Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
Mapping: Lao PDR
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Lao PDR
Why in the News?
The Indian Embassy in Lao PDR has successfully rescued 67 Indian nationals who were trafficked and forced to work in cyber scam centres in the Golden Triangle Special Economic Zone (GTSEZ).

Golden Triangle Special Economic Zone (GTSEZ)
|
About Lao PDR (Laos)
| Details |
|
| Geographical Location |
|
| Political Aspects |
Challenges:
|
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
India with Indonesia
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: India-Indonesia relations;
Why in the News?
Indonesian President Prabowo Subianto’s visit to India as the chief guest at the Republic Day parade highlighted the strong and historic relationship between the two countries.
Evolution of the bilateral relationship between India and Indonesia
|
What are the implications of India-Indonesia bilateral relations?
- Strengthened Strategic Partnership: The agreement to position an Indonesian liaison officer at India’s Information Fusion Centre highlights a commitment to enhance maritime cooperation and information sharing, which is crucial for regional security amidst rising tensions in the South China Sea.
- Collective Security Efforts: Both nations have emphasized the importance of combating terrorism and have agreed to enhance anti-terror cooperation. This reflects a mutual understanding of shared security challenges and the need for collaborative responses.
- Maritime Dialogue: The establishment of early dialogues on maritime security and cyber security indicates a proactive approach to address emerging threats and maintain stability in the Indo-Pacific region.
How will the agreements reached during this visit impact regional security dynamics?
- Promotion of Peaceful Resolutions: By advocating for a “full and effective” Code of Conduct (COC) in the South China Sea, India and Indonesia are positioning themselves as key players in promoting a rules-based order in the region, countering China’s assertive claims.
- Support for International Law: Their joint statement reinforces adherence to international laws, including the 1982 UNCLOS, which could serve as a counterbalance to unilateral actions by China in the South China Sea.
- Enhanced Cooperation with ASEAN: Both countries are likely to strengthen ties with ASEAN nations that share similar concerns about China’s maritime ambitions, fostering a united front in regional diplomacy.
What economic benefits are anticipated from enhanced collaboration?
- Local Currency Transactions: The emphasis on using local currencies for bilateral trade is expected to reduce transaction costs and enhance trade volumes between India and Indonesia, thereby boosting economic ties.
- Increased Trade Opportunities: Enhanced cooperation in sectors such as hydrography and defense could open new avenues for economic collaboration, potentially leading to increased investments and joint ventures.
- Maritime Commerce: By advocating for unimpeded lawful maritime commerce, both nations aim to secure vital trade routes that are crucial for their economies, particularly in light of the South China Sea’s significance as a global trade corridor.
Way forward:
- Strengthen Multilateral Diplomacy: India and Indonesia should continue to collaborate with ASEAN and other regional stakeholders to promote a unified stance on maritime security, focusing on the full implementation of the South China Sea Code of Conduct and adherence to international law.
- Enhance Economic Integration: Both nations should prioritize deepening economic ties through initiatives like local currency transactions and joint ventures in defence and maritime sectors, fostering sustainable growth and bolstering regional economic stability.
Mains PYQ:
Q Mention the significance of straits and isthmus in international trade. (UPSC IAS/2022)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: BIMSTEC
Why in the News?
Delegates recently represented India at the 24th BIMSTEC Senior Officials’ Meeting (SOM) virtually hosted by Thailand.
Key highlights of 24th BIMSTEC Senior Officials’ Meeting
- The discussions focused on priority areas including sustainable development, regional connectivity, security, and people-to-people exchanges.
- Several documents, such as Plans of Action for cooperation, new cooperation mechanisms, and collaboration with external partners, were finalized.
- The meeting also discussed issues related to the upcoming 6th BIMSTEC Summit.
About BIMSTEC
|
Significance of BIMSTEC for Indo-Pacific Goals
- Maritime Connectivity: BIMSTEC unites Bay of Bengal states, strengthening maritime ties that are crucial for an open and inclusive Indo-Pacific.
- Regional Bridge: It links South Asia and Southeast Asia, aligning closely with India’s “Act East” policy and fostering broader Indo-Pacific integration.
- Security Cooperation: Focus on collaborative efforts in maritime security (e.g., counter-piracy, disaster management) supports a stable and secure Indo-Pacific.
- Economic Integration: By promoting trade, investment, and infrastructure development, BIMSTEC bolsters economic growth and connectivity in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Synergy with Other Frameworks: Its emphasis on connectivity, security, and economic cooperation complements initiatives such as ASEAN and the Indian Ocean Rim Association, collectively advancing Indo-Pacific objectives.
PYQ:[2022] Do you think that BIMSTEC is a parallel organisation like the SAARC? What are the similarities and dissimilarities between the two? How are Indian foreign policy objectives realized by forming this new organisation? |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
With Indonesia, India’s opportunity and Beijing’s eye
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: India and Indonesia relations;
Why in the News?
On October 20, Indonesia saw a big change in leadership. Nationalist Prabowo Subianto became president.
What are the implications of Indonesia’s new leadership for India-Indonesia relations?
- Increased Competition with China: Prabowo’s administration may lead to a more assertive Indonesian foreign policy that seeks to leverage its strategic position between China and India. However, the extent of this assertiveness will depend on how Indonesia navigates its growing economic reliance on China while maintaining its sovereignty.
- Potential for Enhanced Cooperation: Despite the challenges posed by China’s influence, India has an opportunity to deepen its engagement with Indonesia. This could involve collaborative efforts in sectors such as defence, maritime security, and trade, particularly given Indonesia’s strategic location and resource-rich economy.
How does Indonesia’s relationship with China impact its foreign policy choices?
- Strategic Balance: Prabowo’s decision to make China his first visit signals Indonesia’s pragmatic balancing between major powers. Despite concerns about China’s assertiveness in the Natuna Sea, Indonesia engages China for its economic clout and investments, especially in sectors like infrastructure and technology.
- Wariness Over Chinese Influence: Indonesia’s hesitance toward China’s extensive control over economic assets provides India an opportunity to position itself as a complementary partner that respects Indonesia’s sovereignty, especially given mutual interests in upholding maritime security in the Indo-Pacific.
- US-Indonesian Relations: Prabowo’s tenuous ties with the U.S. due to historical human rights allegations might encourage him to seek alternative partnerships, where India can play a constructive role in regional stability.
What opportunities exist for India to enhance its economic engagement with Indonesia?
- Energy and Mineral Resources: Indonesia’s rich reserves of coal, palm oil, nickel, and tin offer significant opportunities for India to secure its mineral and energy requirements, which aligns with India’s growing manufacturing and EV industries.
- Infrastructure and Maritime Cooperation: India’s existing partnerships in infrastructure, such as developing the Sabang port, can be expanded to reinforce connectivity and enhance trade routes between the Nicobar Islands and Indonesia.
- Services Sector Collaboration: India’s strength in IT and financial services can support Indonesia in reducing business costs and improving economic efficiency, particularly as it seeks to modernize and diversify its economy.
- Tourism and Cultural Exchange: Given Indonesia’s growing middle class and India’s appeal as a tourist destination, there is potential to expand tourism and cultural exchanges that celebrate shared heritage, including Hindu-Buddhist traditions.
Way forward:
- Strengthen Strategic and Economic Partnerships: India should actively engage Indonesia in joint initiatives across defense, maritime security, and infrastructure, leveraging Indonesia’s strategic location and resources to build a resilient Indo-Pacific framework that counters China’s regional influence.
- Deepen Cultural and Economic Ties: Expanding collaborations in sectors like IT, energy, and tourism, and celebrating shared heritage, will foster goodwill and position India as a trusted and complementary partner to Indonesia, reinforcing mutual growth and stability in the region.
Mains PYQ:
Q Indian Diaspora has an important role to play in South-East Asian countries’ economy and society. Appraise the role of Indian Diaspora in South- East Asia in this context. (UPSC IAS/2017)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
[pib] India’s Statement at the 21st ASEAN-India Summit
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ASEAN Summit
Why in the News?
In alignment with the theme of this year’s ASEAN Summit—“Enhancing Connectivity and Resilience”—PM Modi laid out the following ten key suggestions for strengthening cooperation.
Back2Basics: Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
|
Ten suggestions by PM Modi for ASEAN Connectivity and Resilience:
| No. | Suggestion | Details |
| 1 | ASEAN-India Year of Tourism (2025) | Declare 2025 as ASEAN-India Year of Tourism, with India committing USD 5 million to promote tourism between India and ASEAN. |
| 2 | Celebrating a Decade of India’s Act East Policy | Organize events connecting artists, youth, entrepreneurs, and think tanks, including a Music Festival, Youth Summit, Hackathon, etc. |
| 3 | Women Scientists’ Conclave | Hold an annual Women Scientists’ Conclave under the India-ASEAN Science and Technology Fund to promote collaboration and innovation. |
| 4 | Scholarships for ASEAN Students | Double the Masters scholarships for ASEAN students at Nalanda University and launch a new scholarship program for ASEAN students in agriculture. |
| 5 | Review of ASEAN-India Trade Agreement | Complete the review of the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement by 2025 to enhance economic ties and build a secure, resilient supply chain. |
| 6 | Disaster Resilience | Allocate USD 5 million from the ASEAN-India Fund for disaster resilience, with collaboration between India’s NDMA and ASEAN’s Humanitarian Assistance Centre. |
| 7 | Health Resilience | Institutionalize the ASEAN-India Health Ministers Meeting and invite two experts from each ASEAN country to India’s National Cancer Grid Vishwam Conference. |
| 8 | Digital and Cyber Resilience | Establish a cyber-policy dialogue between India and ASEAN to strengthen digital and cyber resilience. |
| 9 | Promoting a Green Future | Organize workshops on green hydrogen involving experts from India and ASEAN to promote sustainable energy solutions. |
| 10 | Climate Resilience | Promote the “Ek Ped Maa Ke Naam” (Plant for Mother) campaign to encourage tree planting and strengthen climate resilience. |
PYQ:[2016] Evaluate the economic and strategic dimensions of India’s Look East Policy in the context of the post-Cold War international scenario. [2015] India is a member of which among the following? (2015)
Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 3 only (c) 1, 2 and 3 (d) India is a member of none of them |
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2063975
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
Singapore: A partner in India’s growth story
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: India-Singapore Bilateral Relations; ASEAN Countries;
Mains level: India-Singapore Bilateral Relations;
Why in the News?
The PM’s upcoming visit to Singapore offers a chance to reflect on the current state of the relationship. India-Singapore ties are dynamic, continually presenting new opportunities.
India-Singapore Bilateral Relations
|
What is Singapore’s contribution to India’s Growth Story?
- Economic Hub: Singapore is India’s largest trade partner in ASEAN. Singapore serves as a crucial gateway for Indian companies seeking to expand in Southeast Asia, providing a robust platform for trade and investment.
- Largest Source of FDI: It is the leading source of FDI, among the largest sources of External Commercial Borrowings and Foreign Portfolio Investment, accounting for about 17% of total FDI inflows since 2000, with investments exceeding USD 136 billion over the last 22 years.
- Knowledge exchange: Singapore’s status as a hub for Indian talent, especially from IITs and IIMs, facilitates knowledge exchange and enhances India’s capabilities in various sectors
- Cultural Exchange: The strong cultural ties, supported by the Indian community in Singapore, have enriched bilateral relations. Ethnic Indians constitute approximately 9.1% of Singapore’s resident population.
How this relationship can achieve more considering the ASEAN region and Chinese dominance? (Way forward)
- Strategic Partnership: The relationship can be further strengthened by enhancing strategic dialogues and collaborations in areas like security, technology, and sustainability, particularly in the context of the Indo-Pacific region.
- Regional Connectivity: Initiatives like the Trilateral Highway, which aims to connect India with Myanmar and Thailand, can enhance regional connectivity and trade, positioning India and Singapore as central players in ASEAN.
- Countering Chinese Influence: As China asserts its influence in the region, India and Singapore can collaborate more closely to address shared concerns, leveraging their partnership to promote stability and security in Southeast Asia.
- Emerging Technologies: Focusing on emerging sectors such as semiconductors, green technologies, and electric mobility can open new avenues for cooperation, aligning with both nations’ goals for sustainable development.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
Growing Bilateral Relations between India and Vietnam
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bordering countries of Vietnam
Mains level: Importance of Vietnam for India
Why in the news?
During his welcome of Vietnamese Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh, Prime Minister Narendra Modi emphasized the significance of freedom of navigation while subtly referencing China.
Evolution of Bilateral Relations to Strategic Partnership
- Early Relations: Cultural and economic links between India and Vietnam date back to the 2nd century, with significant support from India during Vietnam’s struggles against colonialism and foreign intervention, particularly during the Vietnam War.
- Formal Diplomatic Relations: Official diplomatic relations were established in 1992, marking the beginning of extensive economic ties, including cooperation in oil exploration, agriculture, and manufacturing.
- Upgrade to Strategic Partnership (2007): The relationship was elevated to a “Strategic Partnership” during Vietnamese Prime Minister Nguyen Tan Dung’s visit to India in July 2007. This marked a significant step in formalizing cooperation across various sectors, particularly in defence and security.
- Comprehensive Strategic Partnership (2016): During Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to Vietnam in September 2016, the partnership was further upgraded to a “Comprehensive Strategic Partnership.” This upgrade emphasized enhanced cooperation in defence, trade, and cultural exchanges, as well as a shared commitment to regional security.
Vietnam’s Remarkable Strides under Communist Party of Vietnam (CPV) Leadership
- Economic Development: Under the CPV’s leadership, Vietnam has experienced significant economic growth and development, embracing a foreign policy of independence and multilateralism.
- This approach has positioned Vietnam as a reliable partner in the region, fostering deeper economic ties with countries like India.
- Strategic Investments: Vietnam has actively sought to attract Indian investments in various sectors, including renewable energy, pharmaceuticals, and technology.
- The Vietnamese government has expressed gratitude for India’s support during the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly in vaccine distribution, which has further solidified ties between the two nations.
Building Bridges in Strategic Relationship through Foreign Policy
- Shared Vision for the Indo-Pacific: Both Prime Ministers emphasized their commitment to a free, open, and rules-based Indo-Pacific.
- Indian PM’s assertion that India supports development, not expansionism, reflects a mutual stance against aggressive territorial claims, particularly in the South China Sea, where both nations advocate for adherence to international law.
- Collective Approach to Conflicts: The leaders highlighted the importance of a collective approach to resolving regional conflicts, including those in Myanmar and West Asia.
- This stance underscores their commitment to multilateralism and regional stability, with Vietnam recognizing India’s role as a stabilizing force in the Indo-Pacific.
Significance of the Visit
- Strengthening Strategic Ties: Prime Minister Chinh’s visit signifies a deepening of the strategic partnership, with both sides committing to enhanced cooperation in defence, maritime security, and economic development.
- The agreement on a $300 million credit line for Vietnam’s maritime capabilities is a notable outcome of the discussions.
- Cultural and Economic Connectivity: The visit also marked the signing of multiple agreements across various sectors, including customs, agriculture, and traditional medicine, demonstrating a comprehensive approach to enhancing bilateral relations.
- The establishment of digital payment connectivity is another step towards strengthening economic ties.
Way forward:
- Strengthening Economic and Trade Ties: Both nations should focus on achieving the proposed bilateral trade target of $20 billion by expanding cooperation in key sectors such as renewable energy, technology, and agriculture.
- Enhancing Defense and Security Cooperation: To address regional security challenges, particularly in the context of the South China Sea, India and Vietnam should deepen their defence and security collaboration.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
How will the EU elections impact Southeast Asia?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Pivot to South Asia
Why in the news?
A weak performance by green and left-wing parties, coupled with gains by the far-right, could lead the EU to adopt a more protectionist stance and a less environmentally focused foreign policy.
What happens in the EU parliament?
- Legislative Role and Trade Agreements: The European Parliament must approve all EU free trade agreements. For instance, it is currently involved in negotiations with Southeast Asian countries such as Indonesia, Thailand, and the Philippines. This approval process ensures that any trade agreement aligns with EU standards and regulations.
- Policy Shifts Due to Election Results: The recent gains by far-right factions in the European Parliament could shift legislative priorities. For example, a more nationalist Parliament may prioritize protectionist policies over liberal trade agreements, potentially imposing tariffs or restrictions on imports from Southeast Asia, as seen with past tariffs on Cambodian and Myanmar rice.
- Influence on Environmental and Human Rights Policies: With the Greens and Liberals losing seats, the European Parliament may place less emphasis on environmental sustainability and human rights. This shift could affect initiatives like the Just Energy Transition schemes with countries like Vietnam and Indonesia, which rely on EU support for their green agendas. Reduced focus on these areas could hinder such cooperative efforts.
Changes in the Commission
- Commission Presidency and Coalition Dynamics: Ursula von der Leyen, the incumbent European Commission President from the centre-right European People’s Party (EPP), faces a challenging re-election. She needs to secure 361 votes from Members of the European Parliament (MEPs).
- Shift in Policy Focus: The composition of the new Commission will significantly influence EU policy directions. If von der Leyen allies with the Greens, there could be an intensification of green policies and environmental initiatives, such as the European Green Deal.
- Leadership and Foreign Policy Changes: The departure of EU foreign policy chief Josep Borrell opens the field for new candidates vying to lead the European External Action Service (EEAS). The new leadership could reshape the EU’s foreign policy approach, with potential changes in emphasis on development cooperation and international relations, including those with Southeast Asia. This could affect ongoing initiatives like the Just Energy Transition partnerships with countries like Vietnam and Indonesia.
Pivot to South Asia
- Strategic Partnership and Economic Interests: Southeast Asia is an increasingly important economic partner for the EU. The region’s growing markets and economic dynamism offer significant trade opportunities. For instance, the EU is negotiating free trade agreements with countries like Indonesia, Thailand, and the Philippines, which could enhance trade flows and economic cooperation. Strengthening ties with Southeast Asia helps the EU diversify its trade partners and reduce reliance on traditional markets.
- Environmental and Green Transition Initiatives: Southeast Asia is a crucial region for the EU’s global environmental goals. The EU has invested in green transition initiatives, such as the Just Energy Transition schemes in Vietnam and Indonesia, providing over €20 billion in concessional loans and investments. These initiatives support Southeast Asian countries in adopting sustainable energy practices and combating climate change.
- Geopolitical and Security Considerations: Southeast Asia’s strategic location and geopolitical significance make it a vital region for the EU’s foreign policy. By engaging more deeply with Southeast Asia, the EU can strengthen its influence in a region where other major powers, such as China and the United States, are also vying for influence.
Conclusion: The EU’s evolving policies and leadership will shape its economic, environmental, and geopolitical engagement with Southeast Asia, highlighting the region’s strategic importance and potential for cooperation.
Mains PYQ:
Q Africa was chopped into states artificially created by the accident of European competition. Analyse. (UPSC IAS/2013)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
Preparing for ASEAN-India FTA Review
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITGA), ASEAN
Why in the News?
The Commerce Department is gearing up for the upcoming negotiations on the ASEAN-India FTA review. The ASEAN-India FTA, while beneficial, has led to a widening trade deficit for India.
ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITGA):
Major Concern: Growing Trade Deficit
Because of this, there’s a need to urgently review and change the current trade setup between ASEAN and India. Key Areas of Negotiation
|
About ASEAN
| Details | |
| Establishment | Established in 1967 with the signing of the ASEAN Declaration (Bangkok Declaration). |
| Chairmanship | Rotates annually among member states based on alphabetical order of their names. |
| Objective | To promote political and economic cooperation and regional stability among member countries. |
| Members |
|
| Objectives |
|
| ASEAN Charter |
|
| ASEAN Plus Six |
|
| India and ASEAN |
|
| Delhi Declaration | Identifies Cooperation in the Maritime Domain as a key area of cooperation under the ASEAN-India strategic partnership. |
| Delhi Dialogue | Annual Track 1.5 event for discussing politico-security and economic issues between ASEAN and India. |
| ASEAN-India Centre (AIC) | Undertakes policy research, advocacy, and networking activities with organizations and think tanks in India and ASEAN. |
| Strategic Cooperation | India places ASEAN at the centre of its Indo-Pacific vision of Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR). |
PYQ:[2018] Consider the following countries:
Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN? (a) 1, 2, 4 and 5 (b) 3, 4, 5 and 6 (c) 1, 3, 4 and 5 (d) 2, 3, 4 and 6 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
India Initiates Review of Asean Trade Pact to Boost Domestic Manufacturing
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA)
Mains level: he trade deficit between India and the ASEAN region is primarily due to the following reasons
Why in the news?
The review aims to address concerns such as the inverted duty structure, which puts local manufacturers at a disadvantage.
Trade deficit issue with ASEAN
- High trade deficit: The trade deficit between India and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) has been a significant issue, with the deficit widening to USD 43.57 billion in the last fiscal from USD 25.76 billion in 2021-22 and just USD 5 billion in 2010-11
- Review AITIGA:This has led to a review of the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) by 2025, aiming to address concerns about trade barriers, abuse of the agreement, and the growing trade gap between India and the ASEAN region
ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA)
- The ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) is a trade agreement between the ten member states of ASEAN and India, signed in 2009 and implemented in 2010. The agreement aims to establish a free trade area between the parties, covering trade in physical goods and products, and progressively eliminating duties on 76.4 percent of goods.
The trade deficit between India and the ASEAN region is primarily due to the following reasons:
- Tariff disparities: India’s tariffs were much higher than partner countries, leading to a significant reduction in tariffs for partner countries, which in turn caused India’s imports to grow faster than exports. This imbalance has been widening since 2010-11, the year India entered into an agreement with ASEAN
- Non-tariff barriers and regulations: India’s exports to ASEAN have been affected due to non-reciprocity in FTA concessions, non-tariff barriers, import regulations, and quotas. These factors have hindered India’s ability to fully benefit from the FTA
- Routing of goods from third countries: There have been concerns about the routing of goods from third countries, such as China, to ASEAN countries with minimum value addition and then being imported into India, misusing the India-ASEAN FTA. This practice has contributed to the growing trade deficit
- Limited market access for Indian products: India’s exports of products such as textile clothing, footwear, food products, and minerals don’t have a significant place in ASEAN imports, while there is a higher dependence on products such as vegetables, fuels, chemicals, and metals from ASEAN, which are essential commodities
Conclusion
India’s review of the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement aims to tackle the widening trade deficit by addressing tariff disparities, non-tariff barriers, and the misuse of the agreement, crucial steps toward fostering fair and balanced trade relations.
Mains question for practice
Q Discuss the factors contributing to high deficit between India and ASEAN.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
What happened in Bhutan’s elections?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: India-Bhutan Relations and China Factor
Introduction
- In a significant political development, Tshering Tobgay and the People’s Democratic Party (PDP) emerged victorious in Bhutan’s recent runoff election, marking a pivotal moment in the country’s young democracy.
- Bhutan’s election not only reflects the evolving political dynamics within but also has broader implications for the region, particularly in terms of Bhutan’s relations with India and China.
Bhutan’s Democratic Evolution
- Fair Elections: Unlike some neighbouring countries, Bhutan’s elections have been largely free from tampering or political violence.
- Monarchy to Democracy: Since transitioning from a monarchy to a parliamentary democracy in 2008, Bhutan has seen its democratic processes evolve, with increased party participation and voter choice.
- Challenges: Despite progress, concerns about media censorship and discrimination against minorities persist.
Economic Context of the Elections
- Economic Challenges: Bhutan faces economic difficulties, including a struggling tourism sector, high youth unemployment, and significant emigration for better opportunities.
- Tobgay’s Economic Focus: Tobgay’s campaign centred on addressing these economic issues, promising investment and solutions to curb the emigration trend.
India’s Role and Regional Implications
- India-Bhutan Relations: India remains Bhutan’s largest donor and ally, playing a crucial role in Bhutan’s economic recovery and infrastructure development.
- Hydroelectric Potential: Bhutan’s untapped hydroelectric resources present opportunities for energy trade with India.
- China Factor: Recent years have seen heightened tensions between India and China over Bhutan, especially in the disputed Doklam region.
- Tobgay’s Pro-India Stance: Tobgay is perceived as pro-India, which aligns with India’s strategic interests in the region. His election has been positively received by Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
Conclusion
- Tshering Tobgay’s election victory in Bhutan is a testament to the country’s maturing democracy and its ability to navigate complex economic and geopolitical challenges.
- As Bhutan continues to balance its relationships with major powers like India and China, Tobgay’s leadership will be pivotal in shaping the nation’s future trajectory, both domestically and in the broader South Asian context.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
Review of ASEAN- India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITGA)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITGA)
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- India seeks to modernize the ASEAN India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITGA) to reduce the significant trade deficit with ASEAN nations in February 2023 with a target to complete the revamp by 2025.
About ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITGA)
| Details | |
| Signing Date | August 13, 2009, w.e.f. January 1, 2010. |
| Objectives | Eliminate tariffs and liberalize trade in goods.
Facilitate economic integration between ASEAN and India. |
| Key Features | Gradual reduction and eventual elimination of tariffs
Measures to facilitate trade and customs efficiency |
| Member Countries | ASEAN Members: Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam and India. |
| Economic Impact | Growth in trade between India and ASEAN countries – Diversification of trade basket. |
| Recent Developments | Discussions on reviewing and upgrading the agreement. |
| Challenges | Concerns over trade imbalances.
Potential impact on certain domestic industries in India. |
| Strategic Significance | Part of India’s “Act East” policy.
Step towards broader regional economic integration. |
Need for review
- Significant Trade Partner: ASEAN countries, including Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Brunei, Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar, and Cambodia, accounted for 11.3% of India’s global trade in 2022-23.
- Existing Trade Imbalance: The current trade deficit with ASEAN stands at $43.57 billion, a substantial increase from $7.5 billion per annum when the pact was first implemented.
- Trade Statistics: In 2022-23, India’s exports to ASEAN were valued at $44 billion against imports of $87.57 billion.
- Rebalancing Trade: The primary goal is to address the disproportionate benefits that have favored ASEAN since the agreement’s implementation in 2010.
- Modernization of the Agreement: The focus is on updating the FTA to reflect current global trade dynamics and include new elements like product-specific rules and trade remedies.
Key Areas of Negotiation
- Rules of Origin (ROO): Modifications in ROO are planned to increase market access for Indian products and prevent the rerouting of goods, particularly from China, through ASEAN countries.
- Trade Remedies: A new chapter on trade remedies will aim to protect domestic industries from unfair trade practices and import surges.
- Exclusion of New Areas: The agreement will not expand to cover additional areas like labor, environment, MSMEs, or gender to avoid complicating the pact.
Challenges and Industry Perspectives
- Need for Concessions: While India seeks to balance the trade deficit, concessions may be necessary to ensure mutual benefits.
- Sectoral Focus: Industries such as chemicals, plastics, minerals, leather, textiles, and gems and jewellery are identified for potential growth in exports.
Conclusion
- Strategic Approach: India’s efforts to modernize the AITGA reflect a strategic approach to enhance trade relations while protecting domestic interests.
- Balancing Act: The challenge lies in negotiating terms that benefit both India and ASEAN members, fostering a more equitable trading environment.
- Long-Term Implications: Successful negotiations could significantly impact India’s trade dynamics, potentially reducing the trade deficit and strengthening economic ties with ASEAN nations.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
ASEAN’s China dilemma
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ASEAN
Mains level: ASEAN summit, Indonesia's significant role, China challenges , India's concerns
What’s the news?
- In a recent ASEAN meeting, Indonesia, under the leadership of President Joko Widodo, successfully injected fresh perspectives into long-standing ASEAN stances.
Central idea
- The recent ASEAN meet in Jakarta, under Indonesia’s chairmanship, showcased the country’s adept handling of regional dynamics and its diplomatic finesse. With the president set to step down in 2024, this summit marked a high point in his leadership. Notably, eight ASEAN nations convened, with Myanmar excluded at the political level and Thailand undergoing a governmental transition.
Indonesia’s nuanced approach towards the Indo-Pacific
- Expanding the Arc of Prosperity: President Joko Widodo emphasized the need to expand the arc of prosperity within ASEAN. This highlighted Indonesia’s commitment to regional development and recognized the growing economic importance of the Indo-Pacific.
- ASEAN Indo-Pacific Forum (AIPF): Indonesia’s leadership resulted in the creation of the AIPF. This forum brought together government leaders from ASEAN countries, partner nations, and prominent figures from the business sector to discuss peace and prosperity in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Functional Approach: Indonesia’s approach to the Indo-Pacific was notable for its functional orientation. It emphasized cooperation and collaboration over strategic rivalry, aligning with the Quad’s cooperative outlook.
- Balancing Act with China: While Indonesia’s stance did not explicitly confront China, the absence of China from the AIPF was noticeable. This raises questions about how Indonesia aims to balance its Indo-Pacific approach with its relationship with China.
- Inclusive Dialogue: Indonesia’s strategy sought to position ASEAN as a key player in shaping the Indo-Pacific’s future. It underscored the importance of inclusive dialogue and cooperation for regional stability and prosperity.
- Regional Stability and Prosperity: Indonesia’s approach acknowledges that regional stability and prosperity are best achieved through collaboration and engagement rather than through overt confrontation or rivalry.
Myanmar’s Conundrum
- Exclusion from Political Level: Myanmar’s absence from the political level at the recent ASEAN summit was consistent with the organization’s practice, highlighting the ongoing internal turmoil since the military coup in February 2021.
- Indonesia’s Pragmatic Approach: Indonesia, under its ASEAN Chairmanship, demonstrated a pragmatic stance toward the Myanmar issue, recognizing the limitations of the Five-Point Consensus (5PC) framework intended for dialogue and resolution in Myanmar.
- Office of Special Envoy: Indonesia took a distinctive approach by establishing an office of the special envoy rather than appointing an individual special envoy, allowing for discreet engagement with Myanmar, neighboring nations, India, and ASEAN members.
- Facilitating Dialogue: The 5PC, once seen as a binding decision, is now considered a facilitating initiative, emphasizing Indonesia’s and ASEAN’s acknowledgment of the complexity of the Myanmar situation. This initiative aims to promote dialogue among various segments within Myanmar.
- Hosting of the ASEAN Summit: Myanmar’s exclusion from hosting the 2026 ASEAN summit highlighted the growing disconnect between the nation and the regional bloc. Historically, ASEAN used hosting privileges as leverage to address issues within member states, but their effectiveness in the current context remains uncertain.
China’s Challenge
- Primary Challenge for ASEAN: China poses the foremost challenge to ASEAN, especially concerning the looming big-power rivalry in the region. The call for peace and prosperity in the region is essentially a plea to prevent the United States and China from displaying their rivalry within ASEAN.
- Slow Progress on the Code of Conduct: Progress on the South China Sea (SCS) code of conduct has been sluggish. A significant point of contention is the differing interpretations of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), which creates obstacles to establishing a binding code of conduct.
- China’s Standard Map: China’s introduction of a new standard map that claims the territories of several countries, including those in the South China Sea, has added complexity to the situation. Notably, countries like India, Japan, the Philippines, Vietnam, Malaysia, and Indonesia raised their concerns about this map in bilateral discussions with China.
- Indonesia’s Cautious Approach: Indonesia, as the host of the ASEAN and East Asia Summit (EAS), maintained a cautious approach to the issue of China’s standard map during the summit, where the Chinese Premier was in attendance.
- Contradictions in Progress: The emphasis on UNCLOS and disputes over China’s map contradict the progress that ASEAN claims to have made on the code of conduct. The main purpose of the code is to govern the South China Sea as an international waterway, not as China’s domestic sea, as implied by the map.
Challenges to ASEAN Unity
- Myanmar’s Exclusion: A prominent challenge to ASEAN unity is the exclusion of Myanmar from political-level participation in the recent ASEAN summit. This exclusion stems from the ongoing political crisis in Myanmar, triggered by the military coup in February 2021.
- Thailand’s Transition: Thailand, another ASEAN member, is facing challenges due to its transitional government formed after an election. Consequently, it had official-level representation at the summit, raising concerns about the level of representation within ASEAN during crucial meetings.
India in the context of the ASEAN Indo-Pacific Forum (AIPF)
- Participation in AIPF: India, along with the US, UK, Canada, and Australia, conducted side events at the AIPF. This suggests that India is actively engaged in discussions at the forum.
- Concerns Over China’s New Map: Several countries, including India, raised bilateral concerns with China regarding its new standard map. This map claims territories that other countries consider their own, causing diplomatic tensions.
- Interest in the South China Sea: India has a vested interest in the South China Sea due to its trade and strategic considerations. India has been monitoring developments in the region, including China’s territorial claims and their impact on freedom of navigation.
Why India Needs ASEAN?
- Significant Trade & Commercial Relations: ASEAN is a major destination for India’s service sectors and a vital source of foreign investments.
- Development of North East India: ASEAN provides an alternate route for India’s access to North Eastern India, facilitating development and strategic interests.
- Countering Chinese Expansion: Strengthening ties with ASEAN countries helps India counter Chinese influence in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Maritime Freedom: Collaboration with ASEAN ensures a free and peaceful Indo-Pacific region based on a rules-based order.
- Support for Indian Initiatives: ASEAN’s support is crucial for India’s success in regional policies and initiatives.
- Emerging Market: India benefits from ASEAN’s agricultural and industrial products, while ASEAN relies on India’s demographic dividend.
- Global Reforms: ASEAN’s global influence aligns with India’s vision for reforms in international forums.
- Elevating India’s Global Status: Partnership with ASEAN enhances India’s geopolitical standing.
Strengthening ASEAN’s Position
- ASEAN Outlook on Indo-Pacific (AOIP): ASEAN is actively working to bolster its position by embracing the ASEAN Outlook on Indo-Pacific (AOIP). This strategic framework emphasizes ASEAN’s central role in the Indo-Pacific region, aiming to reinforce its influence and relevance.
- Enhanced Coast Guard Coordination: ASEAN is prioritizing improved coordination among its coast guards. This approach signifies a commitment to safeguarding maritime security and effectively managing potential conflicts in the region’s waters.
- Joint Defense Exercises: ASEAN is engaging in joint defense exercises as part of its efforts to strengthen its position. These exercises are viewed as a robust response to the sluggish progress on the South China Sea (SCS) code of conduct, with the goal of enhancing regional security.
- Addressing Code of Conduct Challenges: The slow progress on the South China Sea code of conduct is a significant concern for ASEAN. To tackle this issue, ASEAN is promoting the AOIP and intensifying security cooperation, reflecting its determination to address the challenges related to the code of conduct.
- Continuity through Troika Leadership: In a bid to maintain continuity and unity within ASEAN, Indonesia has formed a troika with the upcoming chairs, Laos and Malaysia. This arrangement aims to provide guidance and ensure ASEAN’s stability and coherence in the face of ongoing challenges and transitions.
Conclusion
- Indonesia’s leadership during the ASEAN summit deserves commendation for maintaining stability amidst the region’s complex challenges. In a rapidly changing world, ASEAN’s stability remains of paramount importance. Indonesia’s collaboration with the upcoming chairs, Laos and Malaysia, signals continuity in charting ASEAN’s course forward.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
India’s ASEAN Engagement and Upcoming Summits
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ASEAN
Mains level: India-ASEAN Relations

Central Idea
- Prime Minister departed for Indonesia to participate in the 20th ASEAN-India summit and the 18th East Asia Summit (EAS) in Jakarta.
- During the visit, he will meet with leaders from the ten ASEAN countries and attend the EAS, including leaders from ASEAN nations, Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, South Korea, Russia, and the U.S.
Why discuss this?
- India-ASEAN relations have evolved significantly over the years, moving from a distant past to a robust partnership.
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) |
|
| Established | August 8, 1967 |
| Member Countries | Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam |
| Objective | To promote political and economic cooperation and regional stability among member countries. |
| Key Areas of Cooperation | – Economic Integration
– Political and Security Cooperation – Social and Cultural Cooperation |
| Significance | Promotes economic growth, stability, and peace in the Southeast Asian region. It is also a forum for diplomatic dialogue and conflict resolution. |
| ASEAN Secretariat | Jakarta, Indonesia (The ASEAN Secretariat is the organization responsible for coordinating ASEAN activities.) |
Evolution of India-ASEAN Relations
- 1950s and Early 1960s: During this period, India played a significant role in supporting the decolonization efforts of Southeast Asian countries.
- 1960s to 1980s: India maintained some distance from the region due to internal issues and viewed ASEAN as a product of the Cold War.
- 1990s to 2010s: India adopted the ‘Look East Policy,’ leading to a full dialogue partnership with ASEAN in 1995 and becoming a full member of the ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF) in 1996.
- 2010s to Present: India-ASEAN cooperation intensified with the ‘Act East Policy,’ resulting in the elevation to a Strategic Partnership in 2012 and a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership in 2022.
Key Areas of Cooperation
- Trade Relations: The India-ASEAN Free Trade Agreement (AIFTA) and substantial trade volumes have strengthened economic ties, with commodity trade reaching $98.39 billion in the period April 2021-February 2022.
- Business & Investment: ASEAN is a major source of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) for India, with cumulative FDIs from ASEAN to India totaling $117.88 billion between 2000-2021. The ASEAN India-Business Council (AIBC) promotes collaboration between private sector players from India and ASEAN.
- Socio-Cultural Cooperation: Cultural affinities between ASEAN and India foster people-to-people interactions through initiatives like student exchange programs.
- ASEAN-India Projects: Collaboration in agriculture, science & technology, environment, renewable energy, and defense promotes mutual growth. The ASEAN-India S&T Development Fund (AISTDF) contributes $1 million to support joint collaborative R&D research projects.
- Strategic Cooperation: Platforms like the ASEAN Post Ministerial Conference (ASEAN PMC) and ADMM-Plus facilitate dialogue on security issues.
- Defense Cooperation: India is enhancing arms sales and defense ties with ASEAN countries to promote regional security, such as the recent approval by the Philippines for a USD 374 million purchase of the BrahMos shore-based anti-ship missile system in January 2022.
- Technological Cooperation: ISRO’s collaboration supports ASEAN countries in space science and technology.
- Connectivity: Projects like the India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway and Kaladan Multimodal Project enhance regional connectivity.
Why India Needs ASEAN?
- Significant Trade & Commercial Relations: ASEAN is a major destination for India’s service sectors and a vital source of foreign investments.
- Development of North East India: ASEAN provides an alternate route for India’s access to North Eastern India, facilitating development and strategic interests.
- Countering Chinese Expansion: Strengthening ties with ASEAN countries helps India counter Chinese influence in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Maritime Freedom: Collaboration with ASEAN ensures a free and peaceful Indo-Pacific region based on a rules-based order.
- Facing Politico-security Challenges: Cooperation in addressing security threats like climate change, terrorism, and refugee crises benefits both sides.
- Support for Indian Initiatives: ASEAN’s support is crucial for India’s success in regional policies and initiatives.
- Emerging Market: India benefits from ASEAN’s agricultural and industrial products, while ASEAN relies on India’s demographic dividend.
- Global Reforms: ASEAN’s global influence aligns with India’s vision for reforms in international forums.
- Diaspora: Southeast Asia’s significant Indian diaspora fosters cultural ties and people-to-people relations.
- Elevating India’s Global Status: Partnership with ASEAN enhances India’s geopolitical standing.
Challenges to Stronger Cooperation
- Large Trade Deficit: Trade imbalance and issues with the Free Trade Agreement (FTA) have impacted India’s economic relations with ASEAN, with the trade deficit rising from around $5 billion in FY11 to USD 21.8 billion in FY19.
- Balancing China: ASEAN countries’ engagement with China and concerns over military capabilities impact the depth of cooperation with India.
- Delays in Connectivity Projects: Long gestation periods for connectivity projects hinder progress.
- Issues within ASEAN: Different political systems and human rights issues pose challenges to stronger cooperation.
Way Forward
- Enhance Trade Relations: Focus on the blue economy and sustainable development to boost economic ties.
- Accelerate Connectivity Projects: Expedite the completion of infrastructure projects and build new trade and transport linkages.
- Strengthen Regional Role: India must play a more prominent role in the region to address geopolitical challenges.
- Establish Dedicated Departments: Dedicated departments under central ministries can facilitate better cooperation with ASEAN.
Conclusion
- India’s commitment to ASEAN signifies its strategic engagement with the Indo-Pacific region.
- Despite challenges, enhancing cooperation in trade, connectivity, defence, and socio-cultural aspects can pave the way for mutual growth and regional peace.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
Cambodian King’s state visit to India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Angkor Wat
Mains level: India-Cambodia Relations

Central Idea
- Cambodian King Norodom Sihamoni is on his maiden state visit to India to mark the culmination of 70th anniversary of diplomatic relations with India.
Marking 70th Anniversary of Diplomatic Ties
- This visit holds special significance as it is the first state visit by a Cambodian King in nearly six decades, with the last visit being made by King Norodom Sihamoni’s father in 1963.
- India and Cambodia share warm and friendly relations, characterized by deep-rooted people-to-people ties, cultural connections, and a commitment to mutual economic growth.
India-Cambodia Diplomatic Ties: A Backgrounder

[A] Historical Background
| Additional Information | |
| Indianization of Southeast Asia | Spread of Indian religions, cultural practices, art, architecture, and literature across Southeast Asia |
| Funan Kingdom (1st to 6th century CE) | Indian traders establishing commercial links with Funan, leading to the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural practices |
| Chenla Kingdom (6th to 9th century CE) | Emergence of Chenla as an Indianized kingdom with continued Indian cultural and religious influence |
| Khmer Empire (9th to 15th century CE) | Peak of Indian influence, adoption of Hinduism and later Buddhism, construction of monumental temples and structures like Angkor Wat |
| Sanskrit Inscriptions and Literature | Adoption of Sanskrit as court language, creation of inscriptions and literary works in Sanskrit |
| Cultural Exchange and Artistic Influence | Indian art, architecture, and performing arts influencing Cambodian temples, sculptures, and dance forms |
| Royal Ties and Religious Connections | Close connections between ruling elites of the Khmer Empire and Indian kingdoms, the transmission of Buddhist teachings and scriptures from India |
[B] Diplomatic Relations
- Establishment of Diplomatic Ties: India and Cambodia established diplomatic relations in 1952 after Cambodia’s independence from French colonial rule.
- High-Level Visits: Frequent visits by Indian Prime Ministers and Presidents to Cambodia and vice versa to strengthen bilateral relations and political dialogue.
- Bilateral Agreements: Signing of agreements covering areas such as economic cooperation, cultural exchanges, defense, and tourism.
- Resident Diplomatic Missions: Indian Embassy in Phnom Penh and Cambodian Embassy in New Delhi facilitating regular communication and coordination.
- Regional and Multilateral Engagement: Collaboration within organizations like ASEAN and East Asia Summit, providing platforms for regional cooperation and addressing challenges.
Various facets of India-Cambodia Relations
(1) Economic Cooperation
- Growing Bilateral Trade: Focus on sectors like textiles, pharmaceuticals, automobiles, agriculture, and information technology.
- Development Assistance: India’s support in sectors like agriculture, irrigation, human resource development, and capacity building.
- Investment and Joint Ventures: Exploring opportunities for investment and collaborative projects.
(2) Defense and Security Cooperation
- Training and Capacity Building: Defense cooperation through training programs for Cambodian armed forces personnel.
- Defense Dialogues and Exchanges: Regular engagement in discussions on maritime security, counter-terrorism, and defense industry collaboration.
(3) Cultural and Educational Exchanges
- Art, Music, Dance, and Literature: Fostering cultural ties through exchanges and appreciation of each other’s cultural heritage.
- Scholarships and Education: ICCR scholarships facilitate Cambodian students’ higher education in India.
- People-to-People Connections: Cultural festivals, events, and tourism enhance mutual understanding and interactions.
Strategic significance of Cambodia for India
- Geostrategic Location: Cambodia’s position in Southeast Asia provides India with access to crucial sea routes and enhances its engagement in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Regional Connectivity: Cambodia’s connectivity with other ASEAN countries allows India to strengthen regional partnerships and facilitate trade, investment, and people-to-people exchanges as part of its Act East Policy.
- Balancing China’s Influence: Strengthening relations with Cambodia enables India to maintain a balanced approach and counterbalance China’s growing influence in the region.
- Maritime Security: Cambodia’s coastal geography and access to the Gulf of Thailand are strategically important for India’s maritime security concerns. Cooperation with Cambodia supports regional stability and ensures the safety of vital sea routes.
- Economic Engagement: Cambodia’s growing economy and investment potential offer opportunities for India to enhance economic cooperation, boosting trade, investments, and joint ventures for mutual benefit.
- Cultural Diplomacy: Cambodia’s historical and cultural linkages with India provide a foundation for strong cultural and people-to-people ties, enhancing India’s soft power in the region.
- Defense and Security Cooperation: Collaborating with Cambodia in defence and security areas contributes to regional security, including capacity building, joint exercises, and information sharing.
Way Forward
- Strengthen Economic Ties: Expand bilateral trade and investment, explore new sectors, and foster business partnerships.
- Enhance Defense Cooperation: Continue training and capacity-building programs, and deepen discussions on shared security challenges.
- Cultural Exchanges and Tourism: Promote greater cultural understanding, organize more cultural events, and facilitate tourism exchanges.
- People-to-People Contacts: Encourage more interactions between citizens, foster academic collaborations, and promote tourism.
- Regional Cooperation: Engage actively within ASEAN and other regional forums to address common challenges and pursue shared interests.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
ASEAN-India maritime exercise in South China Sea
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ASEAN
Mains level: India-ASEAN Relations
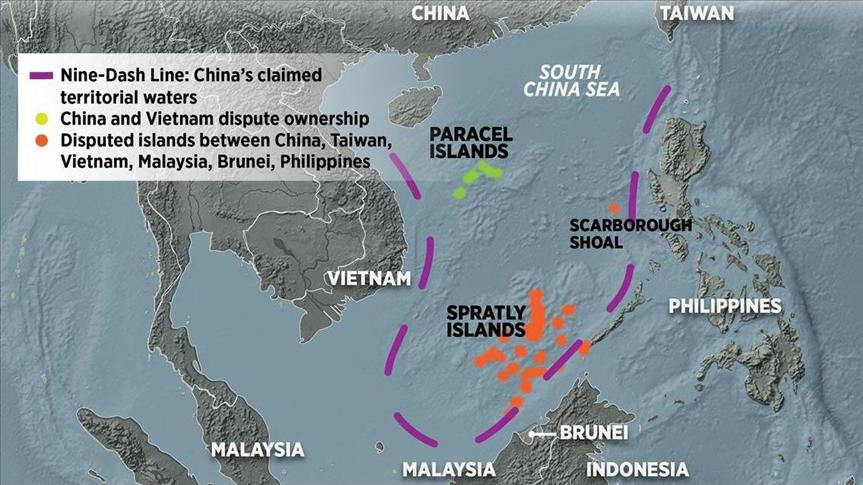
Central idea: The article highlights India’s increasing military cooperation with ASEAN countries, with a special emphasis on the upcoming ASEAN-India Maritime Exercise (AIME) in the South China Sea.
ASEAN-India Maritime Exercise
- The first ASEAN-India Maritime Exercise (AIME) is set to commence on May 2, 2023, with war games to be held in the South China Sea.
- INS Satpura and INS Delhi will participate in the exercise.
- The exercise is divided into two phases: ‘Harbour Phase’ and ‘Sea Phase.’
- The exercise is aimed at fostering close cooperation and conducting seamless operations in the maritime domain between the Indian Navy and ASEAN navies.
About ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations)
| Details | |
| Members | Brunei Darussalam, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam |
| Formation | August 8, 1967 |
| Headquarters | Jakarta, Indonesia |
| Purpose | To promote economic growth, social progress, and cultural development |
| Economic integration | ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) and ASEAN Economic Community (AEC) |
| Political cooperation | ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF) and ASEAN Defense Ministers Meeting (ADMM) |
| Cultural cooperation | ASEAN Socio-Cultural Community (ASCC) |
| Relationship with India | Strategic partnership, trade, and investment |
Why such exercise?
- Defying territorial claims: The South China Sea is a critical waterway that connects the Indian Ocean with the Pacific Ocean, and it is also a contested region where multiple countries have territorial claims.
- Support freedom of navigation: Conducting exercises in this region allows India to demonstrate its commitment to maintaining freedom of navigation and upholding international maritime laws.
- Indo-Pacific Strategy: India’s growing strategic ties with ASEAN are part of its broader Indo-Pacific strategy, which seeks to promote a rules-based order and ensure stability in the region.
- Counterbalancing China: As China’s influence in the Indo-Pacific grows, India sees ASEAN as a key partner in balancing China’s assertiveness and promoting regional stability.
India’s stakes in South China Sea
The South China Sea plays a critical role in India’s security and well-being as-
- Global common: The SCS is not China’s sea, but a global common.
- Unimpeded navigation: It has been an important sea-lane of communication for centuries, and passage has been unimpeded. Indians have sailed these waters for well over 1,500 years with a continuous trading presence.
- Global trade chokepoint: Nearly $200 billion of India’s trade passes through the South China Sea, and thousands of Indian citizens study, work and invest in ASEAN, China, Japan and the Republic of Korea.
Key significance: India’s Responsiveness to ASEAN
India needs to be responsive to ASEAN’s expectations.
- Meeting ASEAN’s aspirations: While strategic partnerships and high-level engagements are important, ASEAN expects longer-lasting buy-ins by India in their future.
- History of lesser importance given by India: ASEAN has taken the initiative time and again to involve India in Indo-Pacific affairs, even though India’s current level of trade or investment with ASEAN does not make a compelling argument.
- Broader perception of India as key partner: ASEAN has deliberately taken a longer-term view, given the importance of regional arrangements for economic recovery and rejuvenation.
Back2Basics: South China Sea Dispute
- It is a dispute over territory and sovereignty over ocean areas, and the Paracels and the Spratlys – two island chains claimed in whole or in part by a number of countries.
- China, Vietnam, the Philippines, Taiwan, Malaysia, and Brunei all have competing claims.
- Alongside the fully-fledged islands, there are dozens of rocky outcrops, atolls, sandbanks, and reefs, such as the Scarborough Shoal.
- China claims by far the largest portion of territory – an area defined by the “nine-dash line” which stretches hundreds of miles south and east from its most southerly province of Hainan.
- Beijing says its right to the area goes back centuries to when the Paracel and Spratly island chains were regarded as integral parts of the Chinese nation, and in 1947 it issued a map detailing its claims.
- It showed the two island groups falling entirely within its territory. Those claims are mirrored by Taiwan.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
What is the East Asia Summit?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: East Asia SUmmit
Mains level: India-ASEAN Relations
Vice President Jagdeep Dhankhar addressed the East Asia Summit on the last day of his visit to Cambodia, as the three-day Association of South East Asian Nations (ASEAN) summit concluded.
East Asia Summit
- Simply, the EAS is an ASEAN initiative and refers to the annual Meeting of Heads of States/Governments of these countries, where they are able to discuss common concerns and interests.
- Beginning in 2005, 16 participating countries comprised EAS, with their first meeting in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
- These members were the 10 ASEAN countries, Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, and the Republic of Korea.
- ASEAN’s 10 member countries are Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- The United States and the Russian Federation joined at the 6th East Asia Summit in 2011.
Why was it created?
- Its creation was based on the idea of enhancing cooperation among East Asian countries and those in the neighbouring regions.
- Six priority areas of cooperation were identified – environment and energy, education, finance, global health issues and pandemic diseases, natural disaster management, and ASEAN Connectivity.
Topics discussed
The following issues have been discussed by the countries
- Chinese claims over the South China Sea
- United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS),
- Terrorism
- Actions of North Korea and
- Conflict situation in Myanmar
EAS’s links with India
- This year marks the 30th anniversary of ASEAN-India relations and is being celebrated as the ASEAN-India Friendship Year.
- In a joint statement, ASEAN-India acknowledged the deep civilizational linkages, maritime connectivity, and cross-cultural exchanges between Southeast Asia and India.
- All these have grown stronger over the last 30 years, providing a strong foundation for ASEAN-India relations.
New developments
- India has announced an additional contribution of USD 5 million to the ASEAN-India science and technology fund.
- It would enhance cooperation in sectors of public health, renewable energy and smart agriculture.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
Why is ASEAN holding a special meeting on Myanmar?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ASEAN
Mains level: Military coup in Myanmar

Foreign ministers from member countries of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) are meeting to discuss an intensifying crisis in Myanmar, 18 months after agreeing a peace plan with its military rulers.
What is ASEAN?
- ASEAN is a political and economic union of 10 member states in Southeast Asia.
- It brings together ten Southeast Asian states – Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam – into one organisation.
- It was established on 8th August 1967 in Bangkok, Thailand with the signing of the Bangkok Declaration by the founding fathers of the countries of Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, Singapore, and the Philippines.
- The preceding organisation was the Association of Southeast Asia (ASA) comprising of Thailand, the Philippines, and Malaysia.
- Five other nations joined the ASEAN in subsequent years making the current membership to ten countries.
Why is the meeting happening?
- ASEAN’s peace effort is the only official diplomatic process in play.
- There has been a failure with the junta unwilling to implement a so-called “five-point consensus” that it agreed to with ASEAN in April 2021.
- The United Nations has backed the ASEAN plan, but with suspicion the generals are paying lip service and buying time to consolidate power and crush opponents before a 2023 election.
- For ASEAN to remain credible as a mediator, it may need to present a new strategy before the summit.
What is the consensus?
- The agreement includes-
- Immediate end of hostilities
- All parties engaging in constructive dialogue
- Allowing an ASEAN envoy to mediate and meet all stakeholders, and
- ASEAN to provide humanitarian assistance.
- So far, the only success cited by ASEAN chair Cambodia has been allowing some humanitarian access, but that has been limited and conditional.
How has the Junta (Military govt. in Myanmar) responded?
- The military government has accused critical ASEAN members of meddling and warned them not to engage.
- It has accused its opponents of trying to sabotage the ASEAN plan and has justified military offensives as necessary to secure the country and enable political talks.
- Instead of advocating for the five-point ASEAN plan, the generals have instead been pushing a five-step roadmap of their own towards a new election, with few similarities.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
Geopolitics follows the geoeconomics and not vice-versa
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: international relations
 Context
Context
- Over the recent years India’s manoeuvres in indo-pacific have highlighted the India’s geopolitical and ambitions. Pandemic and Chinese incursion in Ladakh forced India to move fast to achieve its geopolitical ends. However missing link in India’s endeavour is geoeconomics.
What is mean by geopolitics and geo-economics?
- Geopolitics: is defined as the struggle over the control of geographical entities with an international and global dimension, and the use of such geographical entities for political advantage.
- Geo-economics: is defined as the combination of economic and geographic factors relating to international trade and a governmental policy guided by geoeconomics.
- Geopolitics and geoeconomics are sometimes used interchangeably.
What is the strategy to pursue geopolitical goals in indo-pacific?
- India has managed to emerge as a major pivot of the global Indo-Pacific grand strategic imagination.
- Avoided the temptations to militarise/securitise the Quad (Australia, Japan, India and the United States).
- Which has ensured that the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) states do not feel uneasy by the ever-increasing balance of power articulations in the Indo-Pacific
 What is the missing link in India’s geopolitical strategy?
What is the missing link in India’s geopolitical strategy?
- The missing link in geoeconomics is India’s decision to take to the Indo-Pacific and Quad in a big way.
- While unwilling to join two of the region’s key multilateral trading agreements goes to show that geoeconomics and geopolitics are imagined and pursued parallelly in New Delhi, not as complimenting each other.
- The most recent example is India’s refusal to join the trade pillar of the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF) while deciding to join the three other pillars of the IPEF supply chains, tax and anti-corruption, and clean energy.
India also withdrew from ASEAN led RCEP.
Is the lack of geoeconomic bad for foreign policy?
- The absence of the world’s fifth largest economy from various regional trading platforms will invariably boost China’s geo-economic hegemony in Asia.
- Staying out of IPEF is a bad idea is because for India, it would be hard to integrate itself into the regional and global supply chains without being a part of important regional multilateral trading agreements.
- We have no option but to address some of the deeper challenges plaguing the investment and business environment in India.
- If India is indeed serious about its maritime grand strategy, which cannot be solely military in nature, it needs to get the states in the region to create economic stakes in India (something China has done cleverly and consistently) and vice-versa.
- Another impact of India’s hesitation about joining regional multilateral trading arrangements is its potential regional economic isolation. The less India engages with the region economically, and the more China does so, and given the Sino-Indian rivalry, India might risk getting economically isolated in the broader region.
 What can be done?
What can be done?
- New Delhi should: rethink its geoeconomic choices if it is serious about enhancing its geopolitical influence in the region. Given that India has not closed the door on the trade pillar of the IPEF, we have an opportunity to rethink our position.
- India should: also rethink its decision not to join the RECP and seek to join the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) from which the U.S. walked out and China is seeking to join.
- India should: also proactively lobby to become a part of the Minerals Security Partnership, the U.S.-led 11-member grouping to secure supply chains of critical minerals.
Conclusion
- In the words of external affairs minister Dr. Jaishankar,” geopolitics follows the geoeconomics and not vice-versa”. Geoeconomics is inclusive of geoeconomics. India should integrate itself in multilateral trading platforms and leverage its big market to bargain the best deal for itself.
Mains question
Q. Indias pursuit of geopolitics is futile without inclusion of geoeconomics. Comment.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
Back in news: India- ASEAN Relations
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ASEAN
Mains level: India-ASEAN Relations

The Foreign Minister of Myanmar is unlikely to be part of the 24th ASEAN-India Ministerial summit.
What is the news?
- Myanmar’s absence is the souring ASEAN-Myanmar.
- This is after the coup that overthrew the Aung San Suu Kyi government in Myanmar.
- This shows India’s concern over the junta in Myanmar which has refused to enter into a negotiation
What is ASEAN?
- ASEAN is a political and economic union of 10 member states in Southeast Asia.
- It brings together ten Southeast Asian states – Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam – into one organisation.
- It was established on 8th August 1967 in Bangkok, Thailand with the signing of the Bangkok Declaration by the founding fathers of the countries of Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, Singapore, and the Philippines.
- The preceding organisation was the Association of Southeast Asia (ASA) comprising of Thailand, the Philippines, and Malaysia.
- Five other nations joined the ASEAN in subsequent years making the current membership to ten countries.
India-ASEAN Relations: A Backgrounder
- Look-East Policy in 1992 gave an upthrust to India -ASEAN relation and helped India in capitalizing its historical, cultural and civilizational linkages with the region.
- India entered into a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) in goods with the region in 2003 which has facilitated the bilateral trade which now stands at approximately USD 76 Billion.
- Further, the launch of Act East Policy in 2014 has added a new vigour to India-ASEAN relations.
Significance of ASEAN to India
- ASEAN’s centrality in India’s foreign policy – A cohesive, responsive, and prosperous ASEAN is central to India’s Indo-Pacific Vision and India’s Act East Policy and contributes to Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR).
- Economic – ASEAN is the one of the largest market in the world comparative to the EU and North American markets.
- It’s also the 4th most popular investment destination globally.
- Investment opportunities for Indian businesses – Cost of production is lower in Laos, Cambodia, and Myanmar, which means that Indian firms can gain significantly by investing in these countries.
- Countering China – Cooperation between India and ASEAN is crucial to counter China’s power projection in the region. Both have territorial and border issues with China, disputes over the South China Islands and waters for ASEAN and over land boundaries for India.
- Integration with regional and global supply chains – Increasing engagement with ASEAN is pivotal to facilitate India’s integration with regional and global supply chain movements.
- North-East development – Connectivity projects with the ASEAN nations keeping Northeast India at the centre can ensure the economic growth of the land-locked north-eastern states.
- Collaboration with the ASEAN nations is necessary to counter insurgency in the Northeast, combat terrorism, etc.
- Maritime security – The Indian Ocean carries 90% of India’s trade and its energy sources. Presence of choke points such as the Malacca strait makes the South-East Asian region significant for countering traditional and non-traditional maritime threats like piracy and terrorism.
- Indian Diaspora – About 9-8% of the population in Malaysia and Singapore is of Indian origin, in Myanmar-4% and Indonesia about 0.5%.
Areas of Cooperation
- Economic Cooperation – ASEAN is India’s 4th largest trading partner.
- India signed FTA in goods in 2009 and an FTA in services and investments in 2014 with ASEAN.
- India has a Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) with various countries of the ASEAN region which has resulted in concessional trade and a rise in investments.
- Political Cooperation – ASEAN-India Centre (AIC) was established to undertake policy research, advocacy and networking activities with organizations and think-tanks in India and ASEAN.
- Delhi Dialogue – Annual Track 1.5 event for discussing politico-security and economic issues between ASEAN and India.
- Financial Assistance – India provides financial assistance to the ASEAN nations through various mechanism like ASEAN-India Cooperation Fund, ASEAN-India S&T Development Fund and ASEAN-India Green Fund.
- Connectivity – India has been undertaking several connectivity projects like India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral (IMT) Highway and the Kaladan Multimodal Project.
- India is also trying to establish a Maritime Transportation Agreementwith ASEAN and also Plans for a Railway link between New Delhi in India to Hanoi in Vietnam.
- Socio-Cultural Cooperation – Programmes to boost People-to-People Interaction with ASEAN are organized, such as inviting ASEAN students to India, Special Training Course for ASEAN diplomats, Exchange of Parliamentarians, etc.
- Defence Cooperation – Joint Naval and Military exercises are conducted between India and most ASEAN countries.
- Vietnam has traditionally been a close friend on defense issues, Singapore is also an equally important partner.
- Maritime Cooperation – adopted Delhi Declaration and decided to identify Cooperation in the Maritime Domain as the key area of cooperation under the ASEAN-India strategic partnership.
- India is developing its maiden deep-sea port in a strategically located Sabang port in Indonesia.
REGIONAL COMPREHENSIVE ECONOMIC PARTNERSHIP (RCEP) AGREEMENT
- RCEP is a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) that has been signed between 15 countries including the 10 ASEAN members, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, and New Zealand.
- RCEP was first proposed in 2011 with an aim to create a consolidated market for the ASEAN countries and their trade partners.
- RCEP now forms the world’s largest trade bloc, covering over 2.2 billion people and accounting for 30% of the world’s economy.
- Though India was a part of the RCEP’s negotiations, it dropped out in November 2019, citing significant outstanding issues that remain unresolved.
Reasons behind India pulling out of RCEP
- Trade imbalance with RCEP members – India’s trade deficit with RCEP countries has almost doubled in the last five-six years.
- Chinese Angle – From a geopolitical perspective, RCEP is China-led or is intended to expand China’s influence in Asia. India has already signed FTA with all the countries of RCEP except China.
- Signing of RCEP can lead to cheaper products from China flooding the Indian market.
- Lack of adequate protection for domestic industries – India’s proposals for strict Rules of Origin (to prevent routing of products from non-RCEP countries) and an Auto-trigger mechanism to impose tariffs when imports crossed a certain threshold which were not accepted.
- Lack of Service component – Most developed RCEP countries where India can export services, have been unwilling to negotiate wide-ranging disciplines in services that can create new market access for trade in services in this region.
- Concerns by local industries – A large number of sectors including dairy, agriculture, steel, automobiles, etc had expressed serious apprehensions on RCEP citing dominance of cheap foreign goods would dampen its business.
- India’s FTA experience – India’s FTAs has generally led to greater imports than exports, giving rise to high trade deficits with FTA partners like South Korea, Japan, and ASEAN.
Possible Implications of India not joining RCEP
Protectionist image – Withdrawal from RCEP along with other recent measures like call for self-reliance under Atmanirbhar Abhiyan, etc can be perceived as India taking a protectionist stance in terms of trade policy.
Lost opportunity for India’s export sector – RCEP was envisaged to strengthen Asian supply chains, bring in investments and boost the member countries’ competitiveness in global markets.
Effect on bilateral ties with RCEP countries – There are concerns that the decision will hamper India’s bilateral trade with RCEP member countries as they would be inclined to bolster trade within the bloc.
Lost opportunity in securing a position in the post COVID world: RCEP is expected to help member countries emerge from the economic devastation caused by the pandemic through access to regional supply chains.
Arguments for reviewing India’s decision
- Global Economic Stagnation due to Covid-19 pandemic – RCEP can serve as a bulwark in containing the free fall of the global economy and re-energising economic activity.
- RCEP presents a unique opportunity to support India’s economic recovery, inclusive development, and job creation even as it helps strengthen regional supply chains.
- Economic Realism – India should deter seeing RCEP only from the Chinese perspective.
- India can draw inspiration from Japan & Australia, as they chose to bury their geopolitical differences with China to prioritise what they collectively see as a mutually beneficial trading compact.
- Strategic Need – RCEP’s membership is a prerequisite to having a say in shaping RCEP’s rules, which is necessary to safeguard India’s interests and the interests of several countries that are too small to stand up to the largest member, China.
- As the summary of the final agreement shows, the pact does cover and attempt to address some issues that India had flagged, including rules of origin, trade in services, movement of persons. Therefore, this makes the case of India to review its decision and look RCEP through the lens of economic realism.
Challenges in India-ASEAN Relations
- China factor – India’s effort in this regard is meagre when compared to China’s dominance in the region
- China’s assertive military, political and economic rise, as well as the South China Sea disputes have divided ASEAN without unanimity amongst them.
- Economic challenges – India has an unfavourable balance of trade with the ASEAN nations.
- RCEP deal – India walking out of RCEP can become a sticking point between India and ASEAN, since India’s domestic market was considered a key element in the RCEP negotiations.
- India has not signed RCEP for various reasons like non-transparency in RCEP, RCEP’s non-accounting of India’s service sector relaxations, etc.
- By not signing the RCEP India also lose access to new market opportunities created in East Asia.
- Slow development in Bilateral relations – Many bilateral deals with these nations are yet to be finalised, leading to the halting of various aspects of diplomatic ties.
- Delayed projects – Though India has committed to many connectivity projects, they have not been completed at the rate on par with China
- China, on the other hand, through its BRI, is able to gain the trust of these countries.
India’s pulling out of the RCEP deal shows the limitations of the ties with the ASEAN nations. Maintaining cordial ties, both bilaterally and multilaterally with these nations is essential for both India’s economic and security interests.
South-East Asian nations are looking at India to take on a greater role for the economic integration of the region and for ensuring an open and inclusive Indo-Pacific. Many of the members of the ASEAN perceive India as a much-needed counterbalance to China.
Way Forward
- An alternative economic corridor based multimodal connectivity such as Mekong-India Economic Corridor may be promoted, which will connect Indian coast with unexplored Southeast Asian coast and beyond.
- Strengthening land, air, and sea linkages will enhance people-to-people flows, as well as boost business, investment, and tourism.
- With China having three times more commercial flights than India to Southeast Asia, improving air connectivity between India and ASEAN countries should also be high on the agenda.
- India has proposed setting up of an ASEAN-India Network of Universities (AINU) to enhance our educational ties.
- India can become the military partner after the Atma Nirbar Bharat, Make in India projects are successfully implemented.
- No ASEAN country has close military ties with China as they never trusted China for military alliance.
- Concept of QUAD must be expanded to include the ASEAN countries and become a QUAD+ arrangement.
- Vietnam and Indonesia have expressed a positive note on QUAD in the region.
- Digital technologies – Given the reluctance of ASEAN states to take help from Chinese giants in the field (due to concerns regarding China’s ability to own data), Indian IT sector may take some advantage.
- Strengthening cultural connect – Tourism can be further encouraged between India and the ASEAN with some creative branding by the two sides.
Failure of South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) has made India look outside South Asia towards countries of Southeast Asia for economic and political cooperation.
The ASEAN region has become strategically important for India due to its growing importance in the world politics. And for India to be a regional power as it claims to be, continuing to enhance its relations with ASEAN in all spheres must be a priority.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
India and Vietnam sign Mutual Logistics Agreement
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: South China Sea
Mains level: India’s Necklace of Diamonds Strategy

India and Vietnam signed a MoU on mutual logistics support.
India and other such Logistics Agreements
- Logistics agreements are administrative arrangements facilitating access to military facilities for exchange of fuel.
- It provides for logistical support and increasing operational turnaround of the military when operating away from India.
- India has signed several logistics agreements including with all Quad countries, France, Singapore and South Korea beginning with the Logistics Exchange Memorandum of Agreement (LEMOA) with the U.S. in 2016.
What makes this newer agreement special?
- The MoU is the first such major agreement which Vietnam has signed with any country.
- Both nations signed key pacts including a rare 10-year vision document.
- Both have similar territorial challenges from China.
Why Vietnam is at the centre of India’s policy to counter China?
- India entered the contested region of the South China Sea via Vietnam.
- India signed an agreement with Vietnam in October 2011 to expand and promote oil exploration in the South China Sea.
- It stood by its decision despite China’s challenge to the legality of Indian presence.
- Hanoi has been publicly sparring with Beijing over its claims to the South China Sea for some years now.
- India and Vietnam share a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership since 2016 and defence cooperation is a key pillar of this partnership.
- Vietnam is an important partner in India’s Act East policy.
Significance of such ties
- If China wants to expand its presence in South Asia and the Indian Ocean region, the thinking in New Delhi goes, India can do the same thing in East Asia.
- India can develop robust ties with states on China’s periphery such as Vietnam without giving China a veto on such relationships.
Contributing factor: India’s Necklace of Diamonds Strategy

- Over the past few years, China is expanding its footprint in the Indian Ocean through its ‘Debt Trap Diplomacy’ and ‘String of Pearls Strategy’.
- Through its String of Pearls strategy, China is expanding its footprints to contain Indian hold in the Indian Ocean.
- It is creating a ring around India through strategically placed nations such as at Chittagong (Bangladesh), at Karachi, Gwadar port (Pakistan) and at Colombo, Hambantota (both in Sri Lanka) and other facilities.
What is Necklace of Diamonds Strategy?
- It strategy aims at garlanding China or in simple words, the counter encirclement strategy.
- India is expanding its naval bases and is also improving relations with strategically placed countries to counter China’s strategies.
- Under this strategy, India’s strategic bases include-
- Changi Naval Base, Singapore
- Sabang Port, Indonesia
- Duqm Port, Oman
- Assumption Island, Seychelles
- Chabahar Port, Iran
- Apart from getting direct access to the strategically placed naval bases, India is also developing new naval bases, developing the old bases to garland China.
Conclusion
- India has a perfect antidote for Chinese expansion.
- It has been successful in establishing healthy relations with all the nations on China’s periphery.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
US to host ASEAN leaders
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ASEAN, IPEF
Mains level: Read the attached story
US President Joe Biden will host leaders and top officials of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) in Washington DC.
About ASEAN
- ASEAN is a political and economic union of 10 member states in Southeast Asia.
- It brings together ten Southeast Asian states – Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam – into one organisation.
- It was established on 8th August 1967 in Bangkok, Thailand with the signing of the Bangkok Declaration by the founding fathers of the countries of Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, Singapore, and the Philippines.
- The preceding organisation was the Association of Southeast Asia (ASA) comprising of Thailand, the Philippines, and Malaysia.
- Five other nations joined the ASEAN in subsequent years making the current membership to ten countries.
Why in news?
(A) Political purpose
- ASEAN’s ‘Five Point Consensus’ to end the turmoil in Myanmar has not progressed since it was released in April last year.
- In addition to discussing Myanmar, leaders are also expected to discuss Ukraine as well as regional issues.
(B) Economic purpose
- It is expected to discuss his administration’s economic plan for the region — the Indo Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF) — during this week’s summit.
- The framework will structure cooperation across several pillars from infrastructure and supply chains to taxation.
What is Indo Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF)?
- The proposed IPEF is the Biden administration’s answer to questions about the United States’ economic commitment to the vital Indo-Pacific region.
- IPEF will consist of four “pillars” of work:
- Fair and resilient trade (encompassing seven subtopics, including labor, environmental, and digital standards)
- Supply chain resilience
- Infrastructure, clean energy, and decarbonization
- Tax and anti-corruption
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
China does not have it all its way in the South China Sea
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Countries involve in South China sea dispute
Mains level: Paper 2- South China sea issue
Context
South-East Asian countries are increasingly wary of their giant neighbour.
Background of dispute
- Disputes in the South China Sea go back decades.
- But it was only ten years ago that China, which makes maritime claims for nearly the whole sea, greatly upped the ante.
- Countries involved: They involve Brunei, China, Malaysia, the Philippines, Taiwan and Vietnam, all with contesting claims.
- China provoked a stand-off that left it in control of an uninhabited atoll, Scarborough Shoal, which under un maritime law clearly belongs to the Philippines.
- Then China launched a massive terraforming exercise, turning reefs and rocks into artificial islands hosting airstrips and bases.
China’s strong-arm tactics
- China’s long-term aim is to project Chinese power deep into the South China Sea and beyond, and to hold the Americans away during any conflict.
- The immediate aim, though, is to dominate politically and economically as much as militarily.
- China has challenged oil-and-gas activity by both Indonesia and Malaysia, and sent drilling rigs to both countries’ eezs and continental shelves.
- It has bullied foreign energy companies into dropping joint development with Vietnam and others.
Implications
- China has paid a diplomatic price.
- Impact on relations with ASEAN: Had Mr Xi engaged in none of the terraforming and bullying, China would be better admired among members of the ten-country Association of South-East Asian Nations (ASEAN).
- Naval presence of the US: The United States and its Western allies have upped their naval presence in the sea, welcomed by most ASEAN members.
Negotiation on Code of conduct on South China Sea
- For years China dragged its feet on agreeing with ASEAN a code of conduct on the South China Sea, a principle agreed on 20 years ago in order to promote co-operation and reduce tensions.
- These days, China likes to play willing.
- China is demanding, in effect, the right of veto over ASEAN members’ naval exercises with foreign powers.
- It also wants to keep out foreigners from joint oil-and-gas development.
- Such demands are unacceptable to members.
Conclusion
Despite China’s efforts to establish its wild claims of sovereignty, China has been facing sustained resistance from the ASEAN countries.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
India-ASEAN FTA
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Free Trade Agreement
Mains level: India-ASEAN Relations
The Commerce and Industry Minister has called for a renegotiation of the India-ASEAN free trade agreement (FTA).
Why such move?
- The MCI aims to prevent its misuse by ‘third parties’ and remove trade restrictions as well as non-tariff barriers that he said had hurt Indian exports disproportionately since the pact was operationalized in 2010.
- The focus needed to be on new rules to eliminate misuse ‘by third parties outside ASEAN’, the minister said, hinting at China.
- India had to deal with several restrictive barriers on exports in the ASEAN region, particularly in the agriculture and auto sectors.
About ASEAN
- Members:

- Officially the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, ASEAN is an economic union comprising 10 member states in Southeast Asia.
- It promotes intergovernmental cooperation and facilitates economic, political, security, military, educational, and sociocultural integration between its members and other countries in Asia.
India-ASEAN Free Trade Agreement
- The initial framework agreement for ASEAN–India Free Trade Area (AIFTA) was signed on 8 October 2003 in Bali, Indonesia.
- The FTA came into effect on 1 January 2010.
- The FTA had emerged from a mutual interest of both parties to expand their economic ties in the Asia-Pacific region.
Background of the AIFTA
- India’s Look East policy was reciprocated by similar interests of many ASEAN countries to expand their interactions westward.
- After India became a sectoral dialogue partner of ASEAN in 1992, India saw its trade with ASEAN increase relative to its trade with the rest of the world.
- Between 1993 and 2003, ASEAN-India bilateral trade grew at an annual rate of 11.2%, from US$2.9 billion in 1993 to US$12.1 billion in 2003.
- Total Indian FDI into ASEAN from 2000 to 2008 was US$1.3 billion.
Acknowledging this trend and recognising the economic potential of closer linkages, both sides recognised the opportunities to pave the way for the establishment of an ASEAN–India Free Trade Area (FTA).
Structure of the AIFTA
- The signing of the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement paves the way for the creation of one of the world’s largest FTAs – a market of almost 1.8 billion people with a combined GDP of US$2.8 trillion.
- It sees tariff liberalisation of over 90 percent of products traded between the two dynamic regions, including the so-called “special products”.
- The products include palm oil (crude and refined), coffee, black tea and pepper.
Criticism
While there are many benefits to the ASEAN-India FTA, there is concern in India that the agreement will have several negative impacts on the economy.
- Opening-up its market: This FTA will allow them to increase the market access of their products.
- No specific gains: It is criticised, however, that India will not experience as great an increase in market access to ASEAN countries as ASEAN will in India.
- Export driven ASEAN: The economies of the ASEAN countries are largely export-driven. Considering India’s expansive domestic market, the ASEAN countries will look eagerly towards India as a home for its exports.
- Huge trade deficit: Since the early 2000s, India has had an increasing trade deficit with ASEAN. It is feared that a gradual liberalisation of tariffs and a rise in imported goods into India will threaten several sectors of the economy.
- Inaccessible Markets: As a dominant exporter of light manufacturing products, ASEAN has competitive tariff rates that make it difficult for India to gain access to the industry market in ASEAN countries.
- Cheaper imports: The state of Kerala is an important exporter in the national export of plantation products. It fears that cheap imports of oil palm, rubber, coffee, and fish would lower domestic production, adversely affecting farmers and ultimately its economy.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Foreign Policy Watch: India-ASEAN
Time for an Asian Century
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Challenges in securing RCEP
Asian centrality
- China’s response is a ‘dual circulation’ strategy for self-reliance and military-technological prowess to surpass the U.S.
- The global governance role of the U.S. is already reduced.
- The U.S. now exercises power with others, not over them.
- Despite its military ‘pivot’ to Asia, the U.S. needs India in the Quad, to counterbalance the spread of China’s influence through land-based trade links.
- India, like others in the Quad, has not targeted China and also has deeper security ties with Russia.
- With the ASEAN ‘code of conduct’ in the South China Sea, both the security and prosperity pillars of the U.S.-led Indo-Pacific construct will be adversely impacted.
- Leveraging proven digital prowess to complement the infrastructure of China’s Belt and Road Initiative will win friends as countries value multi-polarity.
Atmanirbhar Bharat and Challenges
- ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’ will leverage endogenous technological strength, data and population.
- With the Rafale aircraft purchase, India has recognised that there will be no technology transfer for capital equipment.
- Military Theatre Commands should be tasked with border defence giving the offensive role to cyber, missile and special forces based on endogenous capacity, effectively linking economic and military strength.
- The overriding priority should be infrastructure including electricity and fibre optic connectivity; self-reliance in semiconductors, electric batteries and solar panels; and skill development.
Conclusion
There are compelling geopolitical and economic reasons for shaping the building blocks of the Asia-led order, which is not yet China-led, to secure an ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’, and place in the emerging triumvirate.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024

