Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Federal structure
Mains level: Paper 2- Evolutio of Centre-State relation in India
Against the backdrop of the ongoing tussle between the states and the Centre over the issue of GST compensation, the article analyses the evolution of federalism and power-sharing in India.
GST and federalism
- At the first sign of stress, the nation unified in a singular system of taxation (GST) turned into a policy of every-state-for-itself.
- Evidence of seriously miscued revenue estimates without pragmatic tax rate, was accumulating at an alarming pace.
- The Comptroller and Auditor-General of India (CAG) recently revealed how a cess meant to remedy shortfalls in GST yields, was retained in central government revenues, in violation of all applicable norms.
- This revelation does little to build trust between the Centre and the States at a time when the States’ facing lack of resource and the central government is advising them to borrow.
- Some states believe that the onus of borrowing should rest with the central government.
Higher borrowing limit for states with conditions
- The central government sanctioned a higher borrowing limit for States through the current year.
- In the bargain, it imposed conditionalities:
- 1) Enforcing a singular standard for the implementation of policies across a vast and diverse country.
- 2) Improving India’s ranking as a place for “doing business”.
- States will have unconditional access to borrowings equivalent to half a percentage point of their gross output.
- But, subsequently, every tranche of a quarter point will be premised on progress in implementing the “one nation, one ration card” scheme, and improvements in the “ease of doing business”.
Federalism in India
- Aside from the contents and definitions sections, the word “federal” occurs in only one operational article of the Indian Constitution, in reference to the apex judicial body created in colonial times.
- When this body was transformed into the Supreme Court at the moment the Constitution came into force, the word seemingly lost all operative value.
- The distribution of powers and responsibilities between various tiers of the governmental system, was achieved without explicit recognition of federalism as a governing principle.
- In actual operational terms, the relationship of Centre and States followed different paradigms through various phases of politics.
- At the time of Independence, the distribution of powers between Centre and States was transformed into an internal discussion of the Congress.
Evolution of power-sharing and politics
- The “Congress system”, as the political scientist Rajni Kothari called it, was seen at one time to have sufficient internal flexibility and resilience to absorb all factional pressures.
- The first challenge came from the cultural terrain, compelling a reluctant national leadership to accept linguistic reorganisation of States.
- And then, as ambitions of nation-building through rapid industrialisation resulted in the possibility of a non-Congress politics.
- The Congress lost power in a number of key States in 1967.
- The polity moved into a new phase when politics was about “waves” at the national or state level either in favour of, or against the Congress.
- From 1989 onwards, politics settled into another distinct phase, when outcomes at the national level were the resultant of very separate State-level results.
Conclusion
Though federal structure could not be free from Centre-State power struggle, that struggle should not come into the development of the nation. In this context, it is the responsibility of the Centre to address the issues facing the state amid pandemic.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CRISPR-Cas9
Mains level: Paper 3- CRISPR-Cas9-Important tool in gene editing
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry for 2020 has been awarded for the discovery of CRISPR Cas9. The two scientists have pioneered the use of CRISPR – Cas9 (CRISPR-associated protein 9) system as a gene-editing tool.
Background of discovery of CRISPR
- In 1987a group of Japanese researchers observed an unusual homologous DNA sequence bearing direct repeats with spacing in a eubacterial gene.
- In subsequent years CRISPR was discovered and showed to be a bacterial adaptive immune system and to act on DNA targets.
- A notable discovery on the use of CRISPR as a gene-editing tool was by a Lithuanian biochemist, Virginijus Šikšnys, in 2012.
- Šikšnys showed that Cas9 could cut purified DNA in a test tube, the same discovery for which both Charpentier and Doudna were given the credit.
- Thus, the exclusion of Siksnys from this year’s Nobel is going to raise discussions.
Issue of gene-edited babies
- The world was alarmed by such a mission in 2018 when Chinese scientist edited genes in human embryos using the CRISPR-Cas9 system which resulted in the birth of twin girls.
- The incident became known as the case of the first gene-edited babies of the world.
- Following the incident, the World Health Organization formed a panel of gene-editing experts.
- The expert panel suggested a central registry of all human genome editing research in order to create an open and transparent database of ongoing work.
Guidelines and regulations in India
- In India, several rules, guidelines, and policies are notified under the Environment Protection Act, 1986 to regulate genetically modified organisms.
- The above Act and the National Ethical Guidelines for Biomedical and Health Research involving human participants, 2017, by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), and the Biomedical and Health Research Regulation Bill implies regulation of the gene-editing process.
- This is especially so in the usage of its language “modification, deletion or removal of parts of heritable material”.
- However, there is no explicit mention of the term gene editing.
Consider the question “What is CRISPR-Cas9? How it helps in the gene-editing? What are the concerns with use of it for gene-editing?”
Conclusion
It is time that India came up with a specific law to ban germline editing and put out guidelines for conducting gene-editing research giving rise to modified organisms.
Back2Basics: What is CRISPR?
- CRISPRs: “CRISPR” stands for “clusters of regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats.”
- It is a specialized region of DNA with two distinct characteristics: the presence of nucleotide repeats and spacers.
- Repeated sequences of nucleotides — the building blocks of DNA — are distributed throughout a CRISPR region.
- Spacers are bits of DNA that are interspersed among these repeated sequences.
- In the case of bacteria, the spacers are taken from viruses that previously attacked the organism.
- They serve as a bank of memories, which enables bacteria to recognize the viruses and fight off future attacks.

Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 3- Delhi air-pollution issue
The article suggests the three-pronged strategy to deal with the emission from transportation and highlights the importance of coordination at various level to deal with the issue of pollution.
Anti-pollution campaign in Delhi
- With air pollution returning to pre-COVID levels, the Delhi administration has launched a major anti-pollution campaign this month.
- The campaign is focused on cutting the deadly smoke from thermal plants and brick kilns in the National Capital Region as well as on chemical treatment of stubble burning from nearby States.
Abating emission from transportation
- Delhi’s long-term solution will depend importantly also on abating emissions from transportation.
- Delhi needs a 65% reduction to meet the national standards for PM2.5.
- Vehicles, including trucks and two-wheelers, contribute 20%-40% of the PM2.5 concentrations.
- Tackling vehicle emissions would be one part of the agenda, as in comparable situations in Bangkok, Beijing, and Mexico City.
Three-part action to combat emissions from transportation
- A three-part action comprises emissions standards, public transport, and electric vehicles.
1) Stricter enforcement of emission controls
- Two-wheelers and three-wheelers were as important as cars and lorries in Beijing’s experience.
- Bangkok ramped up inspection and maintenance to cut emissions.
- The first order of business is to implement the national standards.
2) Strengthening public transport
- Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) around the world show how the sizeable investment cost is more than offset by the benefits, and that financing pays off.
- Delhi has lessons from its BRT experience in designating better BRT lanes, improving the ticketing system and synchronising with the Metro.
- The Supreme Court’s ruling to increase Delhi’s bus fleet and align it with the Metro network must be carried out.
- The ‘odd-even’ number plate policy can help, but the system should reduce exemptions, allow a longer implementation period, and complement it with other measures.
3) Adoption of electric vehicle: A long term solution
- Subsidies and investment will be needed to ensure that EVs are used to a meaningful scale.
- The Delhi government’s three-year policy aims to make EVs account for a quarter of the new vehicles registered in the capital by 2024.
- EVs will gain from purchase incentives, scrappage benefits on older vehicles, loans at favourable interest and a waiver of road taxes.
Need for coordination at various level
- Transport solutions need to be one part of pollution abatement that includes industry and agriculture.
- Delhi’s own actions will not work if the pollution from neighbouring States is not addressed head on.
- Technical solutions need to be underpinned by coordination and transparency across Central, State, and local governments.
- Public opinion matters.
- Citizen participation and the media are vital for sharing the message on pollution and health, using data such as those from the Central Pollution Control Board.
Conclusion
- It is a matter of prioritising people’s health and a brighter future. Once the pandemic is over, Delhi must not stumble into yet another public health emergency. The time to act is now.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Freedom of Navigation Operations
Mains level: Not Much
Indian Navy is scheduled to hold another Passage Exercise (PASSEX) with the US to undertake Freedom of Navigation Operations (FONOP).
Try this question:
Q.What do you mean by Freedom of Navigation Operations (FONOPs)? What are its legal backings? Discuss its significance.
Freedom of Navigation Operations
- FONOPs are closely linked to the concept of freedom of navigation, and in particular to the enforcement of relevant international law and customs regarding freedom of navigation.
- Freedom of navigation has been thoroughly practised and refined, and ultimately codified and accepted as international law under UNCLOS, in a legal process that was inclusive and consent-based.
- The drafting of UNCLOS was driven in part by states’ concerns that strong national maritime interests could lead to excessive maritime claims over coastal seas, which could threaten freedom of navigation.
- FONOPs are outgrowths of this development of international law, based on sovereign equality and international interdependence.
Significance of FONOPs
- FONOPs are a method of enforcing UNCLOS (United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea) and avoiding these negative outcomes by reinforcing freedom of navigation through practice.
- It is exercised by sailing through all areas of the sea permitted under UNCLOS, and particularly those areas that states have attempted to close off to free navigation as defined under UNCLOS.
Back2Basics: UNCLOS
- The Law of the Sea Treaty formally known as the Third United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea was adopted in 1982 at Montego Bay, Jamaica. It entered into force in 1994.
- The convention establishes a comprehensive set of rules governing the oceans and to replace previous U.N. Conventions on the Law of the Sea
- The convention defines the distance of 12 nautical miles from the baseline as Territorial Sea limit and a distance of 200 nautical miles distance as Exclusive Economic Zone limit.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Greater Male Connectivity Project
Mains level: India-Maldives Relations

Following up on India’s announcement of a $500 million package to the Maldives, the Exim Bank of India and the Maldives’s Ministry of Finance signed an agreement for $400 million in Male.
Try this question from 2014:
Q.Which one of the following pairs of islands is separated from each other by the ‘Ten Degree Channel’?
(a) Andaman and Nicobar
(b) Nicobar and Sumatra
(c) Maldives and Lakshadweep
(d) Sumatra and Java
Greater Male Connectivity Project
- The GMCP consists of a number of bridges and causeways to connect Male to Villingili, Thilafushi and Gulhifahu islands that span 6.7 km.
- It would ease much of the pressure of the main capital island of Male for commercial and residential purposes.
- When completed, the project would render the Chinese built Sinamale Friendship bridge connecting Male to two other islands, thus far the most visible infrastructure project in the islands.
- At present, India-assisted projects in the region include water and sewerage projects on 34 islands, reclamation project for the Addl island, a port on Gulhifalhu, airport redevelopment at Hanimadhoo, and a hospital and a cricket stadium in Hulhumale.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Femto Satellites, Micro-gravity
Mains level: Not Much

An experimental satellite developed by three students of Karur (TN) has been selected for launch in sub-orbital space by NASA.
Try this PYQ:
Q.The term ‘IndARC’, sometimes seen in the news, is the name of:
(a) An indigenously developed radar system inducted into Indian Defence
(b) India’s satellite to provide services to the countries of Indian Ocean Rim
(c) A scientific establishment set up by India in Antarctic region
(d) India’s underwater observatory to scientifically study the Arctic region
Indian Sat
- The Indian Sat is made of reinforced graphene polymer. It is 3 cm in size and weighs 64 gm.
- It has its own radio frequency communication to transmit and receive a signal from earth to outer space. The solar cells attached to the satellite generate power for it.
- The photographic film will absorb and measure the cosmic radiation inside the rocket.
- It would study the effect of reinforced graphene polymers in microgravity. It would be in sub-orbital space flight for a few minutes before landing in the ocean.
What is micro-gravity?
- The term micro-g environment is more or less synonymous with the terms weightlessness and zero-g, but with an emphasis on the fact that g-forces are never exactly zero—it is just very small.
- On the ISS, for example, the small g-forces come from tidal effects, gravity from objects other than the Earth, such as astronauts, the spacecraft, and the Sun, and, occasionally, air resistance.
Back2Basics: Femto-satellites
- Femto-satellites are satellites with a mass lower than 100 grams.
- These new categories of satellites are, by concept, low cost devices if they are based on Commercial-of-the-Shelf (COTS) components.
- Some examples of applications are related to low-cost missions with a short time of development.
Kalamsat
- Kalamsat was a communication satellite with a life span of two months launched in 2017.
- The nanosatellite is a 10cm cube weighing 1.2 kg.
- It will be the first to use the rocket’s fourth stage as an orbital platform.
- The fourth stage will be moved to higher circular orbit so as to establish an orbital platform for carrying out experiments.
- It is named after former Indian president Dr APJ Abdul Kalam and was built by an Indian high school student team, led by Rifath Sharook, an 18-year-old from the Tamil Nadu town of Pallapatti.
- It is the world’s lightest and first-ever 3D-printed satellite.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: RKA
Mains level: India's dailry potential
Rashtriya Kamdhenu Aayog (RKA) has started a nationwide campaign to celebrate “Kamdhenu Deepawali Abhiyan” this year on the occasion of Deepawali festival.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Consider the following statements:
- Agricultural soils release nitrogen oxides into the environment.
- Cattle release ammonia into the environment.
- Poultry industry releases reactive nitrogen compounds into the environment.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Rashtriya Kamdhenu Aayog (RKA)
- RKA has been constituted by PM for the conservation, protection and development of cows and their progeny and for giving direction to the cattle development programmes.
- It is a high powered permanent body to formulate policy and to provide direction to the implementation of schemes related to cattle so as to give more emphasis on livelihood generation.
Why need RKA?
- Livestock economy sustains nearly 73 million households in rural areas.
- Even though, the country is the largest producer of milk, the average milk yield in India is only 50% of the world average.
- The low productivity is largely due to deterioration in genetic stock, poor nutrition and unscientific management.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Article 293
Mains level: Paper 2- Federalism and GST
The GST has been hailed as the grand bargain and the success story of the federalism. But the economic disruption caused by the pandemic has put it to test. The article deals with the issue of GST compensation.
Compensating the loss of GST revenue: 2 options
- In the 41st meeting of the GST Council, the Union government had presented the states with two options.
- The Centre had estimated the states’ total loss of GST revenue at Rs 3 lakh crore, of which, Rs 65,000 crore was expected to accrue from the compensation cess.
- Of the remaining Rs 2.35 lakh crore, the loss due to the pandemic was estimated at Rs 1.28 lakh crore.
- The first option was to provide states a special window to borrow Rs 97,000 crore from the RBI, which was later revised to Rs 1.1 lakh crore.
- Under this option, both the interest payments and the repayments would be made from future collections of the compensation cess.
- In the second option, the entire shortfall of Rs 2.35 lakh crore could be borrowed from the market and the states would have to bear the interest costs, but the repayments would be adjusted against future collections of the cess.
- 10 states have rejected both the options and have stated that it is the Centre’s responsibility to compensate the states, and therefore, it should borrow.
Commitment of the Centre
- The minutes of the 7th and 8th GST Council meeting show that most of the states wanted the Centre to commit on paying compensation from the Consolidated Fund of India (CFI).
- On that demand the Union Finance Minister had stated that in case the amount in the GST compensation fund falls short of the compensation payable in any bi-monthly period, the GST Council shall decide the mode of raising additional resources including borrowing from the market which could be repaid by the collection of cess in the sixth year or further subsequent years.
- Thus, there was a clear commitment of the Centre on the issue of compensation and the method of recouping the loss.
Impact on the Centre-State relations
- The payment of compensation has plunged the Union-state relationship to a new low.
- First, not recognising the Centre’s commitment will make states wary of any future reforms involving an agreement with the Centre.
- Second, giving selective press statements to pressurise the states into accepting one or the other option does not infuse confidence.
- Third, there was a statement by the Union finance ministry officials that the GST Council does not have jurisdiction over-borrowing and borrowing is an individual state and Centre’s decision under Article 293 of the Constitution.
- If so, why were the two borrowing options presented to the states in the meeting of the Council?
Way forward
- It is the Centre’s commitment to find the compensation mechanism and borrowing is one of the options — that must be discussed in the Council.
- Furthermore, if the commitment of the Centre is recognised as admitted by the finance minister in the 7th GST council meeting, the Centre should take the responsibility to borrow.
- Both interest payments and repayment of the principal liability can be met from future collections from the cess.
Conclusion
This issue is of immense significance for the future of Centre-state relations. But pressuring states on the basis of political strength will have adverse consequences for the country’s federal structure.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: LTRO, Bonds
Mains level: Paper 30- Measures by the RBI to assure the Government bond holders
The article highlights the measures taken by the RBI in the recent MPC meeting to assure the buyers of the Government bonds and ensuring the policy rate transmission.
Dealing with the rate transmission issue and why it matters
- The gap between the repo rate and the average lending rate of banks is at a record high.
- So, the RBI and the MPC focused on improving rate transmission.
- This gap can be broken up into two parts:
- The first is the gap between the RBI-set repo rate and the rate at which the government of India borrows (the GSec yield).
- It is also called the “term premium” can be influenced by the RBI’s actions.
- The second is the gap between the GSec yield and the rate at which individuals or private firms borrow.
- This gap reflects risk aversion in the financial system and a lack of capacity.
- The RBI has avoided directly influencing the term premium, perhaps to maintain its credibility and independence, staying clear of accusations that it is financing the government’s fiscal deficit.
- However, unless the rate at which the government borrows comes down borrowing costs for the whole economy will stay elevated.
Challenge of Balance-of-Payment surplus (i.e. excess dollars)
- Over the past few months, the country’s foreign currency reserves have been growing at an unprecedented rapid pace.
- This means that India is getting far more dollars than it needs. Three factors are responsible for this.
- 1) Some short-term factors responsible are weak imports and a faster normalisation of exports.
- 2) There have also been structural shifts in India’s economic policy which point to a persistent BoP surplus.
- In addition to low energy prices, policies supporting Atmanirbhar Bharat mean lower imports and the push towards making India a participant in global value chains mean higher exports.
- 3) At the same time, India’s capital account is being opened up: The special-category government of India bonds, for example.
Why BoP surplus is opportunity
- When the excess dollar inflows turn into a deluge, as they have over the past six months, the supply of rupees in the domestic economy also becomes excessive.
- If the RBI can direct this surplus into government bonds, it can maintain its independence and credibility, and at the same time achieve its target of rate transmission.
Measures by the RBI to assure the bond market
- The buyers of government bonds need to feel reassured of not getting hurt by the volatility in bond prices.
- When bond prices rise, the yields fall, and vice versa.
- Banks parking trillions of rupees with the RBI at 3.35 per cent overnight would earn nearly 6 per cent if they bought government bonds.
- That they did not was because they were afraid of the bond prices falling, which would offset the gains from higher rates.
- The increase in the Hold-To-Maturity limits by the RBI by one year to March 2022, has assured the banks that they need not fear booking interim losses if bond prices are volatile.
- The announcement that the RBI would purchase state and central government bonds on the market (even if in small sizes) would provide further comfort.
- The change in assessment of inflation should help buyers of government bonds take the risk.
- Banks or other bond investors that refrained from purchasing government bonds because they felt the RBI would increase interest rates at some point to comply with its legal mandate, would be reassured by this clear communication.
- The targeted refinancing operations (TLTRO) should help bring down borrowing rates in the targeted industries.
Conclusion
Economic challenges may persist for the foreseeable future. The economic scars of the last six months are likely to take time to heal. The RBI and the MPC, which have been proactive, creative and accommodative so far, may have to stay so for a while longer.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: MSP. SAP
Mains level: Paper 3- Issues with the MSP regime
The author analyses the inefficiencies in the MSP regime while comparing it with the sugar sector and the milk sector. The recent agri-reform in the opinion of the author could help to make the Indian agriculture more efficient.
MSP system Vs. Market-driven system
- MSP regime was the creation of the era of scarcity in the mid-1960s.
- Indian agriculture has, since then, turned the corner from scarcity to surplus.
- In a surplus economy, unless we make agriculture demand-driven, the MSP route can spell financial disaster.
- This transition is about changing the pricing mix — how much of it should be state-supported and how much market-driven.
- The new laws are trying to increase the relative role of markets without dismantling the MSP system.
- Currently, no system is perfect, be it the one based on MSP or that led by the markets, but the MSP system is much more costly and inefficient.
- The market-led system will be more sustainable provided we can “get the markets right”.
Issues with the MSP
- A perusal of the MSP dominated system of rice and wheat shows that the stocks with the government are way above the buffer stock norms.
- The economic cost (to FCI) of procured rice comes to about Rs 37/kg and that of wheat is around Rs 27/kg.
- No wonder, market prices of rice and wheat are much lower than the economic cost incurred by the FCI.
- So, grain stocks with the FCI cannot be exported without a subsidy[i.e. export below the cost], which invites WTO’s objections.
- The FCI’s burden is touching Rs 3 lakh crore which is not reflected in the Central budget as the FCI is asked to borrow more and more.
- The FCI can reduce costs if it uses policy instruments like “put options”.
2 Lessons: from sugarcane and milk pricing
1) Populism resulted in making sugar industry globally non-competitive
- In the case of sugarcane, the government announces a “fair and remunerative price” (FRP) [not MSP]to be paid by sugar factories [not paid by the Government].
- While some states like Uttar Pradesh announces its own “state advised price” (SAP).
- The sheer populism of SAP has resulted in cane arrears amounting to more than Rs 8,000 crore, with large surpluses of sugar that can’t be exported.
- This sector has, consequently, become globally non-competitive.
- Unless sugarcane pricing follows the C Rangarajan Committee’s recommendations the problems of the sugar sector will not go away.
2) Success story of milk sector
- In the case of milk co-operatives, pricing is done by the company in consultation with milk federations.
- It is more in the nature of a contract price.
- It competes with private companies, be it Nestle, Hatsun or Schreiber Dynamix dairies.
- The milk sector has been growing at a rate two to three times higher than rice, wheat and sugarcane.
- Today, India is the largest producer of milk — 187 million tonnes annually.
So, how the recent reforms will help the farmers
- As a result of changes in farm laws in the next three to five years companies will be encouraged to build efficient supply lines somewhat on the lines of milk.
- These supply lines — be it with farmers producer organisations (FPOs) or through aggregators — will, of course, be created in states where these companies find the right investment climate.
- These companies will help raise productivity, similar to what has happened in the poultry sector.
- Milk and poultry don’t have MSP and farmers do not have to go through the mandi system paying high commissions, market fees and cess.
Conclusion
The pricing system has its limits in raising farmers’ incomes. More sustainable solutions lie in augmenting productivity, diversifying to high-value crops, and shifting people out of agriculture to high productivity jobs elsewhere, the recent reforms are the steps in this direction.
Back2Basic: What is MSP
- Minimum Support Price (MSP) is a form of market intervention by the Government of India to insure agricultural producers against any sharp fall in farm prices.
- The minimum support prices are announced by the Government of India at the beginning of the sowing season for certain crops on the basis of the recommendations of the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP).
- The minimum support prices are a guarantee price for their produce from the Government.
- The major objectives are to support the farmers from distress sales and to procure food grains for public distribution.
- In case the market price for the commodity falls below the announced minimum price due to bumper production and glut in the market, government agencies purchase the entire quantity offered by the farmers at the announced minimum price.
What are ‘put options’
- Put options give holders of the option the right, but not the obligation, to sell a specified amount of an underlying security at a specified price within a specified time frame.
- Put options are available on a wide range of assets, including stocks, indexes, commodities, and currencies.
- Put option prices are impacted by changes in the price of the underlying asset, the option strike price, time decay, interest rates, and volatility.
- Put options increase in value as the underlying asset falls in price, as volatility of the underlying asset price increases, and as interest rates decline.
- They lose value as the underlying asset increases in price, as volatility of the underlying asset price decreases, as interest rates rise, and as the time to expiration nears.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: RTI
Mains level: Pendency of RTI cases

Fifteen years after the Right to Information (RTI) Act came into force; more than 2.2 lakh cases are pending at the Central and State Information Commissions, which are the final courts of appeal under the transparency law.
Try this question:
Q.“RTI is a tool for empowering ordinary citizens and changing the culture of governance in India.” Discuss.
Right to Information
- RTI is an act of the parliament which sets out the rules and procedures regarding citizens’ right to information.
- It replaced the former Freedom of Information Act, 2002.
- Under the provisions of RTI Act, any citizen of India may request information from a “public authority” (a body of Government or “instrumentality of State”) which is required to reply expeditiously or within 30.
- In case of the matter involving a petitioner’s life and liberty, the information has to be provided within 48 hours.
- The Act also requires every public authority to computerize their records for wide dissemination and to proactively publish certain categories of information so that the citizens need minimum recourse to request for information formally.
Governing of RTI
The Right to information in India is governed by two major bodies:
- Central Information Commission (CIC) – Chief Information commissioner who heads all the central departments and ministries- with their own public information officers (PIO)s. CICs are directly under the President of India.
- State Information Commissions (SIC)– State Public Information Officers or SPIOs head over all the state department and ministries. The SPIO office is directly under the corresponding State Governor.
- State and CIC are independent bodies and CIC has no jurisdiction over the SIC.
Fundamental status of RTI
- RTI is a fundamental right for every citizen of India.
- Since RTI, is implicit in the Right to Freedom of Speech and Expression under Article 19 of the Indian Constitution, it is an implied fundamental right.
Limitation to RTI
- Information disclosure in India is restricted by the Official Secrets Act 1923 and various other special laws, which the new RTI Act relaxes.
- RTI has proven to be very useful but is also counteracted by the Whistle Blowers Protection Act, 2011.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: FELUDA, CAS9, CRISPR
Mains level: CRISPR technology

Union Health Ministry will soon roll out the FELUDA paper strip test for SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis.
Try this PYQ:
Q.What is Cas9 protein that is often mentioned in news?
(a) A molecular scissors used in targeted gene editing
(b) A biosensor used in the accurate detection of pathogens in patients
(c) A gene that makes plants pest-resistant
(d) A herbicidal substance synthesized in genetically modified crops
FELUDA test
- FELUDA is the acronym for FNCAS9 Editor Linked Uniform Detection Assay.
- It uses indigenously developed CRISPR gene-editing technology to identify and target the genetic material of SARS-CoV2, the virus that causes Covid-19.
- According to CSIR, the test matches accuracy levels of RT-PCR tests, considered the gold standard in the diagnosis of Covid-19, has a quicker turnaround time and requires less expensive equipment.
- It is also the world’s first diagnostic test to deploy a specially adapted Cas9 protein to successfully detect the virus.
How does it work?
- The Feluda test is similar to a pregnancy test strip that will just change colour upon detection of the virus and can be used in a simple pathological lab.
- The Cas9 protein is bar-coded to interact with the SARS-CoV2 sequence in the patient’s genetic material.
- The Cas9-SARS-CoV2 complex is then put on the paper strip, where using two lines (one control, one test) makes it possible to determine if the test sample was infected.
Back2Basics: CRISPR technology
- CRISPR is a short form for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats.
- It is a gene-editing technology and finds its use in correcting genetic defects and treating and preventing the spread of diseases.
- The technology can detect specific sequences of DNA within a gene and uses an enzyme functioning as molecular scissors to snip it.
- It also allows researchers to easily alter DNA sequences and modify gene function.
- Moreover, the technology can also be configured for detection of multiple other pathogens in the future.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Blue Flag Beaches
Mains level: Not Much

Eight Indian beaches have got an International Blue Flag Certification, said Union Minister of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
Note the beaches and their respective states. They can be asked in the ”match the pairs” type questions.
Citation needed: *As of now, there are 13 Blue flag awarded beaches in India a/c to wikipedia. But Blue Flag website would provide exact figures (which yet to update the official numbers).
Which are these beaches?
- Shivrajpur (Dwarka-Gujarat)
- Ghoghla (Diu)
- Kasarkod [NOT Kasargod which is in Kerala] and Padubidri (Karnataka)
- Kappad (Kerala)
- Rushikonda (AP)
- Golden Beach (Odisha) and
- Radhanagar (A&N Islands)
Blue Flag Beaches
- The ‘Blue Flag’ beach is an ‘eco-tourism model’ and marks out beaches as providing tourists and beachgoers clean and hygienic bathing water, facilities/amenities, a safe and healthy environment, and sustainable development of the area.
- The certification is accorded by the Denmark-based Foundation for Environment Education.
- It started in France in 1985 and has been implemented in Europe since 1987, and in areas outside Europe since 2001 when South Africa joined.
- It has 33 stringent criteria under four major heads for the beaches, that is, (i) Environmental Education and Information (ii) Bathing Water Quality (iii) Environment Management and Conservation and (iv) Safety and Services.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Skal International Asia Area (SIAA)
Mains level: NA
The UT of Jammu and Kashmir has won the bid to host the 50th annual Skal International Asia Area (SIAA) Congress in 2021 during the annual general meeting recently against four other cities.
Note: Skal International is not an affiliate of the United Nations. This is where a prelims question can pull a nerve.
Skal International
- Skal International is a professional organization of tourism leaders around the world, promoting global tourism and friendship.
- It is a Spain-based tourism body with 15,000 members and 150 chapters across the world.
- The word Skal comes from Scandinavia and has a long tradition. The “Skal” is a bowl containing a welcome drink that is offered to visitors when entering a home.
- Its members, the industry’s managers and executives meet at local, national, regional and international levels to discuss and pursue topics of common interest.
- It is the only international group uniting all branches of the travel and tourism industry.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Raychaudhuri Equation
Mains level: Not Much
The Raychaudhuri Equation in General Relativity, derived by Raychaudhuri is in the spotlight after 2020 Physics Nobel was awarded to Penrose for throwing light on Black Holes.
Try this MCQ:
Q.The Raychaudhuri Equation is sometimes seen in news is related to:
Artificial Intelligence/Cloud Computing/Quantum Mechanics/Space Sciences
What is Raychaudhuri Equation?
- Raychaudhuri (1923–2005) was an Indian physicist, known for his research in general relativity and cosmology.
- In general relativity, the Raychaudhuri equation is a fundamental result describing the motion of nearby bits of matter.
- It was discovered independently by the Indian physicist Amal Kumar Raychaudhuri and the Soviet physicist Lev Landau.
- The equation offers a simple and general validation of our intuitive expectation that gravitation should be a universal attractive force between any two bits of mass-energy in general relativity, as it is in Newton’s theory of gravitation.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Aenigmachanna Gollum
Mains level: NA

Scientists have discovered a new family of bony fish from the Western Ghats and named it Aenigmachannidae.
A stand-alone species being mentioned in the news for the first time (and that too from Southern India) find their way into the prelims. Make special note here. Usually, note the species and its habitat location (IUCN status if available), in the purview of a generic prelims question.
Aenigmachannidae
- Aenigmachanna Gollum has a surprisingly large number of primitive characters, and detailed molecular phylogenetic analyses including of its Mitochondrial DNA suggested an ancient separation from Channidae.
- Many such species were earlier found in the aquifers of Kerala.
- Many of these species are blind, pigment-less, and have peculiar morphological characters that are otherwise not seen in species occurring in surface waters.
Significance of the discovery
- The presence of two unique endemic families of freshwater fish in a small region like Kerala is unparalleled and indicates the exceptional diversity and endemicity of fishes in this part of the world.
- The members of Aenigmachannidae are “living fossils” and comprise an ancient Gondwanan lineage that survived the break-up of the supercontinent and the northward drift of the Indian subcontinent.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bharatmala Project
Mains level: Highways connectivity in India
A total of 322 projects in a length of 12,413 km have been awarded under Bharatmala Pariyojana. Further, 2921 Km has been constructed under the Project till the date.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Consider the following pairs:
National Highway: Cities connected
- NH 4: Chennai and Hyderabad
- NH 6: Mumbai and Kolkata
- NH 15: Ahmedabad and Jodhpur
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) None
Bharatmala Pariyojana
- It is a centrally-sponsored and funded the Road and Highways project.
- It is an umbrella program for the highways sector that focuses on optimizing the efficiency of freight and passenger movement across the country by bridging critical infrastructure.
- The total investment for 83,677 km committed new highways is estimated at ₹5.35 lakh crore making it the single largest outlay for a government road construction scheme.
- It works for the development of Economic Corridors, Inter Corridors and Feeder Routes, National Corridor Efficiency Improvement, Border and International connectivity roads, Coastal and Port connectivity roads and Green-field expressways.
- The ambitious umbrella programme has subsumed all existing Highway Projects including the flagship National Highways Development Project (NHDP), launched in 1998.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: LTRO
Mains level: Paper 3- Stance of MPC amid rising inflation
The article analyses the implications of the recently concluded MPC meeting and predicts the trends for the future.
Highlights of the MPC meeting
- In the October meeting of the monetary policy committee (MPC), repo rate were kept unchanged at 4%, with a continuation of an accommodative stance.
- It chose to ignore elevated levels of CPI inflation as transitory and maintaining focus on supporting growth.
- It appears that the MPC would maintain a status quo on rates through this fiscal year.
- The scope for further easing is anyways limited to 0.50%, as any more easing may affect household financial savings and endanger financial stability.
Ensuring the rate transmission
- With unchanged repo rates, the focus of the liquidity measures announced by the RBI is to further improve transmission of previous rate cuts across a spectrum of market rates and other instruments.
- The RBI Governor assured market participants that the large supply of government bonds in the second half along with a likely pick-up in credit demand, would be accommodated through open market purchases of government bonds.
Reducing the cost of borrowing
- The RBI may have to buy bonds worth ₹1,000 to 1,500 billion in these operations over 2HFY21 keeping pressure on yields [which affects interest rates].
- In a related move, to reduce the cost of borrowings for state governments, the RBI for the first time will buy state government bonds, as a special case for this year.
Other measures
- The extension of enhanced Held to Maturity (HTM) limit of banks on their government bonds portfolio to March 2022.
- A new on-tap targeted LTRO window was announced, for banks to borrow up to ₹1,000 billion from the RBI at a floating rate linked to the repo rate, and invest in corporate paper issued by specific sectors and to provide loans to them.
- In effect, the aim of the central bank is to ensure that lower policy rates determined by the macro-economic fundamentals, are reflected in lower cost of borrowings for the Centre, states and corporates.
Containing inflation
- Inflation outlook for this fiscal and projections for next year indicate that CPI inflation would ease, from an average of 6.8% in Q2 to 4.5% in Q4 and 4.1% by Q4FY22.
- Headline inflation is expected to fall, as supply conditions normalize with progressive unlocking and another year of bumper farm output helps pull down food inflation.
- Higher fuel taxes and import duties are expected to provide an upward push though.
- Effective supply management will therefore be crucial in controlling food inflation and ensuring that it does not turn persistent and feeds into non-food inflation.
Conclusion
- The role of monetary policy in the is limited and the RBI focus will remain on improving transmission of policy signals through banking, bond and credit market channels.
Back2Basics: LTRO
- Long-Term Repo Operation (LTRO) was introduced by the Reserve Bank in February, 2020.
- Through this policy, the central bank would provide liquidity support to commercial banks for a period of 1 to 3 years at the current repo rate, and would accept government securities as collateral in return.
- This is in contrast to the other measures it was providing such as Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) and Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) which provide cash to banks for a period of 1 to 28 days only.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Definition of urban area
Mains level: Paper 2- Need for new definition of urban area
The article the need for liberal and realistic definition of the ‘urban’ area in the next Census and mention the implications of such change.
2 ways to define urban areas
1) Statutory town
- These towns are defined by state governments and place India’s urbanisation rate at 26.7%.
- A statutory town includes all places with a municipality, corporation, cantonment board or notified town area committee.
2) Census-based criteria
- Census adopts three criteria to define what is urban.
- The three criteria are:
- i) a minimum population of 5,000;
- ii) at least 75% of the male main working population engaged in non-agricultural pursuits, and
- iii) a density of population of at least 400 persons per sq km
- This, coupled with statutory towns, pegs India’s urbanisation rate at 31%.
- Total number of towns (state and census) stands at 7,933, together constituting a 377-mn population.
Why there is a need for changing the definition of ‘urban’
- There is growing evidence—mostly from satellite imagery—that India is way more urban than the 2011 Census estimate.
- This is quite plausible because there is a large sum of money allocated for rural development, and it is in the interest of state governments to under-represent urbanisation.
- Besides, the Census’s stringent definition was first carved out in 1961 which do not reflect the realities of the 21st century.
- India won’t be alone in changing these definitions for Census 2021.
- Many countries, such as China, Iran, the UK, among others, have changed the definition of ‘urban’ from one census to another.
Getting the right picture of urbanisation
- A more liberal and realistic definition in the upcoming census will present the actual picture of urbanisation.
- For instance, if we just use the population density criteria like 37 other countries, with the 400 people per sq km threshold, we will add around 500 mn people to the urban share of the population.
- This pegs the urbanisation rate at over 70%!
What will be its implications?
- First, the budgetary allocation will reflect the reality and scales will balance between rural and urban areas.
- Second, the urban areas will not be governed through rural governance structures of Panchayati Raj Institutions.
- Third basic urban infrastructure like sewerage networks, fire services, building regulations, high-density housing, transit-oriented development, piped drinking water supply.
- Fourth, these newly defined urban areas could act as a new source of revenue for funding local infrastructure development.
- This would ease pressure on state finances.
- Lastly, the rethink of urban definition would have an impact on the regional and national economy.
- These newly defined urban areas will open them to new infrastructure such as railway lines, discom services, highway connectivity, creation of higher education institutes which will together increase the connectivity and resource capability at the local level.
- This will not only boost the local economy but also ease pressure on bigger cities and help in cluster level development.
Conclusion
A rethink of urban definition in Census 2021, particularly with some degrowth in urban areas due to Covid, will bode well for India for coming decades in more ways than one.
Source:-
https://www.financialexpress.com/opinion/redefining-cities-a-new-urban-consensus/2102154/
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Various GHGs
Mains level: Hazards of N2O pollution
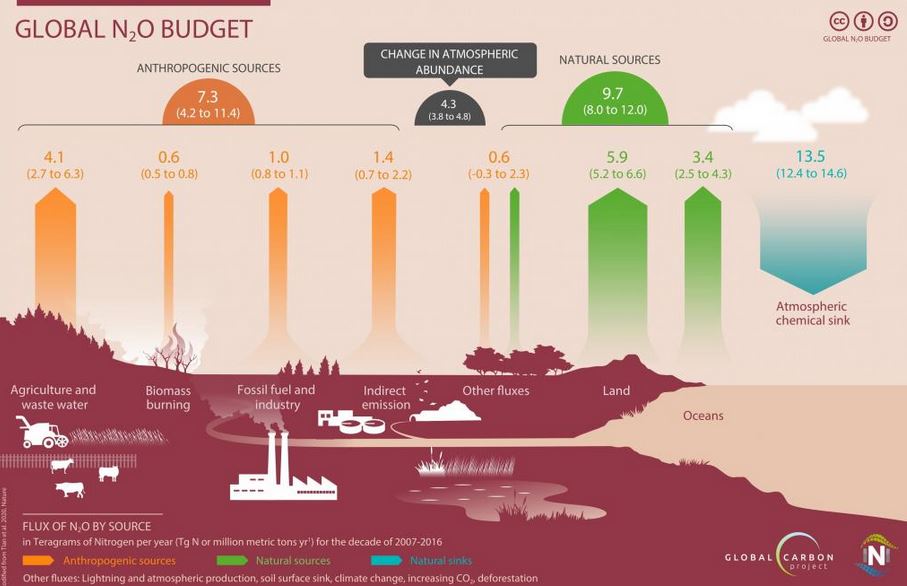
Human emissions of nitrous oxide (N2O) — a greenhouse gas 300 times more potent than carbon dioxide (CO2) — increased by 30 per cent between 1980 and 2016.
Observe the above image carefully and try to find out the major contributor of nitrous oxide emission in the Global N2O Budget.
What is Nitrous oxide?
- Nitrous oxide is a dangerous gas for the sustainable existence of humans on Earth.
- It has the third-highest concentration — after CO2 and methane — in our atmosphere among greenhouse gases responsible for global warming.
- N2O can live in the atmosphere for up to 125 years.
- Most N2O emissions have come from emerging countries like India, China and Brazil.
About the research
- Nitrous oxide global concentration levels have increased from 270 parts per billion (ppb) in 1750 to 331 ppb in 2018 — a jump of 20 per cent.
- The growth has been the quickest in the past five decades because of human emissions.
- The research was conducted through an international collaboration between the International Nitrogen Initiative (INI) and the Global Carbon Project of Future Earth, a partner of the World Climate Research Programme.
Why N2O matters?
- N2O is also the only remaining threat to the ozone layer, for it accumulates in the atmosphere over a long period of time, just like CO2.
- The increase in its emissions means that the climatic burden on the atmosphere is increasing from non-carbon sources as well, while the major focus of global climate change negotiations is currently centred on carbon.
- A major proportion of the N2O emissions in the last four decades came from the agricultural sector, mainly because of the use of nitrogen-based fertilizers.
- The growing demand for food and feed for animals will further increase global nitrous oxide emissions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now








