Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: social justice agenda
Central idea
Bihar’s caste census is a significant step, yet modernizing caste politics faces hurdles with global economic changes, an authoritative government, and assertive Hindutva ideology. To lead in this complexity, Bihar can pioneer a nuanced, coalition-based approach, reshaping caste politics for the 21st century.
Key Highlights:
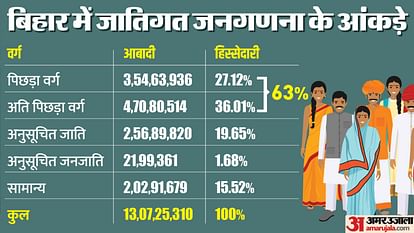
- Historic Steps: Bihar takes significant strides in social justice by conducting a caste census and revealing socio-economic data associated with different castes.
- Leadership Challenge: The RJD-JD(U) coalition faces a critical juncture in utilizing caste survey data for an effective social justice agenda, beyond mere reservation expansions.
- Global Economic Situation: Neoliberal policies demand innovative approaches for mass employment (decent work).
- Authoritarian Regime: India experiences an authoritarian shift impacting constitutional norms and federal structures.
- Upper-Caste Hegemony: A visible rise of aggressive north-Indian Hindu upper-caste dominance through Hindutva ideology.
- Internal Differentiations: Complex internal variations within major caste groups challenge traditional one-dimensional caste politics.
Key Data for enhancing answer quality:
- “Formal Sector Jobs”: Despite market-friendly policies, the formal sector of the Indian economy offers less than 8% of all jobs.
- “Reservation Expansion”: Bihar Chief Minister Nitish Kumar’s announcement of expanding reservations to 65%.
- “Resistance Against Hindutva”: Bihar’s historical role in resisting Hindutva politics, along with other states like Karnataka, Kerala, and Rajasthan.
- “Erosion of Indian Federalism”: The resistance against the erosion of Indian federalism, with Bihar contributing to the assertion of State rights.
Key Terms for value addition:
- Caste Census,
- Neoliberal Policies,
- Authoritarian Regime,
- Hindutva Ideology,
- Internal Caste Differentiations,
- Portrait vs. Proxy Model,
- Evolution of Caste Politics,
- State Rights Assertion,
Challenges:
- Neoliberal Constraints: Limited formal sector jobs despite market-friendly policies pose a challenge for reducing caste inequalities.
- Authoritarian Shift: Constitutional norms, checks and balances eroded by an authoritarian regime, altering the Indian state’s shape.
- Hindutva Ideology: Overt and aggressive upper-caste dominance through Hindutva challenges secularism, creating a one-dimensional Hindu identity.
- Internal Caste Differentiations: Diverse class interests within castes require a coalitional approach, potentially leading to unpredictable consequences.
Analysis:
- Changing Caste Politics: The article highlights the need for evolving caste politics beyond automatic association with social justice, considering the complexities of the present context.
- Role of Lower Castes: Lower caste politics can counter Hindutva, even when focused on community interests, offering resistance to the dominance of upper-caste neo-elites.
- State Rights Assertion: Bihar’s resistance against Hindutva and the act of conducting a caste census assert State rights, contributing to the fight against the erosion of Indian federalism.
- Portrait vs. Proxy Model: The caste survey raises questions about representation—whether elected representatives should resemble the population (portrait model) or act on their behalf (proxy model).
The Way Forward:
- Innovative Social Justice: Bihar has the opportunity to pioneer a new form of caste politics, adapting to the present context, breaking from past habits while upholding the core of the social justice agenda.
- Political Representation: The article questions the idea that sharing the same identity is sufficient for representation, emphasizing the need for effective action on behalf of the represented.
- Balancing Identities: Despite the census favoring larger numbers, Bihar can demonstrate that shared identity is a necessary but not sufficient condition for political representation.
- Championing Federalism: Bihar, along with other states, can lead the resistance against the erosion of Indian federalism, emphasizing the importance of locally-relevant policies.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024