Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CHAMPIONS Portal
Mains level: Not Much
In a major initiative, Union Ministry of MSME has launched CHAMPIONS portal for assisting Indian MSMEs march into the big league as National and Global Champions.
MSME sector has been hit badly by COVID. Initiatives like CHAMPIONS portal are crucial for this sector.
CHAMPIONS Portal
- ‘CHAMPIONS’ is a technology-driven Control Room-Cum-Management Information System.
- The CHAMPIONS is an acronym for Creation and Harmonious Application of Modern Processes for Increasing the Output and National Strength
- As the name suggests, the portal is basically for making the smaller units big by solving their grievances, encouraging, supporting, helping and handholding.
- It is a technology-packed control room-cum-management information system.
Three basic objectives of the CHAMPIONS
1) How to help the MSMEs in this difficult situation in terms of finance, raw materials, labour, permissions, etc.
2) How to help them capture new opportunities like manufacturing of medical accessories and products like PPEs, masks, etc.
3) How to identify the sparks, i.e., the bright MSMEs who can not only withstand but can also become national and international champions.
Technology imbibed in the portal
- In addition to ICT tools including telephone, internet and video conference, the system is enabled by Artificial Intelligence, Data Analytics and Machine Learning.
- It is also fully integrated on a real-time basis with GOI’s main grievances portal CPGRAMS and MSME Ministry’s own other web-based mechanisms.
- The entire ICT architecture is created in house with the help of NIC in no cost. Similarly, the physical infrastructure is created in one of the ministry’s dumping rooms in record time.
A hub and spoke model of network
- As part of the system, a network of control rooms is created in a Hub & Spoke Model.
- The Hub is situated in New Delhi in the Secretary MSME’s office.
- The spokes will be in the States in various offices and institutions of Ministry.
- As of now, 66 state-level control rooms are created as part of the system.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Articles related to Rajya Sabha.
Mains level: Paper 2- Importance of Rajya Sabha.
This article is about Rajya Sabha, the second chamber of our union legislature. Its utility was intensely debated in the Constituent Assembly. Now, after almost seven decades of its existence, we know that the house has proved its utility. So, what was the reasoning of those who were in support of its creation and what those who opposed its creation had on their mind? How bicameralism is connected to federalism? You’ll come to know the answers to these questions after reading the article.
Historical background
- The Rajya Sabha came into being on April 3, 1952 and held its first session on May 13 the same year.
- The central legislature that came into being under the Government of India Act, 1919 was bicameral.
- Under 1919 Act, Council of States had 60 members and Legislative Assembly had 145 members.
- The membership and voting norms for the Council of States were restrictive.
- These restrictions meant only wealthy landowners, merchants and those with legislative experience could enter it.
- Women could neither vote nor seek membership.
- The Government of India Act, 1935 proposed an elaborate and improved version of the second chamber, but this never materialised.
- The Constituent Assembly, which was formed in 1947, after adoption of the Constitution became the Provisional Parliament and made laws till 1952.
Bicameralism and the utility of second house
- Bicameralism is a principle that requires the consent of two differently constituted chambers of Parliament for making or changing laws.
- This principle came into operation in 1787 with the adoption of the U.S. Constitution.
- At present, 79 Parliaments of the world (41% of the total number) are bicameral.
- In The Federalist, the famous essay, it was stated that the second chamber enables a second and reflective expression of representative opinion besides checking the propensity to yield to the impulse of sudden and violent passions.
- French philosopher Montesquieu who said, “The legislative body being composed of two parts, they check one another by the mutual privilege of rejecting”.
- Walter Bagehot later noted that the retarding chamber will impede minor instances of parliamentary tyranny, though it will not prevent or really impede revolution.
Federalism and link with bicameralism
- Federalism has been in vogue since ancient times when some states got together to confer the power of law-making on a central authority.
- But modern federalism is entirely different given the complexity of geographical, regional, social and economic diversities marking the constituent units of a federation or a union.
- It is more so in India. The U.S. is a federation and so is India — each unit has a set of unique features.
- Federalism and bicameralism are linked because the federal character of a nation comprising constituent units can be reflected in, and secured by, a bicameral legislature.
Debate in the Constituent Assembly over need for the second house
- The proposal for the Rajya Sabha as a second chamber was subjected to serious argumentation and had a narrow escape.
- Opponents’ stand: A member of the Constituent Assembly asserted that an Upper House was not essential and viewed it as a creation of imperialism.
- Other member warned that such a chamber would only prove to be a “clog in the wheel of progress” of the nation.
- The proponents’ stand: A supporter of idea felt that it would introduce an element of sobriety and second thought besides lending voice to the constituent units in the legislative scheme of things.
- Ananthasayanam Ayyangar argued that a second chamber would enable the genius of the people to have full play besides checking hasty legislation.
- Replying to the debate on the motion N. Gopalaswami Ayyangar had to make a strong case for the second chamber.
- He argued that the most that we expect the Second Chamber to do is 1) to hold dignified debates on important issues 2) to delay legislation which might be the outcome of passions of the moment until the passions have subsided.
Consider the question, “Examine the role played by the Rajya Sabha as a law-making body. Do you agree that the Rajya Sabha has been successful in fulfilling the role expected of it by the makers of our Constitution?”
Conclusion
The mandate of the Rajya Sabha, as can be gleaned from the Constituent Assembly debates and the experiences of other Parliaments, is legislation — to revise or delay legislation without proving a clog in the wheel of the progress; to represent the interests of the States as a federal chamber, and be a deliberative body holding high-quality debates on important issues.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Emergency provision dealing with internal disturbance/ Provisions related to ordinances
Mains level: Paper 2- Changes made in labour laws without consultation.
The article examines the changes made in the labour laws by several states. The legal route to make these changes are different. While some states used the Emergency provision, others used the Ordinance route. One major issue with these changes is that these were brought in without consultation.
What legal route was used by the States?
- Changes were made by the several state government in the labour laws dealing with the maximum working hours and other provisions.
- These changes have been made through notifications issued by the State governments and will be applicable for the next three months.
- M.P. has also suspended most provisions of the Industrial Disputes Act, 1946 (except those related to retrenchment and layoffs) for 1,000 days for State undertakings.
- In addition, M.P. issued an ordinance to amend two laws.
- The M.P. Industrial Employment Standing Orders Act will apply to establishments with more than 100 workmen (up from the existing threshold of 50), in line with the Central Act.
- The ordinance also enables the government to exempt establishments from the provision of another Act that provided for a labour welfare fund.
- The Uttar Pradesh government has approved an ordinance that exempts establishments from all labour laws for three years with some exceptions.
- As this will override provisions of some Central laws, it will require the assent of the President or, in effect, the assent of the Central government.
- The question is, was there sufficient consultation before all these changes were made?
Constitutional provisions for the legal route taken: Emergency and ordinance
- As per the Constitution, the legislature has the authority to make laws.
- Such laws could delegate powers to the government which are in the nature of detailing some requirements.
- For example, the Factories Act allows State governments to exempt factories from the provisions of the Act during public emergencies for a maximum period of three months.
- A public emergency is defined as a grave emergency whereby the security of India or any part is threatened by war, external aggression or internal disturbance.
- Most States have used this provision, presumably interpreting the current situation as an ‘internal disturbance’.
- Haryana has used a provision that allows relaxation of work hours “to deal with an exceptional press of work”.
- The Constitution also permits Central and State governments to make laws through the issuance of an ordinance when the legislature is not in session.
- Such a law needs to be ratified by the legislature within six weeks of the beginning of the next session. M.P. and U.P. are using this procedure.
Issues with the changes made
- Usually, any change in an Act follows a rigorous process of public consultation, scrutiny by committees of Parliament, and debates in the House before being approved.
- The changes described here have not gone through such a process.
- However, most of these have a three-month time limit, and any extension would need to be approved by the legislature.
The four labour codes
- The Parliament is consolidating 29 existing laws into four codes dealing with- 1) wages, 2) occupational safety and health, 3) industrial relations,4) social security.
- The first of these has been enacted, the Standing Committee on Labour has submitted the report on the next two, and is examining the last.
- The Code on Occupational Safety and Health does not specify the maximum hours of work but empowers the government to do so.
- The Standing Committee report states that the government agreed to incorporate a provision of maximum eight hours per day with overtime permitted for certain types of industry.
Consider the question “Several States made changes in the labour laws to deal with the problems caused by the corona pandemic. Examine the legal provisions used for making such changes by various States. What are the issues with such changes?”
Conclusion
Given the emergency, the government has to take quick action and change the response as the situation evolves. However, that should not be a reason to exclude the processes of consultation with and scrutiny by elected representatives. The legitimacy of state action in a parliamentary democracy comes from the fact that there is constant oversight and check by elected representatives.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: WTO
Mains level: Paper 3- Changes in trade politics in the US and opportunities for India.
The article focuses on the changes in the US trade politics fueled by the corona pandemic. Also there has been a growing demand for abandoning the WTO. So, amid this shift in the US politics, what are the opportunities for India at the global level?
What went wrong with the WTO: The US point of view
- Latest opposition to the WTO was expressed in a forceful article by a US senator, Josh Hawley.
- In his opinion, corona pandemic expresses the hard truth about the modern global economy: it weakens American workers and empowers China’s rise.
- So, what went wrong?
- Capital and goods moved across borders easier than before but so did jobs. And too many jobs left America’s borders for elsewhere.
- As factories closed, workers suffered, from small towns to the urban core.
- So, he wants US to abandon the WTO.
Rise of trade politics in the US
- Under Trump, the Republican Party has turned from the champion to a critic of free trade.
- The Democratic Party, which embraced globalisation since the early 1990s, has seen the erosion of working-class support.
- Elections this year could reveal if the shifting alignments on trade are now cast in stone or if anti-trade sentiment in America is deep and wide.
What alternatives are suggested by the senator?
- In replacing the WTO, Hawley suggests the following two measures-
- 1) The United States must seek new arrangements and new rules, in concert with other free nations, to restore America’s economic sovereignty.
- 2) This, in turn, involves building a new network of trusted friends and partners to resist Chinese economic imperialism.
How this matters for India?
- India will have to take a fresh look at the global economy battered by the coronavirus.
- India should pay close attention to Hawley’s theme on working with “trusted friends and partners” to restructure international trade.
- Hawley is not alone in articulating this view.
- Reuters reported from Washington that the Trump Administration is “turbocharging” an initiative to rearrange the global supply chains currently centered on China.
- This rearrangement of the global supply chain offers an opportunity for India to lead the future global supply chains.
Consider the question, “Critically analyse the opportunities presented to India by the changes in trade politics in the US”.
Conclusion
Hobbled as it was by shaky political coalitions and preoccupied by multiple domestic challenges, India in the mid-1990s struggled to cope with the profound changes in the global economic order. As the world trade system arrives at a contingent moment a quarter of a century later, India is hopefully better prepared.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SRS, IMR
Mains level: Not Much
The Registrar General of India released its Sample Registration System (SRS) bulletin based on data collected for 2018.
Since we are talking about birth rates and death rates, how about revising Demographic Transition Model. Can you recall 4 distinctive stages of Indian Demographic history?
Sample Registration System (SRS)
- The SRS is a demographic survey for providing reliable annual estimates of infant mortality rate, birth rate, death rate and other fertility and mortality indicators at the national and sub-national levels.
- Initiated on a pilot basis by the Registrar General of India in a few states in 1964-65, it became fully operational during 1969-70.
- The field investigation consists of a continuous enumeration of births and deaths in selected sample units by resident part-time enumerators, generally Anganwadi workers and teachers; and an independent retrospective survey every six months by SRS supervisors.
- The data obtained by these two independent functionaries are matched.
Highlights of the data
Birth and death rates
- According to the data released the national birth rate in 2018 stood at 20, and death and infant mortality rates stood at 6.2 and 32, respectively.
- The rates are calculated per one thousand of the population.
- Madhya Pradesh has the worst infant mortality rate in the country while Nagaland has the best.
- Chhattisgarh has the highest death rate, while Delhi has the lowest.
- Bihar continues to remain at the top of the list in the birth rate while Andaman and Nicobar are at the bottom.
Infant mortality
- The data shows that against the national infant mortality rate (IMR) of 32, Madhya Pradesh has an IMR of 48 and Nagaland 4.
- Bihar has the highest birth rate at 26.2 and Andaman and Nicobar Islands has a birth rate of 11.2.
- Chhattisgarh has the highest death rate at 8 and Delhi, an almost entirely urban state, has a rate of 3.3, indicating better healthcare facilities.
- As far as IMR is concerned, the present figure of 32 is about one-fourth as compared to 1971 (129).
- In the last 10 years, IMR has witnessed a decline of about 35 per cent in rural areas and about 32 per cent in urban areas. T
Birth rate
- The birth rate is a crude measure of fertility of a population and a crucial determinant of population growth.
- India’s birth rate has declined drastically over the last four decades from 36.9 in 1971 to 20.0 in 2018.
- The rural-urban differential has also narrowed. However, the birth rate has continued to be higher in rural areas compared to urban areas in the last four decades.
- There has been about an 11 per cent decline in the birth rate in the last decade, from 22.5 in 2009 to 20.0 in 2018. The corresponding decline in rural areas is 24.1 to 21.6, and in urban areas, it is 18.3 to 16.7.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NSG, NPT, Op Smiling Buddha
Mains level: India's nuclear policy
Yesterday, May 11 was celebrated as the National Technology Day. It marks the day on which India successfully test-fired its first nuclear bombs in 1998.
Practice question for mains
Q. India’s nuclear policy of ‘No First Use’ needs a revamp. Examine.
India and nuclear weapons
- India is currently among eight countries in the world that have a publicly known nuclear weapons program.
- At the time of our independence, leaders were opposed to fully embracing nuclear weapons.
- Just two years before in 1945, the world had witnessed the horrific nuclear bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
- Mahatma Gandhi called the use of nuclear weapons morally unacceptable.
Why India did equip itself with nuclear arms?
- Then PM Jawaharlal Nehru was sceptical but kept the door open for future consideration.
- This future beckoned early, as India’s defeat in the 1962 Sino-Indian War gave rise to legitimate fears about national security.
- Then in 1974, India conducted its first nuclear test, codenamed “Smiling Buddha”, at Pokhran in Rajasthan.
- Then-Prime Minister Indira Gandhi called the test a peaceful nuclear explosion.
- India demonstrated to the world that the country could defend itself in an extreme situation and chose not to immediately weaponize the nuclear device it tested at Pokhran.
The Pokhran II tests
- India’s fence-sitting finally ended when it detonated another device in 1998, again at Pokhran.
- Assigned the code name Operation Shakti, the mission was initiated on May 11, 1998.
- The tests consisted of 5 detonations, the first being a fusion bomb while the remaining four were fission bombs.
- One fusion and two fission bombs were tested on May 11, and two more fission bombs on May 13.
- With the tests, India achieved its objective of building fission and thermonuclear weapons with yields up to 200 kilotons.
Aftermath
- After Pokhran-II, Vajpayee had declared India a nuclear state — then the sixth country in the world to join this league.
- Unlike in 1974, India had this time chosen to actively develop its nuclear capabilities, and the tests followed economic sanctions by the United States and Japan. The sanctions were later lifted.
Back2Basics: India’s nuclear programme
- India started its own nuclear programme in 1944 when Homi Jehangir Bhabha founded the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research.
- Physicist Raja Ramanna played an essential role in nuclear weapons technology research; he expanded and supervised scientific research on nuclear weapons and was the first directing officer of the small team of scientists that supervised and carried out the test.
- After independence, PM Nehru authorised the development of a nuclear programme headed by Homi Bhabha.
- The Atomic Energy Act of 1948 focused on peaceful development.
- India was heavily involved in the development of the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty but ultimately opted not to sign it.
- In 1954, two important infrastructure projects were commissioned. The first established Trombay Atomic Energy Establishment at Mumbai (Bombay). The other created a governmental secretariat, Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), of which Bhabha was the first secretary.
Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG)
- The NSG is a multilateral export control regime and a group of nuclear supplier countries that seek to prevent nuclear proliferation by controlling the export of materials, equipment and technology that can be used to manufacture nuclear weapons.
- The NSG was founded in response to the Indian nuclear test in May 1974 and first met in November 1975.
- It was solely aimed to deny advanced technology, and isolate and contain India.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Toda embroidery
Mains level: Not Much

Many women and indigenous Toda artisans from the Nilgiris are producing thousands of stylish, embroidered masks for local residents, police, and sanitary workers.
Recently, the Assamese Gamosa was in new. Now the Pukhoor Embroidery has made it into the list. Keep a note of all such handicrafts. We can expect a match the pair based prelim question.
Toda Embroidery
- The Toda Embroidery, also locally known as “pukhoor” is an artwork among the Toda pastoral people of Nilgiris, in Tamil Nadu, made exclusively by their women.
- The embroidery, which has a fine finish, appears like a woven cloth but is made with the use of red and black threads with a white cotton cloth background.
- Both sides of the embroidered fabric are usable and the Toda people are proud of this heritage.
- This handicraft product is listed as a geographically tagged product and is protected under the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration & Protection) Act (GI Act) 1999.
Related facts
- The local terms used to describe the embroidery work are ‘kuty’ or ‘awtty’ meaning “stitching” and ‘kutyvoy’ meaning the embroidered piece.
- The materials used in this work are roughly woven white cloth, woollen black and red threads with use occasionally of blue threads and manufactured needles.
- The designs developed relate to nature and the daily cycle of life.
- The patterns used in Toda embroidery do not cover many floral motifs but generally cover celestial bodies (like Sun and Moon), reptiles, animals, and horns of buffaloes, made in crimson and black colours.
- Rabbit ears are a constant depiction on the boundary of the embroidered cloth. Another common design in the form of black triangles in a box design is done in honour of their first priest.
- Women who do embroidery consider their work as a “tribute to Nature”.
- As a traditional garment, it is worn by both men and women at all ceremonial occasions and also at funerals. Elderly people of the community wear this cloth daily.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: GK Gokhale
Mains level: Gokhale and his contribution in freedom struggle

The Prime Minister has paid tributes to Gopal Krishna Gokhale on his birth anniversary.
These days, personality-based prelims questions are quite prevalent.
Q.) He wrote biographies of Mazzini, Garibaldi, Shivaji and Shri Krishna; stayed in America for some time; and was also elected to the Central Assembly. He was – (CSP 2018)
a) Aurobindo Ghosh
b) Bipin Chandra Pal
c) Lala Lajpat Rai
d) Motilal Nehru
Gopal Krishna Gokhale (1866-1915)
- Gokhale was a liberal political leader and a social reformer during the Freedom Movement.
- Gokhale was a senior leader of the Indian National Congress (INC) and the founder of the Servants of India Society.
- Through the Society as well as the Congress and other legislative bodies he served in, Gokhale campaigned for Indian self-rule and for social reforms.
Gokhale and INC
- Gokhale became a member of the INC in 1889, as a protégé of social reformer MG Ranade.
- He was the leader of the moderate faction of the Congress party that advocated reforms by working with existing government institutions.
Quest for political reforms
- Gokhale’s mentor, justice M.G. Ranade started the Sarvajanik Sabha Journal.
- Gokhale’s deposition before the Welby Commission on the financial condition of India won him accolades.
- He played a leading role in bringing about Morley-Minto Reforms (1909), the beginning of constitutional reforms in India.
Servants of India Society
- In 1905, when Gokhale was elected president of the INC and was at the height of his political power, he founded the Servants of India Society.
- It aimed to specifically further one of the causes dearests to his heart: the expansion of Indian education.
- The Society took up the cause of promoting Indian education in earnest, and among its many projects organised mobile libraries, founded schools, and provided night classes for factory workers.
Involvement in the government
- In 1899, Gokhale was elected to the Bombay Legislative Council.
- He was also elected to the Imperial Council of the Governor-General of India as a non-officiating member representing Bombay Province.
Mentor to Gandhi
- Gokhale was famously a mentor to Mahatma Gandhi in the latter’s formative years.
- In 1912, Gokhale visited South Africa at Gandhi’s invitation.
- As a young barrister, Gandhi returned from his struggles and received personal guidance from Gokhale, including a knowledge and understanding of India and the issues confronting common Indians.
- By 1931, Gandhi emerged as the leader of the Indian Independence Movement. In his autobiography, Gandhi calls Gokhale his mentor and guide.
His literary works
- In 1908, Gokhale founded the Ranade Institute of Economics.
- He started the English weekly newspaper, The Hitavad (The people’s paper).
- He also published a daily newspaper titled Jnanaprakash, which allowed him to voice his reformist views on politics and society.
With inputs from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gopal_Krishna_Gokhale
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: APY, NPS, PFRDA
Mains level: Old age security concerns addressed by APY

The flagship social security scheme ‘Atal Pension Yojana’ (APY) has completed five years of successful implementation.
Five years of successfull implemention of APY is a significant feat. A statement based prelims question on terms of enrolment of the APY can be asked.
Atal Pension Yojana
- APY is a government-backed pension scheme, primarily targeted at the unorganised sector.
- It is a social security scheme launched by the government on 9th May 2015 to provide a defined pension between Rs 1,000 to Rs 5,000.
- It aims of delivering old age income security particularly to the workers in the unorganised sector with a guarantee of minimum pension after 60 years of age.
Terms of enrolment
- APY can be subscribed by any Indian citizen in the age group of 18-40 years having a bank account and its uniqueness is attributable to three distinctive benefits.
- First, it provides a minimum guaranteed pension ranging from Rs 1000 to Rs 5000 on attaining 60 years of age,
- Secondly, the amount of pension is guaranteed for a lifetime to spouse on death of the subscriber.
- And lastly, in the event of the death of both the subscriber and the spouse, entire pension corpus is paid to the nominee.
Success of the scheme
- The scheme has now 2.23 crores enrolment.
- Apart from remarkable enrolments, the scheme has been implemented comprehensively across the country covering all states and UTs with male to a female subscription ratio of 57:43.
About PFRDA
- Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA) is the statutory authority established by an enactment of the Parliament.
- It aims to regulate, promote and ensure orderly growth of the National Pension System (NPS) and pension schemes to which this Act applies.
- NPS was initially notified for central government employees recruits w.e.f. 1st Jan 2004 and subsequently adopted by almost all State Governments for its employees.
- NPS was extended to all Indian citizens (resident/non-resident/overseas) on a voluntary basis and to corporates for its employees.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SwasthVayu

National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL) Bangalore, a constituent of the lab of CSIR has developed a Non-Invasive BiPAP Ventilator ‘SwasthVayu ’in a record time of 36 days to treat COVID-19 patients.
The name ‘SwasthVayu’ can be tricky to guess, specially after some days. In prelims, UPSC may throw some options related to air pollution.
SwasthVayu
- A ventilator is a machine that provides mechanical ventilation by moving breathable air into and out of the lungs, to deliver breaths to a patient who is physically unable to breathe, or breathing insufficiently.
- BiPAP (Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure) Non-Invasive ventilator is a microcontroller-based precise closed-loop adaptive control system.
- It is a built-in biocompatible “3D printed manifold & coupler” with HEPA filter (Highly Efficient Particulate Air Filter).
Benefits of SwasthVayu
- The major advantage of this machine is that it is simple to use without any specialized nursing, cost-effective, compact and configured with the majority of indigenous components.
- This is ideal for treating COVID -19 patients in Wards, Makeshift Hospitals, dispensaries and home in current Indian COVID 19 scenario.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: APMC, e-NAM
Mains level: Paper 3- Agri-marketing and PDS, scope for improvement
Agriculture is still the mainstay of Indian economy. There are certain problems that persist in the agri-marketing and PDS. The author suggests to use the present corona crisis to embark on the path of the reform in these areas.
Supply lines maintained during the lockdown
- India seems to have contained the mortality rate from Covid-19 to 3.3% which is lower than the global average of about 7 per cent.
- On the food front too, India has done reasonably well.
- Despite initial disruptions in supply lines, India has somehow managed to feed its large population of 1.37 billion.
- In fact, if there is any complaint, it is from the producer’s side that the prices of perishables have collapsed in some parts of the country.
- But, from the consumer’s point of view, even for perishables like milk and vegetables, supply lines were quickly restored and food is easily available in the markets at reasonable prices.
- On keeping supply lines for essential food alive and running, those in the government managing the food logistics surely deserve to be complimented.
Reforms in agri-marketing and PDS
- Agriculture still engages India’s largest workforce.
- And it may be the only sector that registers a respectable growth this year as almost all other major sectors may plummet into negative territory.
- Agriculture sector is in urgent need of the reforms that can help farmers get a better price for their produce with consumers still paying a reasonable price for their food.
- Following ways are suggested for agri-marketing:
- While the APMC markets can keep doing their business as usual, it is time to open channels for direct buying from farmers/farmer producer organisations (FPOs).
- Any registered large buyer, be it processors or retail groups or exporters must be encouraged by providing them with a license, that is valid all over India.
- They should be exempted from any market fee and other cesses as they will not be using the services of the APMC market yards.
- E-NAM can flourish if grading and dispute settlement mechanisms are put in place.
- Private mandis with modern infrastructure need to be promoted in competition with APMCs.
- On the PDS front, we need to move towards cash transfers that can be withdrawn from anywhere in the country.
- Some initiative has already been taken by the Madhya Pradesh and even Uttar Pradesh is now moving along these lines.
- But much more can be done to put India’s agri-marketing and PDS system on a more efficient path.
Consider the question asked by the UPSC in 2014 “There is also a point of view that Agricultural Produce Marketing Committees set up under the State Acts have not only impeded the development of agriculture but also have been the cause of food inflation in India. Critically examine.”
Conclusion
The recovery of the economy, whether it will be V-shape or J-shape, depends upon the package that the government announces. The mega reforms need to be built in this recovery package.
Agriculture Produce Marketing Committee Regulation (APMC) Act.
- All wholesale markets for agricultural produce in states that have adopted the Agricultural Produce Market Regulation Act (APMRA) are termed as “regulated markets”.
- With the exception of Kerala, J & K, and Manipur, all other states have enacted the APMC Act.
- It mandates that the sale/purchase of agricultural commodities notified under it are to be carried out in specified market areas, yards or sub-yards. These markets are required to have the proper infrastructure for the sale of farmers’ produce.
- Prices in them are to be determined by open auction, conducted in a transparent manner in the presence of an official of the market committee.
- Market charges for various agencies, such as commissions for commission agents (arhtiyas); statutory charges, such as market fees and taxes; and produce-handling charges, such as for cleaning of produce, and loading and unloading, are clearly defined, and no other deduction can be made from the sale proceeds of farmers.
- Market charges, costs, and taxes vary across states and commodities.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: G-7, G-20, BRI etc.
Mains level: Paper 2- Recent changes in the global order that were hastened by the pandemic.
The article examines 7 trends that have been emerging in the global order for quite some time now. The corona crisis has only accentuated these trends. So, what are these trends? read to know more.
1. The rise of Asia
- The first trend which became clear in the aftermath of the 2008 global financial crisis is the rise of Asia.
- Economic historians pointed to its inevitability, recalling that till the 18th century, Asia accounted for half the global GDP.
- The Industrial Revolution accompanied by European naval expansion and colonialism contributed to the rise of the West, and now the balance is being restored.
- The 2008 financial crisis showed the resilience of Asian economies.
- And even today, economic forecasts indicate that out of the G-20 countries, only China and India are likely to register economic growth during 2020.
- Asian countries have also demonstrated greater agility in tackling the pandemic compared to the United States and Europe.
- This is not limited to China but a number of other Asian states have shown greater responsiveness and more effective state capacity.
- Consequently, Asian economies will recover faster than those in the West.
2. Decline of the US
- The second trend is the retreat of the U.S.after a century of being in the forefront of shaping the global order.
- The U.S. played a decisive role in shaping the world, from the World Wars to the leadership of the western world during the Cold War, molding global responses to threats posed by terrorism or proliferation or climate change.
- But recent examples show that interventions in Afghanistan and Iraq have become quagmires that have sapped domestic political will and resources.
- President Donald Trump called for “America first” and during the current crisis, the U.S.’s efforts at cornering supplies of scarce medical equipment and medicines and acquiring biotech companies engaged in research and development in allied states, shows that this may mean “America alone”.
- Moreover, even as countries were losing trust in the U.S.’s leadership, its mishandling at the home of the pandemic indicates that countries are also losing trust in the U.S.’s competence.
3. Weakening unity of the EU
- A third trend is the European Union’s continuing preoccupation with internal challenges.
- This internal disruption is generated three factors: 1) EU’s expansion of membership to include East European states 2) Impact of the financial crisis among the Eurozone members 3) Ongoing Brexit negotiations.
- Threat perceptions vary between old Europe and new Europe making it increasingly difficult to reach agreement on political matters e.g. relations with Russia and China.
- Rising populism has given greater voice to Euro-sceptics and permitted some EU members to espouse the virtues of “illiberal democracy”.
- Adding to this is the North-South divide within the Eurozone.
- This divide was seen when austerity measures were imposed on Greece, Italy, Spain and Portugal a decade ago by the European Central Bank.
- These austerity measures were persuaded by the fiscally conservative Austria, Germany and the Netherlands.
- The EU lacked solidarity when Italy was battling the pandemic alone.
- Further damage was done when Italy was denied medical equipment by its EU neighbours who introduced export controls.
- Schengen visa or free-border movement has already become a victim to the pandemic.
- The EU will need considerable soul searching to rediscover the limits of free movement of goods, services, capital and people, the underlying theme of the European experiment of shared sovereignty.
4. Rise of China
- China’s growing economic role has been visible since it joined the World Trade Organization in 2001.
- Its more assertive posture has taken shape under President Xi Jinping’s leadership with the call that a rejuvenated China is now ready to assume global responsibilities.
- In recent years, the U.S.-China relationship moved from cooperation to competition; and now with trade and technology wars, it is moving steadily to confrontation.
- A partial economic de-coupling had begun and will gather greater momentum.
- The Belt and Road Initiative involves investing trillions of dollars in infrastructure building as a kind of pre-emptive move against any U.S. attempts at containment.
- Even if Mr Xi’s leadership comes under questioning, it may soften some aggressive policy edges but the confrontational rivalry with the U.S. will remain.
5. Failure of multinational institutions
- With COVID-19, international and multilateral bodies are nowhere on the scene.
- The World Health Organisation (WHO) was the natural candidate to lead global efforts against the health crisis but it has become a victim of politics.
- The UN Security Council (UNSC), the G-7 and the G-20 are paralysed when the world faces the worst recession since 1929.
- The reality is that these institutions were always subjected to big power politics.
- During the Cold War, U.S.-Soviet rivalry blocked the UNSC on many sensitive issues and now with major power rivalry returning, finds itself paralysed again.
- Agencies such as WHO have lost autonomy over the decades as their regular budgets shrank.
- Budget constraints forced them to increasingly rely on voluntary contributions sourced largely from western countries and foundations.
- The absence of a multilateral response today highlights the long-felt need for reform of these bodies but this cannot happen without collective global leadership.
6. The oil prices
- The two trends were changing energy markets: 1)Growing interest in renewables and green technologies on account of climate change concerns. 2) The U.S. emerging as a major energy producer.
- Now, a looming economic recession and depressed oil prices will exacerbate internal tensions in West Asian countries which are solely dependent on oil revenues.
7. Stability of West Asia
- Long-standing rivalries in the region have often led to local conflicts but can now create political instability in countries where regime structures are fragile.
Consider the question “The Corona crisis contributed to speeding the failure of a global order which had been faltering before the pandemic afflicted the world. Examine the trends that have been accentuated by the pandemic.”
Conclusion
The vaccine may end the corona crisis when it comes, but the unfolding trends in the geopolitics have been altering the world even before the corona crisis and continue to do so after a pandemic is over.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: IBC 2016 provisions.
Mains level: Paper 3- IBC provisions and need for novel approach to deal with the economic fallout of the pandemic.
In this article the author suggests a new approach to deal with multiple bankruptcies and stressed assets that would come up post COVID. So, what is the new approach and how it is different from the existing IBC? Read further.
Why is speed of resolution important?
- First, because it is the only way to revive the economy.
- As revenues have dried up cash flow problems have cascaded down the supply chain.
- Firms will consequently be unable to restart production unless they first get credit to pay their suppliers and workers.
- But impaired firms cannot get credit and impaired banks cannot provide it.
- So, the entire economy will be stuck unless the balance sheet problem is sorted out.
- Second, speed will also minimise the losses from the COVID crisis.
- The value of bankrupt firms decays rapidly over time, and the bill for this loss will have to be borne ultimately by the government.
- So, speed is necessary to contain the damage to the government’s financial position, which has been badly eroded by the COVID crisis.
- But moving quickly will be difficult.
- The only real mechanism that currently exists to handle stress and bankruptcy is the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) system, which has been suspended for six months.
Why the IBC cannot help much?
- Many have therefore argued for bringing the IBC back into operation as soon as possible.
- Why such a strategy would not be very effective? The system is slow, with many cases taking two years or more; it could easily become overwhelmed completely if it is forced to absorb a large new set of bankrupt firms.
- In addition, the IBC envisages that banks maximise their recoveries by auctioning off the bankrupt firms to the highest bidder.
- But in a nation and indeed a world, where all balance sheets are damaged, it is not obvious who would be able to buy these firms, or at what prices.
- So recovery rates from sales could be low, undermining the objective of the exercise.
- Even if strong bidders could be found, there is a fundamental political, even philosophical, question of whether it is really right to take these firms away from their promoters.
- After all, many of these firms did nothing wrong; they got into financial difficulties because of the corona crisis.
So, what is the solution?
- What is needed is a new set of procedures that can utilise much of the existing IBC framework, but are simple, straightforward, and prompt, with a built-in expiry clause.
- Let’s Call them Special Non-Adversarial Procedures (SNAP).
- As soon as the lockdown is largely over, the IBC creditor committees (CoCs) could meet to assess the new wave of NPAs.
- The largest, most complex cases — say, those with debts exceeding Rs 10,000 crore — would be sent to the IBC for regular treatment.
- But all other cases would be eligible under SNAP
- After all, the wider the set of companies that are put back on their feet quickly, the stronger the recovery will be.
How would the SNAP work?
- Under SNAP, CoCs would, over the next three months, examine delinquent firms’ financial records, checking to see whether they are actually viable.
- If so, these firms would be designated as Lockdown Affected Enterprises (LAEs), eligible under SNAP.
- Since the basis of the designation would be that the firm is fundamentally sound but because of COVID impact, an Insolvency Professional (IP) appointed by the CoC would work with existing management (who would continue to run the firm) to arrange for interim finance.
- Then, the IP would assess how much of a debt reduction the firm needs, and within three months would present a specific proposal to the CoC.
- If the CoC can reach a two-third majority in favour of the proposal, the promoter would keep the firm, while the firm would be granted immediately released from bankruptcy.
- Since the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) is already overloaded, it would not be involved at all in SNAP.
- If the CoC cannot reach agreement within the three-month deadline, or if at any subsequent point the firm defaults on its newly reduced debt, it would be sent to the IBC for resolution.
- SNAP would be disbanded by end-December 2020.
Checks and balances under SNAP
- Such a system would have a series of checks and balances, to prevent firms from securing undeserved debt reductions.
- Banks would need to certify that defaulters are truly LAEs.
- IPs would need to certify the size of the debt reduction.
- A large majority of creditor banks would need to agree to the IP’s proposal.
What should be the role of the government in SNAP?
- With these checks and balances in place, the government should then commit to two things.
- First, it should provide some legal cover, ensuring that bankers would not be subject to investigations by the anti-corruption agencies, as long as they followed the LAE rules.
- Second, the public sector banks would be compensated for the costs of the reduction in the value of the asset, automatically and fully.
Major advantage of SNAP
- Besides speed, SNAP would have one further major advantage.
- It would reduce the adversarial nature of the IBC process, arising because promoters are forced to cede their firms.
- Under the proposed system, promoters would not only have incentives to cooperate; they would actually want to take the initiative, applying for LAE designation themselves, in the hopes that they could get back to business as soon as possible.
- Such a system might seem difficult to envisage, but it is certainly feasible: It is a design feature under Chapter 11 of the American bankruptcy act.
- If SNAP succeeds, some of the special procedures could be introduced permanently into the IBC framework, adding a new dimension: Not just liquidation and rehabilitation under new promoters but rehabilitation under existing management.
Way forward
- After SNAP, repair of the financial system would have to go back to addressing the long-standing problems, which will have been aggravated by the crisis.
- Firms that were unviable even before the COVID crisis would be sent directly to the IBC, but with the IBC reformed.
- The government should issue guidelines focusing on the following three-
- 1. Focusing the COCs on the goal of maximising value, disregarding non-commercial objectives.
- 2. Directing the NCLT courts to focus on the CoCs’ adherence to the procedure rather than on the merits of their decisions.
- 3. Increasing competition in the auction by allowing promoters to bid for their assets, as long as they have not been declared wilful defaulters.
- For the power and real estate sectors, a sui generis approach via the creation of a bad bank is still the best way forward.
- Real estate resolutions need to take into account the interests of home-owners, something that is almost impossible to do under the IBC.
Consider the question, “Economic revival after the pandemic would require some tweaks in the IBC as it was not designed to handle such situations. Suggest the ways to handle the bankruptcies more effectively and changes that are desired in the IBC.”
Conclusion
Introducing three-pronged strategy quickly would set the stage for the economic recovery of India: 1) Special, expedited, non-adversarial and time-bound bankruptcy procedures (SNAP) for COVID-affected firms 2) A reformed IBC focused squarely on loss-minimisation 3)Bad banks for stressed assets in the power and real estate sectors.
Back2Baciscs: What is Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code-2016?
- The Code creates time-bound processes for insolvency resolution of companies and individuals. These processes will be completed within 180 days. If insolvency cannot be resolved, the assets of the borrowers may be sold to repay creditors.
- The resolution processes will be conducted by licensed insolvency professionals (IPs). These IPs will be members of insolvency professional agencies (IPAs). IPAs will also furnish performance bonds equal to the assets of a company under insolvency resolution.
- Information utilities (IUs) will be established to collect, collate and disseminate financial information to facilitate insolvency resolution.
- The National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) will adjudicate insolvency resolution for companies. The Debt Recovery Tribunal (DRT) will adjudicate insolvency resolution for individuals.
- The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India will be set up to regulate functioning of IPs, IPAs and IUs.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not Much
Mains level: Inter-state workers migration
Context
- Following the novel coronavirus pandemic, the nationwide lockdown announced on March 24 at short notice has caused immense distress to migrant workers around the country.
- Hundreds have been seen trying to walk home to Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal and Odisha from their places of work in Rajasthan, Delhi, Maharashtra, Gujarat and so forth.
Try a mains question on this issue:
Inter state migrants face social, economic and cultural shocks. Discuss some steps taken by center and state governments. Also suggest further reforms.
Inter-State workers: Where is their almighty?
- Recently, 16 migrant labourers who were trying to return to Madhya Pradesh, their home State, on foot were killed when a goods train ran over them.
- Questions are being raised about their welfare and the lack of legal protection for their rights.
- Those working in the field of labour welfare have recalled a 1979 law to regulate the employment and working conditions of inter-State migrants.
- The lack of serious implementation has led to their rights being ignored.
What about occupational safety?
- As part of the present regime’s efforts towards consolidating and reforming labour law, a Bill has been introduced in Parliament called the Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions Code, 2019.
- The proposed code seeks to merge 13 labour laws into a single piece of legislation.
- The Inter-State Migrant Workmen (Regulation of Employment and Conditions of Service) Act, 1979, is one of them.
- Activists fear that specific safeguards given to migrant workers may be lost as a result of this consolidation.
Inter-State Migrant Workmen Act, 1979: What does the law envisage?
- The Act seeks to regulate the employment of inter-State migrants and their conditions of service.
- It is applicable to every establishment that employs five or more migrant workmen from other States; or if it had employed five or more such workmen on any day in the preceding 12 months.
- It is also applicable to contractors who employed a similar number of inter-State workmen.
- The Act would apply regardless of whether the five or more workmen were in addition to others employed in the establishment or by the contractors.
- It envisages a system of registration of such establishments. The principal employer is prohibited from employing inter-State workmen without a certificate of registration from the relevant authority.
- The law also lays down that every contractor who recruits workmen from one State for deployment in another State should obtain a licence to do so.
What are the beneficial provisions for inter-State migrants in it?
- The provision for registration of establishments employing inter-State workers creates a system of accountability and acts as the first layer of formalizing the utilization of their labour.
- It helps the government keep track of the number of workers employed and provides a legal basis for regulating their conditions of service.
- As part of the licensing process, contractors are bound by certain conditions.
- These include committing them to provide terms and conditions of the agreement or any other arrangement on the basis of which they recruit workers.
- In no case, shall the wages be lower than what is prescribed under the Minimum Wages Act.
What does the proposed Code say on migrant workers?
- The attempt to consolidate laws relating to occupational safety, health and working conditions means that many separate laws concerning various kinds of workers and labourers will have to be repealed.
- The proposed law seeks to repeal 13 Acts such as the Factories Act, Mines Act, Dock Workers’ Act, the Inter-State Migrant Workmen Act, and other enactments relating to those working in plantations, construction, cinema, beedi and cigarette manufacture, motor transport, and the media.
What does the news law promise for migrant workers?
- Regarding inter-State migrant workers, the Act includes them in the definition of ‘contract labour’.
- At the same time, an inter-State migrant worker is also separately defined as a person recruited either by an employer or a contractor for an establishment situated in another State.
- The Code has a chapter on ‘contract labour and inter-State migrant workers’, but the Parliamentary Standing Committee has recommended that the provisions relating to migrant workers be covered in a separate chapter.
- The Code contains provisions similar to the 1979 Act regarding registration of establishments, licensing of contractors and the inclusion of terms and conditions on hours of work, wages and amenities.
- Further, both the old Act and the proposed Code envisage the payment of a displacement allowance and a journey allowance to inter-State migrant workers.
Trade Union’s response
- Even though the Code seeks to preserve many of the protections and rights are given to inter-State workers, trade unions feel that it is always better to have a separate enactment.
- The unprecedented distress and misery faced by migrant workers due to the current lockdown have drawn attention to beneficial legislation dedicated to their welfare.
- The Centre of Indian Trade Unions (CITU) has highlighted the fact that both the States where they work and home States have obligations cast upon them in the existing law.
- Despite the fact that it has been poorly implemented at all, labour unions feel that preserving the separate enactment and enforcing it well is a better option than subsuming it under a larger code.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Various laws mentioned
Mains level: Lockdown and its impacts on Labour
- Amid the coronavirus-induced lockdown, an increasing number of states that include Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan and Gujarat have pushed through changes to their labour laws by way of amendments — ordinances or executive orders.
- They aim to provide some sort of blanket exemption to employers from labour laws.
Practice Question
Q. Multiplicity of Labour laws in India has done little to address the plight of Labourers. Critically comment in context to the nationwide lockdown imposed due to the coronavirus outbreak.
What is the move all about?
- Most states cleared an ordinance exempting businesses from the purview of most labour law provisions for the next three years.
- However, labour laws related to bonded labour, deployment of women and children and timely payment of salaries are not changed.
Changes in the law
- The changes in the labour laws will apply to both the existing businesses and the new factories being set up in the state.
- Similarly, the Madhya Pradesh government has also suspended many labour laws for the next 1000 days.
- Few important amendments are:
- Employers can increase working hours in factories from 8 to 12 hours and are also allowed up to 72 hours a week in overtime, subject to the will of employees.
- The factory registration now will be done in a day, instead of 30 days. And the licence should be renewed after 10 years, instead of a year. There is also the provision of penalty on officials not complying with the deadline.
- Industrial Units will be exempted from majority of the provisions of the Industrial Disputes Act, 1947.
- Organisations will be able to keep workers in service at their convenience.
- The Labour Department or the labour court will not interfere in the action taken by industries.
- Contractors employing less than 50 workers will be able to work without registration under the Contract Labour (Regulation and Abolition) Act, 1970.
Major relaxations to new industrial units are:
-
- Exempted from provisions on ‘right of workers’, which includes obtaining details of their health and safety at work, to get a better work environment which include drinking water, ventilation, crèches, weekly holidays and interval of rest, etc.
- Exempted from the requirement of keeping registers and inspections and can change shifts at their convenience.
- Employers are exempt from penalties in case of violation of labour laws.
Rationale Behind the Changes in Labour Laws
- States have begun easing labour laws to attract investment and encourage industrial activity.
- To protect the existing employment, and to provide employment to workers who have migrated back to their respective states.
- Bring about transparency in the administrative procedures and convert the challenges of a distressed economy into opportunities.
- To increase the revenue of states which have fallen due to closure of industrial units during Covid-19 lockdown.
- Labour reform has been a demand of Industries for a long time. The changes became necessary as investors were stuck in a web of laws and red-tapism.
- Businesses and economic activities have slowed down due to which labour welfare has also been affected due to the national lockdown.
What are the Indian Labour Laws?
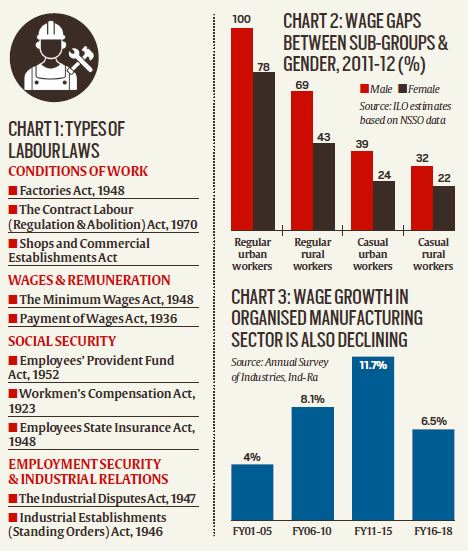
- Labour falls in the Concurrent List and there are many laws enacted by the Centre that a state cannot just brush aside.
- Estimates vary but there are over 200 state laws and close to 50 central laws. And yet there is no set definition of “labour laws” in the country.
Their types
Broadly speaking, they can be divided into four categories. Refer to the image.
- The main objectives of the Factories Act, for instance, are to ensure safety measures on factory premises and promote the health and welfare of workers.
- The Shops and Commercial Establishments Act, on the other hand, aims to regulate hours of work, payment, overtime, a weekly day off with pay, other holidays with pay, annual leave, employment of children and young persons, and employment of women.
- The Minimum Wages Act covers more workers than any other labour legislation.
- The most contentious labour law, however, is the Industrial Disputes Act, 1947 as it relates to terms of service such as layoff, retrenchment, and closure of industrial enterprises and strikes and lockouts.
Why are labour laws often criticised?

- Indian labour laws are often characterized as “inflexible”. Most of them are inadequate to make the sector formalized.
- At present 90% of India’s workers are parts of the informal economy. The Chart shows, even the organised sector are increasingly employing workers without formal contracts.
- Others have also pointed out that there are too many laws, often unnecessarily complicated, and not effectively implemented. This has laid the foundation for corruption and rent-seeking.
Issues with the recent relaxation
1.Exploitation
- The state of UP has summarily suspended almost all labour laws including the Minimum Wages Act.
- Hence this move is characterized as “creating an enabling environment for exploitation”.
- That’s because far from being a reform, which essentially means an improvement from the status quo, the removal of all labour laws will not only strip the labour of its basic rights but also drive down wages.
- For instance, what stops a firm from firing all existing employees and hiring them again at lower wages.
- For one, as Chart 3 shows, even before the Covid-19 crisis, thanks to the deceleration in the economy, wage growth had been moderating.
- Moreover, there was always a wide gap between formal and informal wage rates. For example, a woman working as a casual labourer in rural India earns just 20% of what a man earns in an urban formal setting.
- If all labour laws are removed, most employment will effectively turn informal and bring down the wage rate sharply. And there is no way for any worker to even seek grievance redressal.
2.Informalization
- Moreover, far from pushing for a greater formalization of the workforce, this move will in one go turn the existing formal workers into informal workers as they would not get any social security.
3. Will reduce demand in the economy
- Scrapping labour laws to save on labour costs will not help start the economy but will do exactly the opposite.
- It will reduce wages, lower earnings (particularly of low wage workers) and reduce consumer demand.
4.Unlikely to spur economic growth?
- Theoretically, it is possible to generate more employment in a market with fewer labour regulations.
- However, as the experience of states that have relaxed labour laws in the past suggests, dismantling worker protection laws have failed to attract investments and increase employment.
- It is unproven if they can cause an increase in worker exploitation or deterioration of working conditions. However, in the long run, employment will not increase, because of several reasons.
5. Enacted without any scrutiny:
- Usually, any change in an Act follows a rigorous process of public consultation, scrutiny by committees of Parliament, and debates in the House before being approved.
- The changes described here have not gone through such a process.
- However, most of these have a three-month time limit, and any extension would need to be approved by the legislature.
What else could have been done?
1.Allow two shifts
- There is already too much-unused capacity. Firms are shaving off salaries up to 40% and making job cuts. The overall demand has fallen. Which firm will hire more employees right now, he asked.
- If the intention was to ensure more people have jobs, then states should not have increased the shift duration from 8 hours to 12 hours.
- They should have allowed two shifts of 8-hours each instead so that more people can get a job.
- This move and the resulting fall in wages will further depress the overall demand in the economy, thus hurting the recovery process.
2.Partnered with the industry

- Most governments have done across the world have partnered with the industry and allocated 3% or 5% of the GDP towards sharing the wage burden and ensuring the health of the labourers.
- Moreover, beyond labour regulations, firms face a lot of other hurdles like the shortage of skilled labour and the weak enforcement of contracts etc.
- Time demands to secure the labour most than their employers.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ELISA Test, Antigen, Antibodies
Mains level: Not Much
Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR)-National Institute of Virology (NIV) at Pune has developed and validated the indigenous IgG ELISA test “COVID KAVACH ELISA” for antibody detection for COVID-19.
Our thumb rule suggests that the ELISA test is being used only for the diagnosis of HIV infection. Right?
But the ELISA test is a broader term to diagnose antibody-antigen interaction after certain virus infection to a person. UPSC can test your basic knowledge of core biology with a question based on this concept.
What is ELISA test?

- ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) is a plate-based assay technique designed for detecting and quantifying substances such as peptides, proteins, antibodies and hormones.
- Other names, such as enzyme immunoassay (EIA), are also used to describe the same technology.
- In an ELISA, an antigen must be immobilized on a solid surface and then complexed with an antibody that is linked to an enzyme.
- Detection is accomplished by assessing the conjugated enzyme activity via incubation with a substrate to produce a measurable product.
- The most crucial element of the detection strategy is a highly specific antibody-antigen interaction.
What are antibodies?
- An antibody is a large, Y-shaped protein produced mainly by plasma cells that are used by the immune system to neutralize pathogens such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses.
- There are five immunoglobulin classes (isotypes) of antibody molecules found in serum: IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE and IgD.
- They are distinguished by the type of heavy chain they contain.
Application of ELISA
- Presence of antigen or the presence of antibody in a sample can be evaluated
- Determination of serum antibody concentrations in a virus test
- Used in the food industry when detecting potential food allergens
- Applied in disease outbreaks- tracking the spread of disease e.g. HIV, bird flu, common, colds, cholera, STD etc
Significance
- Robust antibody tests are critical for surveillance to understand the proportion of the population exposed to infection.
- The test will have the advantage of testing 90 samples together in a single run of 2.5 hours.
- Moreover, ELISA based testing is easily possible even at the district level as the ELISA kit has an inactivated virus.
- There are also minimal bio-safety and bio-security requirements as compared to the real-time RT-PCR test.
- The test has the advantage of having much higher sensitivity and specificity as compared to the several rapid test kits which have recently flooded the Indian market.
Limitations
- Since the ELISA test is based on the detection of antibodies, it can only help in knowing if the person has been previously infected by a coronavirus.
- It takes one-three weeks for the antibodies to develop in response to infection.
- So, if a person who has been recently infected by the virus is tested during the window period (the time taken to develop antibodies) the result will turn out to be negative.
- But a repeat test after a couple of weeks will indicate the true infection status.
How it is different from the PCR test?
- While the RT-PCR, which detects the RNA of the coronavirus, enables detection of current infection, it will not be useful if the testing is carried out days after the infection clears as the virus will no longer be present.
- However, antibodies developed in response to the coronavirus infection will be present in the blood for a longer duration and hence the ELISA test can help detect past infection.
- The maximum time the antibodies will be present in the body is not known for coronavirus.
Back2Basics: Reverse Transcriptase – Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Test
- It uses a technique that creates copies of a segment of DNA. ‘Polymerase’ refers to the enzymes that make the copies of DNA.
- Kary Mullis, the American biochemist who invented the PCR technique, was awarded the Nobel Prize for Chemistry in 1993.
- The ‘chain reaction’ is how the DNA fragments are copied, exponentially — one is copied into two, the two are copied into four, and so on.
- However, SARS-COV-2 is a virus made of RNA, which needs to be converted into DNA. For this, the technique includes a process called reverse transcription.
- A ‘reverse transcriptase’ enzyme converts the RNA into DNA. Copies of the DNA are then made and amplified.
- A fluorescent DNA binding dye called the “probe” shows the presence of the virus. The test also distinguishes SARS-COV-2 from other viruses.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Florence Nightingale
Mains level: Not Much

The 200th birth anniversary of Florence Nightingale, founder of modern nursing, falls tomorrow on May 12.
Personality based questions sometimes find their way in the Prelims. For example:
Q) A recent movie titled The Man Who Knew Infinity is based on the biography of – (CSP 2016)
(a) S. Ramanujan
(b) S. Chandrasekhar
(c) S. N. Bose
(d) C. V. Raman
Who was Florence Nightingale?
- Nightingale (1820-1910), who had considerable mathematical skills, is credited with being the first healthcare professional to use data to show that infection control improves health outcomes.
- Through her career, she stressed a practice that is relevant as ever today — handwashing.
Nurse and mathematician
- Her signature effort came during the Crimean War (1854-56), when she answered a government call for nurses and took a posting in Turkey.
- This is where she earned the name ‘Lady with the Lamp’, for walking around patients’ beds at night, holding a lamp. Here she did her pioneering work with statistics.
- When she arrived, diseases such as cholera and typhus were rife in the hospitals.
- Nightingale collected data, calculated the mortality rate, and showed that an improvement of sanitary methods would reduce the number of deaths.
- The mortality rate dropped from 60% to 42.7% by February 1855, and to 2.2% by the spring.

- She used her data to create graphics, the most famous of which is a polar area diagram (pictured) that used areas to represent variations in death rate.
- The blue wedges from the center of the circle represent area for the deaths from Preventable or Mitigable diseases, the red wedges measured from the center is deaths from wounds, & the black wedges measured from the center is the deaths from all other causes.
- The blue wedges, representing death by sickness, are far bigger than those representing wounds.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Mapping: Islands in the Pacific
Mains level: Not Much

Approximately four months after COVID-19 was first detected, the South Pacific Islands have not yet reported any cases of the infectious disease.
Closely observe the map. Note important islands. UPSC may shift its traditional focus from middle east/central asia to this region. These days, Pacific and Indo-Pacific region carry a decent importance.
We can expect MCQs asking to arrange these islands in north-south / east-west direction.
Which South Pacific islands have recorded cases of COVID-19?
- Fiji recorded its first case of COVID-19 on March 19.
- Guam, a territory of the US in the South Pacific, witnessed an outbreak among the staff of the US navy.
- New Caledonia also recorded its first COVID-19 cases in mid-March, with links to overseas travel.
- The Solomon Islands, the Cook Islands, Tonga, Tuvalu, Vanuatu, the Marshall Islands, Palau and Nauru have no recorded cases of COVID-19.
What impact will COVID-19 have on Pacific island nations?
- A widespread outbreak of COVID-19 will have a disastrous impact on these island nations.
- Although these islands are popular with tourists, the outer islands and rural villages are home to indigenous populations.
- Most of these areas have a very basic infrastructure for healthcare, with larger hospitals and medical centres located in bigger towns.
- Even in everyday circumstances, these small medical centres struggle due to the lack of medical supplies.
- The socio-cultural factors, like the prevalence of large families in this region, also make the individuals susceptible to community transmission.
- There is also a lack of access to running water, making sanitation difficult.
- Environmental factors like the seasonal tropical cyclone that swept through the region in April, led to the displacement of hundreds of people in the Solomon Islands, Fiji, Vanuatu and Tonga.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Sal Forest Tortoise
Mains level: NA

A recent study by ecologists in the Wildlife Institute of India, Dehradun, has found that the area designated as a protected area network has only a small overlap with the actual habitat of Sal forest tortoise. Over 90% of the potential distribution of the species falls outside the current protected area’s network.
What you should focus on?
On map, identify areas where Sal forest tortoise are found.
Revise the map of various Forest system of India and their characteristics as well.
Also…..Is tortoise a mammal or an amphibian?…..or something else??
Sal Forest/ Elongated Tortoise
- Also known as the elongated tortoise (Indotestudo elongata), the sal forest tortoise, recently assessed as Critically Endangered, is heavily hunted for food.
- It is collected both for local use, such as decorative masks, and international wildlife trade.
- The Sal forest tortoise is widely distributed over eastern and northern India and Southeast Asia.
- It is one of the only four land tortoises found in India. It is legally protected under Schedule IV of the Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 as amended up to 2006.
- According to the IUCN, the population of the species may have fallen by about 80% in the last three generations (90 years).
About Sal Forest
- It is a forest type dominated by a single plant species, commonly known as Sal tree (Shorea robusta).
- It belongs to the category ‘Tropical Moist Deciduous Forest’.
- The distribution of Sal forests is controlled by the conditions of topography, geology, and soil.
- Sal forests are mainly distributed in the South and Southeast Asia, occurring along the base of Tropical Himalayas from Assam to Punjab, in the eastern districts of Central India, and on the Western Bengal Hills.
Also read the complete series on-
Natural Vegetation and Wildlife- Part 1 | An Overview of Natural Vegetation Types Found in India
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SAGAR Programme
Mains level: India's SAGAR policy of Indian Ocean Region

As part of India’s outreach amidst the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, ships have departed for Maldives, Mauritius, Seychelles, Madagascar and Comoros, to provide Food Items, COVID related Medicines including HCQ Tablets and Medical Assistance Teams under Mission Sagar.
Mission SAGAR, unlike other missions, can create confusion with the name and its purpose. Make note of such special cases. UPSC can ask such questions as one liner MCQs.
Mission SAGAR
- As part of the mission, INS Kesari would enter the Port of Male in the Republic of Maldives, to provide them 600 tons of food provisions.
- The deployment is in consonance with the PMs vision of Security and Growth for All in the Region ‘SAGAR’.
- This deployment is in line with India’s role as the first responder in the region and builds on the excellent relations existing between these countries to battle the COVID-19 pandemic and its resultant difficulties.
- The operation is being progressed in close coordination with the Ministries of Defence and External Affairs, and other agencies of the govt.
Back2Basics
SAGAR Programme (Security and Growth for All in the Region)
- SAGAR is a term coined by PM Modi in 2015 during his Mauritius visit with a focus on the blue economy.
- It is a maritime initiative which gives priority to the Indian Ocean region for ensuring peace, stability and prosperity of India in the Indian Ocean region.
- The goal is to seek a climate of trust and transparency; respect for international maritime rules and norms by all countries; sensitivity to each other`s interests; peaceful resolution of maritime issues; and increase in maritime cooperation.
- It is in line with the principles of the Indian Ocean Rim Association.
IORA (Indian Ocean Rim Association)
- Established in 1997 in Ebene Cyber City, Mauritius.
- First established as Indian Ocean Rim Initiative in Mauritius on March 1995 and formally launched in 1997 by the conclusion of a multilateral treaty known as the Charter of the IORA for Regional Cooperation.
- It is based on the principles of Open Regionalism for strengthening Economic Cooperation particularly on Trade Facilitation and Investment, Promotion as well as Social Development of the region.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now













