WORLD BANK GROUP

- The World Bank Group (WBG) is a family of five international organizations that make leveraged loans to developing countries. It is the largest and most famous development bank in the world and is an observer at the United Nations Development Group. Its five organizations are the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD), the International Development Association (IDA), the International Finance Corporation (IFC), the Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA) and the International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID).
The World Bank
- The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD), better known as the World Bank, was established at the same time as the International Monetary Fund to tackle the problem of international investment.
- The World Bank (IBRD) is an inter-governmental institution, corporate in form, whose capital stock is entirely owned by its member-governments. Initially, only nations that were members of the IMF could be members of the World Bank; this restriction on membership was subsequently relaxed.
International Development Association
- The International Development Association (IDA) is the part of the World Bank group that helps the world’s poorest countries. Overseen by 173 shareholder nations, IDA aims to reduce poverty by providing loans (called “credits”) and grants for programs that boost economic growth, reduce inequalities, and improve people’s living conditions.
- IDA complements the World Bank’s original lending arm—the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD). IBRD was established to function as a self-sustaining business and provides loans and advice to middle-income and credit-worthy poor countries. IBRD and IDA share the same staff and headquarters and evaluate projects with the same rigorous standards.
- IDA is one of the largest sources of assistance for the world’s 771 poorest countries, 39 of which are in Africa, and is the single largest source of donor funds for basic social services in these countries.
- IDA lends money on concessional terms. This means that IDA credits have a zero or very low interest charge and repayments are stretched over 25 to 40 years, including a 5- to 10-year grace period. IDA also provides grants to countries at risk of debt distress.
- In addition to concessional loans and grants, IDA provides significant levels of debt relief through the Heavily Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) Initiative and the Multilateral Debt Relief initiative (MDRI).
IFC
- The IFC was established in 1956 to support the growth of the private sector in the developing world.
- While the World Bank (IBRD and IDA) provides credit and non-lending assistance to governments, the IFC provides loans and equity financing, advice, and technical services to the private sector.
The Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA)
- It is an international financial institution which offers political risk insurance and credit enhancement guarantees. Such guarantees help investors protect foreign direct investments against political and non-commercial risks in developing countries. MIGA is a member of the World Bank Group and is headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States.
- MIGA is owned and governed by its member states, but has its own executive leadership and staff which carry out its daily operations. Its shareholders are member governments which provide paid-in capital and have the right to vote on its matters.
INTERNATIONAL MONETARY FUND
You must remember that the name World Bank does not refers to a bank in conventional sense (this is because it performs development function). And International Monetary Fund or IMF performs the lending function(which we associate with banks).

Structure and Size of IMF:
The International Monetary Fund:
- 188 countries member.
- Headquarters: Washington, D.C.
- It has 2,300 staff members.
Functions of IMF
The International Monetary Fund functions :
- The IMF is basically a lending institution which gives advances to members in need.
- It is the mentor of its members’ monetary and exchange rate policies.
- To maintain the stability in Exchange rate system around the World.
Operations of IMF and World Bank :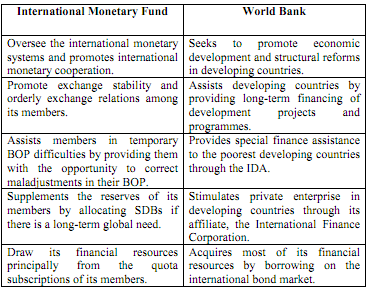
source
ADB
Asian Development Bank (ADB) was set up to fight poverty in Asia and the Pacific. ADB is a multilateral development finance institution dedicated to reducing poverty in Asia and the Pacific. Established in 1966, ADB is now owned by 63 members, mostly from the region. The headquarters is in Manila with 24 other offices around the world.
AIIB & NDB

- The New Development Bank (NDB) is established by The BRICS states (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa). According to the Agreement on the NDB, “the Bank shall support public or private projects through loans, guarantees, equity participation and other financial instruments.” Moreover, the NDB “shall cooperate with international organizations and other financial entities, and provide technical assistance for projects to be supported by the Bank
- The bank is headquartered in Shanghai, China. The first regional office of the NDB will be opened in Johannesburg, South Africa
AIIB
Why Has India joined the AIIB?
There are many reasons for it:
- India is preparing start a large number of infrastructure projects, but they’re short of money, so they need help from China. Of course they can get money from ADB or WB, but they also need to find a balance between China and USA.
- It’s a great chance to develop economy links between India and China. These two countries both has huge market, and they also keep a rapid growth of economy.
- Though AIIB is a Chinese-lead financial institution, India is welcomed to play a important role in it. It’s the reason why the UK, Germany and France all want to be a member of AIIB.
WTO
Introduction
World Trade Organization, as an institution was established in 1995. It replaced General Agreement on Trade and Tariffs (GATT) which was in place since 1946.
UNO
The United Nations is an international organization founded in 1945 after the Second World War by 51 countries committed to maintaining international peace and security, developing friendly relations among nations and promoting social progress, better living standards and human rights.
The United Nations was the second multipurpose international organization established in the 20th century that was worldwide in scope and membership. Its predecessor, the League of Nations, was created by the Treaty of Versailles in 1919 and disbanded in 1946.
UN TIMELINE:

Organisation Structure of UN :

General Assembly:
- The General Assembly is the main deliberative, policymaking and representative organ of the United Nations.
- It is Comprise of all 193 Members of the United Nations.
- It provides a unique forum for multilateral discussion of the full spectrum of international issues covered by the Charter.
Security Council:
- IT has primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security.
- It has 15 Members, consisting of 5 permanent members—China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States—and 10 non-permanent members.
- Non Permanent seats are held for two-year terms, with member states voted in by the General Assembly on a regional basis
- Five permanent members hold veto power over UN resolutions, allowing a permanent member to block adoption of a resolution, though not debate.
- The presidency of the Security Council rotates alphabetically each month
Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) :
- It is the principal organ to coordinate the economic, social and related work of the United Nations and the specialized agencies and institutions.
- Voting in the Council is by simple majority; each member has one vote.
- The president is elected for a one-year term and chosen amongst the small or middle powers represented on ECOSOC.
- ECOSOC has 54 members, which are elected by the General Assembly for a three-year term.
- Seats on the Council are allotted based on geographical representation with fourteen allocated to African States, eleven to Asian States, six to Eastern European States, ten to Latin American and Caribbean States, and thirteen to Western European and other States.
- The work of specialised agencies and programmes of UN like WHO, FAO, UNESCO etc. is coordinated by ECOSOC.
Trusteeship Council :
- It was established in 1945 by the UN Charter to provide international supervision for 11 Trust Territories placed under the administration of 7 Member States, and ensure that adequate steps were taken to prepare the Territories for self-government and independence.
- By 1994, all Trust Territories had attained self-government or independence. Its work completed, the Council has amended its rules of procedure to meet as and where occasion may require.
The International Court of Justice:
- It is the UN’s main judicial organ.
- It is located at the Hague in the Netherlands
- It settles legal disputes between states and gives advisory opinions to the UN and its specialized agencies. Its Statute is an integral part of the United Nations Charter.
- ICJ has 15 judges, who serve 9-year terms; each from a different nation, elected by the General Assembly and Security Council.
- The Court settles legal disputes between nations only and not between individuals, in accordance with international law. If a country does not wish to take part in a proceeding it does not have to do so, unless required by special treaty provisions. Once a country accepts the Court’s jurisdiction, it must comply with its decision.
- The Court can only hear a dispute when requested to do so by one or more States. It cannot deal with a dispute of its own motion.
- Difference between the International Court of Justice (ICJ) and the International Criminal Court (ICC)
- The International Court of Justice has no jurisdiction to try individuals accused of war crimes or crimes against humanity. As it is not a criminal court, it does not have a prosecutor able to initiate proceedings.
- International Criminal Court set up under the Rome Statute. It was established as an independent international organization in 2002 and is not governed by the UN.
- All UN member states are automatically members of the ICJ; Nations must individually become members of the ICC.
- The ICJ settles disputes between member states, with their consent, on issues of sovereignty, trade, natural resources, treaty violations, treaty interpretation, and etc.
- The ICC tries individual people for genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes, and crimes of aggression, according to the Rome Statute.
- The ICJ issues both binding judgments and advisory opinions. Its judgments may then be enforced by the Security Council if the state fails to comply. The ICC, on the other hand, hands down criminal prosecutions or acquittals.
Secretariat:
- It carries out the day-to-day work of the Organization.
- It services the other principal organs and carries out tasks as varied as the issues dealt with by the UN: administering peacekeeping operations, surveying economic and social trends, preparing studies on human rights, among others.


Bhai isko padhne ke liye 2 din chaiye 😛
The content should be updated to current data.
In the section of differences between ICJ and ICC below statement is incorrect:
“All UN member states are automatically members of the ICC; Nations must individually become members of the ICJ”
I think they are swapped with each other. To become a member of ICC one needs to sign the Rome Statue while for ICJ, all UN members are automatically members of it.
If I’m wrong, please correct me.
Correction is done. Thanks for pointing it out.