Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: 7th Schedule
Mains level: Federalism issue raised by the Agricultural Bills
Fifteenth Finance Commission chairman N.K. Singh has called for a fresh look at the Constitution’s Seventh Schedule, which forms the basis for allocating subjects to the Centre and States.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Which of the following provisions of the Constitution of India have a bearing on Education?
- Directive Principles of State Policy
- Rural and Urban Local Bodies
- Fifth Schedule
- Sixth Schedule
- Seventh Schedule
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3, 4 and 5 only
(c) 1, 2 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 4 and 5
Why such calls by Mr NKS?
- Singh said these issues needed urgent consideration to reinforce trust in fiscal federalism.
- He urged a review of both the Seventh Schedule and Article 282 of the Constitution so as to give more flexibility to States in implementing centrally sponsored schemes.
- Many have argued that the trust between various forms of government is waning.
- Since the farmers’ agitation, these are seen through the prism of suspicion and mistrust.
Q. The federal organisation of powers under the Constitution’s Seventh Schedule needs review. In light of this, examine the problems faced by the distribution and suggest the challenge the review would face.
What is the Seventh Schedule?
- This Schedule of the Indian Constitution deals with the division of powers between the Union government and State governments.
- It defines and specifies the allocation of powers and functions between Union & States. It contains three lists; i.e. 1) Union List, 2) State List and 3) Concurrent List.

The Union List
- It is a list of 98 (Originally 97) numbered items as provided in the Seventh Schedule.
- The Union Government or Parliament of India has exclusive power to legislate on matters relating to these items.
The State List
- It is a list of 59 (Originally 66) items.
- The respective state governments have exclusive power to legislate on matters relating to these items.
The Concurrent List
- There are 52 (Originally 47) items currently in the list.
- This includes items which are under the joint domain of the Union as well as the respective States.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CITES
Mains level: Exotic species trade
Last month, the Supreme Court upheld an Allahabad High Court order granting immunity from investigation and prosecution if one declared illegal acquisition or possession of exotic wildlife species.
Q.What are Zoonotic Diseases? Discuss how the illicit trade in wildlife has resulted in the spread of zoonotic diseases of the scale of the ongoing COVID-19?
Voluntary disclosure scheme
- The MoEFCC has come out with an advisory on a one-time voluntary disclosure amnesty scheme.
- It allows owners of exotic live species that have been acquired illegally, or without documents, to declare their stock to the government between June and December 2020.
- The scheme aims to address the challenge of zoonotic diseases and regulate their import. In its current form, however.
- It shall develop an inventory of exotic live species for better compliance under the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES).
- However, the amnesty scheme is just an advisory, not a law
What kind of exotic wildlife is covered?
- The advisory has defined exotic live species as animals named under the Appendices I, II and III of the CITES.
- It does not include species from the Schedules of the Wild Life (Protection) Act 1972.
- So, a plain reading of the advisory excludes exotic birds from the amnesty scheme.
Why need such a scheme?
- The Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI), which enforces anti-smuggling laws, says India has emerged as a big demand centre for exotic birds and animals.
- There has been an increase in smuggling of endangered species from different parts of the world.
- Most of these exotic wildlife is imported through Illegal channels and then sold in the domestic market as pets.
- The long international border and air routes are used to source consignments from Bangkok, Malaysia and other top tourist destinations in South East Asia, as well as from Europe into India.
Back2Basics: CITES
- CITES stands for the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora.
- It is as an international agreement aimed at ensuring “that international trade in specimens of wild animals and plants does not threaten their survival”.
- It was drafted after a resolution was adopted at a meeting of the members of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) in 1963.
- It entered into force on July 1, 1975, and now has 183 parties.
- The Convention is legally binding on the Parties in the sense that they are committed to implementing it; however, it does not take the place of national laws.
- India is a signatory to and has also ratified CITES convention in 1976.
CITES Appendices
- CITES works by subjecting international trade in specimens of selected species to certain controls.
- All import, export, re-exports and introduction from the sea of species covered by the convention has to be authorized through a licensing system. It has three appendices:
- Appendix I includes species threatened with extinction. Trade-in specimens of these species are permitted only in exceptional circumstances.
- Appendix II provides a lower level of protection.
- Appendix III contains species that are protected in at least one country, which has asked other CITES Parties for assistance in controlling trade.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: QKD
Mains level: Quantum Mechanics and its development in India

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully demonstrated communication between its two labs using Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) technology.
Q. What is Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) Technology? Discuss how it enables secure communication networks. (150W)
What is QKD Technology?
- Quantum key distribution (QKD) is a secure communication method which implements a cryptographic protocol involving components of quantum mechanics.
- It enables two parties to produce a shared random secret key known only to them, which can then be used to encrypt and decrypt messages.
- It gives the ability of the two communicating users to detect the presence of any third party trying to gain knowledge of the key.
- This is a result of a fundamental aspect of quantum mechanics: the process of measuring a quantum system, in general, disturbs the system.
- By using quantum superposition or quantum entanglement and transmitting information in quantum states, a communication system can be implemented that detects data leak.
How does it work?
- In the QKD, encryption keys are sent as qubits in a fibre optic cable. Time-bin encoding is used to encode qubit on a photon.
- Quantum computing uses qubits as basic resources, similar to how bits are used as basic resources in classical computing.
- The QKD is designed in a way that if an illegitimate entity tries to read the transmission, it will disturb the qubits – which are encoded on photons.
- This will generate transmission errors, leading to legitimate end-users being immediately informed.
Advantages of using QKD
- It allows the detection of data leak or hacking because it can detect any such attempt.
- It also allows the process of setting the error level between the intercepted data in dependence.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Plasmodium parasite
Mains level: Malaria in India
A not very common type of malaria, Plasmodium Ovale, has been identified in a jawan in Kerala.
Try this PYQ:
Q. Widespread resistance of malarial parasite to drugs like chloroquine has prompted attempts to develop a malarial vaccine to combat malaria.
Why is it difficult to develop an effective malaria vaccine?
(a) Malaria is caused by several species of Plasmodium
(b) Man does not develop immunity to malaria during natural infection
(c) Vaccines can be developed only against bacteria
(d) Man is only an intermediate host and not the definitive host
What is Malaria?
- Malaria is caused by the bite of the female Anopheles mosquito if the mosquito itself is infected with a malarial parasite.
- There are five kinds of malarial parasites — Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium vivax (the commonest ones), Plasmodium malariae, Plasmodium ovale and Plasmodium knowlesi.
- Therefore, to say that someone has contracted the Plasmodium ovale type of malaria means that the person has been infected by that particular parasite.
- Malaria is treated with prescription drugs to kill the parasite. Chloroquine is the preferred treatment for any parasite that is sensitive to the drug.
Plasmodium Ovale
- P ovale rarely causes severe illness and there is no need for panic.
- Symptoms include fever for 48 hours, headache and nausea, and the treatment modality is the same as it is for a person infected with P vivax.
- P ovale is no more dangerous than getting a viral infection.
- It is termed ovale as about 20% of the parasitised cells are oval in shape.
Burden of Malaria in India
- In 2018, the National Vector-borne Disease Control Programme (NVBDCP) estimated that approximately 5 lakh people suffered from malaria.
- 63% of the cases were of Plasmodium falciparum.
- The recent World Malaria Report 2020 said cases in India dropped from about 20 million in 2000 to about 5.6 million in 2019.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Digital Voter ID
Mains level: Election reforms
The Election Commission (EC) is keen to make the Elector’s Photo Identity Card or EPIC available in electronic form.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Regarding DigiLocker, sometimes seen in the news, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- It is a digital locker system offered by the Government under Digital India Programme.
- It allows you to access your e-documents irrespective of your physical location.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Digital Voter ID Card
- The digital voter card is not expected to look too different from its physical form.
- It will be available as a PDF file and can be downloaded on one’s phone or computer.
- The soft copy may also have a QR code that will carry the voter’s enrolment details such as name and date of birth and address.
- This is still just a proposal and needs to be approved by the Election Commission.
How to avail it?
- To avail this facility, an eligible voter will have to provide her mobile number or email address to the EC machinery at the time of applying for enrolment in the voters’ list.
- Once her name is included in the electoral roll, she will be intimated through an SMS or email.
- The new voter can then download the Voter Card through OTP (One Time Password) authentication.
- Existing voters may have to re-verify their details with the EC (similar to the Bank KYC process) and provide their email or mobile phone number to get their cards in the electronic form.
Benefits offered
- An electronic card will help the EC save costs on printing and distributing a hard copy of EPIC.
- The EC feels that voters too will find it useful to have the PDF file of her voter card on her phone.
- This will do away with the necessity of first producing a voter’s slip on the day of voting.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CERC
Mains level: Paper 3- Renewable energy markets
The article takes stock of the progress India made on renewable energy capacity and the steps taken for its trade through the creation of green markets.
India increasing share of renewable energy
- As a signatory to the Paris Climate Agreement, India is committed to increasing its share of renewable energy capacity to 450 GW by 2030.
- India has an installed renewable energy capacity of 89 GW.
- India has today become the most attractive destination for investment in the renewable sector.
- During the last six years, has attracted over Rs 4.7 lakh crore of investment, including FDI of about Rs 42,700 crore.
- India witnessed 20% CAGR growth in the renewable generation since FY16 while total electricity generation saw 4.3% growth in the same period.
- The current levelised cost of energy (LCOE) for large scale solar in India is around Rs 2.5 per kWh, compared to ~Rs 12 in 2010.
Factor’s responsible
- Waiver of inter-state transmission charges for the sale of solar and wind power, the renewable purchase obligation (RPO) trajectories for states, focus on maintaining the sanctity of contracts, permitting FDI in the renewable sector have accelerated the progress.
Trading in renewable power
- Most renewable power generation companies in India are committed to selling their power to consumers—mostly discoms under the long-term Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs).
- It is also a matter of gratification that most generation companies have adopted a robust system of forecasting and scheduling of power.
- It is in this context, the CERC was approached for creating a market for green energy.
- Ultimately, the CERC approved trading of renewable energy contracts under Green Term Ahead Market (GTAM) on the energy exchange.
- The green market commenced trade on August 21, in day-ahead contingency (DAC) and intra-day contracts in both solar and non-solar segments.
- The green market has now launched two more options—daily and weekly.
- This will further strengthen the market and allow participants to buy green energy through contracts available for trade in all the segments.
- The energy will be delivered to the market participants leveraging the national, regional and state-level transmission and distribution network.
- With robust value proposition such as transparency, competitive prices, flexibility, and payment security and financial savings that the exchange market offers, a pan-India green market has the potential to drive and facilitate the country to meet its renewable energy targets.
- The green market will ultimately encourage green generators to adopt multiple models of sale and trading.
Conclusion
Going forward, the introduction of new segments such as green day-ahead market, long-duration green contracts, contract for difference (CfD), etc, will play a crucial role in furthering sustainability goals, and ensuring that all the renewable energy generated within the country is dispatched in the most efficient manner through a pan India wide exchange-based energy markets.
Source:-
https://www.financialexpress.com/opinion/renewable-energy-generation-betting-on-the-green-power-market/2147657/
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Middle Easet
Mains level: The gulf and anti-semitism
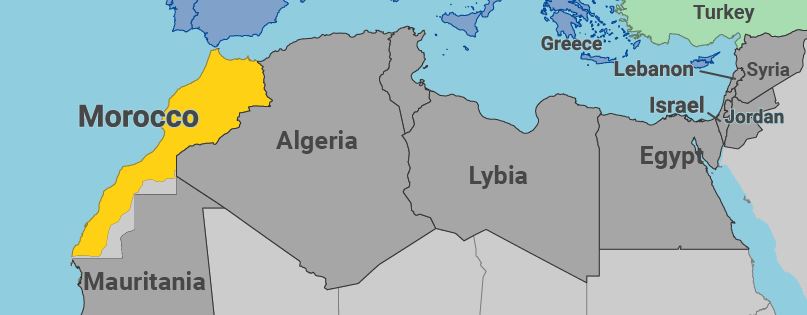
Morocco has become the fourth Arab nation this year to recognise Israel after interventions by the US.
Must read:
Israel and Morocco
- After the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain and Sudan, Morocco is the fourth Arab State since August to commit to establishing diplomatic relations with the Jewish State.
- Morocco and Israel had respectively maintained liaison offices in Tel Aviv and Rabat in the 1990s, before closing them in 2000.
- Israeli PM Netanyahu anticipated direct flights between the two countries soon.
- Palestinian officials condemned the agreement, saying it encouraged Israel’s denial of their rights.
For the sake of Western Sahara

- The White House said the US would recognise Morocco’s claim over Western Sahara as part of the deal with Israel.
- The US recognised Moroccan sovereignty over the entire Western Sahara territory.
- A former Spanish colony, it was annexed by Morocco in 1975.
- Since then it has been the subject of a long-running territorial dispute between Morocco and its indigenous Saharawi people.
- Morocco says it has always been part of its territory, while the African Union recognizes it as an independent state.
- A 16-year-long insurgency ended with an UN-brokered truce in 1991 and the promise of a referendum on independence, which has yet to take place.
Ground realities
- The latest move by the Trump administration will not necessarily have an immediate impact on the ground because the dispute is seen as greater than the whims of the American president.
- However, Trump’s backing of Morocco’s claim to sovereignty over Western Sahara is a big deal because it diminishes the hope of a people who have aspired for the independence of that territory for decades.
- The UN is still mandated to oversee a referendum for the independence of Western Sahara – although this hasn’t materialized since 1991.
Why Arab countries are normalizing their ties with Israel?
- Economics: The Gulf States see opportunities for trade and more. The deal helps the ambitious gulf, who has built themselves into military power as well as a place to do business.
- Common enemy: The UAE has used its already well-equipped armed forces in Libya and Yemen. But its most serious potential enemy is Iran, just on the other side of the Gulf.
- For the Iron wall: Normalizing its relations with gulf is a genuine achievement for the Israelis who is a believer in the strategy first described in the 1920s of an “Iron Wall” between the Jewish state and the Arabs.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: IoT , AI
Mains level: Internet based applications

In a first, BSNL launches world’s largest NB-IoT to provide connectivity for millions of unconnected machines, sensors and industrial IoT devices across the country.
What is NB-IoT?
- NB-IoT is a Low Power Wide Area (LPWA) technology that works virtually anywhere.
- It will connect many more devices to the Internet of Things and make many new applications a reality.
- It is optimized for applications that need to communicate small amounts of data over long periods of time.
- Since it operates in licensed spectrum, it is secure and reliable providing guaranteed quality of service.
- It connects devices more simply and efficiently on already established mobile networks and handles small amounts of fairly infrequent 2‑way data, securely and reliably.
And the best is, it provides-
- very low power consumption
- excellent extended range in buildings and underground
- easy deployment into the existing cellular network architecture
- network security & reliability
- lower component cost
Back2Basics: Internet of Things (IoT)
- The IoT describes the network of physical objects—“things”—that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies for the purpose of connecting and exchanging data with other devices and systems over the Internet.
- The definition of the IoT has evolved due to the convergence of multiple technologies, real-time analytics, AI, sensors, and embedded systems.
- In the consumer market, IoT technology is most synonymous with products pertaining to the concept of the “smart home”, including devices and appliances.
- It supports one or more common ecosystems and can be controlled via devices associated with that ecosystem, such as smartphones and smart speakers e.g. Alexa.
Remember this PYQ?
When the alarm of your smartphone rings in the morning, you wake up and tap it to stop the alarm which causes your geyser to be switched on automatically. The smart mirror in your bathroom shows the day’s weather and also indicates the level of water in your overhead tank. After you take some groceries from your refrigerator for making breakfast, it recognises the shortage of stock in it and places an order for the supply of fresh grocery items. When You step out of your house and lock the door, all lights, fans, geysers and AC machines get switched off automatically. On your way to office, your car warns you about traffic congestion ahead and suggests an alternative route, and if you are late for a meeting, it sends a message to your office accordingly.
In the context of emerging communication technologies, which one of the following terms best applies to the above scenario?
(a) Border Gateway Protocol
(b) Internet of Things
(c) Internet Protocol
(d) Virtual Private Network
Also read:
[Burning Issue] Internet of Things (IoT)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Shakti, Disha Act
Mains level: Women safety
In a bid to curb crimes against woman and children in Maharashtra, the state cabinet unveiled the ‘Shakti Act.’ The Act is modelled on the lines of Andhra Pradesh’s Disha Act, which was brought last year after a veterinarian was raped and murdered in Hyderabad.
Why have stringent laws have consistently failed to instill any fear in rapists?
Shakti Act: Key Provisions
- It proposes stringent punishment including the death penalty and heavy fines for the culprits.
- Special police teams and separate courts will be set up for investigation and trial of cases against women and children.
- The perpetrators if found guilty will be punished with imprisonment for life for not less than ten years but may extend to the remainder of natural life or with death in cases which have characteristics of being heinous in nature.
- A sum of Rs 10 lakh will be given to an acid attack victim for plastic surgery and facial reconstruction and the amount will be collected as fine from the convict.
- The investigation shall be completed within a period of 15 working days from the date of registration of an offence. This can be extended by 7 days.
- After a charge sheet is filed trial shall be conducted on a day-to-day basis and completed within a period of 30 working days.
- Some cases will be tried in-camera for the recording of evidence of victims and witnesses who are vulnerable.
Enforcement, not the law
- Despite several laws, incidences of rapes continue unabated.
- In fact, now we hear cases of extreme brutality.
- The general perception is that since the laws have been made more stringent, so the rapists resort to extreme measures in a bid to destroy the evidence.
- One thing is very clear, Laws alone cannot provide a solution to this problem.
What should be done?
- Law provides for speedy investigations and fast track of trials in rape cases.
- What we need is better policing, making public spaces safer for women, ensuring round the clock surveillance of isolated areas and deployment of police at all strategic points.
- Prevention and not punishment is the solution and that requires concerted efforts on part of all the stakeholders.
- It is not harsher punishments that will deter. It is the fear of being caught and not being spared.
- The message should go out loud and clear that no one is above the dignity and safety of women in our country.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: UN Population Award
Mains level: Not Much
HelpAge India has been presented the UN Population Award for 2020 (institutional category), according to a release issued by UNFPA.
Try this PYQ:
Q.The Partnership for Action on Green Economy (PAGE), a UN mechanism to assist countries transition towards a greener and more inclusive economies, emerged at:
(a) The Earth Summit on Sustainable Development 2002, Johannesburg
(b) The United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development 2012, Rio de Janeiro
(c) The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change 2015, Paris
(d) The World Sustainable Development Summit 2016, New Delhi
UN Population Award
- Each year, the Committee for the UNPA honours an individual and/or institution in recognition of outstanding contributions to population and reproductive health questions and to their solutions.
- The Award was established by the General Assembly in 1981, in resolution 36/201, and was first presented in 1983. It consists of a gold medal, a diploma and a monetary prize.
- The Committee for the Award is comprised of 10 UN Member States, with UN Secretary-General and UNFPA Executive Director serving as ex-officio members.
- Nominations for the award are accepted through 31 December of each year.
Whats’ so special this year?
- For the first time in the history of the UNPA, the honour is being conferred on an Indian institution.
- HelpAge India, which has been working for ‘the cause and care of disadvantaged older persons to improve their quality of life’ for over four decades, is the first Indian institution to receive this award.
- The last time the Award came to an Indian was 28 years ago, back in 1992, when it was awarded to Mr J.R.D. Tata as an individual laureate.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Aurora Borealis
Mains level: Aurora and the science behind

Northern Lights, also known as aurora borealis could be visible in regions such as in the northern parts of Illinois and Pennsylvania in the US.
Try this PYQ:
What is a coma, in the context of Astronomy?
(a) Bright half of material on the comet
(b) Long tail of dust
(c) Two asteroids orbiting each other
(d) Two planets orbiting each other
Aurora
- Auroras occur when charged particles ejected from the Sun’s surface — called the solar wind — enter the Earth’s atmosphere.
- While flowing toward Earth, the fast-moving solar wind carries with it the Sun’s magnetic field, which disrupts the magnetosphere — the region of space around Earth in which the magnetic field of our planet is dominant.
- When the Sun’s magnetic field approaches Earth, the protective magnetic field radiating from our planet’s poles deflects the former, thus shielding life on Earth.
- However, as this happens, the protective fields couple together to form funnels, through which charged solar wind particles are able to stream down to the poles.
- At the north and south poles, the charged particles interact with different gases in the atmosphere, causing a display of light in the sky.
- This display, known as an aurora, is seen from the Earth’s high latitude regions (called the auroral oval), and is active all year round.
Behind the name
- In the northern part of our globe, the polar lights are called aurora borealis or Northern Lights and are seen from the US (Alaska), Canada, Iceland, Greenland, Norway, Sweden and Finland.
- In the south, they are called aurora australis or southern lights and are visible from high latitudes in Antarctica, Chile, Argentina, New Zealand and Australia.
Where is it observed?
- Generally, the auroral oval is usually witnessed far up in the Polar Regions or the high latitude regions of Europe, like in Norway.
- But occasionally, the oval expands, and the lights become visible at lower latitudes.
- This happens during periods of high solar activity, such as the arrival of solar storms.
- Solar activities include solar flares, solar energetic particles, high-speed solar wind and Coronal Mass Ejections (CME).
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Various water borne disease
Mains level: Drinking water issues
Over 550 people in Eluru town of Andhra Pradesh’s West Godavari district have been suffering from convulsions, seizures, dizziness and nausea.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Which of the following can be found as pollutants in the drinking water in some parts of India?
- Arsenic
- Sorbitol
- Fluoride
- Formaldehyde
- Uranium
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2, 4 and 5 only
(c) 1, 3 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Eluru illness
- The All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) has found traces of lead and nickel in blood samples of 25 victims out of the 45 samples sent by the state government.
- The primary suspicion is on water contamination by heavy metals. Scientists suspect that pesticide or insecticide has seeped into drinking water sources.
- Experts from Hyderabad who collected water, blood, and food samples say there are indications of lead contamination but can confirm this only after detailed test reports.
Possible cause: Water contamination
- Eluru receives water through canals from both Godavari and Krishna rivers.
- The canals pass through agricultural fields where runoff laced with pesticides mixes with water in the canals. Many aspects of the mystery illness have baffled scientists.
- People who only use packaged drinking water have also fallen sick.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Iran's nuclear deal
Mains level: Paper 2- Iran nuclear deal and challenges
The article analyses Iran’s response to the recent killing of its top nuclear scientist. Instead of responding to the provocation, Iran has decided to wait and watch the new U.S. administrations response.
Background of nuclear deal with Iran
- In 2015, the P5+1 nations-China, France, Russia, the U.K. and the U.S., plus Germany- reached an agreement with Iran to curb the country’s nuclear programme.
- It was expected that the agreement would lead to a new beginning in West Asia, however, this did not happen.
- Washington saw Iran’s nuclear programme, which was at an advanced stage in 2015, as a national security problem and tackled it via diplomacy.
- However, for Israel and Saudi Arabia, Iran’s nuclear programme was not the problem but was part of the larger geopolitical challenges Iran posed.
- The problem was Iran itself: Tehran’s influence across West Asia, its backing for non-state militias, and its ambition to emerge as a dominant pillar in the region.
- The Donald Trump administration took an entirely different line towards Iran.
- It pulled the U.S. out of the nuclear deal, despite United Nations certification that Iran was compliant with its terms, and reimposed sanctions on Tehran.
Israels
- Iran wants to set back Iran’s nuclear programme by taking out a prominent scientist and scuttle the possible revival of the nuclear deal.
- If Iran does not retaliate, it shows that Iran’s deterrence is getting weaker, which could trigger more such attacks from its rivals.
- If it retaliates, it could escalate the conflict, giving the outgoing Trump administration and Isarael reasons to launch heavier strikes on Iran’s nuclear facilities, closing off the diplomatic path.
Iran’s response and challenges in it
- Instead of walking into the trap of provocation, Iran’s Parliament passed a Bill that obliges the government to enrich uranium to a higher level, from less than 5% now to 20%.
- This is a technical step away from the weapons-grade level of 90%.
- And stop access for UN inspectors to the country’s top nuclear facilities in two months if sanctions relief is not given.
- Within two months, Mr. Biden will be in the White House.
Conclusion
Iran is taking a calculated risk by enhancing its nuclear programme, which can be reversed if talks are revived. But it is leaving the Israel problem unaddressed, for now. This leaves the region vulnerable to a prolonged crisis.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: POSHAN Abhiyan
Mains level: Paper 2- Analysing the contribution of POSHAN Abhiyan
POSHAN Abhiyan has completed 1000 days. The article analyses the challenges country face on the nutrition front which has been exacerbated by the Covid-19 induced disruptions.
Severity and impact of malnutrition
- Malnourished children tend to fall short of their real potential — physically as well as mentally.
- That is because malnutrition leaves their bodies weaker and more susceptible to illnesses.
- In 2017, a staggering 68% of 1.04 million deaths of children under five years in India was attributable to malnutrition, reckoned a Lancet study in 2019.
- Without necessary nutrients, their brains do not develop to the fullest.
- Malnutrition places a burden heavy enough for India, to make it a top national priority.
- About half of all children under five years in the country were found to be stunted (too short) or wasted (too thin) for their height, estimated the Comprehensive National Nutrition Survey, carried out by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare with support of UNICEF three years ago.
POSHAN Abhiyan against the background Covid-19 disruption
- The Prime Minister’s Overarching Scheme for Holistic Nutrition (POSHAN) Abhiyaan in 2018, led to a holistic approach to tackle malnutrition.
- Under it, the government strengthened the delivery of essential nutrition interventions.
- COVID-19 is pushing millions into poverty making them vulnerable to malnutrition and food insecurities.
- Pandemic-prompted lockdowns disrupted essential services — such as supplementary feeding under anganwadi centres, mid-day meals, immunisation, and micro-nutrient supplementation which can exacerbate malnutrition.
- Leaders from academia, civil society, development partners, community advocates and the private sector have come together as part of ‘commitment to action’.
- The ‘commitment to action’ includes commitments around sustained leadership, dedicated finances, multi-sectoral approach and increased uninterrupted coverage of a vulnerable population under programmes enhancing nutrition.
Financial commitments
- India already has some of the world’s biggest early childhood public intervention schemes such as the Integrated Child Development Scheme, the mid-day meal programme, and Public Distribution System.
- India needs to ensure coverage of every single child and mother.
- To ensure this, the country needs to retain its financial commitments for nutrition schemes.
- Economic insecurities often force girls into early marriage, early motherhood, discontinue their schooling, and reduce institutional deliveries, cut access to micronutrient supplements, and nutritious food.
- Accelerating efforts to address these will be needed to stop the regression into the deeper recesses of malnutrition.
Conclusion
It takes time for nutrition interventions to yield dividends, but once those accrue, they can bring transformative generational shifts. Filling in the nutrition gaps will guarantee a level-playing field for all children and strengthen the foundations for the making of a future super-power.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ICDS program
Mains level: Paper 2- Role of Anganwadi centres in ICDS
The article highlights the role of Anganwadi’s in the effective implementation and service delivery under the ICDS.
Gaps in the utilisation of services by ICDS
- The economic fallout of COVID-19 makes the necessity of quality public welfare services more pressing than ever.
- The Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) programme is one such scheme.
- ICDS caters to the nutrition, health and pre-education needs of children till six years of age as well as the health and nutrition of women and adolescent girls.
- However, recent reports have shown gaps in the utilisation of services.
Recasting the Anganwadi centres
- Anganwadi centres (AWCs) could become agents of improved delivery of ICDS’s services.
- According to government data, the country has 13.77 lakh Anganwadi centres (AWCs).
- These centres have expanded their reach, but they need to play a much larger role in anchoring community development.
- Nearly a fourth of the operational AWCs lack drinking water facilities and 36 per cent do not have toilets.
- In 2015, the NITI Aayog recommended better sanitation and drinking water facilities, improved power supply and basic medicines for the AWCs.
- NITI Aayog also suggested that these centres be provided with the required number of workers, whose skills should be upgraded through regular training.
- It has acknowledged the need to improve anganwadi centres.
- The Central government’s Saksham Anganwadi Scheme aims to upgrade 2.5 lakh such centres across the country. It is up to the state governments to take up the baton
- Only a limited number of AWCs have facilities like creche, and good quality recreational and learning facilities for pre-school education.
- An approach that combines an effective supplementary nutrition programme with pedagogic processes that make learning interesting is the need of the hour.
Steps taken for effective implementation of ICDS
- Effective implementation of the ICDS programme rests heavily on the combined efforts of the anganwadi workers (AWWs), ASHAs and ANMs.
- The Centre’s POSHAN Abhiyaan has taken important steps towards building capacities of AWWs.
- Technology can also be used for augmenting the programme’s quality.
- AWWs have been provided with smartphones and their supervisors with tablets, under the government schemes.
- Apps on these devices track the distribution of take-home rations and supplementary nutrition services.
- The data generated should inform decisions to improve the programme.
- In Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, anganwadi centres have been geotagged to improve service delivery.
- Gujarat has digitised the supply chain of take-home rations and real-time data is being used to minimise stockouts at the anganwadi centres.
Conclusion
Government must act on the three imperatives. First, while infrastructure development and capacity building of the anganwadi remains the key to improving the programme, the standards of all its services need to be upscaled. Second, states have much to learn from each other’s experiences. Third, anganwadi centres must cater to the needs of the community and the programme’s workers.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Federal structure
Mains level: Paper 2- Federalism in India and factors sustaining it
The article analyses the various factor that helped in sustaining the federal structure in India.
Flexible federalism
- The Indian Constitution was designed to be opportunistic about federalism.
- As BR Ambedkar had put it, “India’s Draft Constitution can be both unitary as well as federal according to the requirements of time and circumstances.”
- This flexible federalism is still the default common sense of Indian politics.
- The concerns about security, state-building, and economic development are always given preference over the idea of federalism.
4 factors sustaining federalism in India
1) Linguistic and cultural diversity in India
- The first was a genuine concern about whether a centralised state could accommodate India’s linguistic and cultural diversity.
- The States Reorganisation Act and the compromises on the issue of languages was a victory for federalism.
- It allowed India to use federalism to accommodate linguistic diversity.
- So long as regional linguistic identities are not threatened there is no natural source of resistance to centralisation.
2) Distribution of political power
- The rise of coalition governments, economic liberalisation, regional parties, seemed to provide a basis for political federalism.
- Political federalism is quite compatible with financial, and administrative centralisation.
- Fragmentation of power effectively meant was that each state could bargain for certain things, or very strong leaders could veto central proposals.
- However, it is striking that the period of fragmented power, strong chief ministers, didn’t act to strengthen the institutions of federalism.
3) Political and institutional culture
- The third thing that sustains federalism is the political and institutional culture.
- But the culture of political parties ruling at the Centre was committed to the most extreme interpretation of flexible federalism, including procedural impropriety to oust opponents.
- Because of the increasing presidentialisation of national politics, the attribution of policy successes or failures might change, diminishing the stature of chief ministers considerably.
- The other source of institutional culture might be the Supreme Court.
- There was mostly a bi-partisan consensus on honouring the technical recommendations of institutions like the Finance Commission.
4) Asymmetrical federalism
- The fourth thing that sustained federalism was “asymmetrical federalism” — special exemptions given to various states.
- But asymmetrical federalism has always been subject to three pressures.
- For Kashmir, asymmetrical federalism came to be seen as the source, not the resolution, of the security threat.
- Even in the North-east, local conflicts within the scheme of asymmetrical federalism and discourse of security allowed the Centre to step in.
- And increasingly, there will be pressure on the question: Which laws under asymmetrical federalism are compatible with Article 14 of the Indian Constitution?
GST and Decentralisation in states
- The most far-reaching change in the Indian Constitution on federalism was GST.
- It does increase centralisation in the system.
- But it is a product of the cooperation of the states, who still have a significant role in shaping it.
- The states did push back against the possibility of the Centre reneging on its commitment on payments.
- Most states are reluctant to honour more decentralisation within, to rural and urban bodies.
- The Centre disproportionately controls resources in India; but very few states have shown a zeal to increase their own financial headroom by utilising whatever powers they might have on taxation.
Consider the question “How federalism in India is different from the U.S.? What are the factors responsible for its sustenance in India?”
Conclusion
The flexible federalism will be bent in all kinds of ways. But it is important to remember that this mess is not a product of Centre versus states. It has been co-produced by a political culture in both Centre and the states.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Various COPs, UNFCCC
Mains level: Progress of global climate action

China’s announcement of achieving net-zero by 2060 is a stepping stone in the fight against climate change. But it means nothing until countries share the goals they intend to follow.
Why are we reading this news?
We often get to hear that UPSC suddenly switches to basics after maneuvering over current affairs. This news is a perfect example which strikes the balance between basics and current affairs.
Climate change: A disaster in making
- Anthropogenic climate change can be traced back to the industrial revolution.
- The atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) greenhouse gas has increased to 415 parts per million (ppm) from 280 ppm since then.
- A global momentum, therefore, was required to get all countries on board.
Realization of climate action: Birth of UNFCCC
- The idea led to the formation of the United Nations Framework for Climate Change Convention (UNFCCC, also known as ‘The Convention’) in 1992, at the Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro.
- The convention divided the countries on the basis of their differing commitments: Annex I and II consisted of industrialized and developed countries and Non-Annex I comprised developing countries.
Wait! You need not remember everything* in this newscard. But, have walk through the timeline; it will concretize your idea about the global climate action and the possible way forward.
A timeline

The Conference of Parties (CoP) is the supreme decision-making body at the convention and comprises states that are party to it.
COP 1:
- At CoP1 in Berlin 1995, the Convention highlighted the shortcomings of UNFCCC — the voluntary nature of the agreement.
- It stressed how no substantive action was taken to address the cause against climate change, which in turn put forward the need for “legally binding” actions.
COP 2:
The proposal of legally binding targets was further emphasised upon in COP2 in Geneva in 1996.
COP 3:
- In COP3 in Kyoto in 1997, the legally binding targets were approved of by different countries. They came to be known as the Kyoto Protocol.
- It is considered to be one of the most important steps despite its late acceptance for it paved the way for further negotiations through legally binding targets for Annex I countries and establishment of carbon markets.
- The mechanisms proposed by Kyoto Protocol to reduce emissions included Joint Implementation, Clean Development Mechanisms (CDM) and Emissions Trading.
COP 4 and COP 5:
In COP4 in 1998 and COP5 in 1999, the rulebook for implementing the Kyoto Protocol was on the process with the adoption of the Buenos Aires Plan of Action in COP4, along with continued negotiation efforts in COP5.
COP 7:
- In COP7 in Marrakesh in 2001, the guidelines for flexible mechanisms of joint implementation, CDM markets, emissions trading was agreed upon. It came to be known as the Marrakesh Accord.
- It was particularly important because mitigation efforts had already started and special attention was given to developing countries.
- It asked them to build their capacities and ensuring technology transfer through least developed countries (LDC) Fund, special climate change fund (SCCF) and adaptation fund.
COP 8:
The COP8 in 2002, which was held in “New Delhi”, emphasised on adaptation measures and stressed that poverty alleviation and development were the utmost priority of developing countries.
COP 10:
- The future course of action was discussed in COP10 in Montreal in 2005 after Russia ratified the Protocol in 2004 at COP10 in Argentina.
- A two-track approach was formed, which included the constructive implementation of UNFCCC as well as formation an ad-hoc committee for the Kyoto Protocol.
COP 15:
- Copenhagen COP 2009 was set by the ad-hoc working group on Kyoto protocol formed during Montreal COP 2005.
- The group agreed to have a deal in 2009 regarding a legally binding climate regime from 2012-2020.
- The discussions lost track when developed countries started advocating for burden-sharing with developing countries.
COP 16:
- The disappointment of Copenhagen was turned into an opportunity in Cancun 2010, where the Copenhagen Accord was accepted.
- It looked forward to a second commitment period for the Kyoto Protocol and established the Cancun Adaptation Framework.
- For the first time, a temperature target of 2 degrees Celsius was included. The Green climate fund was formed and developed countries agreed to contribute.
COP 17:
- Following Cancun, Durban COP 2011 took place wherein the seed of the Paris Agreement was sown.
- The seed started sprouting in Doha COP 2012, where countries decided to avoid the gap between Kyoto and next legal climate regime.
- So, the second regime of Kyoto was decided from 2012-2020. The third pillar of loss and damage was incorporated for the first time.
COP 20:
In COP in Lima in 2014, countries submitted their own climate ambitions in the form of intended nationally determined contributions (INDCs).
COP 21: The Pathbreaker
- In 2015, the Paris agreement was finally adopted and the INDCs were annexed to it.
- It was agreed that the Paris agreement would start from 2021.
- 2015 was known as a year of multilateral agreements because, in addition to the Paris agreement, sustainable development goals and Sendai Framework was also adopted.
- 2015, therefore, came out to be a successful year.
Post Paris Agreement
- The retreat of developed countries: In all these post-2020 talks, developed countries tactfully avoided their pre-2020 commitments by not ratifying the Kyoto protocol.
- Post-Paris discussions for the finalization of the Rulebook began.
- Most were finalised in 2018, except the market mechanism and measurement, reporting and verification (MRV) of greenhouse gas which are due in COP26 in 2021.
Agenda for next COP in 2021
- The next COP will be in 2021 in Glasgow with two sets of agendas for discussion.
- The first will be to complete the rule-book of Paris Agreement implementation, whose two aspects regarding Sustainable Development Mechanism (SDM) architecture and MRV framework are yet to be completed.
- The second will be to ensure smooth implementation of the Paris Agreement from 1st January 2021.
- Countries are expected to revise their NDCs as the present course of activities is projected to cause an increase in temperature of 2.8-3 C rise.
The situation today: Nothing beyong big promises
- China’s recent announcement of achieving net-zero by 2060 comes across as the stepping stone of future climate change mitigation efforts.
- Political announcements, however, mean nothing until countries actually share the goals they intend to follow.
- On the contrary, India is the only country whose NDCs are in line with the 2 degrees Celsius target.
- Another substantial happening in the domain of climate change includes Joe Biden’s promise of joining the Paris Agreement; it would bring the US back to the GCF fund.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PM-WANI
Mains level: Internet connectivity, Digital divide

In a bid to improve wireless connectivity, the Union Cabinet approved setting up of the public WiFi was part of the Prime Minister WiFi Access Network Interface (PM- WANI).
Do you know?
According to TRAI, in most major economies, for 50%-70% of their total usage time, mobile users use WiFi technology to communicate. However, in India, this figure is less than 10%.
PM- WANI
- The WiFi will be provided through public data offices (PDOs) for which there will be no licence, registration or any other fees.
- The PDO, to be set up along the lines of public calling office, can be a mom-and-pop store in the area or the common services centre present in various small towns, gram panchayats, and villages in the country.
- The PDOs can either provide the internet on other own or lease it from other telecom and internet service providers.
The centre-stage: Public Data Offices (PDO)
- The idea of a PDO was first floated by the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) in 2017.
- Like a PCO, the PDO allows users to connect to a public WiFi system for a limited session depending on the internet pack chosen by the user.
- These internet packages can either by charged on per minute or per hour basis by the PDOs.
Licensing of PDOs
- There will be no licence for PDOs. A simple registration system will be put in place for PDO aggregators as well as app providers, which will be approved within seven days of the application being submitted.
- In addition to the PDOs, there will also be PDO aggregators, which will look after the authorisation and accounting of PDOs.
A note for users
- A third layer will of app providers, available for download on the Play Store as well as the Apple Store, will enable users to register for using the public WiFi at a particular place.
- Users, however, will not be required to download different apps, as a single app will provide seamless connectivity to any PDO across the country.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Various IVC sites
Mains level: IVC
A new study has found the presence of animal products, including cattle and buffalo meat, in ceramic vessels dating back about 4,600 years at seven Indus Valley Civilization sites in present-day Haryana and Uttar Pradesh.
The Karnataka Assembly has passed the controversial Karnataka Prevention of Slaughter and Preservation of Cattle Bill, 2020, amid protests.
Beef politics has always gained traction in India being a cheap source of protein for masses versus religious sentiments of the fundamentalists.
How was the study conducted?
- The study is the first to look into the absorbed lipid residues in pottery from multiple sites, including Rakhigarhi, Farmana and Masudpur.
- Lipids are relatively less prone to degradation and have been discovered in pottery from archaeological contexts around the world.
Key findings
- The high proportions of cattle bones suggest a cultural preference for beef consumption across Indus populations, supplemented by the consumption of mutton/lamb.
- The study found little evidence of dairy products. However, there could be regional differences as a recent study of vessels in Gujarat had found evidence of dairy products.
- About 50-60% of domestic animal bones found at Indus Valley sites come from cattle/buffalo.
- It says that at Harappa, 90% of the cattle were kept alive until they were three or three-and-a-half years, suggesting that females were used for dairying production, whereas male animals were used for traction.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: BTCA
Mains level: Digital banking facilitation measures
The Union Ministry of Finance and UN-Based Better Than Cash Alliance (BTCA) organized a joint Peer learning exchange on fintech solutions for responsible digital payments at the last mile.
Make a note here that it is a BTCA is a global partnership with diverse funding, a UN office as its secretariat and Indian being its member.
Better Than Cash Alliance
- The BTCA is a global partnership of 75 governments, companies, and international organizations that accelerates the transition from cash to digital payments in order to reduce poverty and drive inclusive growth.
- The United Nations Capital Development Fund serves as the secretariat. It was created in September 2012.
- The Alliance is funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, Citi, MasterCard, Omidyar Network, USAID, and Visa Inc.
- By the time it launched, the program was already being rolled out in Peru, Kenya, Colombia, and the Philippines.
India and the BTCA
- India became a member of the alliance in 2015 to digitize payments to achieve financial inclusion and to share success stories from Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana, the world’s largest financial inclusion program.
- The alliance is working with several state governments towards the goal of building knowledge and programs where people, governments, and businesses can make and receive digital payments.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now









