From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Budapest Convention
Mains level: Internal and External Security; Challenges of Cybersecurity in India
Why in the News?
Over 5,000 unemployed/employed Indians are reportedly trapped in Cambodia and forced to work into cyber fraud, resulting in an estimated Rs 500 crore loss in India over six months.
Present Cybersecurity Status of India:
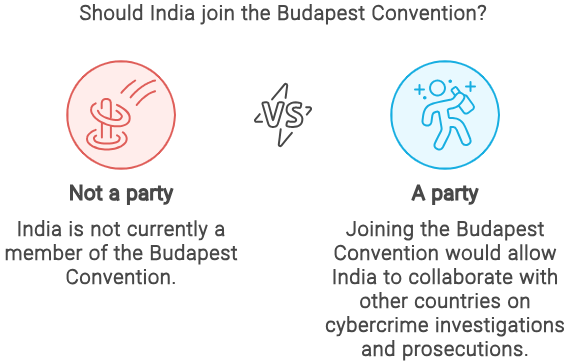
What is the Budapest Convention? Is India a party to it?
|
Indian Nationals vs. Organised Crimes in the South Asian Region:
- Most web applications use the Chinese language to perform financial fraud, thereby not ruling out the Chinese connection.
- Financial crimes such as digital arrest, stock market scams, investment scams, and romance or dating scams account for a loss of over ₹1,776 crores in 89,054 cases in the first four months of the year spurt in organized crime from Southeast Asia.
- Numerous Indian nationals employed within a suspected fraudulent operation based in Sihanouk City, Cambodia, have voiced their grievances against their employers.
What are the causes of the increase in Organized Financial Fraud?
- Weak Prevention Measures: Online Platforms in India at present account for 89% of all fraud incidents, with 40% of companies losing over $1 million.
- Rapid Digitization and Payment Systems: After the pandemic, there was a massive shift, with the average Indian company now operating at least more than two online platforms in the normal course of business.
- This has made it easier for fraudsters to operate anonymously and target a large number of victims.
- Informal Investigation and Prosecution: India lacks the standardized data formats protocol system from the core banks itself. This makes it difficult to track devices and jurisdictional issues in interstate cases.
- Lack of Deterrence: With only 26% of victims able to recover lost funds, fraudsters are encouraged to target individuals and organizations. The total value of frauds reported in 2021-22 was a staggering ₹60,414 crore.
- Lack of Awareness: Sharing sensitive financial details with others or storing them insecurely it makes a common man vulnerable to fraud.
What are the Initiatives taken by the government to tackle cyber crimes in India?
- National Cyber Security Strategy 2020: Currently being formulated to enhance cyber awareness and strengthen cybersecurity through more rigorous audits.
- Draft Personal Data Protection Bill, 2018: Based on the recommendations of the Justice BN Srikrishna Committee, this bill aims to secure citizens’ data.
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C): Approved in October 2018, this initiative addresses all types of cybercrimes in a comprehensive and coordinated manner.
- National Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In): Functions as the nodal agency for coordinating all cybersecurity efforts, emergency responses, and crisis management.
- National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC): Established to protect and ensure the resilience of critical information infrastructure.
Way Forward:
- Update and Enforce Laws: Regularly update the Information Technology Act and other relevant laws to address emerging cyber threats and ensure strict enforcement.
- Upgrade Cyber Defense Systems: Invest in advanced cybersecurity technologies and infrastructure to protect critical information systems.
- Training Law Enforcement: Provide specialized training for law enforcement agencies to equip them with the skills needed to investigate and prosecute cybercrimes.
- Collaborate with Industry: Foster partnerships between the government and private sector to share threat intelligence and best practices.
Mains question for practice:
Q Discuss the current challenges of cybersecurity in India, citing examples of recent trends in cybercrime. What measures have been taken by the Indian government to address these challenges? 15M
Mains PYQ
Q What are the different elements of cyber security? Keeping in view the challenges in cyber security, examine the extent to which India has successfully developed a comprehensive National Cyber Security Strategy.(UPSC IAS/2022)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024