Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Particulate Matter
Mains level: Pollution induced mortality in India

Air pollution now biggest health risk in India, says the State of Global Air 2020 Report.
State of Global Air Report
- The State of Global Air report brings into one place the latest information on air quality and health for countries around the globe.
- It is produced annually by the Health Effects Institute and the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation’s Global Burden of Disease project.
India’s exposure to pollution
- Long-term exposure to outdoor and household air pollution contributed to over 1.67 million annual deaths from stroke, heart attack, diabetes, lung cancer, chronic lung diseases and neonatal diseases in India in 2019.
- Overall, air pollution was now the largest risk factor for death among all health risks, the report noted.
- Outdoor and household particulate matter pollution also contributed to the deaths of more than 1,16,000 Indian infants in their first month of life last year.
- For the youngest infants, most deaths were related to complications from low birth weight and preterm birth.
A comparison with peers
- India faced the highest per capita pollution exposure — or 83.2 μg/cubic metre — in the world.
- It is followed by Nepal at 83.1 μg/cubic metre and Niger at 80.1.
- Countries with the least population exposure are below 8 micrograms (μg) per cubic metre.
Back2Basics: Particulate Matter
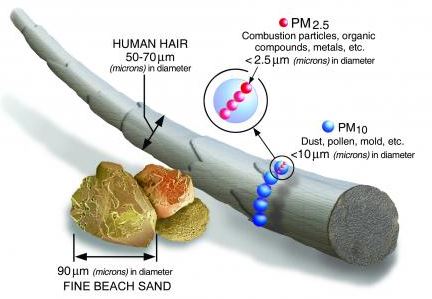
- PM is the term for a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets found in the air. Some particles, such as dust, dirt, soot, or smoke, are large or dark enough to be seen with the naked eye.
- Others are so small they can only be detected using an electron microscope.
- Particle pollution includes:
- PM10 : inhalable particles, with diameters that are generally 10 micrometres and smaller; and
- PM2.5: fine inhalable particles, with diameters that are generally 2.5 micrometres and smaller.
Sources of PM
- These particles come in many sizes and shapes and can be made up of hundreds of different chemicals.
- Some are emitted directly from a source, such as construction sites, unpaved roads, fields, smokestacks or fires.
- Most particles form in the atmosphere as a result of complex reactions of chemicals such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, which are pollutants emitted from power plants, industries and automobiles.
Harmful effects of PM
- Particulate matter contains microscopic solids or liquid droplets that are so small that they can be inhaled and cause serious health problems.
- Some particles less than 10 micrometres in diameter can get deep into your lungs and some may even get into your bloodstream.
- Of these, particles less than 2.5 micrometres in diameter, also known as fine particles or PM2.5, pose the greatest risk to health.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
