Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Thwaites Glacier
Mains level: Sea level rise and its impact
In the Antarctic floats a massive glacier, roughly the size of Britain, whose melting has been a cause of alarm for scientists over the years. Now, a new study has pinned the cause of the melting to the presence of warm water at a vital point beneath the glacier.
Thwaites Glacier
- The Thwaites Glacier is 120 km wide at its broadest, fast-moving and melting fast over the years.
- Because of its size (1.9 lakh square km), it contains enough water to raise the world sea level by more than half a metre.
- Studies have found the amount of ice flowing out of it has nearly doubled over the past 30 years. Today, Thwaites’s melting already contributes 4% to global sea level rise each year.
- It is estimated that it would collapse into the sea in 200-900 years. Thwaites is important for Antarctica as it slows the ice behind it from freely flowing into the ocean.
- Because of the risk it faces — and poses — Thwaites is often called the Doomsday Glacier.
What has the new study found?
- A 2019 study had discovered a fast-growing cavity in the glacier.
- More recently researchers detected warm water at a vital point below the glacier.
- Scientists dug a 600-m-deep and 35-cm-wide access hole, and deployed an ocean-sensing device called Icefin to measure the waters moving below the glacier’s surface.
- The study reported water at just two degrees above freezing point at Thwaites’s “grounding zone” or “grounding line”.
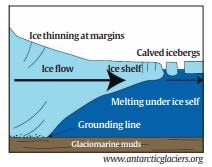
What is the grounding line?
- The grounding line is the place below a glacier at which the ice transitions between resting fully on bedrock and floating on the ocean as an ice shelf.
- The location of the line is a pointer to the rate of retreat of a glacier.
- When glaciers melt and lose weight, they float off the land where they used to be situated. When this happens, the grounding line retreats.
- That exposes more of a glacier’s underside to seawater, increasing the likelihood it will melt faster.
- This resulted in the glacier speeding up, stretching out, and thinning, causing the grounding line to retreat ever further.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024