From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: India’s ministerial portfolio system and its features
Why in the News?
- President Droupadi Murmu administered oaths to the Central Council of Ministers (CoM) of the new NDA government, comprising a larger team compared to the previous term.
- The Council includes 30 cabinet ministers, five Ministers of State (Independent Charge), and 36 Ministers of State, with the Prime Minister leading the team.
About Central Council of Ministers
- The Central CoM is a crucial part of India’s governance system.
- Members: It consists of the Prime Minister (Head), Cabinet Ministers, Ministers of State, and Deputy Ministers.
- History:
- Portfolio System: The system of the CoM finds its roots in the Indian Councils Act of 1861, introduced by Lord Canning going parallel with the British Parliamentary System.
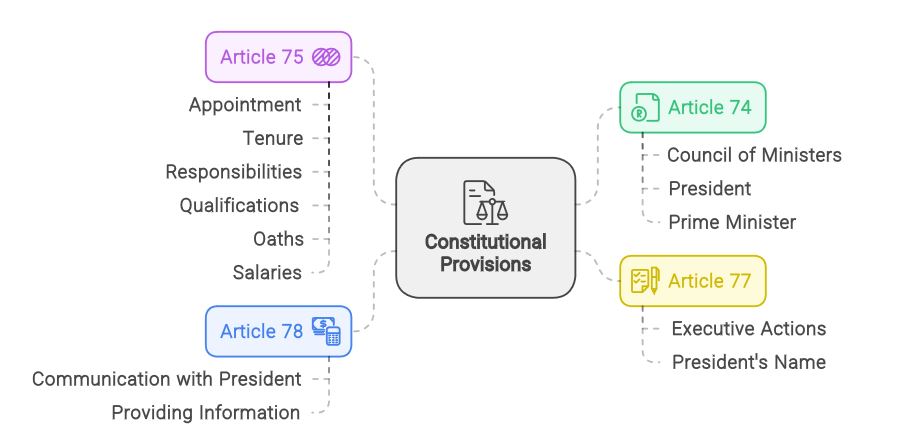
Constitutional Provisions
Articles 74 to 78 in Part V of the Indian Constitution broadly deal with the Central Council of Ministers.
Union Executive: The Union Executive encompasses the President, Vice-President, Prime Minister, Union Council of Ministers, and Attorney General of India, collectively responsible for the country’s administration.
Role of the Prime Minister
|
Functions and Duties of CoM
1. Policy Formulation and Implementation:
- Formulating Policies: The Council of Ministers, particularly the Cabinet, is tasked with formulating policies crucial for the nation’s development and welfare.
- Policy Coordination: It ensures coordination among various government departments and agencies for effective policy implementation.
2. Executive Functions:
- Real Executive Authority: The Council of Ministers acts as the real executive authority, exercising executive powers on behalf of the President.
- Administration: It oversees the day-to-day administration of the country, ensuring the smooth functioning of government affairs.
- Emergency Powers: During emergencies, the Council of Ministers advises the President on the exercise of emergency powers and crisis management.
3. Legislative Functions:
- Bills and Legislation: Ministers actively participate in the legislative process by introducing bills, piloting them through Parliament, and ensuring their passage.
- Policy Advocacy: They advocate for government policies and bills in Parliament, engaging in debates and discussions to garner support.
- Budgetary Process: The Council of Ministers prepares and presents the annual budget, guiding fiscal policies and financial allocations.
4. Financial Management:
- Budget Preparation: It plays a significant role in preparing the national budget, and outlining revenue and expenditure plans for the fiscal year.
- Financial Administration: The Council oversees financial administration, ensuring compliance with budgetary provisions and efficient resource utilization.
- Taxation and Fiscal Policy: Ministers propose taxation measures and formulate fiscal policies to promote economic growth and stability.
Who are the Cabinet Ministers?
- The Cabinet Ministers are senior members of the Central Council of Ministers who head key government departments or ministries.
- Typically, Cabinet Ministers are appointed by the Prime Minister and are part of the Cabinet, which is the core decision-making body in the government.
- Each Cabinet Minister typically manages a specific portfolio aligned with the government’s priorities and responsibilities.
- Examples: Minister of Finance, Minister of Home Affairs, Minister of Defence, Minister of External Affairs, Minister of Health, Minister of Education, and others.
|
Difference between Ministers of State (Independent Charge) and Ministers of State:
| Ministers of State (Independent Charge) | Ministers of State | |
| Authority | Have independent portfolios | Assist Cabinet Ministers |
| Reporting Structure | Directly report to PM/President | Report to and assist Cabinet Ministers |
| Accountability | Fully responsible for their departments | Assist Cabinet Ministers in tasks |
| Protocol Status | Equivalent to Cabinet Ministers in status | Lower protocol status |
| Attendance in Cabinet Meetings | May attend if their portfolios are discussed | Not regular attendees |
PYQ:[2013] Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 [2007] Assertion (A): The Council of Ministers in the Union of India is collectively responsible both to the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha. Reason (R): The Members of both the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha are eligible to be the Ministers of the Union Government. Choose the correct Code: (a) Both A are R are true and R is the correct explanation of A (b) Both A and R are true but R is not a correct explanation of A (c) A is true but R is false (d) A is false but R is true |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
