From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Polygraph Test, Judments mentioned
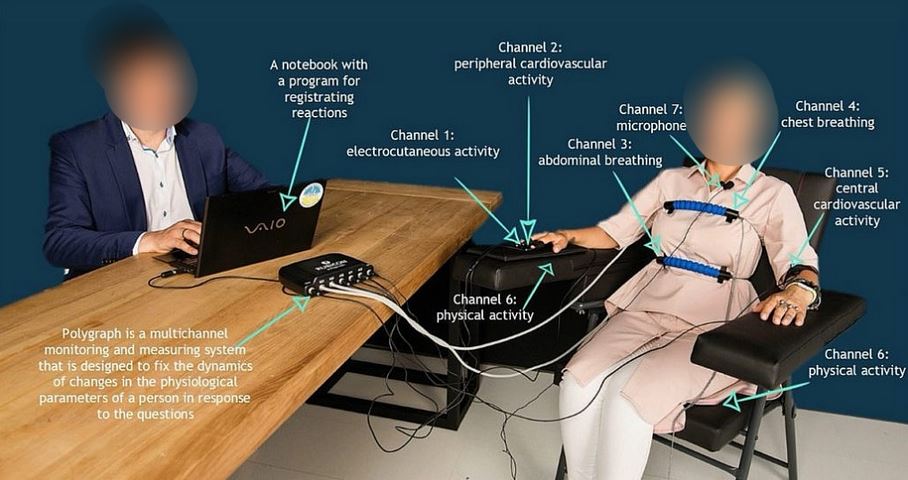
Why in the News?
The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) concluded polygraph tests on the accused in the Kolkata Rape and Murder Case.
About Polygraph Tests in India
| Details | |
| Definition | A procedure measures physiological responses like blood pressure, pulse, respiration, and skin conductivity while a subject answers questions to detect deception. |
| Physiological Indicators | • Heart Rate and Blood Pressure: Monitored for changes. • Respiratory Rate: Tracks breathing patterns. • Galvanic Skin Response (GSR): Measures skin’s electrical conductance, which varies with moisture levels. |
| Procedure | • Sensor Connection: Attached to the chest, fingertips, and arm. • Baseline Questions: Establish physiological response baselines. • Control and Relevant Questions: Analyzed to identify deceptive responses by comparing physiological changes. |
| Constitutional Provisions | • Article 20(3): Protects against self-incrimination; necessitates consent for polygraph tests. • Article 21: Concerns about potential violations of the right to life and privacy due to mental torture aspects of polygraph tests. |
| Legal and Judicial Rulings | • Selvi vs. State of Karnataka (2010): Tests must be voluntary with informed consent. • D.K. Basu vs. State of West Bengal (1997): Involuntary tests could violate the Right to Life and Privacy. |
| Admissibility in Court | According to the Indian Evidence Act, 1871, results from polygraph tests are not admissible as evidence in court. |
| Guidelines | National Human Rights Commission Guidelines (1999): Establish consent and procedural requirements for administering polygraph tests to align with human rights standards. |
PYQ:[2018] Right to Privacy is protected as an intrinsic part of Right to Life and Personal Liberty. Which of the following in the Constitution of India correctly and appropriately imply the above statement? (a) Article 14 and the provisions under the 42nd Amendment to the Constitution. (b) Article 17 and the Directive Principles of State Policy in Part IV. (c) Article 21 and the freedoms guaranteed in Part III. (d) Article 24 and the provisions under the 44th Amendment to the Constitution. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
