From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Silicosis and its health implications
Why in the News?
UK researchers suggest stricter daily silica dust exposure limits in industries could save 13,000 lives as per British Medical Journal Thorax.
What is Silicosis?
- Silicosis is a lung disease that results in the hardening of the lungs. It is caused by inhaling silica dust or crystals, commonly found in soil, sand, concrete, mortar, granite, and artificial stone.
- Silicosis is a chronic disease that develops slowly, often after 10 to 20 years of exposure.
- Silicosis can lead to other severe conditions, including lung cancer, tuberculosis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
| Note: Silicosis is a recognized disease under the Mines Act (1952) and the Factories Act (1948). |
Causes of Silicosis:
- Workers in industries such as construction, mining, oil and gas extraction, kitchen engineering, dentistry, pottery, and sculpting are at high risk.
- The cutting, drilling, or breaking down of materials containing silica releases fine dust into the air.
As per National Programme on Elimination of Silicosis in India
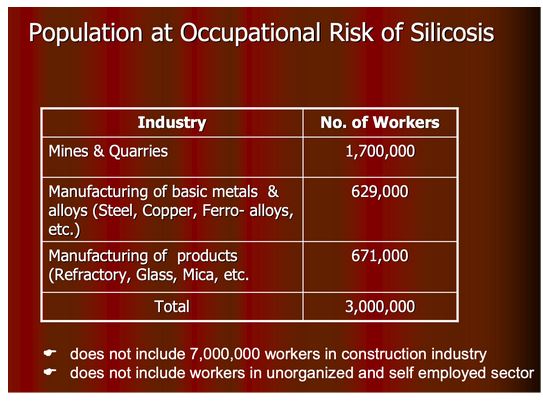
Remedies for Silicosis:
Currently, there is no cure for silicosis, and treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications.
Preventive measures:
- Water Suppression Techniques: Using water or foam to suppress dust at the source.
- Proper Ventilation: Ensuring adequate airflow in work environments to reduce dust accumulation.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Providing workers with masks and respirators that filter out fine particles.
- Regular Monitoring: Implementing regular health checks for workers and monitoring air quality in workplaces.
Case study related to reducing Silica Dust Exposure
|
PYQ:[2019] Why is there a great concern about the ‘microbeads’ that are released into environment? (a) They are considered harmful to marine ecosystems. (b) They are considered to cause skin cancer in children. (c) They are small enough to be absorbed by crop plants in irrigated fields. (d) They are often found to be used as food adulterants. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
