
Yesterday, February 28th was celebrated as National Science Day. In 1986, the Govt. of India designated this Day, to commemorate the announcement of the discovery of the “Raman effect”.
CV Raman
- Raman conducted his Nobel-prize winning research at IACS, Calcutta.
- While he was educated entirely in India, Raman travelled to London for the first time in 1921, where his reputation in the study of optics and acoustics was known to physicists such as JJ Thomson and Lord Rutherford.
- The Raman Effect won scientist Sir CV Raman the Nobel Prize for physics in 1930.
- It was also designated as an International Historic Chemical Landmark jointly by the American Chemical Society (ACS) and the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science (IACS).
- His speciality was the study of vibrations and sounds of stringed instruments such as the Indian veena and tambura, and Indian percussion instruments such as the tabla and mridangam.
The Raman Effect
- In 1928, Raman discovered that when a stream of light passes through a liquid, a fraction of the light scattered by the liquid is of a different colour.
- While Raman was returning from London in a 15-day voyage, he started thinking about the colour of the deep blue Mediterranean.
- He wasn’t convinced by the explanation that the colour of the sea was blue due to the reflection of the sky.
- As the ship docked in Bombay, he sent a letter to the editor of the journal Nature, in which he penned down his thoughts on this.
- Subsequently, Raman was able to show that the blue colour of the water was due to the scattering of the sunlight by water molecules.
- By this time he was obsessed with the phenomenon of light scattering.
Observing the effect
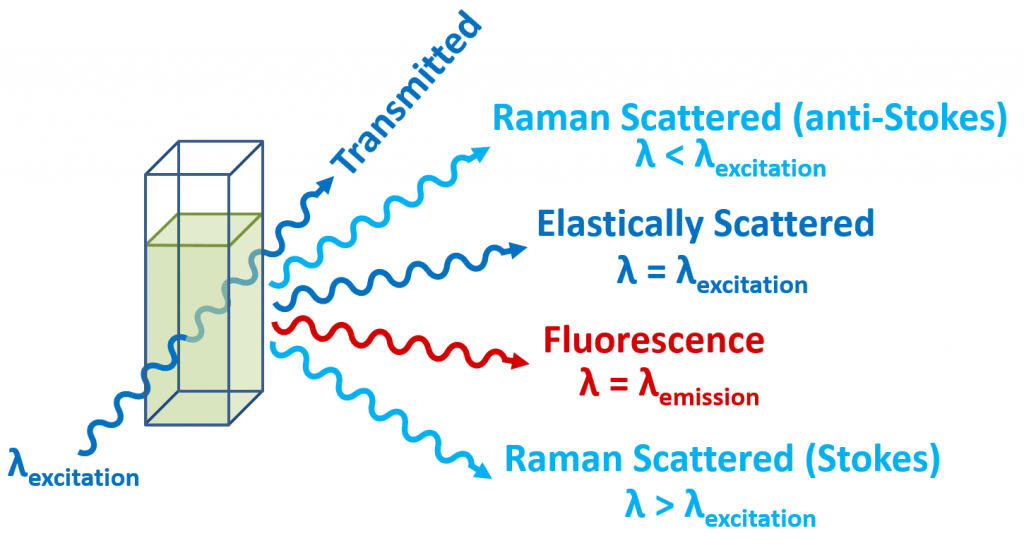
- The Raman Effect is when the change in the energy of the light is affected by the vibrations of the molecule or material under observation, leading to a change in its wavelength.
- Significantly, it notes that the Raman effect is “very weak” — this is because when the object in question is small (smaller than a few nanometres), the light will pass through it undisturbed.
- But a few times in a billion, light waves may interact with the particle. This could also explain why it was not discovered before.
- In general, when light interacts with an object, it can either be reflected, refracted or transmitted.
- One of the things that scientists look at when light is scattered is if the particle it interacts with is able to change its energy.
Applications
- Raman spectroscopy is used in many varied fields – in fact, any application where non-destructive, microscopic, chemical analysis and imaging is required.
- Whether the goal is qualitative or quantitative data, Raman analysis can provide key information easily and quickly.
- It can be used to rapidly characterize the chemical composition and structure of a sample, whether solid, liquid, gas, gel, slurry or powder.

