Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: AMRUT
Mains level: Paper 1-Urbanisation and issues
The article brings out the issues in the rural-urban binary, which leads to the disparity in the allocation of resources to the urban areas.
Congestion and health issues in cities
- The congestion in large cities has turned out to be their worst enemy during this pandemic.
- Congestion is most evident in slums in large cities and poses a grave health and environmental challenges.
- Yet, the Centre’s allocation for the rural component of the Swachh Bharat Mission is about seven times more than for urban areas.
- Class I cities have 1.4 beds per 1,000 people. (with the population more than 1 lakh)
- However, the urban support under the National Health Mission is just three per cent of the total allocation, while 97 per cent of the funds are set aside for rural areas.
Issues with the present urban development programs
- The Jawaharlal Nehru National Urban Renewal Mission (2005-2014) allocated the bulk of funds to large cities: 70 per cent to large cities and 30 per cent to smaller towns.
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) and the Smart Cities Mission, focus on Class I cities.
- Both these schemes provide funds for the more developed cities that already have relatively better infrastructure.
- But these schemes overlook the nearly seven crore people who live in smaller towns.
- These are towns that lag behind in services and infrastructure as compared to the big cities.
Consider the question “The rural-urban binary has led to the policy formulation in which there is a huge disparity in the allocation of resources and attention on the urban area. Comment.”
Conclusion
The pandemic has forced us to reflect on the unequal and unplanned development of urban settlements and the absence of infrastructure to provide for the teeming millions. The challenges of urban poverty and congestion cry for more attention, more government support.
Original article:
https://indianexpress.com/article/opinion/columns/coronavirus-covid-19-pandemic-india-urban-cities-6520574/
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SSC/PC
Mains level: Debate over suitablity of women in combat roles of Indian Army
The Ministry of Defence (MoD) has issued the formal Government Sanction Letter for grant of Permanent Commission (PC) to women officers in the Army.
Try this question for mains:
Q.“Concern for equality of sexes or political expediency should not influence defence policies.” Discuss on lines with the debate over the induction of women in the armed forces.
Also read: https://www.civilsdaily.com/burning-issue-women-in-armed-forces/
Why such an order?
- The order follows a Supreme Court verdict in February that directed the government that women Army officers be granted PC and command postings in all services other than combat.
- Following this, Army Chief had said it was an enabling one and gives a lot of clarity on how to move forward.
- He had stated that the same procedure for male SSC officers will be followed for women to give PC.
Women in Army: Background of the case

- The induction of women officers in the Army started in 1992.
- They were commissioned for a period of five years in certain chosen streams such as Army Education Corps, Corps of Signals, Intelligence Corps, and Corps of Engineers.
- Recruits under the Women Special Entry Scheme (WSES) had a shorter pre-commission training period than their male counterparts who were commissioned under the Short Service Commission (SSC) scheme.
- In 2006, the WSES scheme was replaced with the SSC scheme, which was extended to women officers. They were commissioned for a period of 10 years, extendable up to 14 years.
- Serving WSES officers were given the option to move to the new SSC scheme or to continue under the erstwhile WSES.
- They were to be, however, restricted to roles in streams specified earlier — which excluded combat arms such as infantry and armoured corps.
2 key arguments shot down
- The Supreme Court rejected arguments against a greater role for women officers, saying this violated equality under the law.
- They were being kept out of command posts on the reasoning that the largely rural rank and a file will have problems with women as commanding officers. The biological argument was also rejected as disturbing.
- While male SSC officers could opt for permanent commission at the end of 10 years of service, this option was not available to women officers.
- They were, thus, kept out of any command appointment, and could not qualify for a government pension, which starts only after 20 years of service as an officer.
- The first batch of women officers under the new scheme entered the Army in 2008.
Arguments by the Govt
- The Centre had mentioned several reasons behind the differential treatment of women officers.
- It had proposed that women officers with up to 14 years of service would be granted a permanent commission, while those above 14 years would be permitted to serve for up to 20 years and retire with pension without being considered for permanent commission.
- It also stated that those with more than 20 years of service would immediately be released with pension
- This order did not grant permanent commission to women with over 14 years of service, and hence discriminatory.
- Furthermore, the 2019 order granted permanent commission only for staff appointments and not command appointments.
- The centre justified this by stating that that the units in Army are composed entirely of male soldiers, who are mostly from rural backgrounds and thus, are not mentally prepared to accept women officers in the command of units.
- It also stated that the lower physical capacity of women officers would be a challenge for them to command units wherein officers are expected to lead the men from the front and need to be in prime physical condition to undertake combat tasks.
- The government also stated that the adverse conditions, including two unsettled borders and internal security situations in the northeast and Jammu and Kashmir, have a major bearing on the employment of women officers in light of their physiological limitations.
- Also, it had stated that the isolation and hardships would eat into their resolve and that they have to heed to the call of pregnancy, childbirth and family.
- The government also argued that women ran the risk of capture by the enemy and being taken as prisoners of war.
SC Criticized the Government’s Note
- Reflects Poorly on Women: The note had shown women officers in a poor light, saying isolation and hardships would eat into their resolve and that they would have to heed to the call of pregnancy, childbirth and family. The note had mentioned that women ran the risk of capture by enemy and taken prisoner of war.
- Patriarchal Notion: The court held that the the note reflected the age-old patriarchal notion that domestic obligations rested only with women.
- Sex Stereotype: The court also dismissed the point that women are physiologically weaker than men as a “sex stereotype”.
- Offence to dignity of Indian Army: The court noted that challenging abilities of women on the ground of gender is an offence not only to their dignity as women but to the dignity of the members of the Indian Army – men and women – who serve as equal citizens in a common mission.
Implications of the judgement
- The SC did away with all discrimination on the basis of years of service for grant of PC in 10 streams of combat support arms and services, bringing them on a par with male officers.
- It has also removed the restriction of women officers only being allowed to serve in staff appointments, which is the most significant and far-reaching aspect of the judgment.
- It means that women officers will be eligible to the tenant all the command appointments, at par with male officers, which would open avenues for further promotions to higher ranks for them.
- It also means that in junior ranks and career courses, women officers would be attending the same training courses and tenanting critical appointments, which are necessary for higher promotions.
Back2Basics: Permanent Commission (PC) Vs. Short Service Commission (SSC)
- SSC means an officer’s career will be of a limited period in the Indian Armed Forces whereas a PC means they shall continue to serve in the Indian Armed Forces, till they retire.
- The officers inducted through the SSC usually serve for a period of 14 years. At the end of 10 years, the officers have three options.
- A PC entitles an officer to serve in the Navy till he/she retires unlike SSC, which is currently for 10 years and can be extended by four more years, or a total of 14 years.
- They can either select for a PC or opt-out or have the option of a 4-years extension. They can resign at any time during this period of 4 years extension.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Open Credit Enablement Network (OCEN)
Mains level: Credit facilities for MSMEs
A new credit protocol infrastructure called the OCEN protocol is set to be launched very soon.
Practice question for mains:
Q. What is Open Credit Enablement Network (OCEN)? How it is expected to be a gamechanger in the micro-credit facilitation services in India?
Open Credit Enablement Network (OCEN)
- OCEN is a credit protocol infrastructure, which will mediate the interactions between loan service providers, usually fintech and mainstream lenders, including all large banks and NBFCs.
- It is developed by a think tank, Indian Software Products Industry Round Table (iSPIRT).
- With this, a credit will become more accessible for a large number of entrepreneurs and small businesses in the country.
- Private equity and venture capital players, angel investors, high net worth individuals and others also could be part of this exercise as investors.
How will it work?
- iSpirit is partnering with key leaders such as SBI, HDFC Bank Ltd., ICICI Bank Ltd., IDFC First Bank Ltd., Axis Bank Ltd. etc. for this new credit rail.
- Account Aggregators which will be using these APIs to embed credit offerings in their applications, and will be called ‘Loan Service Providers’, which will play a crucial role in democratizing access to credit, and lowering interest rates for customers.
Why need OCEN?
- The cost of lending being too high in India, small value loans becomes very unfeasible.
- OCEN which seeks to connect lenders to marketplaces and thereby to borrowers is a technology system.
- If implemented, the technology can democratize lending to micro-enterprises and street vendors in a big way.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bats and thier natural role
Mains level: Illict wildlife trade and its prevention
The COVID pandemic has magnified our fear of bats, but their conservation is crucial to prevent such events from arising again.
Try this PYQ from CSP 2014:
Q.Consider the following:
- Bats
- Bears
- Rodents
The phenomenon of hibernation can be observed in which of the above kinds of animals?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) Hibernation cannot be observed in any of the above
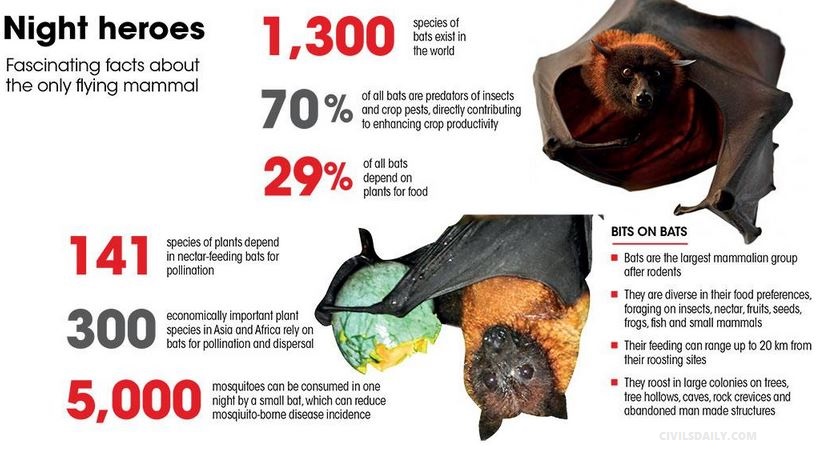
Bats
- Bats are the largest mammalian group after rodents, with over 1,300 species making up a quarter of all mammals.
- They occur on all continents except Antarctica and are particularly diverse in South Asia, with 114 species of insect-eating bats and 14 fruit bats, also known as “flying foxes”, occurring in India.
- They roost in large colonies on trees, tree hollows, caves, rock crevices and abandoned manmade structures.
- They play a unique role in maintaining ecosystem structure, making a singular contribution to our food production, economy and well-being.
- They are the only mammals capable of true flight and have a unique sonar-based echolocation mechanism to capture prey at night.
Their significance
1) Seed dispersal
- About 29 per cent of all bats depend upon plants for food.
- The diet of fruit-eating bats consists largely of flowers and fruits such as mangoes, bananas, guavas, custard apples, figs, tamarind and many species of forest trees.
- Therefore, bats play a vital role in seed dispersal and forest regeneration. Studies have shown that seedlings raised from bat dispersed seeds show higher germination and vigorous growth.
2) Pollination
- Studies have found that bats play a vital role in pollination, mainly of large-flowered plants, and in crop protection.
- Fruit bats (Megachiroptera) being large, require big flowers with copious amounts of nectar.
- Bats are major pollinators for many species of mangroves which are important for coastal ecosystems and local livelihoods.
3) Production boost
- Insects are a major problem for agriculture, destroying up to 26 per cent of the annual production of crops worldwide every year, roughly amounting to $470 billion.
- Insectivorous bats, which make up 70 per cent of all bat species, are voracious predators of nocturnal insects and crop pests.
- Some large insectivorous bats are also reported to feed on small rodents. Thus they contribute directly to enhancing the crop productivity with tremendous economic impact.
4) Soil fertility
- Bats contribute significantly to soil fertility and nutrient distribution due to their large numbers, high mobility and varied habitats for roosting and foraging.
- Bat droppings provide organic input to soil and facilitate nutrient transfer, contributing to soil fertility and agricultural productivity. The practice is harmless vis-a-vis human health.
5) Health benefits
- Several species of bats, in fact, contribute to human health by reducing populations of mosquitoes and other insect vectors that spread malaria, dengue, chikungunya and other diseases.
- It is reported that a small bat may feed on almost 5,000 mosquitoes each and every feeding night far more than other measures adopted to eliminate them.
Their conservation
- According to the IUCN, about 5 per cent of bats are categorised as endangered and another 11 per cent are data deficient.
- Further, some species of fruit bats are categorised under Schedule 5 of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1973, along with other vermin species like rats, making it difficult to legally conserve them.
Conclusion
- The pandemic has demonstrated that conservation of biodiversity and natural habitats is absolutely essential to prevent such events from arising again.
- Understanding the role played by bats helps us appreciate how their absence can greatly affect all facets of our lives.
- Viruses don’t jump directly from bats or other animals to humans.
- Rather, illicit trade in wildlife, high levels of hunting for the consumption of wild meat, and destruction of natural habitats are responsible for this.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: COVID-19 Law Lab
Mains level: Health Policy measures against COVID-19

The UN agencies have started a portal called the COVID-19 Law Lab to host all recent legal enactments to fight the novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic.
Note the following things about COVID-19 Law Lab:
1) It is an online portal and not a cubical laboratory
2) Parent agency includes the UN and WHO
3) It is the first collation of health-related laws and protocols of the countries
COVID-19 Law Lab
- This digital portal hosts all legal steps taken by 190 countries to fight the pandemic.
- The UNDP, the WHO, the Joint UN Programme on HIV/AIDS and the O’Neill Institute for National and Global Health Law at Georgetown University have collaborated for this initiative.
- The collation initiative aims at dissemination of procedures and practices for effective enactment of health-related laws.
- It is expected to be the most expansive collation of laws and procedures related to a health emergency.
Why need such a repository?
- The pandemic has led to confusion over treatment and management protocols.
- Some 220 countries/territories have enacted various procedures backed by various enabling laws related to epidemics and health emergency.
- Laws and policies that are grounded in science, evidence and human rights can enable people to access health services, protect themselves from COVID-19 and live free from stigma, discrimination and violence.
- Sharing medicines and formulae for even general treatment has been a big challenge due to restrictive laws and trade practices.
- As health is global, legal frameworks need to be aligned with international commitments to respond to current and emerging public health risks.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Siddi Tribals
Mains level: NA

The Siddi community gets its first lawmaker in Karnataka. They are included as the Scheduled Tribes in Karnataka.
Try this question from CSP 2019:
Q.Consider the following statements about Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in India:
- PVTGs reside in 18 States and one Union Territory.
- A stagnant or declining population is one of the criteria for determining PVTG status.
- There are 95 PVTGs officially notified in the country so far.
- Irular and Konda Reddi tribes are included in the list of PVTGs.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1, 2 and 4
(d) 1, 3 and 4
Siddi Tribe
- The Siddi also known as Sidi, Siddhi, Sheedi or Habshi, are an ethnic group inhabiting India and Pakistan.
- They are sometimes referred to as Afro-Indians. They are descended from the Bantu peoples of the East African region.
- Similarly, another term for Siddis, habshi, is held to be derived from the common name for the captains of the Abyssinian ships that also first delivered Siddi slaves to the subcontinent.
- They are primarily Muslims, although some are Hindus and others belong to the Catholic Church.
How they came to India?
- The first Siddis are thought to have arrived in India in 628 AD at the Bharuch port. Several others followed with the first Arab conquest of the subcontinent in 712 AD.
- The latter groups are believed to have been soldiers with Muhammad bin Qasim’s Arab army and were called Zanjis.
- In the Delhi Sultanate period prior to the rise of the Mughals in India, Jamal-ud-Din Yaqut was a prominent Siddi slave-turned-nobleman who was a close confidant of Razia Sultana.
- Siddis were also brought as slaves by the Deccan Sultanates. They also served in the Navy of Shivaji Maharaj.
- Several former slaves rose to high ranks in the military and administration, the most prominent of which was Malik Ambar.
- Later the Siddi population was added to via Bantu peoples from Southeast Africa that had been brought to the Indian subcontinent as slaves by the Portuguese.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Issues with higher education
The issues of quality of higher education explain the lack of employability of Indian youth. This article examines the issue and suggests the approach to deal with the issue.
Three learning outcomes
- The first is to provide knowledge in the relevant discipline to the students.
- Second, imparting students with the skills needed for their jobs/enterprises.
- Third, students are expected to play a constructive role in shaping the society and the world at large, the values and ideals of a modern, progressive society.
- The teaching-learning process is expected to mould their character accordingly.
Issues with the education system
- Apart from a handful of institutions in the technology, management and liberal arts streams a vast majority of other students just meander through college and acquire a degree.
- There is a huge gulf between the curriculum taught in the colleges and actual job requirements.
- It is common to hear even the brightest of students mention that they learnt more on the job than through their curriculum in college.
Focus more on training
- If most of the students learn so much on the job, it raises several questions.
- Why should we bestow so much importance on a syllabus?
- And why do we take such massive efforts to evaluate students’ knowledge of that syllabus through exams?
- What we can do is completely re-evaluate the syllabus frequently considering the changing needs of the time.
- We can have substantive industrial internships while retaining only a very basic outline of essential concepts.
- The evaluation too can be a mix of regular assignments, performance in the internship.
Consider the question “The lack of employability in the youth of India could be a huge hurdle in India’s aim to reap the benefits of demographic dividend. Examine the reasons for and suggest the measures to deal with the issue.”
Conclusion
The higher education sector has multiple stakeholders and multiple vested interests. In normal times, maintaining the status quo or implementing incremental and marginal reforms was all one could hope for. The pandemic has opened the doors for ushering in massive, bold and transformational reforms. As John Lewis said, “If not now, then when?”
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Jask Port
Mains level: Paper 2- Iran-China deal and concerns for India
Two events which happened in quick succession raised concern in India. Iran’s decision to continue the railway project on its own and the reports of deal with China, both the events weighs heavily on India’s interests. This article examines the future course of action which India must adopt in such a situation.
Context
- Iran and China are close to concluding a 25-year strategic partnership.
- This is being linked to reports that Iran has decided to undertake the construction of the Chabahar-Zahedan railway line on its own.
- The project has not been handed over to China — at least not yet — so the “India loses, China wins” narrative is premature.
What does the China-Iran deal indicate?
- China attaches importance to Iran, which is a key source of energy supplies, a part of Belt and Road Initiative, and a potentially lucrative market.
- However, like India, China has also in parallel cultivated closer relations with Saudi Arabia and the UAE.
- China continues to have a strong relationship with Israel.
- As China’s economic, military and technological capabilities have increased, its profile in this strategically important region has also expanded.
What should be India foreign policy approach towards Iran
- While acknowledging changed regional geopolitical landscape, India should pursue continue the policy of maintaining positive relations with Iran, the Arab states and Israel.
- India will have more room for manoeuvring in the region by continuing to maintain a strong and friendly relationship with Iran.
- One should also not exclude the possibility of a Democratic US President reviving the Iran nuclear deal.
- The revival of the deal will open the door for US and European companies to resume business with Iran.
- It is the reinstatement of severe economic sanctions that has led Iran to turn to China, but the latter has remained cautious.
- The pursuit of a closer security partnership with the US does not mean that India should follow the US lead on its other important relationships.
Concerns for India
- While maintaining the relations, India should not monitor closely the development of relations between China and Iran, which could complicate our security interests on our western flank.
- Of particular concern is a reference to China constructing a new port at Jask at the mouth of the Hormuz strait.
- If the port were operated by China, India’s maritime security would be at further risk.
- It would also be of deep concern to the Arab states who will suffer from any closing of the Hormuz Strait while Iran remains less affected.
- This is an issue on which the Arab states may well react adversely to China.
- India, too, should press its concerns on Iran while working on a counter-strategy.
Consider the question “Balancing the contrasts has been the basis of India’s relations with Iran. Comment.”
Conclusion
India should continue its engagement with Iran while pressing for its concerns at the same time in particular when it comes to Iran’s relations with China endangering India’s interest.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Provisions under 10th Schedule
Mains level: Paper 2- Anti-defection law, 10th Schedule
The growing trend of the toppling of the government by luring the MLAs of ruling party. The SC needs to reconsider the floor test usually ordered in such cases. The article analyses this issue here.
Reading Article 191(2) and 10th Schedule
- Article 191(2) declares that a person shall be disqualified from being a member of the legislative assembly or legislative council of a state if he is so disqualified under the Tenth Schedule.
- The Tenth Schedule to the Constitution contains “provisions as to disqualification on ground of defection”.
- Tenth Schedule also fixes the relationship between a member and a political party which selected him as a candidate.
- It also provides one of the grounds for disqualification: “If he voluntarily gives up his membership of such political party”.
- The decision as to disqualification is left to the absolute discretion of the Speaker.
Constitutional morality and 10th Schedule
- Tenth Schedule brings to the fore the need to emphasise “constitutional morality”.
- Constitutional morality means “strict adherence to the core principles of constitutional democracy”.
- So, Constitutional transgressions by MLAs coming through a “party platform” to serve the people for five years (Article 172), cannot be accepted.
- In so doing, these MLAs forget the oath, taken under Article 188 of the Constitution to bear true faith and allegiance to the Constitution of India as established by law.
- Legislators do not have absolute freedom to behave in any way they like.
Issues with the floor test
- When ruling party MLAs are lured with rewards, political or otherwise, then the “floor test” becomes constitutionally immoral and unjust.
- This will amount to circumventing the Tenth Schedule through engineered defections through the judicial process.
- It is high time the judiciary revisited the use of a “floor test” to prove a majority in a legislature.
Consider the question “Examine the ways in which a member of the house is deemed to have given up his membership under the 10th Schedule as interpreted in the various judgements. Also, analyse the implications of conducting a floor test in a situation when members of the ruling party are lured with rewards.”
Conclusion
Judiciary must take note of the toppling of the majority government through luring of the MLAs and subsequent floor test by the courts. The floor test in such a situation needs reconsideration.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Strategic and non-strategic sectors
Mains level: Disinvestment of CPSEs
The government will soon come out with a policy on strategic sectors and simultaneously kick into motion a process of complete privatization for companies in the non-strategic sectors.
Try this question for mains:
Q. “Privatisation of CPSEs can lead to the conversion of public monopoly to a private monopoly.” Analyse.
What are Strategic and Non-strategic Sectors of India?
- An industry is considered strategic if it has large innovative spillovers and if it provides a substantial infrastructure for other firms in the same or related industries.
- Earlier, the strategic sectors were defined on the basis of industrial policy.
- The government classified Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs) as ‘strategic’ and ‘non-strategic’ on the basis of industrial policy that keeps on changing from time-to-time.
According to this, the Strategic sector PSUs are:
- Arms & Ammunition of defence equipment
- Defence aircraft & warships
- Atomic energy
- Applications of radiation to agriculture, medicine and non-strategic industry
- Railways
Banking, insurance, defence, and energy are likely to be part of the strategic sector list. All other PSUs apart from the strategic sectors fall under Non-strategic Sector including Power Discoms.
A change in policy post-Atmanirbhar
- Under the Self-sufficiency move, the proposed policy would notify the list of strategic sectors requiring the presence of at least one state-owned company along with the private sector.
- In all other sectors, the government plans to privatize public sector enterprises, depending upon the feasibility.
- The number of enterprises in strategic sectors will be only one to four, and others would be privatized/merged/brought under a holding company structure.
Will it help privatization?
- The government has already set in motion privatization plans for large PSU companies BPCL, Air India, Container Corporation of India, and Shipping Corporation of India.
- Budget 2020-21 had announced plans to sell part of the Centre’s stake in LIC through an initial public offer (IPO), and the sale of equity in IDBI Bank to private, retail and institutional investors.
- The emphasis on privatization could see companies in chemicals and infrastructure space being privatized, while the government has stated its intent to reduce the number of state-owned banks.
- This could see some smaller banks being privatized in due course.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Tenth Schedule
Mains level: Issues over Judicial discretion in Anti-defection

A Supreme Court Bench is scheduled to hear an appeal filed by the Rajasthan Assembly Speaker’s office challenging the State High Court order to defer anti-defection proceedings against former Deputy CM.
Try these questions:
Q. “The anti-defection law works best as an insurance against violation of the people’s mandate for a party, but it cannot be made a tool to stifle all dissent.” Discuss.
—–
Q.Which one of the following Schedules of the Constitution of India contains provisions regarding anti-defection? (CSP 2014)
(a) Second Schedule
(b) Fifth Schedule
(c) Eighth Schedule
(d) Tenth Schedule
What is the issue?
- The petition said the HC has crossed its jurisdiction by asking the Speaker to put off his decision on the disqualification notices issued to dissident MLAs.
- The HC order was an affront to the powers of the Speaker.
- The High Court’s interim order granting extended time to rebel MLAs to file their replies to anti-defection notices amounted to a violation of Article 212 (courts not to inquire into the proceedings of the legislature).
Backed by Tenth Schedule
- The petition said that judicial review of ongoing anti-defection proceedings was limited.
- Notice is much prior to any final determination or decision on disqualification.
- The proceedings, including the notice, are in the realm of the legislative proceedings under Paragraph 6(2) of the Tenth Schedule, the Speaker’s office argued.
Citing the Kihoto Hollohan case
- The petition referred to the Constitution Bench judgment of the top court in the Kihoto Hollohan case in 1992 in this context.
- Judicial review cannot be available at a stage prior to the making of a decision by the Speaker/Chairman and a prior action would not be permissible.
- Nor would interference be permissible at an interlocutory stage of the proceedings, the verdict says.
Must read:
Kihoto Hollohan Order (1992)
What does the dissident MLAs have to say?
- The dissident MLAs had challenged the constitutionality of Paragraph 2(1)(a) of the Tenth Schedule which makes “voluntarily giving up membership of a political party” liable for disqualification.
- The MLAs had argued that the provision infringed their right to dissent.
- But the Speaker’s office countered that Paragraph 2 (1)(a) of the Tenth Schedule was the law of the land.
- A mere challenge to its constitutionality cannot efface it from the statute book.
Back2Basics
Explained: Anti-defection law and its evolution
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Criticality of the nuclear reactors
Mains level: India's nuclear energy policy

The indigenously designed 700 MWe reactor at the Kakrapar Atomic Power Project has achieved Criticality.
Try this PYQ from CSP 2013:
Q. The known forces of nature can be divided into four classes, viz, gravity, electromagnetism, weak nuclear force and strong nuclear force. With reference to them, which one of the following statements is not correct?
(a) Gravity is the strongest of the four
(b) Electromagnetism act only on particles with an electric charge
(c) Weak nuclear force causes radioactivity
(d) Strong nuclear force holds protons and neutrons inside the nuclear of an atom.
What is ‘Criticality’ in Atomic/Nuclear Power Plants?
- Reactors are the heart of an atomic power plant, where a controlled nuclear fission reaction takes place that produces heat, which is used to generate steam that then spins a turbine to create electricity.
- Fission is a process in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or smaller nuclei, and usually some by-product particles.
- When the nucleus splits, the kinetic energy of the fission fragments is transferred to other atoms in the fuel as heat energy, which is eventually used to produce steam to drive the turbines.
- For every fission event, if at least one of the emitted neutrons on average causes fission, a self-sustaining chain reaction will take place.
- A nuclear reactor achieves criticality when each fission event releases a sufficient number of neutrons to sustain an ongoing series of reactions.
Controlling Criticality
- When a reactor is starting up, the number of neutrons is increased slowly in a controlled manner. Neutron-absorbing control rods in the reactor core are used to calibrate neutron production.
- The control rods are made from neutron-absorbing elements such as cadmium, boron, or hafnium.
- The deeper the rods are lowered into the reactor core, the more neutrons the rods absorb and the less fission occurs.
- Technicians pull up or lower down the control rods into the reactor core depending on whether more or less fission, neutron production, and power are desired.
- If a malfunction occurs, technicians can remotely plunge control rods into the reactor core to quickly soak up neutrons and shut down the nuclear reaction.
Why is this achievement significant?
- It is the biggest indigenously developed variant of the Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor (PHWR).
- The PHWRs, which use natural uranium as fuel and heavy water as moderator, is the mainstay of India’s nuclear reactor fleet.
- Until now, the biggest reactor size of the indigenous design was the 540 MWe PHWR, two of which have been deployed in Tarapur, Maharashtra.
- India works to ramp up its existing nuclear power capacity of 6,780 MWe to 22,480 MWe by 2031.
- The 700MWe capacity constitutes the biggest component of the expansion plan.
Back2Basics: India’s PHWR technology
- PHWR technology started in India in the late 1960s with the construction of the first 220 MWe reactor, Rajasthan Atomic Power Station, RAPS-1 under the joint Indo-Canadian nuclear co-operation.
- Canada supplied all the main equipment for this first unit, while India retained responsibility for construction, installation, and commissioning.
- For the second unit (RAPS-2), import content was reduced considerably, and indigenization was undertaken for major equipment.
- Following the withdrawal of Canadian support in 1974 after Pokhran-1, Indian nuclear engineers completed the construction, and the plant was made operational with a majority of components being made in India.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Madhubani paintings
Mains level: Not Much

An artist known as the ‘mask man’ of Bihar dispatches masks with hand-painted Madhubani motifs all over India.
Also read:
[Prelims Spotlight] Indian Paintings and Handicrafts
Madhubani Paintings
- Madhubani art (or Mithila painting) is a style of Indian painting, practised in the Mithila region of Bihar.
- This painting is done with a variety of tools, including fingers, twigs, brushes, nib-pens, and matchsticks and using natural dyes and pigments.
- It is characterized by its eye-catching geometrical patterns.
- It was traditionally created by the women of various communities in the Mithila region of the Indian subcontinent.
- This painting as a form of wall art was practised widely throughout the region; the more recent development of painting on paper and canvas mainly originated among the villages around Madhubani.
- It is these latter developments that led to the term “Madhubani art” being used alongside “Mithila Painting.”
Its features
- It uses two-dimensional imagery, and the colours used are derived from plants. Ochre, Lampblack and Red are used for reddish-brown and black, respectively.
- It mostly depicts people and their association with nature and scenes and deities from the ancient epics.
- Natural objects like the sun, the moon, and religious plants like tulsi are also widely painted, along with scenes from the royal court and social events like weddings.
- Generally, no space is left empty; the gaps are filled by paintings of flowers, animals, birds, and even geometric designs.
- Madhubani art has five distinctive styles: Bharni, Kachni, Tantrik, Godna and Kohbar.
- This painting has also received a GI (Geographical Indication) status.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Lonar Crater Lake, Pleistoscene epoch
Mains level: Not Much

The colour of Lonar lake water in Maharashtra’s Buldhana district turned pink due to a large presence of the salt-loving ‘Haloarchaea’ microbes, a probe carried out by a Pune-based institute has concluded.
Make a note of all saltwater lakes in India. Few of them are Pulicat, Pangong Tso, Chilika, and Sambhar Lakes etc.
Haloarchaea’ microbes
- Haloarchaea or halophilic archaea is a bacteria culture which produces pink pigment and is found in water saturated with salt.
- The increased salinity and pH facilitated the growth of halophilic microbes, mainly Haloarchaea.
- Basically, it is the biomass of these microbes and because of that, the surface of the water turned red or pink and as soon as the biomass subsided, the colour disappeared.
- The scientist said the colour of the lake is now returning to original as the rainy season has kicked in, allowing dilution of the water.
- Initially, it was thought for the red-pigmented Dunaliella algae due to which the water might have turned pink.
- Because of that, the salinity and pH/alkalinity levels have also come down and green algae have started growing in the water body.
About Lonar Lake
- Lonar Lake, also known as Lonar crater, is a notified National Geo-heritage Monument, saline (pH of 10.5), Soda Lake, located at Lonar in Buldhana district, Maharashtra.
- It was created by an asteroid collision with earth impact during the Pleistocene Epoch.
- It is one of the four known, hyper-velocity, impact craters in basaltic rock anywhere on Earth.
- It sits inside the Deccan Plateau—a massive plain of volcanic basalt rock created by eruptions some 65 million years ago.
- Its location in this basalt field suggested to some geologists that it was a volcanic crater.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Non-Personal Data
Mains level: Paper 3- Key stakeholder in the regulation of Non-Personal Data
The article examines the structures and role of key stakeholders in regulation of Non-Personal Data as per the report submitted by the committee headed by Kris Gopalakrishnan.
Context
- There is a realisation that data should be unlocked in public interest beyond the use by a few large companies
- Data, in many cases, are not just a subject of individual decision-making but that of communities, such as in the case of ecological information.
- Therefore, it is critical that communities are empowered to exercise some control over how the data are used.
- Recently the Non-Personal Data committee released a governance framework, which raises many concerns.
Following are the key stakeholder as defined in the report
1)Data principals
- As per the report, the first keyholders are data principals, who/ which can be individuals, companies or communities.
- The idea of communities as data principals is introduced ambiguously by the report.
- The report does not address the translation of offline inequalities and power structures to data rights.
2) Data custodians
- Data custodian is the one who undertake collection, storage, processing, and use of data in a manner that is in the best interest of the data principal.
- The details in this section are unclear.
- It is not specified if the data custodian can be the government or private companies only.
- It is also not clear what best interest is, especially when several already vague and possibly conflicting principal communities are involved.
- It is also not clear how communities engage with the custodian.
- Suggestion that data custodians can monetise the data they hold is especially problematic as this presents a conflict of interest with those of the data principal communities.
3) Data trustees
- The report talks about data trustees as a way for communities to exercise data rights.
- Trustees can be governments, citizen groups, or universities.
- There is no clarity on how “trust” is extended and fructified with the community, and how trustees are empowered to act on behalf of the community.
- The principles of a legal trust and the fiduciary responsibility that come with role of trustees are critical.
- Trustees, by definition, are bound by a duty of care and loyalty towards the principal and thus work in their best interests.
- Trustee has to negotiate on behalf of Data Principals’ data rights with technology companies and regulators.
- This thinking is not reflected in the report.
- Also, the relationship between the data principal communities and the trustees is not clear.
How will the ‘Trust’ function?
- The report explains data trusts comprising specific rules and protocols for containing and sharing a given set of data.
- Trusts can hold data from multiple custodians and will be managed by public authority.
- But the power, composition and functions of the trust are not established.
- One possible way to simplify the ecosystem would be to consider data trusts as a type of custodian.
- So that trustees can represent the community and act on behalf of the data principals.
Consider the question “What do you understand by Non-Personal Data. Examine its utility and need to treat as a public good.”
Conclusion
The committee should organise broader consultations to ensure that the objective of unlocking data in public interest and through collective consent does not end up creating structures that exacerbate the problems of the data economy and are susceptible to regulatory capture.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 2- Options in dealing with China
There are several options which India could explore in dealing with China with less cost but significant effectiveness. Diplomacy is one of them. What are the other options? Read the article to know…
Context
- China’s aggression and Galwan valley incident dismantles the Border Agreements of 1993, 1996, 2005 and 2013.
- Understanding China’s objectives become critical in this situation.
Analysing China’s objectives
- Humbling India in the eyes of Asia and the world was all important for China.
- Despite China’s territorial aggression, it would be a mistake to think that China is preparing for a conflict over territory.
- China is well aware that it cannot be certain whether it will emerge a victor from an all-out conflict with India.
- China cannot afford to jeopardise its future for the present.
- China has been intent on transforming the Asian region in its own image, and, simultaneously, seeking to become a continental and a maritime power.
What are the options to deal with China
- India may well find non-military tools not only more cost-effective but also less risky.
- 1) Exploiting the current widespread opposition to China, India must try to create international opinion in its support regarding border violations.
- 2) Cultivation of foreign leaders with a view to draw their specific attention to China’s aggressive policies and designs is the second option.
- India’s involvement with the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) should prove invaluable in this respect.
- 3) India must also overhaul its ‘messaging’ capacity.
- It should make greater use of technology to send across its message and ideas in its vicinity and across the globe, highlighting its peaceful intentions in stark contrast to China’s aggressive policies and tactics.
- 4) India must pay particular attention to relations with countries in its neighbourhood, such as Nepal and Bangladesh, and allies such as Iran and Vietnam.
- Relationship with these countries seems to have frayed at the edges, with India being more intent on strengthening relations with the West.
- Smaller countries of Asia, which constantly face China’s aggressive interference in their internal affairs, have not received much support from India, and this needs India’s attention.
- 5) India’s true strength is its unity in diversity. A truly united and resilient India is the best antidote to China’s attempts to humble India.
- China has never been able to properly understand, the strength India seems to derive from its spiritual, religious and cultural attributes, which are a part of its civilisational heritage.
- 6) India would do well to take pole position in propagating ‘Himalayan Buddhism’ which China has been seeking to subvert to achieve its ends.
Consider the question “To counter the challenges manifested by China through recent events India needs to explore along with other options the subtler tools of power available to it. Examine the other tools available with India.”
Conclusion
Military no doubt project the country’s power but there are other options with less cost and significant benefits. India should focus on these options as well while dealing with China.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: RAISE initiative
Mains level: Paper 3-Energy efficiency and safety
The Ministry of Power has launches Retrofit of Air-conditioning to improve Indoor Air Quality for Safety and Efficiency (RAISE) – a joint initiative of EESL and USAID.
Possible prelims question:
Q. The MAITREE programme recently seen in news is related to:
Trade/Energy Efficiency/Climate Change/ Strategic Relations
RAISE Initiative
- It aims to ensure cleaner and greener office spaces in the country.
- This is a part of the larger initiative developed for healthy and energy-efficient buildings, in partnership with US Agency for International Development’s (USAID) MAITREE programme.
Why RAISE?
- Poor air quality has been a concern in India for quite some time and has become more important in light of COVID pandemic.
- As people return to their offices and public spaces, maintaining good indoor air quality is essential for occupant comfort, well-being, productivity and overall public health, the statement noted.
About MAITREE programme
- The Market Integration and Transformation Program for Energy Efficiency (MAITREE) is a part of the US-India bilateral Partnership between the Ministry of Power and USAID.
- It is aimed at accelerating the adoption of cost-effective energy efficiency as a standard practice within buildings and specifically focuses on cooling.
Back2Basics: EESL
- Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL), under the administration of Ministry of Power, is working towards mainstreaming energy efficiency.
- It is implementing the world’s largest energy efficiency portfolio in the country.
- EESL aims to create market access for efficient and future-ready transformative solutions that create a win-win situation for every stakeholder.
About USAID:
- USAID is the world’s premier international development agency and a catalytic actor driving development results.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 3- India fiscal response to Covid-19
For all the talks over the size of Atmanirbhar package, India’s response turns out to be inadequate when compared with the other countries with similar levels of per capita income. This article analyses the same.
Context
- India’s fiscal response is compared to countries which are similar in GDP per capita, state capacity, and structure of the labour force.
- Before the Atmanirbhar Bharat package, India lagged significantly behind comparable developing countries.
- As of early July, the gap seems to have narrowed.
Comparison and challenges
- Due to the blurring of the distinction between fiscal and monetary components, ensuring comparable and accurate figures for fiscal responses is a challenge.
- For example, the total Atmanirbhar package is billed at 10% of GDP by the government.
- While the headline number for India’s fiscal response in international databases is around 4% of GDP.
- But some estimated that the new fiscal outlay is around 1.7% of GDP.
- Vietnam, Indonesia, Pakistan, and Egypt, all while averaging less stringent measures than those in India, have announced stimulus measures that are as large or more substantial, as a share of GDP.
Demand-side interventions in the package
- The one significant demand-side intervention in the Atmanirbhar Bharat package was ₹40,000 crore of additional outlay for the MGNREGA.
- Most other demand-side measures involve the frontloading, consolidation, or rerouting of existing funds.
How developing countries are financing responses
- Developing countries are resorting to drastic means to finance COVID-19 responses.
- Actions so far include the amendment of legal budget limits.
- Some are also exploring enhanced issuance of bonds-including a ‘pandemic bond’ by Indonesia.
- Central banks in many emerging economies are experimenting with purchases of public and private bonds in the secondary market (quantitative easing).
- Or some are directly purchasing government bonds on the primary market (monetising the deficit).
- In India, the debate continues over whether the Indian government should invoke the “escape cause” in the FRBM Act.
- Escape clause will enable the central bank to directly finance the deficit.
Cash transfer: Lessons for India
- Demand-side interventions announced by other developing countries could provide lessons for additional measures in India.
- Of the World Bank’s list of 621 measures across 173 countries, half were cash-based.
- While only 2% related to public works, a clear indication of the popularity of cash transfers over public works for income support,
- Countries have also significantly expanded coverage of their cash transfer programmes from pre-COVID-19 levels.
- Bangladesh and Indonesia have increased the number of beneficiaries by 163% and 111%, respectively.
- Indonesia’s cash schemes now cover more than 158 million people or 60% of the population.
- Additionally, the Indonesia central government has directed village authorities to focus their budgets on a cash-for-work programme.
Suggestions for India
- India could take these actions about cash transfers into account in decisions about expanding existing transfer programmes or even creating new ones.
- India has been a leader in employment guarantee policies with its flagship MGNREGA programme.
- This is the right time to expand entitlements MGNREGA.
- There is a need to introduce an urban version of the MGNREGA.
- In India, one reason for the subdued fiscal response and the resort to monetary measures is a concern with the debt-to-GDP ratio.
- However, aggregate demand and confidence in the economy have slumped and may not recover for many months.
- Additional fiscal outlay -would save lives and jobs today and might prevent a protracted slowdown.
Consider the question “How India fares in comparison with other countries over its fiscal response to Covid? Also examine the utility of income support schemes related to public works against the cash transfer schemes adopted by the other countries.”
Conclusion
Not spending more now, therefore, might only worsen the debt-to-GDP ratio if growth remains depressed. The fiscal outlay in the form of cash and in-kind transfers and expanded public works schemes is the need of the hour.
Original op-ed:
https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/op-ed/the-covid-19-fiscal-response-and-indias-standing/article32154153.ece
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Serological survey
Mains level: Paper 2- Health and pandemic control measures
A Serological Survey was recently conducted in New Delhi to determine the exposure of the novel coronavirus among the population.
Try this question from CSP 2019:
Which one of the following statements is not correct?
(a) Hepatitis B virus is transmitted much like HIV.
(b) Hepatitis B, unlike Hepatitis C, does not have a vaccine.
(c) Globally, the number of people infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses is several times more than those infected with HIV.
(d) Some of those infected with Hepatitis Band C viruses do not show the symptoms for many years.
Serological Survey
- A serological survey seeks to assess the prevalence of the disease in a population by detecting the presence of specific antibodies against the virus.
- A serological test is performed to diagnose infections and autoimmune illnesses. It can also be conducted to check if a person has developed immunity to certain diseases.
- The survey included the IgG Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) test which estimates the proportion of the population exposed to SARS-CoV-2 infection.
- The IgG test is not useful for detecting acute infections, but it indicates episodes of infections that may have occurred in the past.
- The test has been approved by ICMR for its high sensitivity and specificity.
Highlights of the Survey
- The study found the presence of antibodies in 22.86 percent of the people surveyed.
- It indicated that a large number of infected persons remain asymptomatic.
Why needed such survey?
- Since it is not possible to test everyone in the population, serological studies are used as a tool to make an estimate of the extent of disease spread in the community.
Conclusions from the survey
- Results show that a significant proportion of the population is still vulnerable to contracting the novel coronavirus infection.
- Containment measures need to continue with the same rigour.
- Non-pharmacological interventions such as physical distancing, use of face mask/cover, hand hygiene, cough etiquette and avoidance of crowded places etc. must be followed strictly.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NFC
Mains level: Paper 3- Urban floods and related issues
At least 43 years after India’s first and last commission on floods was constituted, there is no national-level flood control authority in the country so far.
Try this question for mains:
Q. What are the various causes of urban floods in India?
National Flood Commission
- Rashtriya Barh Ayog or the National Flood Commission (NFC) was set up by the Ministry of Agriculture and Irrigation in 1976.
- It aimed to study India’s flood-control measures after the projects launched under the National Flood Control Programme of 1954 failed to achieve much success.
NFCs recommendation
- In 1980, the NFC made 207 recommendations and four broad observations:
- First, it said there was no increase in rainfall in India and, thus, the increase in floods was due to anthropogenic factors such as deforestation, drainage congestion and badly planned development works.
- Second, it questioned the effectiveness of the methods adopted to control floods, such as embankments and reservoirs, and suggested that the construction of these structures be halted until their efficacy was assessed.
- Third, it said there have to be consolidated efforts among the states and the Centre to take up research and policy initiatives to control floods.
- Fourth, it recommended a dynamic strategy to cope with the changing nature of floods. An analysis of the report suggested that the problem began with the methods of estimating flood-prone areas of the country.
Why revive NFC?
- An accurate estimate is crucial for framing flood management programmes.
- The NFC estimated that the total area vulnerable to floods in 1980 was around 40 million hectares.
- There is another problem. The very definition of the flood-prone area does not reflect the effectiveness of the flood management works undertaken.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now








