From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SSLV, PSLV, GSLV
Mains level: Not Much

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has said that the satellite onboard its’ maiden Small Satellite Launch Vehicle “are no longer usable” after the SSLV-D1 placed them in an elliptical orbit instead of a circular one.
What is SSLV?
- The SSLV is a small-lift launch vehicle being developed by the ISRO with payload capacity to deliver:
- 600 kg to Low Earth Orbit (500 km) or
- 300 kg to Sun-synchronous Orbit (500 km)
- It would help launching small satellites, with the capability to support multiple orbital drop-offs.
- In future a dedicated launch pad in Sriharikota called Small Satellite Launch Complex (SSLC) will be set up.
- A new spaceport, under development, near Kulasekharapatnam in Tamil Nadu will handle SSLV launches when complete.
- After entering the operational phase, the vehicle’s production and launch operations will be done by a consortium of Indian firms along with NewSpace India Limited (NSIL).
Vehicle details
(A) Dimensions
- Height: 34 meters
- Diameter: 2 meters
- Mass: 120 tonnes
(B) Propulsion
- It will be a four stage launching vehicle.
- The first three stages will use Hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene (HTPB) based solid propellant, with a fourth terminal stage being a Velocity-Trimming Module (VTM).
SSLV vs. PSLV: A comparison
- The SSLV was developed with the aim of launching small satellites commercially at drastically reduced price and higher launch rate as compared to Polar SLV (PSLV).
- The projected high launch rate relies on largely autonomous launch operation and on overall simple logistics.
- To compare, a PSLV launch involves 600 officials while SSLV launch operations would be managed by a small team of about six people.
- The launch readiness period of the SSLV is expected to be less than a week instead of months.
- The SSLV can carry satellites weighing up to 500 kg to a low earth orbit while the tried and tested PSLV can launch satellites weighing in the range of 1000 kg.
- The entire job will be done in a very short time and the cost will be only around Rs 30 crore for SSLV.
Significance of SSLV
- SSLV is perfectly suited for launching multiple microsatellites at a time and supports multiple orbital drop-offs.
- The development and manufacture of the SSLV are expected to create greater synergy between the space sector and private Indian industries – a key aim of the space ministry.
Back2Basics: Various Orbits of Satellites
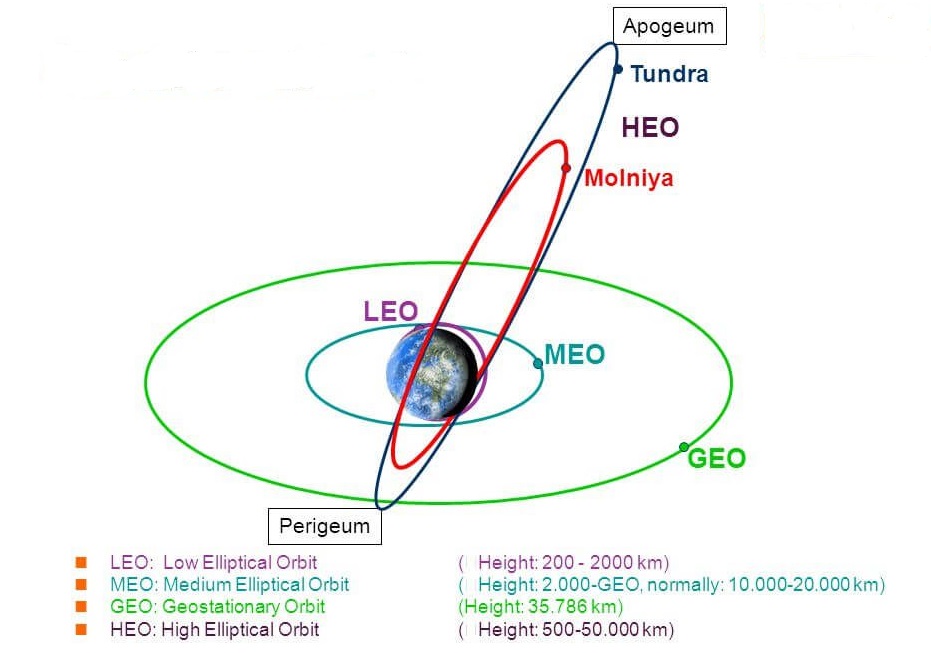
[1] Geostationary orbit (GEO)
- Satellites in geostationary orbit (GEO) circle Earth above the equator from west to east following Earth’s rotation – taking 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds – by travelling at exactly the same rate as Earth.
- This makes satellites in GEO appear to be ‘stationary’ over a fixed position.
- In order to perfectly match Earth’s rotation, the speed of GEO satellites should be about 3 km per second at an altitude of 35 786 km.
- This is much farther from Earth’s surface compared to many satellites.
- GEO is used by satellites that need to stay constantly above one particular place over Earth, such as telecommunication satellites.
- Satellites in GEO cover a large range of Earth so as few as three equally-spaced satellites can provide near-global coverage.
[2] Low Earth orbit (LEO)
- A low Earth orbit (LEO) is, as the name suggests, an orbit that is relatively close to Earth’s surface.
- It is normally at an altitude of less than 1000 km but could be as low as 160 km above Earth – which is low compared to other orbits, but still very far above Earth’s surface.
- Unlike satellites in GEO that must always orbit along Earth’s equator, LEO satellites do not always have to follow a particular path around Earth in the same way – their plane can be tilted.
- This means there are more available routes for satellites in LEO, which is one of the reasons why LEO is a very commonly used orbit.
- It is most commonly used for satellite imaging, as being near the surface allows it to take images of higher resolution.
- Satellites in this orbit travel at a speed of around 7.8 km per second; at this speed, a satellite takes approximately 90 minutes to circle Earth.
[3] Medium Earth orbit (MEO)
- Medium Earth orbit comprises a wide range of orbits anywhere between LEO and GEO.
- It is similar to LEO in that it also does not need to take specific paths around Earth, and it is used by a variety of satellites with many different applications.
- It is very commonly used by navigation satellites, like the European Galileo system of Europe.
- It uses a constellation of multiple satellites to provide coverage across large parts of the world all at once.
[4] Polar Orbit
- Satellites in polar orbits usually travel past Earth from north to south rather than from west to east, passing roughly over Earth’s poles.
- Satellites in a polar orbit do not have to pass the North and South Pole precisely; even a deviation within 20 to 30 degrees is still classed as a polar orbit.
- Polar orbits are a type of low Earth orbit, as they are at low altitudes between 200 to 1000 km.
[5] Sun-synchronous orbit (SSO)
- SSO is a particular kind of polar orbit. Satellites in SSO, travelling over the polar regions, are synchronous with the Sun.
- This means they are synchronised to always be in the same ‘fixed’ position relative to the Sun.
- This means that the satellite always visits the same spot at the same local time.
- Often, satellites in SSO are synchronised so that they are in constant dawn or dusk – this is because by constantly riding a sunset or sunrise, they will never have the Sun at an angle where the Earth shadows them.
- A satellite in a Sun-synchronous orbit would usually be at an altitude of between 600 to 800 km. At 800 km, it will be travelling at a speed of approximately 7.5 km per second.
[6] Transfer orbits and geostationary transfer orbit (GTO)
- Transfer orbits are a special kind of orbit used to get from one orbit to another.
- Often, the satellites are instead placed on a transfer orbit: an orbit where, by using relatively little energy from built-in motors, the satellite or spacecraft can move from one orbit to another.
- This allows a satellite to reach, for example, a high-altitude orbit like GEO without actually needing the launch vehicle.
- Reaching GEO in this way is an example of one of the most common transfer orbits, called the geostationary transfer orbit (GTO).
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
