Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SWAMIH Fund
Mains level: Housing for all
Union Minister for Finance has informed that so far Rs 8767 crore has been approved for 81 projects under Special Window for Affordable and Mid-Income Housing (SWAMIH) Investment Fund I.
Try this MCQ:
Q.The SWAMIH Fund recently seen in news is related to:
(a) Higher Education (b) MSMEs (c) Housing (d) Highways
SWAMIH Fund
- In November 2019, the Finance Minister had cleared a proposal to set up a ‘Special Window’ called SWAMIH in to provide priority debt financing for the completion of stalled housing projects.
- SWAMIH Investment Fund has been formed to complete the construction of stalled, brownfield, RERA registered residential developments that are in the affordable housing / mid-income category.
- The Sponsor of the Fund is the Secretary, Department of Economic Affairs, Ministry of Finance, and Government of India on behalf of the Government of India.
- The fund is set up as a Category-II AIF (Alternate Investment Fund) debt fund registered with SEBI and would be professionally run.
Why need such funds?
- Several real estate projects have suffered due to a combined effect of two changes in the real estate sector.
- On one hand, incremental launches and slow sales have increased unsold inventory in each project.
- While the effect has then got compounded by the fact that consumer preference is now towards completed projects rather than under-construction projects.
- This preference has developed as consumers are largely avoiding taking project completion risk and instead are more inclined to completed projects.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: IndSAT
Mains level: Study in India Program

The Ministry of HRD conducted the first-ever Indian Scholastic Assessment (IND-SAT) Test 2020 under its ‘Study in India’ programme.
Try this MCQ:
Q.The INDSAT recently seen in news is a:
a) Free-to-air educational TV channels for school education
b) A satellite for educational purposes
c) IMD weather forecasting system
d) Online examination for foreign students in India
INDSAT Exam
- The Indian Scholastic Assessment or IND-SAT is a standardized online proctored test for students seeking scholarships with Study in India (SII).
- This exam is to gauge the capability and tenacity of students applying to study in India.
- The scores will serve as a criterion to shortlist the meritorious students for the allocation of scholarships for undergraduate as well as postgraduate programmes under ‘Study in India’ programme.
- The exam is conducted in the proctored internet mode by the National Testing Agency.
What makes it special?
- Nearly five thousand candidates from Nepal, Ethiopia, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Uganda, Tanzania, Rwanda, Sri-Lanka, Kenya, Zambia, Indonesia and Mauritius appeared for the exam.
About Study in India
- The Study in India is a programme of MHRD under which foreign students come to study in 116 select higher education institutions in India for undergraduate and postgraduate programmes.
- The selection of the students is based on their merit in class 12 / school-leaving exam.
- About top 2000 students are given scholarships, while some others are given fee discounts by the institutions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 2-Pandemic and SDGs
Context
- As lockdown eases, return to business as usual is unimaginable in Asia and Pacific which was already off track to meet the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Efforts to respond to the pandemic have revealed how many people in our societies live precariously close to poverty and hunger.
Progress towards SDGs in pandemic
- The SDGs can serve as a beacon in these turbulent times.
- SDGs are a commitment to eradicate poverty and achieve sustainable development, globally, by 2030.
- The pandemic has exposed fragility and systemic gaps in many key systems.
- Countries have used workable strategies during pandemic to accelerate progress related to development goals and strengthen resilience.
- Countries have taken steps to extend universal health care systems and strengthen social protection systems.
- Accurate and regular data have been key to such efforts.
- Innovating to help the most disadvantaged access financing and small and medium-sized enterprise credits have also been vital.
- Several countries have taken comprehensive approaches to various forms of discrimination, particularly related to gender and gender-based violence.
- Partnerships with the private sector and financing institutions, have played a critical role in fostering creative solutions.
Focus on green recovery in Asia-Pacific countries
- Countries in Asia and the Pacific are developing ambitious new strategies for green recovery and inclusive approaches to development.
- South Korea recently announced a New Deal based on two central pillars: digitisation and decarbonisation.
- Many countries in the Pacific are focusing on “blue recovery,” which promote more sustainable approaches to fisheries management.
- India recently announced operating the largest solar power plant in the region.
- China is creating more jobs in the renewable energy sector than in fossil fuel industries.
Suggestions for policymaking
- We need a revolution in policy mindset and practice- following are part of the transformations needed.
- 1) Inclusive and accountable governance systems.
- 2) Adaptive institutions with resilience to future shocks.
- 3) Universal social protection and health insurance.
- 4) Stronger digital infrastructure.
Consider the question “Pandemic has highlighted the fragility of our systems. But it also emphasised the need to strive to achieve the SDGs. Comment.”
Conclusion
With the onslaught of pandemic disrupting us, we should base our recovery and progress trajectory firmly towards achieving SDGs.
Back2Basics: SDGs
Sustainable Development Goals and India
- The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), otherwise known as the Global Goals, are a universal call to action to end poverty, protect the planet and ensure that all people enjoy peace and prosperity.
- The 17 Goals build on the successes of the Millennium Development Goals, while including new areas such as climate change, economic inequality, innovation, sustainable consumption, peace and justice, among other priorities.
- The goals are interconnected – often the key to success on one will involve tackling issues more commonly associated with another.
- The SDGs work in the spirit of partnership and pragmatism to make the right choices now to improve life, in a sustainable way, for future generations.
- They provide clear guidelines and targets for all countries to adopt in accordance with their own priorities and the environmental challenges of the world at large.
The SDGs are an inclusive agenda. They tackle the root causes of poverty and unite us together to make a positive change for both people and planet. “Poverty eradication is at the heart of the 2030 Agenda, and so is the commitment to leave no-one behind,” UNDP Administrator Achim Steiner said. “The Agenda offers a unique opportunity to put the whole world on a more prosperous and sustainable development path. In many ways, it reflects what UNDP was created for.”
The Goals

Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Contempt of court
Mains level: Paper 2- Contempt of court and issues
The article discusses the issues that law for contempt of the court give rise to. The practice has monarchical origins. Its continuance conflicts with the ideals of democracy.
Objective
- The objective for contempt is stated to be to safeguard the interests of the public if the authority of the Court is denigrated and public confidence in the administration of justice is weakened or eroded.
- Need to “respect the authority and dignity of the court” has monarchical origins.
Issues in India
- With adjudicatory role having been handed over to judges, showing extreme deference to judges does not sit well with the idea of a democracy.
- But the definition of criminal contempt in India is extremely wide, and can be easily invoked.
- Justice V.R. Krishna Iyer famously termed the law of contempt as having a vague and wandering jurisdiction, contempt law may unwittingly trample upon civil liberties.
- Criminal contempt is completely asynchronous with our democratic system which recognises freedom of speech and expression as a fundamental right.
- Excessively loose use of the test of ‘loss of public confidence’, combined with a liberal exercise of suo motu powers, can be dangerous.
- It can amount to the Court signalling that it will not suffer any kind of critical commentary about the institution at all.
Lessons from other democracies
- Contempt has practically become obsolete in foreign democracies.
- Canada ties its test for contempt to real, substantial and immediate dangers to the administration.
- American courts also no longer use the law of contempt in response to comments on judges or legal matters.
- In England, too, the legal position has evolved.
Approach of Indian judiciary
- Truth and good faith were not recognised as valid defences until 2006, when the Contempt of Courts Act was amended.
- Indian courts have not been inclined to display the same maturity and unruffled spirit as their peers in the other democracies.
Consider the question “A law for criminal contempt is completely asynchronous with our democratic system which recognises freedom of speech and expression as a fundamental right. Examine the issue in India context and suggest the major to strike the balance.”
Conclusion
Besides needing to revisit the need for a law on criminal contempt, even the test for contempt needs to be evaluated. If such a test ought to exist at all, it should be whether the contemptuous remarks in question actually obstruct the Court from functioning. It should not be allowed to be used as a means to prevent any and all criticism of an institution.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 3- Information war against India
Information war waged against India from across the border needs consideration. Three factors have triggered the war in the realm of information. This article examines the way in which it is perpetrated.
Factors
- Following three triggers are responsible for Pakistan’s information war.
- 1) The Balakot attack of February 2019.
- Balakot demolished Pakistan’s presumed nuclear equivalence that guaranteed that India would not retaliate against terrorist attacks
- 2) The return of the BJP government in the May 2019 elections-which signalled that India would follow aggressive muscular policy.
- 3) The August 2019 revision of Article 370.
- The Article 370 decision demolished the centrepiece of Pakistan’s nationalism build on Kashmir.
- The move also raised apprehensions about India’s plans for Pakistan Occupied Jammu and Kashmir.
- These developments have forced it to shift the emphasis of its anti-India strategy from fomenting terrorism supported by an information war component to an information war supported by terrorism.
How the information war is waged
- The ISI and the Inter-Services Public Relations (ISPR) two main instruments for the furtherance of this policy.
- The ISPR has, over the years, recruited thousands of youth, trained them in the mechanics of social media and used them to project anti-India themes.
- The core Pakistani objective is to demolish “Brand India” by attacking its key components — an inclusive and secular society, democratic polity, decisive government, a developing economic powerhouse and strong foreign policy.
- The expectation is that such a strategy would adversely impact India’s secular and democratic credentials, scare foreign investment and lead to questions about its international image.
- The key platforms for this strategy are Twitter, WhatsApp, YouTube and Facebook.
- A large number of fake social media accounts, especially on Twitter, have been created.
- The use of handles with phoney Middle Eastern identities is the latest addition to its bag of tricks.
Themes of information war
- Internal developments and dissent in India have been manipulated, packaged and used to develop a narrative damaging India’s social fabric.
- On J&K, the key themes are: Kashmir is a “disputed territory” awaiting solution under the UN resolutions; India needs to talk to Pakistan to resolve the issue and since India refuses to talk, there must be international intervention, the Indian Army is violating the human rights of Kashmiris.
Consider the question “Internet has made waging information war easier. Examine the threat posed by the information war to Indian polity. Suggest the measures to contain the threat emanating from the information war.”
Conclusion
Even though the Indian polity is strong, such persistent venomous attacks can temporarily damage our social fabric. We must not allow ourselves, wittingly or unwittingly, to fall prey to such machinations to polarise society, even temporarily.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Discretionary powers of Governor
Mains level: Speaker vs Governor Tussle
A Constitution Bench judgment of the Supreme Court has held that a Governor is bound to convene a meeting of the Assembly for a floor test on the recommendation of the Cabinet.
Try this question for mains:
Q. “Time and again, the courts have spoken out against the Governor acting in the capacity of an all-pervading super-constitutional authority.” Analyse.
Resolving the deadlock
- The judgment is significant in the present deadlock between the CM and the Governor over the summoning of an Assembly session for a floor test.
- The Governor can summon, prorogue and dissolve the House only on the aid and advice of the Council of Ministers with the Chief Minister as the head.
The Nabam Rebia Case
- The five-judge Constitution Bench judgment of the Supreme Court cited the Nabam Rebia versus Deputy Speaker on July 13, 2016.
- It held that a Governor cannot employ his ‘discretion’, and should strictly abide by the “aid and advice” of the Cabinet to summon the House.
- It held that the discretionary power of the Governor is extremely limited and entirely liable to judicial review.
- The judgment was a consequence of then Arunachal Pradesh Governor J.P. Rajkhowa’s decision to advance the Assembly session, a move which led to unrest in the State and resulted in the President’s rule.
- The Constitution Bench held Mr. Rajkhowa’s decision to be a violation of the Constitution.
Governor’s discretion: Limited to specified areas
- The Supreme Court highlighted that Article 163 of the Constitution does not give the Governor a “general discretionary power to act against or without the advice of his Council of Ministers.
- The court said the Governor’s discretionary powers are limited to specified areas like giving assent or withholding/referring a Bill to the President or appointment of a CM or dismissal of a government which has lost of confidence but refuses to quit, etc.
Back2Basics: Governor’s Discretionary Powers
The governor can use his/her discretionary powers:
- When no party gets a clear majority, the governor has the discretion to choose a candidate for the chief minister who will put together a majority coalition as soon as possible.
- He can impose president’s rule.
- He submits reports on his own to the president or on the direction of the president regarding the affairs of the state.
- He can withhold his assent to a bill and send it to the president for his approval.
- During emergency rule per Article 353, he can override the advice of the council of ministers if specifically permitted by the president.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Landfills
Mains level: Social and environmental threats posed by Landfills
The Ghazipur landfill site rises by nearly 10 metres a year and is expected to surpass the height of Qutub Minar and other vertical structures in the country.
Try this PYQ from CSP 2016:
Q.What can be the impact of excessive/inappropriate use of nitrogenous fertilizers in agriculture?
- Proliferation of nitrogen-fixing microorganisms in soil can occur.
- Increase in the acidity of soil can take place.
- Leaching of nitrate to the ground-water can occur.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
What are Landfills?
- A landfill site, also known as a tip, dump, rubbish dump, garbage dump, or dumping ground, is a site for the disposal of waste materials.
- Some landfill sites are also used for waste management purposes, such as temporary storage, consolidation and transfer, or for various stages of processing waste material, such as sorting, treatment, or recycling.
Threats posed by landfills
Landfills have the potential to cause a number of issues. Infrastructure disruption, such as damage to access roads by heavy vehicles, may occur amongst others.
1) Leachate
- When precipitation falls on open landfills, water percolates through the garbage and becomes contaminated with suspended and dissolved material, forming leachate.
- If this is not contained it can contaminate groundwater.
2) Decomposition gases
- Rotting food and other decaying organic waste create decomposition gases, especially CO2 and CH4 from aerobic and anaerobic decomposition, respectively.
- Both processes occur simultaneously in different parts of a landfill.
3) Other threats
- Poorly run landfills may become nuisances because of vectors such as rats and flies which can spread infectious diseases.
- The occurrence of such vectors can be mitigated through the use of daily cover.
- Other potential issues include wildlife disruption due to occupation of habitat and animal health disruption caused by consuming waste from landfills, dust, odour, noise pollution, and reduced local property values.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Seismic noise
Mains level: Seismic activity and thier monitoring
The seismic noise level has dropped by as much as 50 per cent between March and May due to lockdowns this year, according to researchers.
Ever heard of space-based monitoring of seismic activities? This topic creates a scope for potential prelims question…
What is Seismic Noise?
- Seismic noise refers to vibrations within the Earth, which are triggered by natural and man-made phenomena like earthquakes, volcanoes and bombs.
- Seismometers, specialised devices that record ground motions, also capture seismic noise.
- Everyday human activity — such as road traffic, manufacturing in factories, the sound produced by planes roaring overhead, or simply people walking down the street.
- The sound signals created by human beings are often referred to as anthropogenic seismic noise.
- Seismic noise acts almost like background sound for seismologists — it is the unwanted component of signals recorded by a seismometer.
Variations in noise levels
- The level of anthropogenic seismic noise recorded varies based on a number of factors.
- Highly-populated urban areas will generate more vibrations from human activity than less densely populated regions.
- Timing too plays an important role. The degree of seismic noise is found to be much lower during public holidays.
Why is this important to record this noise?
- Due to this, scientists will be able to spot weaker signals.
- Such small signals tell us about a geological fault making seismic hazard assessment more accurate.
- This means that scientists will have a better shot at monitoring a whole range of seismogenic behaviour, including the smallest earthquakes or the early signs of a volcanic eruption.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Kashmir Saffron
Mains level: Not Much

The J&K administration has issued the certificate of geographical indication (GI) registration for saffron grown in the Kashmir Valley.
Must read:
GI Tags in news for 2020 Prelims
All time GI tags in news
Kashmir saffron
- It is cultivated and harvested in the Karewa (highlands) in some regions of Kashmir, including Pulwama, Budgam, Kishtwar and Srinagar.
- It is a very precious and costly product. Iran is the largest producer of saffron and India is a close competitor.
- It rejuvenates health and is used in cosmetics and for medicinal purposes.
- It has been associated with traditional Kashmiri cuisine and represents the rich cultural heritage of the region.
- Saffron cultivation is believed to have been introduced in Kashmir by Central Asian immigrants around 1st Century BCE. In ancient Sanskrit literature, saffron is referred to as ‘bahukam’.
3 Types
The saffron available in Kashmir is of three types —
- ‘Lachha Saffron’, with stigmas just separated from the flowers and dried without further processing;
- ‘Mongra Saffron’, in which stigmas are detached from the flower, dried in the sun and processed traditionally; and
- ‘Guchhi Saffron’, which is the same as Lachha, except that the latter’s dried stigmas are packed loosely in air-tight containers while the former has stigmas joined together in a bundle tied with a cloth thread
Whats’ so special about Kashmir Saffron?
- The unique characteristics of Kashmir saffron are its longer and thicker stigmas, natural deep-red colour, high aroma, bitter flavour, chemical-free processing, and high quantity of crocin (colouring strength), safranal (flavour) and picrocrocin (bitterness).
- It is the only saffron in the world grown at an altitude of 1,600 m to 1,800 m AMSL (above mean sea level), which adds to its uniqueness and differentiates it from other saffron varieties available the world over.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ravines, Chambal River
Mains level: Features of badland topography
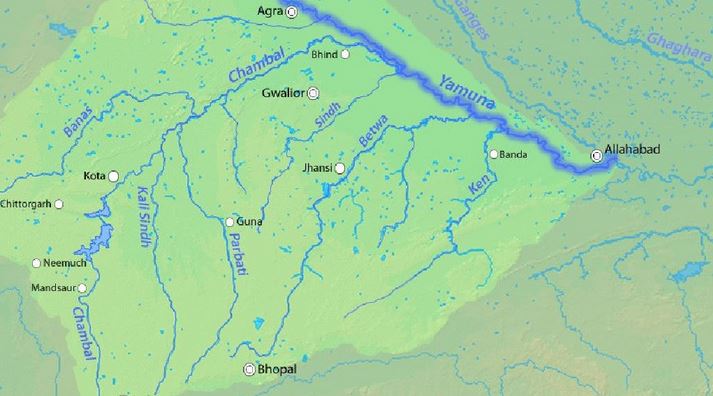
Union Minister of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare held a meeting with World Bank representatives to bring large Ravines of Gwalior–Chambal region under agriculture.
Try this question for mains:
Q.What is Badland Topography? Discuss the scope of their utilization as arable land in India.
What are Ravines?

- Badland topography is a major feature of the Chambal valley is characterized by an undulating floodplain, gullies and ravines.
- Ravines are a type of fluvial erosional feature and are formed as a result of constant vertical erosion by streams and rivers flowing over semi-arid and arid regions.
How are they formed?
- Researchers consider the regional climate as a major factor in the formation of ravines.
- Climate indeed plays a huge role by supplying the water in the form of rain or snow as well as providing the temperature variations.
- However, the ravines of Chambal are a bit difficult to be explained solely on climatic terms.
- The region through which the Chambal River flows does not receive enough rainfall to create ravines that are 60–80 m deep.
- Researchers have attributed neotectonic activities to the Chambal ravines genesis.
Other factors
- It is well known that rivers are full of energy and actively erode in their initial phases and progressively become passive as they attain their base levels.
- But sometimes, due to tectonic movements, the base level may be lowered further thus energizing the river and reactivating the erosion. This is known as River Rejuvenation.
- Moreover, wind erosion has also contributed to the formation of Chambal ravines.
Back2Basics: What are Badlands?
- Badlands are erosional landforms of highly dissected morphology that are created on soft bedrock in a variety of climate conditions.
- They develop in arid to semiarid areas where the bedrock is poorly cemented and rainfall is generally heavy and intermittent.
- The dry, granular surface material and light vegetation are swept from the slopes during showers, leaving the gullies bare.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Parliamentary vs presidential system
Mains level: Paper 2- Issues with the parliantary system of government
The article brings out the flaws in the parliamentary system of government in India and makes the case for the parliamentary system.
Problems with our parliamentary system
- Our parliamentary system has created a unique breed of legislator, largely unqualified to legislate.
- Those legislators has sought election only in order to wield executive power.
- It has produced governments dependent on a fickle legislative majority.
- Fickle majority leads the government to focus more on politics than on policy or performance.
- Current system has distorted the voting preferences of an electorate that knows which individuals it wants to vote for but not necessarily which parties.
- It has given rise to parties that are shifting alliances of selfish individual interests, not vehicles of coherent sets of ideas.
- It has forced governments to concentrate less on governing than on staying in office, and obliged them to cater to the lowest common denominator of their coalitions.
Problems with party system in India
- Parliamentary system, devised in Britain — is based on traditions which simply do not exist in India.
- The parties in England are clearly defined, each with a coherent set of policies and preferences that distinguish it from the next.
- In India, a party is all-too-often a label of convenience which a politician adopts and discards frequently.
- So, a politician changing a party is not treated as an unusual event in India.
- In the absence of a real party system, the voter chooses not between parties but between individuals.
- The candidates are usually chosen on the basis of their caste, their public image or other personal qualities.
- So, voters vote for a legislature not to legislate but in order to form the executive.
4 Problems with choosing executive from Parliament
- 1) It limits executive posts to those who are electable rather than to those who are able.
- Though he can bring some members in through the Rajya Sabha, but it too has been largely the preserve of full-time politicians, so the talent pool has not been significantly widened.
- 2) It puts a premium on defections and horse-trading. The anti-defection Act of 1985 has failed to cure the problem.
- 3) Legislation suffers. Most laws are drafted by the executive — in practice by the bureaucracy.
- The ruling party inevitably issues a whip to its members in order to ensure unimpeded passage of a bill.
- The parliamentary system does not permit the existence of a legislature distinct from the executive.
- Accountability of the government to the people, through their elected representatives, is weakened.
- 4) For those parties who do not get into government Parliament or Assembly serves as a theatre for the demonstration of their power to disrupt.
Case for presidential system
- A directly elected chief executive at Centre and State would be free from vulnerabilities of coalition support politics, would have the stability of tenure free from a legislative whim.
- He/she will be able to appoint a cabinet of talents, be able to devote his or her energies to governance, and not just to government.
- The Indian voter will be able to vote directly for the individual he or she wants to be ruled by.
- The president will truly be able to claim to speak for a majority of Indians rather than a majority of MPs.
The risk of dictatorship
- The only serious objection to the presidential system is that it carries with it the risk of dictatorship.
- The fear is of an imperious president, immune to parliamentary defeat and impervious to public opinion, ruling the country by fiat.
- But under the current parliamentary system, a leader with absolute majority and subservient legislature could act in the same manner.
Consider the question “Examine the differences between the presidential system and the parliamentary system of government. Do you think that the parliamentary system has served well in the Indian context?”
Conclusion
With the needs and challenges of one-sixth of humanity before our leaders, we must have a democracy that delivers progress to our people.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: API
Mains level: Paper 3- Issues of dominance of some platforms on the internet and solution
We are familiar with the dominance of some platforms on the internet. That dominance start to create problems. This article discusses the issues with dominance and suggests the solution drawing on the success of UPI.
Platforms on the internet
- Platforms are technology layers that leverage the internet to bring together producers, resellers and consumers.
- Platforms reduce transaction costs by cutting out intermediaries.
- Amazon started by selling books but became a profitable giant by creating the e-commerce platform called Amazon Marketplace.
- The most valuable companies today are platforms for search, social interaction, advertising, insurance, travel, real estate, etc.
Issues with the platforms
- 1)The promise of the internet was disintermediation, but the process has hit a speed breaker with major platforms taking on the role of mediation.
- 2) There may be multiple platforms in the game to start with, but due to network effects and the non-portability/lock-in, only a few monopolies space.
- 3) Big platforms have tried to create a sort of cartel in which to trap the customers while fencing off the rest of the internet.
- 4) The platforms amass data about users which is used to influence user behaviour, which is not limited to guiding the buying decisions.
So, what is the solution?
Let’s look at the success story of the UPI
- Unified Payment Interface (UPI) is a set of protocols that standardises the language of money transfer.
- It is an interface: a simple and structured protocol for instructions and a clearinghouse that relays well-formed requests to concerned parties for execution.
- Once the language is there, a user may choose any app to link their bank account to a UPI ID and make a pay or collect request involving any other bank account.
- UPI handled 1.3 billion transactions in June 2020, overtaking the aggregate number of transactions of all legacy “platforms”.
- UPI succeeded because it treated all players, big or small, equally.
- This allowed third-party innovators to drive adoption by creating solutions that addressed the need of the people.
Solution: Adopting of open protocols
- Application Programming Interfaces (or API) are protocols that define the meaning of data exchanged between two computers.
- Universally accepted API definitions could allow a cabbie to be discovered by any cab aggregator app the rider may choose.
- In healthcare, it could facilitate finding a doctor, booking an ambulance, taking out insurance, filing a claim, sharing a medical report or purchasing medicines from a pharmacy.
Advantages of open protocols
- Open protocols create ecosystems that are non-rivalrous and non-excludable by design.
- Even smallest of application developers or start-ups can offer low-cost, locally relevant solutions using the protocol.
- We can address the needs of the diverse business community and achieve much greater penetration for e-commerce than the 10 per cent of today.
- Open systems have the potential to transform education, food delivery, by enabling entrepreneurs to compete on their quality and reputation alone.
- Portability from one application to another, privacy and data empowerment will be some of the issues taken care of.
- We can reduce our dependence on foreign platforms.
Consider the question “What are APIs? Examine the issues created by the dominant internet platforms and how the adoption of open protocols for API could address the problem?”
Conclusion
With such a huge potential in APIs open protocols, the government must bring out the policy for the creation of open protocols and realise the untapped potential it offers.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: 10th Schedule
Mains level: Paper 2- Role of judiciary and Speaker
The article discusses the relation between the judiciary and the legislature. Recent development in Rajasthan assembly serves as the backdrop.
Context
- The political tussle in Rajasthan entered the High Court and the Supreme Court.
- The Supreme Court itself proposed to rule on the larger question of the jurisdiction of courts to entertain such pleas.
Historical background
- The President of India made a presidential reference to the Supreme Court on the relative powers of legislative assemblies and constitutional courts.
- The Supreme Court held that there is a broad separation of essential powers of each organ of the State.
- However, the Court went on to hold that a judge who entertains a petition challenging any order of the legislature does not commit contempt of the said legislature.
- Since then court have restrained themselves from interfering in the workings of legislative assemblies or Parliament is concerned.
- The sole exception is under the anti-defection law-after a final order of disqualification has been passed.
Let’s look into Kihoto Hollohan’s case
- Constitution bench of the Supreme Court in 1992 held that the Speaker acting in a disqualification matter acts as a tribunal and is subject to judicial review.
- However, the same judgment makes it clear that the Court will not intervene at an interim stage.
- The same judgment further holds the Speakers/Chairmen hold a pivotal position in the scheme of Parliamentary democracy and are guardians of the rights and privileges of the House.
Let’s now look into Rajasthan episode
- In this case, issuance of a possible disqualification notice by the Speaker, has been contested in constitutional courts.
- Even in routine petitions against notices of proposed administrative actions, the petitioner is told to answer the show cause notice and to challenge the final action only.
- The Rajasthan High Court, however, entertained a petition to challenge the Speaker’s authority to decide, if MLAs had committed an act of defection.
- The Rajasthan High Court reserved its judgment, requested the Speaker to defer further proceedings and proceeded to direct him to await judgment.
Co-equality of Constitutional authorities
- Rajasthan assembly Speaker moved the Supreme Court, questioning the court’s power to direct a Constitutional authority.
- The principle of law applied is that Constitutional authorities cannot issue directions to each other.
- They can, at best, make a polite request.
- The single judge in Calcutta, recorded in his judgment that the Supreme Court was only co-equal with the High Court, as a Constitutional Court.
- Appellate powers of the Supreme Court did not make it a superior authority to which the High Court was subordinate.
- Ever since, the Supreme Court has been careful to couch its orders as requests to any High Court, or Constitutional authority.
- Constitutional courts have followed the same principle, in addressing other Constitutional authorities.
Role of judiciary in maintaining the balance
- Unnecessary conflict between organs of state may well invite some Speaker, backed by a solid majority at State and Centre, to defy the courts.
- Courts are apolitical but keep getting pulled into political thickets, especially in matters of mass defections resulting in regime change.
- The walls of separation between constitutional organs, once breached, cannot be then repaired against future intrusions.
Consider the question “Analyse fine balance Indian Consitution strikes between the various Constitutional authorities. Also examine how role of judiciary in dealing with the anti-defection law.”
Conclusion
Even under a sovereign Constitution, parliamentary and legislative supremacy in their areas of working must be respected.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Currency Swap
Mains level: Cryptocurrency and its feasiblity
The RBI has agreed to a $400 million currency swap facility for Sri Lanka till November 2022.
Practice question for mains:
Q. What are Currency Swaps? Discuss the efficacy of Currency Swap Agreements for liberalizing bilateral trade.
Why such move by RBI?
- The RBI’s action follows a recent bilateral ‘technical discussion’ on rescheduling Colombo’s outstanding debt repayment to India.
- Following the outbreak of COVID-19 in the region, India had proposed a virtual meeting to discuss the request. Sri Lanka owes $960 million to India.
- In turn, Sri Lanka would facilitate, protect and promote a liberal ecosystem for Indian investors.
What are Currency Swaps?
- A currency swap, also known as a cross-currency swap, is an off-balance sheet transaction in which two parties exchange principal and interest in different currencies.
- Currency swaps are used to obtain foreign currency loans at a better interest rate than could be got by borrowing directly in a foreign market.
How does it work?
- In a swap arrangement, RBI would provide dollars to a Lankan central bank, which, at the same time, provides the equivalent funds in its currency to the RBI, based on the market exchange rate at the time of the transaction.
- The parties agree to swap back these quantities of their two currencies at a specified date in the future, which could be the next day or even three months later, using the same exchange rate as in the first transaction.
- These swap operations carry no exchange rate or other market risks, as transaction terms are set in advance.
Why does one need dollars?
- FPIs investors look for safer investments but the current global uncertainty over COVID outbreak has led to a shortfall everywhere in the global markets.
- This has pulled down foreign exchange reserves of many small and developing countries.
- This means that the government and the RBI cannot lower their guard on the management of the economy and the external account.
Benefits of currency swap
- The absence of an exchange rate risk is the major benefit of such a facility.
- This facility provides the flexibility to use these reserves at any time in order to maintain an appropriate level of balance of payments or short-term liquidity.
- Swaps agreements between governments also have supplementary objectives like the promotion of bilateral trade, maintaining the value of foreign exchange reserves with the central bank and ensuring financial stability (protecting the health of the banking system).
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Khazan farming, Salim Ali Bird Sanctuary
Mains level: Integrated Farming System, Khazan etc.

The Salim Ali Bird Sanctuary in low-lying floodplains of Goa is characterized by an estuarine agricultural system called Khazan farming.
Try this question from our AWE initiative:
How far is the Integrated Farming System (IFS) helpful in sustaining agricultural production? (10 Marks)
Khazan Farming
- The low-lying floodplains of Goa host an estuarine agricultural system called Khazan farming.
- This system is a carefully designed topo-hydro-engineered agro-aquacultural ecosystem mainly based on the regulation salinity and tides.
How does it work?
- Centuries ago, people in this region reclaimed low-lying brackish coastal floodplains and mangrove forests.
- They constructed bunds using locally available material to prevent the ingress of saltwater, which killed the halophilic mangroves.
- To control the flow of tidal waters, they built openings in bunds fitted with one-way gates.
- These channels would fill in with the oncoming tide and bring with them fish, crab and shrimp, and the gates would automatically shut when the water level was equal on both sides.
- This prevented the water from overflowing into the fields used to grow paddy and which has a low tolerance to salt.
- When the tide receded, these gates would open outwards automatically, allowing the water to drain out.
- During this time, a bag net was set at the gate to catch fish that had entered in earlier.
Benefits of Khazan
- Every bit of space was precious and used efficiently — the bunds were used to grow a variety of vegetables.
- The Khazan system allowed for the farmer and the fisher to harmoniously coexist and was the key to sustaining what is considered Goa’s staple — fish, curry and rice.
Why is it neglected these days?
- Today, for various reasons, but primarily due to post-independence agrarian reforms of 1961, these lands largely lie fallow and are in a state of decay.
- Lack of cultivation and maintenance of the bunds and sluice gates is leading to their breaching and the natural reclamation of these fallow lands by mangroves.
- Moreover, mangroves are protected by law and it is illegal to cut them.
- Areas that have these trees growing on them also come under the purview of the coastal regulation zone (CRZ); according to the 2011 notification, the mangrove areas are classified as CRZ I and cannot be developed upon.
Back2Basics: Salim Ali Bird Sanctuary
- The Salim Ali Bird Sanctuary is Goa’s smallest protected area — it comprises barely two square kilometres of lush mangrove forests.
- The sanctuary is located on Chorão, one of Goa’s estuarine islands in the Mandovi river approximately five kilometres from capital Panaji.
- The sanctuary and its surrounds are home to marsh crocodiles, smooth-coated otter, the unique glossy-marsh snake that feeds on crabs, mud lobsters, sap-sucking sea slugs, among others.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NCDC and its formation
Mains level: Institutional failures in NCDC
India’s premier organisation mandated to collect data about diseases, the NCDC is failing in its task as the spread of COVID-19 continues unabated.
Practice question for mains:
Q. Health infrastructure in India is hardly capable of handling any pandemic. Critically comment.
About the National Centre for Disease Control
- The NCDC carries out nationwide disease surveillance through its Integrated Disease Surveillance Programme (IDSP).
- It is a vertical programme under Directorate General of Health Services.
Its formation
- This programme has been present in the country in different avatars since 1997 when the National Surveillance Programme for Communicable Diseases was set up.
- This was upscaled to the Integrated Disease Surveillance Project in 2004, with assistance from the World Bank, to address the demands of the WHO’s International Health Regulations, 2005.
- Under this, each country had to assess public health emergencies of international concern within 48 hours and report them to WHO within the next 24 hours.
- It was then included in the 12th Plan (2012-17) under the Union Health Ministry and renamed IDSP.
Mandate of the NCDC
To aid the process of an investigation, NCDC has put down 10 steps that need to be followed for each outbreak:
- Determine the existence of an outbreak
- Confirm the diagnosis
- Define a case
- Search for cases
- Generate hypothesis using descriptive findings
- Test hypothesis with the analytical study
- Draw conclusions
- Compare hypothesis with established facts
- Communication of findings
- Execute preventive measures
Why did NCDC fail?
- IDSP’s manual says weekly and monthly updates are mandatory for each State and UTs even if no outbreaks are reported.
- But this has never been observed to date.
- There is an overlap between the diseases being followed by IDSP and other agencies like the National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme
- The fact that IDSP does not collect mortality data was also a concern. Moreover, the IDSP was not investigating zoonotic diseases.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Kumhar Sashaktikaran Yojana (KSY)
Mains level: Welfare schemes for various vulnerable sections of population
The Centre has distributed 100 electric potter wheels to 100 trained artisans under the KSY.
Try this question from CSP 2018:
Q. Consider the following provisions under the Directive Principles of State Policy as enshrined in the Constitution of India:
- Securing for citizens of India a uniform civil code.
- Organising village panchayats.
- Promoting cottage industries in rural areas.
- Securing for all the workers reasonable leisure and Cultural opportunities.
Which of the above are the Gandhian Principles that are reflected in the DPSP?
(a) 1, 2 and 4
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1, 3 and 4
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Kumhar Sashaktikaran Yojana
- KSY is an initiative of the Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) for the empowerment of potters’ community in the remotest of locations in the country.
- It reaches out to the potters in U.P., M.P., Maharashtra, J&K, Haryana, Rajasthan, West Bengal, Assam, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Telangana and Bihar.
Benefits provided
This program provides the following support to potters.
- Training for advanced pottery products
- Latest, new technology pottery equipment like the electric Chaak
- Market linkages and visibility through KVIC exhibitions
Back2Basics: KVIC
- The KVIC is a statutory body formed in April 1957 under the ‘Khadi and Village Industries Commission Act of 1956’.
- It is an apex organisation under the Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises, with regard to khadi and village industries within India.
- It seeks to plan, promote, facilitate, organise and assist in the establishment and development of khadi and village industries in the rural areas.
- Its head office is in Mumbai, whereas its six zonal offices in Delhi, Bhopal, Bangalore, Kolkata, Mumbai and Guwahati.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: DNA/RNA
Mains level: Not Much
The famous British scientist and virologist Rosalind Franklin is remembered across the world on her birth centenary who worked to construct the double-helix structure of DNA.

Try this PYQ from CSP 2019:
DNA/RNA has been an all-time favourite of UPSC!
Q.‘RNA interference (RNAi)’ technology has gained popularity in the last few years. Why?
- It is used in developing gene-silencing therapies.
- It can be used in developing therapies for the treatment of cancer.
- It can be used to develop hormone replacement therapies.
- It can be used to produce crop plants that are resistant to viral pathogens.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 4
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1 and 4 only
Rosalind Franklin (1920-1958)
- She was an English chemist and X-ray crystallographer whose work was central to the understanding of the molecular structures of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), RNA (ribonucleic acid), viruses, coal, and graphite.
- Although her works on coal and viruses were appreciated in her lifetime, her contributions to the discovery of the structure of DNA were largely recognised posthumously.
DNA breakthrough
- In 1952, Raymond Gosling, a graduate student at King’s College London, took a historic X-ray photograph under Franklin’s supervision.
- Photo 51, as it is called, demonstrates the now-familiar, double-helix structure of DNA.
Why is she remembered now?
- The world is currently gripped in a pandemic, and her pioneering research in virology provided a crucial early step in the search for cures, vaccinations and tests.
- During the Second World War, Franklin carried out research into coal and graphite that proved important for gas-masks, the PPE of that time.
- It is because of Franklin, her collaborators and successors, that today’s researchers are able to use tools such as DNA sequencing and X-ray crystallography to investigate viruses such as COVID-10.
Back2Basics: DNA/RNA 
- Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and Ribonucleic acid (RNA) are perhaps the most important molecules in cell biology, responsible for the storage and reading of genetic information that underpins all life.
- They are both linear polymers, consisting of sugars, phosphates and bases, but there are some key differences which separate the two.
- These distinctions enable the two molecules to work together and fulfil their essential roles.
- DNA encodes all genetic information and is the blueprint from which all biological life is created. And that’s only in the short-term.
- In the long-term, DNA is a storage device, a biological flash drive that allows the blueprint of life to be passed between generations.
- RNA functions as the reader that decodes this flash drive. This reading process is multi-step and there are specialized RNAs for each of these steps.
Three types of RNA
- Messenger RNA (mRNA) copies portions of genetic code; a process called transcription and transports these copies to ribosomes, which are the cellular factories that facilitate the production of proteins from this code.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA) is responsible for bringing amino acids, basic protein building blocks, to these protein factories, in response to the coded instructions introduced by the mRNA. This protein-building process is called translation.
- Finally, Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a component of the ribosome factory itself without which protein production would not occur.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
South Korea’s technological advancement and manufacturing capabilities can be helpful in India’s economic growth and human resource development. Seoul’s successful development story of the last few decades can complement Modi’s vision of making a “New India” by 2022.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Debt monetisation, RBI balance sheet etc
Mains level: Paper 3-Ways to raise funds to finance the stimulus package
The article analyses the issues with suggestions like printing of currency and using forex reserves to finance the stimulus. They also lead to an increase in government debts.
Context
- Prime Minister announced a stimulus package of ₹20 trillion to fight the economic fallout of the covid pandemic.
- Since then, several unorthodox ideas have been floated to raise funds for it without straining government finances.
- Among the suggestions are the printing of currency, and using foreign exchange reserves or household gold.
Let’s look at entries in the RBI’s balance sheets
- On the liabilities side of it is the currency in circulation, commercial bank reserves and government reserves.
- On the asset side of it is forex reserves, government securities and gold.
- The balancing item represents the central bank’s equity and accumulated surplus.
Let’s look at 3 options suggested above and issues with them-
1) Printing currency
- Doing this would increase the liabilities of the RBI under “currency in circulation”.
- But it first needs to acquire assets to offset this increase in liability.
- These assets could be government securities, forex reserves or gold.
- Thus, one way for the government to finance its expenditure would be to issue government bonds and ask RBI to print currency with which to subscribe to such bonds.
- This is known as deficit monetization.
- It is important to note that for the central bank to print money, the government would have to issue bonds to it.
- It will increase government debt.
2) Monetisation of gold held by household
- This would first involve the government buying gold from households in exchange for its bonds.
- Then, the accumulated gold would be bought by RBI from the government with newly printed currency.
- In this case, instead of creating new money to acquire government bonds, RBI would be doing the same to acquire gold.
- This too involves the Centre taking on additional debt.
- Moreover, gold monetization schemes in the past have yielded only mild success.
3) Using RBI’s forex reserves
- Against every dollar of forex reserves shown by RBI on the asset side, an equivalent rupee amount has already been created on the liability side.
- This is because whenever RBI acquires foreign currency, it pays for it using the Indian rupee.
- Thus, no additional currency can be printed against such already-acquired reserves.
- The only way our forex reserves can be used for generating additional resources is by pledging them to a third party.
- The pledging of RBI’s assets to raise funds is done only under extreme circumstances, for instance, during the 1991 balance of payments crisis.
- We are certainly not in a situation that warrants a repeat of an exercise where RBI’s assets, be it gold or forex reserves, have to be mortgaged.
So, what is the way out?
- There are only three ways to finance government expenditure: taxes, debt and asset sales.
- Taxes and asset sales can pitch in a bit towards the stimulus bill.
Consider the question “Examine the ways in which government can raise the funds to finance the stimulus package and also discuss the issues with each move.”
Conclusion
There is no escaping the fact that we are staring at a higher build-up of government debt in the future. When we stop harbouring the notion that we can pay the stimulus bill without any deterioration in government finances, we will be able to see the bitter truth: There is no such thing as a free lunch.
Read more about the issue here:
India’s rising Forex Reserves
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now








