Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Reports on Tobacco Consumption in India
Mains level: Implementing and Catching Up with Industry
Why in the News?
Tobacco is a leading preventable cause of disease which affects nearly 26 crore Indians and 60 lakh industry workers, posing significant health risks.
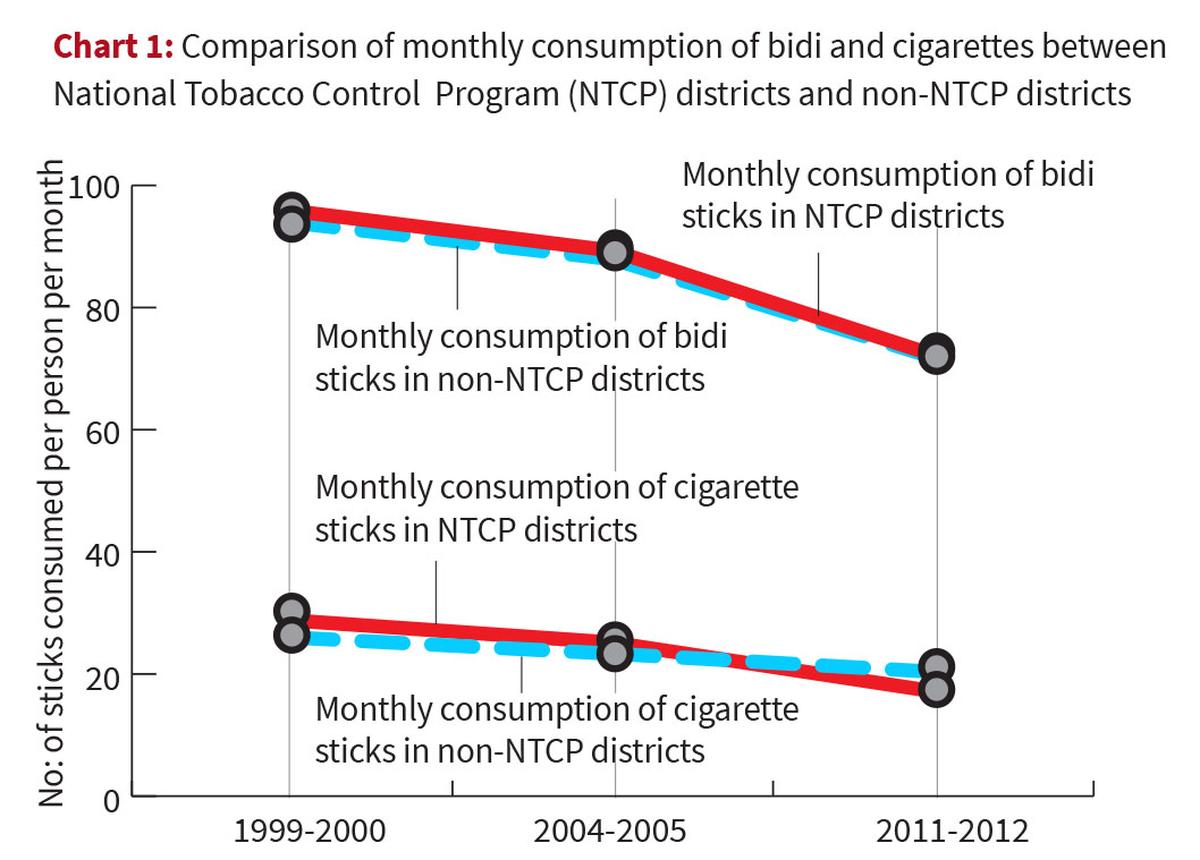
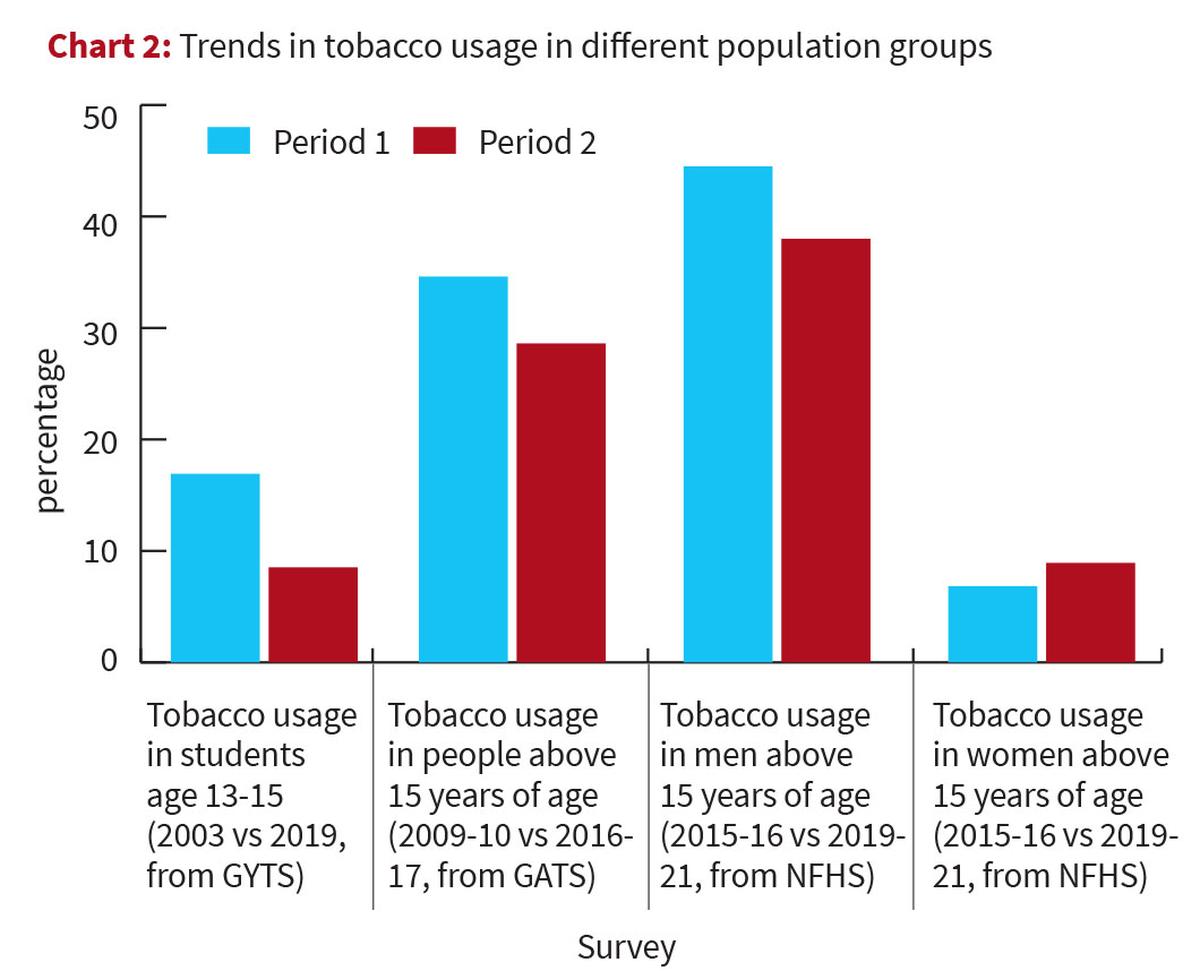
Reports on Tobacco Consumption in India
|
What is the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC)?
- The WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC) is an international treaty adopted by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2003. It is a legally binding treaty.
- It means that countries that have ratified it are obligated to implement the measures outlined in the convention within their national jurisdictions.
- It addresses the global health risks associated with tobacco use and provides a comprehensive framework for governments and organizations to implement effective tobacco control policies and strategies.
Challenges in India: Lobbying by the Tobacco Industry
- The tobacco industry exerts substantial influence on policy-making to maintain low tax rates and evade stricter regulations.
- Government Engagement: Both in-service and retired government officials often engage with the tobacco industry. Example: A retired Indian Administrative Services officer joined the board of Godfrey Phillips as an independent director.
- Government Stake: The Central government holds a 7.8% stake in ITC Ltd., India’s largest tobacco company.
- Tax Exemptions: Continuous exemptions of cess on bidis and smaller tobacco manufacturers. Persistent extensions of these exemptions despite the harmful effects of tobacco.
Tax Measures and Lobbying
|
- Thus, India’s score has worsened since 2021, indicating increased interference by the tobacco industry in governance.
Initiatives taken by the Government:
- Cigarette and Other Tobacco Products Act (COTPA) 2003: It regulates the advertisement, promotion, and sponsorship of tobacco products, prohibits smoking in public places, mandates pictorial health warnings on tobacco product packaging, and sets rules for the sale of tobacco products to minors.
- Awareness on Media: India is the first country in the world to implement the larger steps through implementing warnings on OTT platform content when actors are seen using tobacco products.
- Awareness of Product: India has implemented prominent and graphic pictorial health warnings on tobacco product packaging.
Challenges in Implementation
- Poor Enforcement: Existing measures are not strictly implemented, leading to widespread non-compliance, especially among smokeless tobacco products (SLTs).
- Indirect Advertisements: Surrogate advertisements (e.g., using elaichi to promote tobacco brands) circumvent direct advertising bans, undermining control efforts.
- Inadequate Fines: Penalties for violations of COTPA regulations have not been updated since 2003, making them ineffective deterrents.
Way forward:
- Update COTPA Fines and Penalties: Revise and significantly increase fines for violations of COTPA regulations to create a stronger deterrent.
- Strengthen Border and Market Surveillance: Improve customs and market surveillance to combat smuggling and illicit trade of tobacco products.
Mains question for practice:
Q Discuss the various measures undertaken by the Indian government to control tobacco consumption. Evaluate the effectiveness of these measures and suggest improvements. 15M
Tobacco Board of India
|
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024