From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: UNCCD Reports; Global Land Outlook Thematic Report
Mains level: UNCCD; Land Degradation; f
Why in the News?
The UN Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) recently published the “Global Land Outlook Thematic Report” on Rangelands and Pastoralists, revealing that up to 50% of Rangelands are degraded.
About UNCCD:
- UNCCD adopted in 1994 (effectively from 1996), is a legally binding agreement that aims to protect and restore land and combat desertification and drought.
- It is one of the three Rio Conventions (the other two being – the Convention on Biological Diversity (UNCBD) and United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC)).
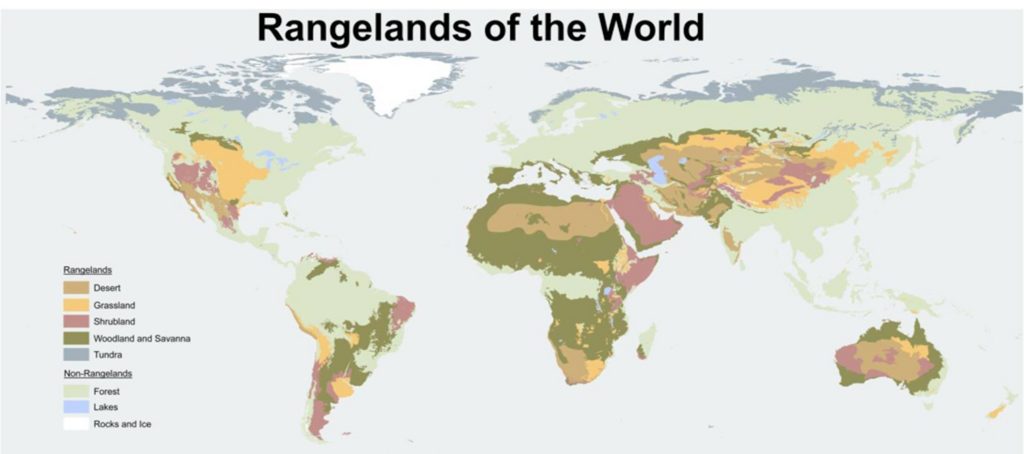
What is the Rangeland?
World areas that are most acutely affected by Rangeland Degradation:
|
How does it impact the Food chain?
- Over two billion people, including small-scale herders, ranchers, and farmers, depend on healthy rangelands for their livelihoods, underscoring the critical link between rangeland health and food chain cycle.
- Up to 50% of rangelands are degraded due to various factors including overuse, misuse, climate change, and biodiversity loss, posing a severe threat to food security.
The Economic significance of Rangelands:
- Livestock Grazing and Agriculture: Rangelands are crucial for livestock production, providing natural forage for cattle, sheep, goats, and other herbivores. This grazing land supports the meat and dairy industries, which are vital to the global food supply and rural economies.
- Eco-tourism and hunting: These areas support a wide range of wildlife, contributing to biodiversity and offering opportunities for eco-tourism and hunting, both of which generate significant income for local economies.
- Ecosystem Services: Rangelands provide vital services like water filtration, carbon storage, and soil preservation, yielding economic advantages through climate regulation and conservation.
- Income and employment opportunities: Harvesting these resources provides income and employment opportunities for rural populations. The economic contributions made by different countries are as follows:
- Ethiopia: Livestock production from rangelands accounts for 19% of the country’s GDP.
- India: Livestock from rangelands contributes 4% to the national GDP.
- Brazil: As a major beef producer, Brazil generates one-third of its agribusiness GDP from cattle livestock, producing 16% of the world’s beef.
What is the innovative approach presented by the UNCCD Report?
- The past estimates by UNCCD of degraded rangeland of roughly 25% are significantly underestimated, where the actual loss of rangeland’s health and productivity was potentially reaching up to 50%.
- Conceptual Approach: The report outlines a new conceptual approach designed to help policymakers stabilize, restore, and manage rangelands more effectively.
- This new approach is supported by detailed case studies from nearly every world region, which provide important lessons from both the successes and failures in rangeland management.
- Core Recommendation – Protect Pastoralism: The report emphasizes the importance of protecting pastoralism a traditional, mobile way of life based on pasture-based livestock production as a key strategy for sustainable rangeland management.
Conclusion: Many countries like the U.S. and Canada makingare trying to reintroduce bison, an animal with significant cultural importance to indigenous peoples. This initiative aims to promote rangeland health and enhance food security.
Mains PYQ:
Q The process of desertification does not have climate boundaries. Justify with examples.(UPSC IAS/2020)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024