
- Around the world, nuclear energy representatives, as well as some politicians, have called for the expansion of atomic power.
- Other countries have also supported plans to build new nuclear plants, arguing that the energy sector will be even more damaging for the climate without it.
Feasibility of Nuclear Energy
- High cost of construction: Due to the high costs associated with nuclear energy, it also blocks important financial resources that could instead be used to develop renewable energy.
- Renewables are better: Those renewables would provide more energy that is both faster and cheaper than nuclear.
- High water consumption: During the world’s increasingly hot summers, several nuclear power plants have already had to be temporarily shut down due to water scarcity.
Conclusion
- Taking into account the current overall energy system, nuclear energy is by no means CO2 neutral.
- The contribution of nuclear energy is viewed too optimistically.
- In reality construction, times are too long and the costs too high to have a noticeable effect on climate change. It takes too long for nuclear energy to become available.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: GOCO Model
Mains level: Defence modernization issues
The Army’s ambitious plan for modernization of the Army Base Workshops (ABWs) and implementation of the ‘Government-owned, contractor-operated (GOCO)’ model is delayed, the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) said in its report.
What is GOCO Model?
- The GOCO model was one of the recommendations of the Lt. Gen. DB Shekatkar (Retd.) committee to enhance combat capability and re-balancing defence expenditure.
- In GOCO model, the assets owned by the government will be operated by the private industries.
- Under the GOCO model, the private companies need not make investments on land, machinery and other support systems.
What is the current system?
- Maintenance, repair and overhaul (MRO): The Army follows the traditional ‘womb to tomb’ life cycle support management for maintenance, repair and overhaul (MRO) of its costly equipment.
- Corps of Electronics and Mechanical Engineers (EME): It is responsible for the MRO system.
Need for GOCO Model
- High end technologies: In the last three decades, there has been a quantum jump in military technology and the MRO of military equipment has become very complex.
- Lack of infrastructure: However, some repairs and overhauls have run into problems on account of lack of infrastructure, spares and expertise.
- Poor performance of Corps: The infrastructure, expertise and work culture has not kept pace with time, leading to below par and inefficient performance.
Benefits offered by the GOCO Model
- Time savings: The main advantage of the model is that the targets are achieved in lesser time frame.
- Competitiveness: Also, it will boost competitiveness among the private entities paving way to newer technologies.
- Efficiency: The GOCO model will bring in corporate culture, leading to efficiency and accountability.
- Expertise: Private operators can easily go into partnership with Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM), both for expertise and spares.
- Manpower saving: The government can save on manpower — 12,500 personnel workforce of the ABWs.
- Technical training: This model also opens avenues for absorbing trained retired personnel, which can be built into the contract.
Major issues with GOCO
- Costly affair: The corporate world is driven by market forces, which means the GOCO model will be more costly. In most cases, private operators will want better infrastructure, which would have to be upgraded or replaced at government cost.
- Corporate management: Private operators may not have the expertise to deal with military equipment; they are also unlikely to absorb the existing manpower and will want a younger and better-trained workforce.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: JCPOA
Mains level: US sanctions on Iran
As Iran has refused to hold direct talks with the U.S., European officials will shuttle between the Iranian and American delegations, exchanging talking points and seeking common ground over the nuclear deal.
Do you know how the enmity between Iran and the US came into reality? We hope you have watched the Argo (2012) movie for sure!
Context
- After a gap of five months, Iran, Russia, China and the European countries resumed negotiations in Vienna to revive the 2015 nuclear agreement, known as the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA).
- The 2015 JCPOA agreement sought to cut Iran off a possible path to a nuclear bomb in return for lifting of economic sanctions.
What is JCPOA?
- The Iran nuclear agreement, formally known as the JCPOA is a landmark accord reached between Iran and several world powers, including the United States, in July 2015.
- Under its terms, Iran agreed to dismantle much of its nuclear program and open its facilities to more extensive international inspections in exchange for billions of dollars’ worth of sanctions relief.
Expected outcomes of the deal
- Curb on nuclear program: Proponents of the deal said that it would help prevent a revival of Iran’s nuclear weapons program.
- Increasing regional engagement: It would thereby reduce the prospects for conflict between Iran and its regional rivals, including Israel and Saudi Arabia.
Background of the JCPOA
- Iran had previously agreed to forgo the development of nuclear weapons as a signatory to the Nuclear Nonproliferation Treaty, which has been in force since 1970.
- However, after the overthrow of the Pahlavi dynasty in 1979, Iranian leaders secretly pursued this technology.
- In 2007, U.S. intelligence analysts concluded that Iran halted its work on nuclear weapons in 2003 but continued to acquire nuclear technology and expertise.
- Prior to the JCPOA, the P5+1 had been negotiating with Iran for years, offering its government various incentives to halt uranium enrichment.
Issues with the deal
(1) US withdrawal
- The deal has been in jeopardy since President Donald Trump withdrew the US from it in 2018.
- In retaliation for the US, Iran resumed some of its nuclear activities.
(2) Iran’s insistence over sanctions removal
- In 2021, President Joe Biden said the US will return to the deal if Iran comes back into compliance, though Iran’s leaders have insisted that Washington lift sanctions first.
- Iran now has indicated that he will take a harder line than his predecessor in nuclear negotiations.
Who are the participants?
- The JCPOA, which went into effect in January 2016, imposes restrictions on Iran’s civilian nuclear enrichment program.
- At the heart of negotiations with Iran were the five permanent members of the UN Security Council (China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States) and Germany—collectively known as the P5+1.
- The European Union also took part. Israel explicitly opposed the agreement, calling it too lenient.
- Some Middle Eastern powers, such as Saudi Arabia, said they should have been consulted or included in the talks because they would be most affected by a nuclear-armed Iran.
What did Iran agree to?
- Nuclear restrictions: Iran agreed not to produce either the highly enriched uranium or the plutonium that could be used in a nuclear weapon.
- Monitoring and verification: Iran agreed to eventually implement a protocol that would allow inspectors from the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), the United Nations’ nuclear watchdog.
What did the other signatories agree to?
- Sanctions relief: The EU, United Nations, and United States all committed to lifting their nuclear-related sanctions on Iran. However, many other U.S. sanctions on Iran, some dating back to the 1979 hostage crisis, remained in effect.
- Weapons embargo: The parties agreed to lift an existing UN ban on Iran’s transfer of conventional weapons and ballistic missiles after five years if the IAEA certifies that Iran is only engaged in civilian nuclear activity.
How has the deal affected Iran’s economy?
- Prior to the JCPOA, Iran’s economy suffered years of recession, currency depreciation, and inflation, largely because of sanctions on its energy sector.
- With the sanctions lifted, inflation slowed, exchange rates stabilized, and exports—especially of oil, agricultural goods, and luxury items—skyrocketed as Iran regained trading partners, particularly in the EU.
- After the JCPOA took effect, Iran began exporting more than 2.1 million barrels per day (approaching pre-2012 levels, when the oil sanctions were originally put in place).
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Health Accounts Estimates: 2017-18
Mains level: Health expenditure in India

Out-of-pocket expenditure (OOPE) as a share of total health expenditure and foreign aid for health has both come down as per the findings of the National Health Accounts (NHA) estimates for India for 2017-18.
What is National Health Accounts (NHA)?
- The NHA estimates are prepared by using an accounting framework based on internationally accepted System of Health Accounts 2011, provided by the World Health Organization (WHO).
- It is released by Ministry of Health & Family Welfare.
- It describes health expenditures and flow of funds in the country’s health system over a financial year of India.
- It answers important policy questions such as what are the sources of healthcare expenditures, who manages these, who provides health care services, and which services are utilized.
- It is a practice to describe the health expenditure estimates according to a global standard framework, System of Health Accounts 2011 (SHA 2011), to facilitate comparison of estimates across countries.
Objective of the NHA
- To describe the Current Health Expenditures (CHE).
The details of CHE are presented according to
- Revenues of healthcare financing schemes: – entities that provide resources to spend for health goods and services in the health system;
- Healthcare financing schemes: entities receiving and managing funds from financing sources to pay for or to purchase health goods and services;
- Healthcare providers: entities receiving finances to produce/ provide health goods and services;
- Healthcare functions: It describes the use of funds across various health care services.
About NHA (2017-2018)
- The 2017-18 NHA estimates shows government expenditure on health exhibiting an increasing trend and growing trust in public health care system.
- With the present estimate of NHA 2017-18, India has a continuous Time Series on NHA estimates for both government and private sources for five years since 2013-14.
- These estimates are not only comparable internationally, but also enable the policy makers to monitor progress towards universal health coverage as envisaged in the National Health Policy, 2017.
Key Highlights
Increase in GDP share: The NHA estimates for 2017-18 clearly show that there has been an increase in the share of government health expenditure in the total GDP from 1.15% in 2013-14 to 1.35% in 2017-18.
Increase in govt share in expenditures: In 2017-18, the share of government expenditure was 40.8%, which is much higher than 28.6% in 2013-14.
Per-Capita increase in expenditure: In per capita terms, the government health expenditure has increased from Rs 1042 to Rs.1753 between 2013-14 to 2017-18.
Focus on total healthcare: The primary and secondary care accounts for more than 80% of the current Government health expenditure.
Social security expenditure: The share of social security expenditure on health, which includes the social health insurance program, Government financed health insurance schemes, and medical reimbursements made to Government employees, has increased.
Decline in foreign aid: The findings also depict that the foreign aid for health has come down to 0.5%, showcasing India’s economic self-reliance.
Decline in OOPE: The government’s efforts to improve public health care are evident with out-of-pocket expenditure (OOPE) as a share of total health expenditure coming down to 48.8% in 2017-18 from 64.2% in 2013-14.
Way forward
- After 18 months of Covid-19, financial year 2017-18 appears to be from another era.
- However, learnings from that year’s NHA help us to plan for health system strengthening in the post-Covid years.
- The special financing packages for Covid emergency response, announced by the central government in 2020 and 2021, represent an extraordinary situation.
- The resolve to increase public financing for health must remain strong even after Covid.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: 5G technology
Mains level: Useful data about 5G in India
India 5G subscriptions are set to reach 500 mn by 2027, said Ericsson in its report.
Ericsson Mobility Report
- The report has added that the total number of smartphone subscriptions is expected to be 810 million at the end of 2021.
- It is projected to grow at a compounded annual growth rate of 7%, exceeding 1.2 billion by 2027.
5G penetration in India
- 5G telecom services are likely to account for 39% of mobile subscriptions or about 500 million subscriptions in India at the end of 2027.
- 4G is expected to remain the dominant technology in India in 2027.
- 4G subscriptions are expected to reduce from 68% of mobile subscriptions in 2021 to 55% in 2027 as subscribers migrate to 5G.
- However, 4G subscriptions are forecast to drop from 790 million in 2021 to 710 million in 2027, showing an annual average decline of 2%.
Back2Basics: 5G Technology
- 5G or fifth generation is the latest upgrade in the long-term evolution (LTE) mobile broadband networks.
- It mainly works in 3 bands, namely low, mid and high-frequency spectrum — all of which have their own uses as well as limitations.
Three bands of 5G
- The low band spectrum has shown great promise in terms of coverage and speed of internet and data exchange, the maximum speed is limited to 100 Mbps (Megabits per second).
- This means that while telcos can use and install it for commercial cellphones users who may not have specific demands for very high-speed internet, the low band spectrum may not be optimal for specialised needs of the industry.
- The mid-band spectrum, on the other hand, offers higher speeds compared to the low band but has limitations in terms of coverage area and penetration of signals.
- Telcos and companies, which have taken the lead on 5G, have indicated that this band may be used by industries and specialized factory units for building captive networks that can be molded into the needs of that particular industry.
- The high-band spectrum offers the highest speed of all the three bands, but has extremely limited coverage and signal penetration strength.
- Internet speeds in the high-band spectrum of 5G have been tested to be as high as 20 Gbps (gigabits per second), while, in most cases, the maximum internet data speed in 4G has been recorded at 1 Gbps.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NPK fertilizers, Soil Health Card
Mains level: Soil Health Management
National Productivity Council (NPC) has carried out a study on ‘Soil Testing Infrastructure for Faster Delivery of Soil Health Card in India’ in 2017.
What did the study find?
- In the study it was found that application of fertilizer and micronutrients based on Soil Health Card (SHC) recommendations resulted in 8-10% of savings.
- It has led to an overall increase in the yield of crops to the tune of 5-6% reported by adopting the SHC recommendations.
About Soil Health Card Scheme
- Soil Health Card (SHC) scheme is promoted by the Department of Agriculture & Co-operation under the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare.
- An SHC is meant to give each farmer soil nutrient status of his/her holding and advice him/her on the dosage of fertilizers and also the needed soil amendments, that s/he should apply to maintain soil health in the long run.
- SHC is a printed report that a farmer will be handed over for each of his holdings.
- It will be made available once in a cycle of 2 years, which will indicate the status of soil health of a farmer’s holding for that particular period.
- The SHC given in the next cycle of 2 years will be able to record the changes in the soil health for that subsequent period.
Parameters of SHC:
- N, P, K (Macro-nutrients)
- Sulfur (S) (Secondary- nutrient)
- Zn, Fe, Cu, Mn, Bo (Micronutrients)
- pH, EC (Electrical conductivity) , OC (Organic content)
Try this PYQ:
Q. The nation-wide ‘Soil Health Card Scheme’ aims at:
- expanding the cultivable area under irrigation.
- enabling the banks to assess the quantum of loans to be granted to farmers on the basis of soil quality.
- checking the overuse of fertilizers in farmlands.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Post your answers here.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 3- Changing patterns in saving and investment
Context
We are witnessing the change where the cult of savers has changed into investors. They are looking for a good return and willing to take the risk.
Changing the behaviour of the savers
- There is a new wave of savings and investments in the country that is evolving quite fast.
- Crypto exchanges assure you that they are safe.
- But it is the exchange that is safe, not the value of the coin, which will be driven by the market.
- The equity boom is on, and all the unicorns have delivered excellent results.
- That’s why bank deposits are no longer on our plates.
- Banks discouraging deposits: Interestingly, banks today are discouraging deposits with low rates as this is the only way they can manage their balance sheets.
- Low-interest rate: There are few deployment avenues and paying 5 per cent interest to savers and investing the deposits at 3.35 per cent in the reverse repo auction is a sub-optimal game.
How safe is investment in cryptocurrencies?
- From equities, there has been a swift shift to cryptos, which is still a grey area.
- The regulators/government are wondering what to do. The issue will be discussed in the winter session of Parliament.
- But investments have been made and there is no stopping this global wave.
- Currency with no underlying asset: Making money on a currency that has no underlying asset like a metal or other currency and is traded on faith is unique; especially Bitcoin, whose originator is not known by face but by just a name.
Gaming as a skill
- There is another door to a new kind of gaming where you make money by making teams and following the matches.
- The law was first silent, and then confused.
- But it finally accepted gaming as a skill.
- Logically, soon we should be able to bet on matches too, if all this is in order.
Conclusion
We are witnessing a change in the pattern of holding onto money, where savings get transformed to investment and risk appetite changes from conservative to aggressive. Will this change? Probably not, in the near future, as long as conventional deposits continue to give inferior returns.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Parliamentary Privileges
Mains level: Parliamentary Conduct and decorum of the houses
Twelve Opposition members of the Rajya Sabha were suspended for the entire winter session for unprecedented acts of misconduct, unruly and violent behavior and intentional attacks on security personnel.
Decorum of the Parliament
- Freedom of speech is one of the most important privileges enjoyed by Members of Parliament.
- This freedom is circumscribed, however, by the necessity of maintaining order and decorum when debate is taking place.
- Thus discipline, decorum and dignity of Parliament are of paramount importance for the efficient functioning and success of parliamentary institutions.
- All over the world concerns have been expressed about the decline of discipline, decorum and dignity of legislative bodies.
Maintaining the Decorum
- MPs are required to adhere to certain rules of parliamentary etiquette.
- For example the Lok Sabha rulebook specifies that MPs are not to interrupt the speech of others, maintain silence and not obstruct proceedings by hissing or making running commentaries during debates.
- Newer forms of protest led to these rules being updated in 1989.
- Now, members should not shout slogans, display placards, tear up documents in protest, and play a cassette or a tape recorder in the House.
- Rajya Sabha has similar rules. To conduct the proceedings smoothly, the rulebook also gives certain, similar powers to the presiding officers of both Houses.
Power of Suspension
- The presiding officer of each House can direct an MP to withdraw from the legislative chamber for grossly disorderly conduct.
- The MP then has to remain absent from the proceedings of the House for the remainder of the day.
- The presiding officers can also “name” an MP for “persistently and wilfully obstructing the business” of the House.
- In such a case, usually, the Parliamentary Affairs Minister moves a motion for suspending the offending MP from the service of the House.
- The suspension can last until the end of the session.
Why are such disruptions frequent in the Parliament?
- The reluctance and procrastination of the treasury benches to face discussions is the main cause for disorder in Parliament.
- In most cases, disorders in the House arise out of a sense of frustration felt by members due to lack of opportunities to make his point.
- They are perhaps easier to deal with. What is more difficult to tackle is planned parliamentary offences and deliberate disturbances for publicity or for political motives.
Way forward
- Debate is central to democracy, and therefore there should be more debate and fewer disruptions.
- The majority party is responsible for governing and should take other parties into confidence.
- The Opposition should play a constructive role in Parliament and be allowed to put forward its views and express itself in a dignified manner.
- The presiding officers must help the Opposition in raising issues uncomfortable to the government.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Dual system of Policing
The Dual Command System of Policing is being implemented in Bhopal and Indore.
What is the ‘Dual Command’ System?
- Under the dual command system, the District Magistrate and the Superintendent of Police (SP) share powers and responsibilities in a district.
- Under this structure, the DM is entrusted with issuing arrest warrants, licenses while the SP has powers and responsibilities to investigate crime and make arrests.
- The system is designed to ensure a lower concentration of power and making the police more accountable to the DM at the district level.
How does the commissionerate system empower the police?
- Under the police commissionerate system, the powers of both policing and magistracy are concentrated with the commissioner, who is directly accountable to the state government and the state police chief.
- The commissioner of police under the commissionerate system exercises the powers and duties of a District Magistrate.
- These powers are also available to any officer under the commissioner who is not below the rank of an Assistant Commissioner of Police.
- The police are also empowered to conduct externment proceedings and issue written orders to remove a person from their jurisdiction of the commissionerate for a maximum of two years.
Need for such system
Various committees constituted to suggest police reforms have recommended implementation of a police commissioner system.
- Rapidly urbanized cities: This is for cities which have witnessed rapid urbanization and have a population of more than 10 lakhs.
- Better accountability: In the 6th report of the National Police Commission, it noted that as compared to police in districts, police in commissionerate in small areas had a better account of themselves.
- Complex security threats: It further pointed out that in urban areas, the changing dynamism and growing complexities of security threats required a swift and prompt response.
- Quick responsivity: Usually in large urban areas, law and order situations develop rapidly, requiring a speed and effective operational response from the police.
- Avoiding delayed action: In districts where the SPs and DMs do not have an understanding, orders to swiftly act are rarely issued in time which aggravates the situation.
Issues with the system
- Power-sharing: There needs to be some clarity on what powers will be taken away from the revenue officers, collectors, SDMs and how it will impact the society before implementing it.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Tundra Satellite, Various types of Orbits
Mains level: Not Much
Russia has successfully placed into orbit a military satellite believed to be part of the Kremlin’s early warning anti-missile system. This launch could be delivering a Tundra satellite.
Tundra Satellite
- The Tundra or EKS (Edinaya Kosmicheskaya Sistema) series of satellites is the next generation of Russian early-warning satellites.
- The development of the EKS started in 2000.
- These satellites carry a secure emergency communications payload to be used in case of a nuclear war.
- They are launched on Soyuz-2-1b Fregat boosters into Molniya-orbits, inclined highly elliptical 12 h orbits.
What are Tundra Orbits?
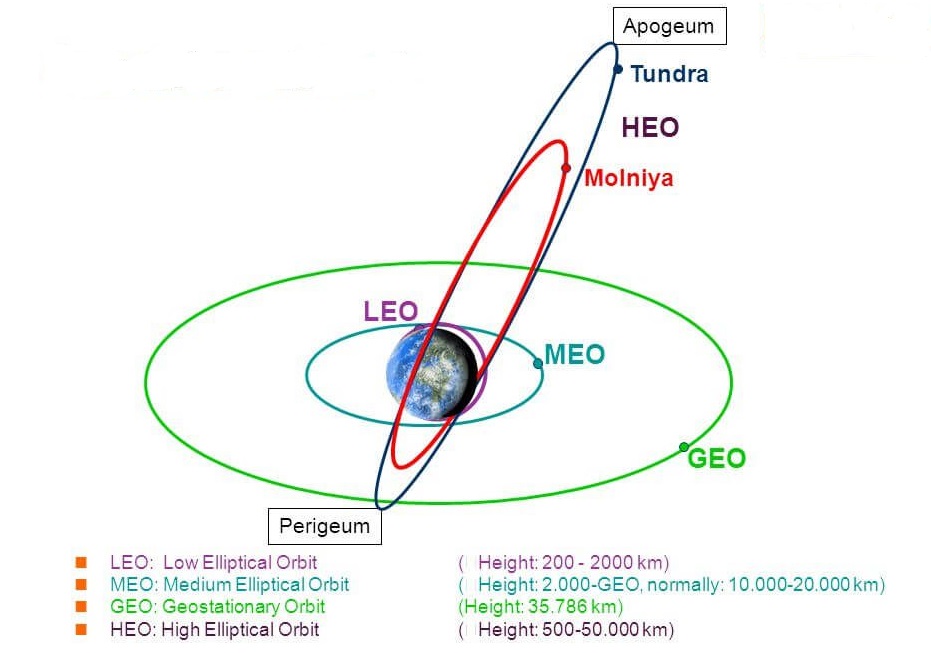
- A Tundra orbit is a highly elliptical geosynchronous orbit with a high inclination (approximately 63.4°), an orbital period of one sidereal day.
- A satellite placed in this orbit spends most of its time over a chosen area of the Earth, a phenomenon known as apogee dwell.
- It makes satellites particularly well suited for communications satellites serving high latitude regions.
- The ground track of a satellite in a Tundra orbit is a closed figure 8 with a smaller loop over either the northern or southern hemisphere.
- This differentiates them from Molniya orbits designed to service high-latitude regions, which have the same inclination but half the period and do not hover over a single region.
Back2Basics: Types of Orbits
[1] Geostationary orbit (GEO)
- Satellites in geostationary orbit (GEO) circle Earth above the equator from west to east following Earth’s rotation – taking 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds – by travelling at exactly the same rate as Earth.
- This makes satellites in GEO appear to be ‘stationary’ over a fixed position.
- In order to perfectly match Earth’s rotation, the speed of GEO satellites should be about 3 km per second at an altitude of 35 786 km.
- This is much farther from Earth’s surface compared to many satellites.
- GEO is used by satellites that need to stay constantly above one particular place over Earth, such as telecommunication satellites.
- Satellites in GEO cover a large range of Earth so as few as three equally-spaced satellites can provide near-global coverage.
[2] Low Earth orbit (LEO)
- A low Earth orbit (LEO) is, as the name suggests, an orbit that is relatively close to Earth’s surface.
- It is normally at an altitude of less than 1000 km but could be as low as 160 km above Earth – which is low compared to other orbits, but still very far above Earth’s surface.
- Unlike satellites in GEO that must always orbit along Earth’s equator, LEO satellites do not always have to follow a particular path around Earth in the same way – their plane can be tilted.
- This means there are more available routes for satellites in LEO, which is one of the reasons why LEO is a very commonly used orbit.
- It is most commonly used for satellite imaging, as being near the surface allows it to take images of higher resolution.
- Satellites in this orbit travel at a speed of around 7.8 km per second; at this speed, a satellite takes approximately 90 minutes to circle Earth.
[3] Medium Earth orbit (MEO)
- Medium Earth orbit comprises a wide range of orbits anywhere between LEO and GEO.
- It is similar to LEO in that it also does not need to take specific paths around Earth, and it is used by a variety of satellites with many different applications.
- It is very commonly used by navigation satellites, like the European Galileo system of Europe.
- It uses a constellation of multiple satellites to provide coverage across large parts of the world all at once.
[4] Polar Orbit
- Satellites in polar orbits usually travel past Earth from north to south rather than from west to east, passing roughly over Earth’s poles.
- Satellites in a polar orbit do not have to pass the North and South Pole precisely; even a deviation within 20 to 30 degrees is still classed as a polar orbit.
- Polar orbits are a type of low Earth orbit, as they are at low altitudes between 200 to 1000 km.
[5] Sun-synchronous orbit (SSO)
- SSO is a particular kind of polar orbit. Satellites in SSO, travelling over the polar regions, are synchronous with the Sun.
- This means they are synchronised to always be in the same ‘fixed’ position relative to the Sun.
- This means that the satellite always visits the same spot at the same local time.
- Often, satellites in SSO are synchronised so that they are in constant dawn or dusk – this is because by constantly riding a sunset or sunrise, they will never have the Sun at an angle where the Earth shadows them.
- A satellite in a Sun-synchronous orbit would usually be at an altitude of between 600 to 800 km. At 800 km, it will be travelling at a speed of approximately 7.5 km per second.
[6] Transfer orbits and geostationary transfer orbit (GTO)
- Transfer orbits are a special kind of orbit used to get from one orbit to another.
- Often, the satellites are instead placed on a transfer orbit: an orbit where, by using relatively little energy from built-in motors, the satellite or spacecraft can move from one orbit to another.
- This allows a satellite to reach, for example, a high-altitude orbit like GEO without actually needing the launch vehicle.
- Reaching GEO in this way is an example of one of the most common transfer orbits, called the geostationary transfer orbit (GTO).
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Sahel Region
Mains level: Great Green Wall Project

Africa’s Great Green Wall (GGW) program to combat desertification in the Sahel region is an important contribution towards combating climate change, Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) said in a study.
Note the countries swept by the GGW project on the African map.
About GGW Program

- The Great Green Wall project is conceived by 11 countries located along the southern border of the Sahara and their international partners, is aimed at limiting the desertification of the Sahel zone.
- Led by the African Union, the initiative aims to transform the lives of millions of people by creating a mosaic of green and productive landscapes across North Africa.
- The initial idea of the GGW was to develop a line of trees from east to the west bordering the Saharan Desert.
- Its vision has evolved into that of a mosaic of interventions addressing the challenges facing the people in the Sahel and the Sahara.
Why was such project incepted?
- The project is a response to the combined effect of natural resources degradation and drought in rural areas.
- It aimed to restore 100 million hectares of degraded land by 2030; only four million hectares had been restored between 2007 and 2019.
- It is a partnership that supports communities working towards sustainable management and use of forests, rangelands and other natural resources.
- It seeks to help communities mitigate and adapt to climate change, as well as improve food security.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now










