ISRO Missions and Discoveries
125 Years of Kodaikanal Solar Observatory (KoSO)
Why in the News?
The Department of Posts has released a commemorative postage stamp to mark 125 years of the Kodaikanal Solar Observatory (KoSO)—one of India’s oldest and most significant astronomical research centres dedicated to studying the Sun.
About the Kodaikanal Solar Observatory (KoSO):
- Founding: Established in the late 19th century, KoSO was established in 1899 after atmospheric surveys by Charles Michie Smith.
- Location: It is located in Kodaikanal, Tamil Nadu, in the Palani Hills, chosen for its excellent sky conditions.
- Early Observations: Initially focused on observing sunspots, solar prominences, and solar radiation.
- Modern Equipment: Now equipped with the H-alpha telescope (for flares and prominences) and WARM (for high-resolution sunspot imaging).
- Institutional Role: Became part of the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) in April 1971.
- Scientific Importance: KoSO contributes to understanding the Sun’s effect on Earth’s climate and space weather.
Important Observations / Discoveries:
- Evershed Effect (1909): Discovered by John Evershed, it was the first observation of radial gas outflows in sunspots, a key finding in solar physics.
- Historic Solar Archive (1904–2017): Created one of the world’s longest continuous solar datasets.
- Digitization: First Indian observatory to digitise solar data (since 1984); currently maintains a digital archive of 1.48 lakh images (~10 TB).
- Wider Scientific Work: Extended research into cosmic rays, radio astronomy, ionospheric physics, and stellar astrophysics over the decades.
| [UPSC 2016] Discuss India’s achievements in the field of Space Science and Technology. How the application of this technology has helped India in its socio-economic development? |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Chandrayaan-5 (LUPEX Mission) enters Preliminary Design Phase
Why in the News?
India and Japan have begun the preliminary design phase of the Chandrayaan-5 mission, also known as LUPEX (Lunar Polar Exploration).
Back2Basics: Legacy of Chandrayaan Missions
|
About Chandrayaan-5/LUPEX Mission:
- It is a collaborative mission between ISRO and JAXA.
- Approval: Cabinet approval for the mission was granted on March 10, 2025.
- Launch: It will carry a 6.5-tonne payload and launch aboard Japan’s H3 rocket in 2027–28.
- Collaboration: The lander is being developed by ISRO and the 350-kg rover by JAXA.
- Duration: The mission is expected to last 100 days, with a possible extension of one year.
- Mission Goals and Objectives:
-
- Explore water and regolith in the lunar south pole’s Permanently Shadowed Regions (PSRs).
- Drill into the Moon’s surface, analyse soil samples, and perform in-situ experiments.
- Assess water content, quality, and analyse surface volatiles using advanced instrumentation.
- Exploration of the far side of the Moon.
Scientific Collaboration and Instruments:
- A total of 7 scientific instruments will be onboard the mission.
- ISRO’s Contribution: Development of the lander; creation of one sensor in a major four-sensor instrument.
- JAXA’s Contribution: Development of the rover and three sensors in the same instrument; Rover is designed to climb 25° inclines and operate on a complex battery charging protocol.
- ESA (European Space Agency): Developing a mass spectrometer.
- NASA: Contributing neutron spectrometers.
| [UPSC 2009] In the context of space technology, what is Bhuvan, recently in the news?
Options: (a) A mini satellite launched by ISRO for promoting the distance education in India (b) The name given to the next Moon Impact Probe, for Chandrayaan-II (c) A geoportal of ISRO with 3D imaging capabilities of India* (d) A space telescope developed by India |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
[pib] Measuring Helium Abundance in the Sun
Why in the News?
Researchers at the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) have successfully estimated the abundance of Helium in the Sun’s photosphere with precision for the first time.
![[pib] Measuring Helium Abundance in the Sun](https://d18x2uyjeekruj.cloudfront.net/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/sun.jpg)
About Helium in the Sun’s Photosphere:
- Helium is the second most abundant element in the Sun after Hydrogen and plays a key role in understanding solar composition, opacity, and energy transport.
- However, measuring its precise abundance in the Sun’s photosphere has been challenging due to the absence of observable Helium spectral lines in visible light.
- Traditionally, Helium abundance was estimated using indirect methods like extrapolating data from hotter stars, solar wind observations, and seismological studies of the Sun’s interior.
- These methods lacked direct photospheric observations, making the estimates less accurate.
- Accurate measurements of Helium are essential for modelling the Sun’s opacity and energy transport. This also has broader implications for understanding the composition of other stars.
Novel Method Recently Discovered:
- Researchers from the IIA introduced a novel method to directly estimate Helium abundance in the Sun’s photosphere.
- This technique uses spectral features from Magnesium (Mg) and Carbon (C), overcoming the challenge of no direct Helium spectral lines.
- Spectral lines from Mg, C, and hydrogenated molecules (MgH, CH, C2) were used to infer Helium abundance.
- Equivalent Width analyses and spectrum synthesis techniques helped model the behavior of these elements in varying Helium-to-Hydrogen ratios.
- The Helium-to-Hydrogen ratio in the Sun’s photosphere was found to be 0.1, consistent with previous studies. This confirms the validity of the new method.
| [UPSC 2023] Diffusion of light in the atmosphere takes place due to:
Options: (a) Carbon dioxide (b) Dust particles* (c) Helium (d) Water vapors |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Comprehensive Remote Sensing Observation on Crop Progress (CROP)
Why in the News?
The ISRO through its CROP remote sensing framework, has estimated that the total wheat production from eight major wheat-growing states will reach 122.724 million tonnes by March 31, 2025.
About CROP:
- CROP is a semi-automated and scalable framework developed by ISRO’s National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC).
- The primary goal of CROP is to provide a real-time view of the sowing, growth, and harvest progress of crops, especially wheat during the Rabi season.
- CROP utilizes data from multi-source remote sensing satellites to monitor agricultural areas across India.
- Technological Components of CROP:
-
- EOS-04 (RISAT-1A): Provides Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data for crop monitoring, especially under varied weather conditions.
- EOS-06 (Oceansat-3): Offers optical remote sensing data for agricultural monitoring.
- Resourcesat-2A: Used for high-resolution optical imaging, focusing on agricultural areas for precise crop monitoring.
Key Features of the Study:
- The study used a combination of SAR and optical data to accurately assess crop progress during the 2024-25 Rabi season.
- The wheat sown area, as of March 31, 2025, stands at 330.8 lakh hectares, which is in line with the figures reported by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare (324.38 lakh hectares as of February 4, 2025).
- Wheat production in the eight major wheat-growing states is estimated to be 122.724 million tonnes by March 31, 2025, based on the data gathered through the remote sensing method.
| [UPSC 2019] For the measurement/estimation of which of the following are satellite images/remote sensing data used?
1. Chlorophyll content in the vegetation of a specific location 2. Greenhouse gas emissions from rice paddies of a specific location 3. Land surface temperatures of a specific location Select the correct answer using the code given below. Options: (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3* |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
50 years since the launch of Aryabhata
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Aryabhata
Why in the News?
50 years ago on April 19, 1975, India marked a major milestone in its space history with the successful launch of Aryabhata, its first satellite.
About Aryabhata
- Aryabhata, India’s first satellite, was launched on April 19, 1975, with Soviet assistance from the Kapustin Yar Cosmodrome.
- Named after the ancient Indian mathematician and astronomer Aryabhata, the satellite was a significant milestone in India’s space journey.
- It had a unique 26-sided polyhedron design, measuring 1.4 meters in diameter and weighing 360 kg.
- The satellite’s faces were covered with solar panels, except for the top and bottom.
- Aryabhata orbited the Earth every 96.3 minutes with an inclination of 50.7 degrees, and its apogee and perigee were 619 km and 563 km, respectively.
- Its mission was to conduct experiments in solar physics and X-ray astronomy.
- Despite experiencing a power failure after 5 days, Aryabhata continued transmitting data for several more days, completing a remarkable 17 years in orbit.
- This success was pivotal for India, establishing the country’s space capabilities.
Inception of India’s Space Program:
|
| [UPSC 2007] Consider the following statements:
1. In the year 2006, India successfully tested a full-fledged cryogenic stage in rocketry. 2. After USA, Russia and China, India is the only country to have acquired the capability for use of cryogenic stage in rocketry. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only * (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Aditya-L1 Mission: Scientists observe a Flareless Coronal Mass Ejection
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Aditya L1 Mission, CMEs
Why in the News?
India’s first solar mission, Aditya-L1, has made a significant scientific observation—a flareless Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) using the Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC) Payload.
About Flareless Coronal Mass Ejection (CME)
- A Flareless CME is a solar eruption that occurs without an associated solar flare.
- Unlike typical CMEs, which are often linked to intense bursts of electromagnetic radiation, flareless CMEs result from magnetic instabilities in the solar corona without sudden energy releases.
Key Features of Flareless CMEs:
- No Solar Flare Trigger: Unlike most CMEs, they do not originate from an intense energy burst.
- Magnetic Instability Driven: Plasma ejection occurs due to internal rearrangements in the Sun’s magnetic field.
- Gradual Energy Release: These CMEs may expand more slowly compared to CME-flare events.
- Scientific Significance: Helps differentiate CME mechanisms from flare activities, improving space weather forecasts.
About the Aditya-L1 Mission
- Aditya-L1 is India’s first space-based observatory dedicated to solar studies.
- Launched by ISRO, it is positioned at Lagrange Point 1 (L1), about 1.5 million km from Earth.
- It takes 125 days to reach L1, where gravitational equilibrium allows continuous solar observation.
- It is India’s second space observatory after AstroSat (2015).
- Mission Objectives:
- Study the solar corona, photosphere, chromosphere, and solar wind dynamics.
- Monitor solar activity, flares, and CMEs to predict space weather events.
- Provide early warnings for geomagnetic storms affecting Earth’s satellites and power grids.
- Scientific Instruments:
-
- Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC): Observes the solar corona and tracks CMEs.
- Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT): Captures images of the Sun’s lower atmosphere.
- Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEXS): Measures soft X-ray emissions from the Sun.
- High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer (HEL1OS): Detects high-energy solar X-rays.
- Aditya Solar Wind Particle Experiment (ASPEX): Studies solar wind particles and their impact on space weather.
- Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya (PAPA): Analyzes plasma properties in the solar wind.
- Magnetometer: Measures magnetic field variations at L1.
PYQ:[2022] If a major solar storm (solar flare) reaches the Earth, which of the following are the possible effects on the Earth ? 1. GPS and navigation systems could fail. 2. Tsunamis could occur at equatorial regions. 3. Power grids could be damaged. 4. Intense auroras could occur over much of the Earth. 5. Forest fires could take place over much of the planet. 6. Orbits of the satellites could be disturbed. Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 3 and 4 only (c) 1, 3, 4 and 6 only (d) 2, 5 and 6 only |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO undocks SpaDex Satellites in First Attempt
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PSLV-C60 SpaDeX Mission
Why in the News?
India achieved a major milestone in space docking technology with the successful undocking of satellites under the SpaDeX mission, marking ISRO’s first-ever undocking operation on March 14, 2025, just two months after the initial docking.
With this success, India joins an elite group of nations—the U.S., Russia, and China—that have demonstrated space docking and undocking capabilities.
What is PSLV-C60 SpaDeX Mission?
- The PSLV-C60 SpaDeX Mission is a landmark mission aimed at demonstrating in-space docking and undocking technology.
- This mission would position India as the fourth country in the world to master space docking, following the US, Russia, and China.
- Objective:
- To demonstrate the docking, undocking, and rendezvous capabilities of two satellites in low-Earth orbit (LEO).
- Facilitate power transfer between docked spacecraft, an essential capability for future space missions.
- Satellites: (Each weighing 220kg.)
- SDX01 (Chaser): Equipped with a High-Resolution Camera (HRC).
- SDX02 (Target): Carries a Miniature Multispectral Payload (MMX) and a Radiation Monitor (RadMon).
- Configuration:
- The satellites will be launched using the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV-C60) in a core-alone (CA) configuration, meaning without strap-on boosters.
- They will be placed in a 476-km circular orbit with an inclination of 55°.
- Post-Docking:
- After the docking demonstration, the satellites will continue standalone missions for two years, conducting imaging, natural resource monitoring, and radiation environment studies.
- Significance: It is a strategic step towards several ambitious space objectives, including:
- Preparing for the Gaganyaan human spaceflight program
- Enabling Chandrayaan-4 lunar sample return missions
- Developing the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS), India’s proposed space station35
What is Space Docking?
|
PYQ:[2018] “The experiment will employ a trio of spacecraft flying in formation in the shape of an equilateral triangle that has sides one million kilometres long, with lasers shining between the craft.” The experiment in question refers to- Options: (a) Voyager-2 (b) New Horizons (c) LISA Pathfinder (d) Evolved LISA |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Successful PHTA Test of ISRO’s Semi-Cryogenic Engine
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Successful PHTA Test of ISRO's Semi-Cryogenic Engine
Why in the News?
ISRO successfully conducted a hot test on the semi-cryogenic engine (SE2000), a key step towards finalizing the cryogenic stage for future launch vehicles. This Power Head Test Article (PHTA) is the first hardware test for semi-cryogenic engines.
About the SE2000 Engine
- The SE2000 engine is a semi-cryogenic rocket engine developed by ISRO to enhance propulsion for future heavy-lift launch vehicles.
- It is designed to power the booster stages of rockets, increasing payload capacity and efficiency.
- The engine operates on a Liquid Oxygen (LOX) and Refined Kerosene (RP-1) combination, unlike traditional cryogenic engines that use LOX and Liquid Hydrogen (LH2).
- Key features of the SE2000 engine:
- Thrust capability: 2000 kN (kilonewtons), making it one of ISRO’s most powerful engines.
- Higher density impulse: Provides better efficiency than LOX-LH2 combinations.
- Cost-effective: Kerosene is cheaper and easier to handle than liquid hydrogen.
- Storage advantages: Kerosene can be stored at ambient temperatures, unlike liquid hydrogen, which requires -253°C for storage.
- The engine is expected to enhance the performance of LVM3 and will be used in ISRO’s Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV).
- Applications of the SE2000 engine:
- Heavy-lift launch missions with increased payload capacity.
- Future space exploration programs, including human spaceflight missions like Gaganyaan.
- Reusable launch vehicles, contributing to cost-effective and sustainable space travel.
What is the PHTA Test?
- The PHTA test is a crucial hardware test conducted as part of the SE2000 semi-cryogenic engine development process.
- It is designed to validate key engine subsystems before full-scale integration and testing.
- Purpose of the PHTA test:
- Ensure subsystems perform as expected under operational conditions.
- Evaluate pressure, temperature, thrust efficiency, and fuel combustion.
- Identify potential technical issues before moving to full engine testing.
- A previous attempt in July 2023 was aborted due to technical issues at ISRO’s Mahendragiri facility.
Back2Basics: Semi-Cryogenic vs. Cryogenic Engines
|
PYQ:[2018] With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements: 1. PSLVs launch the satellites useful for Earth resources monitoring whereas GSLVs are designed mainly to launch communication satellites. 2. Satellites launched by PSLV appear to remain permanently fixed in the same position in the sky, as viewed from a particular location on Earth. 3. GSLV Mk III is a four-stage launch l vehicle with the first and third stages l using solid rocket motors; and the second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 (c) 1 and 2 (d) 3 only |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
First Detailed Map of Moon’s South Pole Area made from Chandrayaan Data
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Moon’s South Pole
Why in the News?
Astronomers are studying the first detailed geological map of the Moon’s South Pole, created by India’s Chandrayaan-3’s Vikram lander, which landed on August 23, 2023.
About the Geological Map of the Moon’s South Pole:
- First High-Resolution Map:
- This map is created by PRL Ahmedabad, Panjab University, and ISRO, using data from Chandrayaan-3’s Pragyan rover.
- It offers new insights into the Moon’s formation and evolution.
- Confirmation of a Magma Ocean:
- Pragyan’s Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer detected molten rock beneath the surface.
- This confirms a global magma ocean in the Moon’s early history.
- Age and Crater Mapping:
- Landing site estimated to be 3.7 billion years old, similar to Earth’s early evolution.
- Schomberger Crater identified as the primary source of impact debris.
- Importance for Lunar and Planetary Studies:
- Preserved craters help understand the history of asteroid impacts.
- Provides insights into the formation of the Earth-Moon system.
Why is the Moon’s South Pole a Key Focus for Space Missions?
- Water Ice Reserves:
- Permanently shadowed craters hold large water ice deposits, first confirmed by Chandrayaan-1 (2009).
- Crucial for future lunar colonies and deep-space missions.
- Harsh but Valuable Environment:
- Extreme cold (as low as -250°C) preserves ancient materials.
- Continuous sunlight in some areas makes it ideal for solar power.
- Scientific and Strategic Importance:
- Craters contain pristine material from the early Solar System.
- NASA, China, and Russia plan permanent research bases in the region.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
PARAS-2 Spectrograph
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PARAS-2 Spectrograph
Why in the News?
Scientists at PRL, Ahmedabad, discovered the exoplanet TOI-6038A b, a dense sub-Saturn-sized planet with a mass of 78.5 Earth masses and a radius of 6.41 Earth radii, using the PARAS-2 spectrograph at Mount Abu Observatory.
About TOI-6038A b
|
About PARAS-2 Spectrograph:
- PARAS-2 (PRL Advanced Radial-velocity All-sky Search-2) is a state-of-the-art high-resolution spectrograph designed for exoplanet detection.
- The development of PARAS-2 began in mid-2018 and was successfully installed at the telescope site in mid-2022.
- It is the highest-resolution stabilized radial velocity (RV) spectrograph in Asia, operating at a precision level of 30 cm/s.
- It is installed at PRL’s 2.5-meter telescope at the Mount Abu Observatory, benefiting from high-altitude, clear sky conditions.
- Key Features of PARAS-2:
-
- Operates in the 380-690 nm waveband, making it suitable for studying a wide range of celestial objects.
- Resolution of ~107,000, the highest in Asia, enabling ultra-precise exoplanetary studies.
- Ultra-stable temperature and pressure environment: Maintained at 24 ± 0.001 °C and 0.005 ± 0.0005 mbar, ensuring minimal instrumental drift.
- Uses a Uranium Argon Hollow Cathode Lamp (UAr HCL) for calibration, achieving a velocity precision of better than 2 m/s.
- Advanced optical fiber system for capturing stellar light and spectral calibration data simultaneously.
- It uses the radial velocity method, which detects tiny wobbles in a star’s motion caused by the gravitational pull of an orbiting planet.
- These wobbles cause shifts in the star’s light spectrum, allowing scientists to determine a planet’s presence, mass, and orbital period.
- It can detect minute stellar movements, making it ideal for finding low-mass exoplanets like super-Earths.
PYQ:[2015] The term ‘Goldilocks Zone’ is often seen in the news in the context of: (a) the limits of habitable zone above the surface of the Earth |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO’s 100th launch: why this is significant?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Space mission;
Why in the News?
In its first launch of 2025, the Indian Space Research Organisation achieved the milestone of 100 launches.
What does the 100th launch signify for India’s space capabilities?
The 100th launch underscores ISRO’s growth since its establishment in 1969, showcasing its evolution into a reliable launch partner for both domestic and international satellites.
- Technological Advancement: This launch utilized an indigenous cryogenic engine, highlighting India’s advancements in rocket technology. The GSLV series has been instrumental in increasing payload capacity and efficiency during satellite launches, contributing to ISRO’s reputation as a formidable player in the global space arena.
- Contribution to Navigation Systems: The NVS-02 satellite is part of India’s Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC) system, which enhances India’s capabilities in terrestrial, aerial, and maritime navigation.
- This satellite will replace the IRNSS-1E satellite and improve the accuracy and reliability of navigation services across India and surrounding regions.
What are the future plans for ISRO following this milestone?
- Ambitious Missions: Following this milestone, ISRO aims to undertake several high-profile missions, including a sample return mission from the Moon, a mission to Venus, and the establishment of an Indian space station. These initiatives are part of ISRO’s broader goal to expand its capabilities and presence in space exploration.
- Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV): ISRO is developing a heavier rocket called the NGLV, which will be capable of carrying up to 30,000 kg to low Earth orbit. This vehicle will feature a reusable first stage to enhance cost-effectiveness in launches.
- Expansion of Infrastructure: Plans are underway to build a third launch pad at Sriharikota to accommodate increased launch frequency and support human spaceflight missions alongside commercial launches.
How will private sector involvement shape ISRO’s future missions?
- Collaboration and Innovation: The PSLV-C60 mission exemplified successful collaboration between ISRO and private startups, allowing non-government entities to deploy payloads for in-orbit experiments.
- This initiative fosters innovation by enabling startups to test their technologies using ISRO’s infrastructure, thereby reducing costs and encouraging diverse contributions to India’s space capabilities.
- Transitioning Operational Responsibilities: ISRO aims to transfer more operational tasks to private companies, allowing them to manage activities traditionally handled by the agency.
- This shift is intended to increase efficiency and scalability within the space sector, empowering private entities to take on significant roles in satellite launches and other space activities, thus expanding India’s overall capabilities.
- Commercialization of Space Activities: The government has focused on increasing India’s share of the global space economy from 2% to 10% over the next decade through public-private partnerships.
Way forward:
- Strengthening Public-Private Synergy: ISRO should continue fostering collaboration with private players by expanding access to launch infrastructure, streamlining regulatory frameworks, and incentivizing innovation through initiatives like IN-SPACe and NSIL.
- Focus on Heavy-Lift and Reusability: Prioritizing the development of the Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV) with reusable technology will enhance cost-effectiveness, positioning India as a competitive player in the global commercial space sector.
Mains PYQ:
Q India has achieved remarkable successes in unmanned space missions including the Chandrayaan and Mars Orbiter Mission, but has not ventured into manned space mission. What are the main obstacles to launching a manned space mission, both in terms of technology and logistics? Examine critically. (UPSC IAS/2017)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Mission SCOT
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Mission SCOT
Why in the News?
Onboard SpaceX’s Transporter-12 mission, Indian space surveillance firm Digantara successfully launched SCOT (Space Camera for Object Tracking), the world’s first commercial Space Situational Awareness (SSA) satellite.
About Mission SCOT:
| Details |
|
|
| Aims and Objectives |
|
|
| Features/Significance |
|
|
| Contribution to India’s Growth |
|
PYQ:[2010] In the context of space technology, what is “Bhuvan”, recently in the news? (a) A mini satellite launched by ISRO for promoting the distance education in India (b) The name given to the next Moon Impact Probe, for Chandrayan-II (c) A geoportal of ISRO with 3D imaging capabilities of India (d) A space telescope developed by India |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Third launchpad at Satish Dhawan Space Center, Sriharikota
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Launh stations in India
Why in the News?
The Union Cabinet approved the construction of a third launchpad at Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh. In 2024, PM laid the foundation stone for ISRO’s second rocket launchport at Kulasekarapattinam in Tamil Nadu’s Thoothukudi district. (The first one being the Dr Abdul Kalam Island, Odisha.)
Who was Satish Dhawan?
|
About the New Launchpad
- The new launchpad at Sriharikota aims to bolster India’s space capabilities.
- It will support Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV) missions and enhance ISRO’s capacity to launch advanced satellites and spacecraft.
- Significance: This is India’s sole operational spaceport, serving as the hub for spacecraft and satellite launches since its inception.
How and why was Sriharikota selected as the Launch Site?
- 1960s Search: India’s search for an ideal launch site began in the 1960s when the country decided to develop indigenous satellites and launch vehicles.
- Vikram Sarabhai, the father of India’s space program, tasked EV Chitnis to identify a site on the east coast.
- Survey and Acquisition: By October 1968, approximately 40,000 acres of land were acquired in Sriharikota.
- Reasons for Choosing Sriharikota:
- East Coast Location: Launching rockets eastward takes advantage of Earth’s rotational speed, adding an extra velocity boost of 450 m/s, especially beneficial for geostationary satellites.
- Proximity to the Equator: Rockets launching near the equator require less energy to reach geostationary orbits, making the location ideal for such missions.
- Uninhabited Area: The site’s sparse population minimizes risks during rocket launches and component re-entry.
- Access to the Sea: Proximity to the Bay of Bengal ensures that rocket debris falls into the sea, avoiding hazards to land or human settlements.
- Strategic Accessibility: Adequate access to resources, infrastructure, and government support facilitated the development of a robust launch facility.
PYQ:[2018] With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Why ISRO’s ‘docking’ mission today is critical for India’s space ambitions?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Space sector;
Why in the News?
Recently, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) launched its Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX) in space with a PSLV rocket.
What is SpaDeX mission?
What is Space Docking?
|
What is the significance of India’s achievement in space docking technology?
- Joining an Elite Club: With the successful completion of the SpaDeX mission, India becomes only the fourth country in the world, after the United States, Russia, and China, capable of conducting space docking operations. This positions India as a key player in global space exploration and technology.
- Foundation for Future Missions: The docking capability is crucial for various upcoming missions, including India’s plans for a lunar sample return mission (Chandrayaan-4) and establishing its own space station by 2035. The ability to dock spacecraft allows for complex missions that require multiple launches and assembly in orbit.
How does the SpaDeX mission contribute to India’s future space exploration goals?
- Support for Lunar Missions: SpaDeX is designed to demonstrate technologies necessary for future lunar missions, particularly for Chandrayaan-4, which will involve multiple components that need to be docked in space before proceeding to the Moon.
- Bharatiya Antariksh Station: The mission is a critical step towards building the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS), which will consist of several modules that must be docked together in orbit. The first module is expected to launch by 2028.
- Satellite Servicing and Interplanetary Missions: The docking technology developed through SpaDeX will facilitate satellite servicing missions and interplanetary missions, enhancing India’s capabilities in space exploration.
What technological advancements were demonstrated through the SpaDeX mission?
- Innovative Docking Technology: The mission showcases advanced docking techniques using two small satellites (SDX01 and SDX02), which require high precision due to their smaller size compared to typical spacecraft. This necessitates more intricate maneuvering during the docking process.
- New Sensors and Systems: SpaDeX employs various new sensors such as Laser Range Finders and Rendezvous Sensors to ensure accurate measurements during docking.
- Additionally, it utilizes a new processor for determining relative positions and velocities, paving the way for future autonomous docking systems.
- Biological Experiments: For the first time, ISRO is conducting biological experiments in space with the CROPS (Compact Research Module for Orbital Plant Studies), which will study plant growth under microgravity conditions. This adds a new dimension to India’s space research capabilities.
Way forward:
- Enhancing Autonomous Docking Systems: Focus on developing fully autonomous docking capabilities for complex missions, enabling seamless execution of lunar, interplanetary, and modular space station operations.
- Strengthening Collaborative Ventures: Leverage international partnerships to exchange expertise and expand applications of docking technology in satellite servicing, resupply missions, and deep-space exploration.
Mains PYQ:
Q What is India’s plan to have its own space station and how will it benefit our space programme?(UPSC IAS/2019)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO SpaDEx PSLV-C60 Launch
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ISRO SpaDEx PSLV-C60 Launch
Why in the News?
ISRO’s PSLV will launch 2 satellites, SDX01 and SDX02, into a 476-km circular orbit in the first week of January to conduct the Space Docking Experiment (SpaDEx), marking India’s entry into the elite group of nations capable of mastering Space Docking.
What is PSLV-C60 SpaDeX Mission?
- The PSLV-C60 SpaDeX Mission is a landmark mission aimed at demonstrating in-space docking and undocking technology.
- This mission would position India as the fourth country in the world to master space docking, following the US, Russia, and China.
- Objective:
- To demonstrate the docking, undocking, and rendezvous capabilities of two satellites in low-Earth orbit (LEO).
- Facilitate power transfer between docked spacecraft, an essential capability for future space missions.
- Satellites: (Each weighing 220kg.)
- SDX01 (Chaser): Equipped with a High-Resolution Camera (HRC).
- SDX02 (Target): Carries a Miniature Multispectral Payload (MMX) and a Radiation Monitor (RadMon).
- Configuration:
- The satellites will be launched using the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV-C60) in a core-alone (CA) configuration, meaning without strap-on boosters.
- They will be placed in a 476-km circular orbit with an inclination of 55°.
- Post-Docking:
- After the docking demonstration, the satellites will continue standalone missions for two years, conducting imaging, natural resource monitoring, and radiation environment studies.
- Significance: It is a strategic step towards several ambitious space objectives, including:
- Preparing for the Gaganyaan human spaceflight program
- Enabling Chandrayaan-4 lunar sample return missions
- Developing the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS), India’s proposed space station35
What is Space Docking?
|
PYQ:[2018] With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Deepening India’s steps as a key space-faring nation
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: ISRO Mission;
Why in the News?
India has set ambitious objectives for its space programme over the next two decades, focusing on the development of powerful, reusable rockets like the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)’s upcoming Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV).
What are the recent achievements of India’s space program?
- Chandrayaan-3 Mission: India successfully achieved a soft landing near the lunar south pole with its Chandrayaan-3 mission, marking a historic milestone as the fourth country to do so. This mission demonstrated India’s growing technological capabilities in space exploration.
- Aditya L1 Mission: Launched as India’s first space-based solar observatory, Aditya L1 aims to study the outer atmosphere of the Sun, contributing valuable data to solar science.
- Gaganyaan Preparations: ISRO is actively working on the Gaganyaan mission, which aims to send Indian astronauts into orbit by 2025. This includes extensive testing of human-rated launch vehicles and crew escape systems.
- Budget Increases: The Indian government allocated approximately $1.5 billion to the Department of Space for 2024-2025, reflecting a commitment to enhance space capabilities and infrastructure.
How is India planning to expand its human spaceflight and exploration capabilities?
- Gaganyaan Mission: This mission is pivotal for establishing India’s human spaceflight capabilities, with plans for multiple uncrewed test flights leading up to a manned mission. The first crewed flight is targeted for late 2024.
- Lunar Exploration Goals: India plans to achieve a crewed lunar landing by 2040 and establish a lunar space station to facilitate ongoing research and exploration efforts on the Moon.
- Bharatiya Antariksha Station: The establishment of India’s first space station in low Earth orbit is planned by 2035, serving as a platform for scientific research and technology testing.
- Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV): The development of the NGLV will enhance India’s heavy-lift capabilities, crucial for supporting human missions and larger payloads in future explorations.
What role does international collaboration play in India’s space ambitions?
- Commercial Partnerships: India has engaged in collaborations with international companies like SpaceX for satellite launches, showcasing an openness to leveraging foreign technology and expertise in its space endeavours.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Recent reforms have opened up India’s space sector to increased foreign investment, fostering partnerships that can enhance technological capabilities and innovation within the domestic industry.
- Collaborative Research and Development: By exploring foreign collaboration opportunities, Indian corporations can access advanced rocket technologies and expertise that may not currently exist within the country, accelerating development timelines for projects like reusable rockets.
Way forward:
- Strengthen Private Sector Engagement: India should actively encourage partnerships with domestic and international private companies to accelerate the development of advanced space technologies, such as reusable rockets and heavy-lift vehicles, ensuring a competitive edge in global space exploration.
- Expand International Collaborations: India should deepen its space collaborations with countries and space agencies globally, particularly in research, technology sharing, and joint missions, to leverage global expertise and enhance its own space capabilities.
Mains PYQ:
Q India has achieved remarkable successes in unmanned space missions including the Chandrayaan and Mars Orbiter Mission, but has not ventured into manned space mission. What are the main obstacles to launching a manned space mission, both in terms of technology and logistics? Examine critically. (UPSC IAS/2017)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
New NASA-ISRO Satellite ‘NISAR’ to revolutionise Earth monitoring
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NISAR Satellite
Why in the News?
- The NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) satellite is aimed at advancing our understanding of Earth’s natural processes and environmental changes.
- Set to be launched into Low Earth Orbit (LEO), NISAR will act as a comprehensive Earth observation observatory.
About NISAR Satellite:
| Details | |
| Collaboration | • Joint mission between NASA (United States) and ISRO (India). |
| Purpose | • Designed to monitor Earth’s natural processes and environmental changes, contributing to disaster preparedness, climate research, and sustainable management. |
| Launch Date | • Planned for early 2025. |
| Launch Location | • Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Andhra Pradesh, India. |
| Launch Vehicle | • ISRO’s Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark II (GSLV Mk II). |
| Orbit | • Low Earth Orbit (LEO). |
| Dual-Band Radar System | • L-band radar (provided by NASA): Penetrates dense vegetation and tracks ground motion. • S-band radar (provided by ISRO): Enhances precision for surface monitoring. |
| Day and Night Functionality | • Operates 24/7, unaffected by weather conditions. |
| Large Antenna | • Diameter: 12 meters. • Structure: 39-foot reflector made from gold-plated wire mesh to focus radar signals effectively. |
| Features | • Scans Earth’s entire surface every 12 days.
• Measures surface changes with accuracy down to fractions of an inch. • Can penetrate vegetation and soil layers, providing 3D reconstructions of subsurface structures. |
| Areas of Study | • Ecosystems and Environmental Changes (forest biomass, deforestation, wetlands, agricultural lands, glaciers, and ice sheets). • Natural Disasters (seismic shifts, volcanic bulging, landslides, and tsunamis). |
| Benefits and Applications | • Disaster Preparedness: Early warning data for natural disasters. • Infrastructure Monitoring: Tracks structural changes in critical infrastructure. • Environmental and Climate Research: Studies carbon storage, vegetation dynamics, and climate change impacts. |
| Unique Advantages | • Largest collaboration between NASA and ISRO. • Successfully tested in thermal vacuum conditions in Bengaluru in 2023. |
PYQ:[2015] The term ‘IndARC’ sometimes seen in the news, is the name of? (a) An indigenously developed radar system inducted into Indian Defence. (b) India’s satellite to provide services to the countries of Indian Ocean Rim. (c) A scientific establishment set up by India in Antarctic region. (d) India’s underwater observatory to scientifically study the Arctic region. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Europe’s Proba-3 Mission to arrive in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Proba-3 Mission

Why in the News?
- India is set to launch the European Space Agency’s (ESA) PROBA-3 Mission in December from the Sriharikota spaceport.
- The mission will use ISRO’s PSLV rocket to place two satellites in orbit, designed to study the Sun’s corona, or outer atmosphere.
About Proba-3 Mission:
| Details | |
| Mission Name | PROBA-3 (Project for On-Board Autonomy-3) |
| Objective | Study the Sun’s corona by creating an artificial eclipse with precision formation flying of two satellites |
| Launch Date and Location | December 4, 2024, from Sriharikota spaceport, India, via ISRO’s PSLV-XL rocket |
| Orbit | Highly elliptical orbit, ranging from 600 km to 60,000 km, with a 19.7-hour orbital period |
| Satellites | Two satellites:
|
| Alignment Precision | Millimeter-level alignment to block the Sun’s light and allow continuous corona observation |
| Key Scientific Goals | Observe solar phenomena, such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections, to improve space weather forecasting |
| Unique Features | First ESA mission dedicated to precision formation flying, using smaller, agile satellites for cost-effective observation |
| International Collaboration | Jointly developed by ESA and ISRO, with contributions from France, Belgium, and the Netherlands |
| Communication Support | Managed via antenna in Santa Maria (Azores) and ground station in Redu (Belgium) |
| Significance | Advances solar research and international collaboration; enhances space weather insights, supporting infrastructure on Earth |
PYQ:[2016] What is ‘Greased Lightning-10 (GL-10)’, recently in the news? (a) Electric plane tested by NASA (b) Solar-powered two-seater aircraft designed by Japan (c) Space observatory launched by China (d) Reusable rocket designed by ISRO |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Does the Sun rotate?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Sun’s Rotation

Why in the News?
Indian astronomers at the Kodaikanal Solar Observatory (KSO) have achieved a groundbreaking feat by mapping, for the first time, the variation in the Sun’s rotation speed from its equator to its poles.
Sun’s Rotation: Key Facts
- Unlike a solid body, the Sun exhibits differential rotation, meaning different parts of the Sun rotate at different speeds.
- The rotation speed varies depending on latitude, with faster rotation near the equator and slower rotation toward the poles.
- This variation is primarily due to the Sun’s composition of gaseous plasma rather than solid material.
Rotation Period Variation by Latitude:
- Equatorial Regions: The rotation period at the equator is the fastest, around 24.47 days (sidereal rotation).
- Sunspot Zones (about 16 degrees latitude): Rotation slows slightly, with a period of about 27.3 days.
- Higher Latitudes (up to 75 degrees): Rotation slows significantly; for example, at 75 degrees latitude, the rotation period is about 33.4 days.
- Poles: The slowest rotation occurs at the poles, with a period around 31.1 days.
Sidereal vs. Synodic Rotation Periods:
- Sidereal Rotation Period: The time taken for the Sun to complete one full rotation relative to distant stars. It varies by latitude, from 24.47 days at the equator to around 33.4 days at higher latitudes.
- Synodic Rotation Period: This is the time for a fixed feature on the Sun to appear in the same position when observed from Earth. It is longer than the sidereal period due to Earth’s own movement around the Sun, averaging around 26.24 days.
Why Differential Rotation Occur?
- Gaseous Plasma Composition: The Sun is composed of plasma—a hot, ionized state of matter—which allows its different regions to rotate at different speeds.
- Convective Zone Dynamics: The outer convective layer of the Sun contributes to differential rotation. Plasma circulates, rising and sinking, which influences the rotational speed at different latitudes.
Scientific Implications
- Solar Dynamo Theory: The differential rotation of the Sun is central to theories about the solar dynamo—the process that generates the Sun’s magnetic field.
- Mystery of Differential Rotation: Despite extensive research, the exact mechanism behind the Sun’s differential rotation remains an active area of investigation in solar physics.
PYQ:[2013] Consider the following phenomena 1. Size of the sun at dusk 2. Colure of the sun at dawn 3. Moon being visible at dawn 4. Twinkle of stars in the sky 5. Polestar being visible in the sky Which of the above are optical illusions? (a) 1, 2 and 3 (b) 3, 4 and 5 (c) 1, 2 and 4 (d) 2, 3 and 5 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Hanle Dark Sky Reserve Star Party observed in Ladakh
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Hanle Dark Sky Reserve

Why in the News?
Expert astro-photographers and astronomers have gathered at the Hanle Dark Sky Reserve from for the second Star Party.
Star Party and Its Details
|
About Hanle Dark Sky Reserve (HDSR)
- The HDSR is a designated area in Changthang region of eastern Ladakh created to control man-made light pollution and protect the naturally dark night skies.
- It spans approximately 1,073 square kilometers and is home to the Indian Astronomical Observatory, operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA).
- Established to promote astronomy and astrophotography, it offers some of the darkest skies in India, ideal for astronomical research.
- Hanley is also the home to second-highest optical telescope in the world, established in 2001 by IIA.
Special Features of HDSR and the Surrounding Region
- High Altitude: Hanle is situated at a high altitude, providing clearer skies with minimal atmospheric interference.
- Minimal Light Pollution: The region has low light pollution, which makes it perfect for observing faint celestial objects.
- Dry Climate: The dry weather in the region contributes to excellent visibility, reducing the impact of humidity on astronomical observations.
Significance of HDSR
- Astrophotography and Research: The dark skies allow for detailed observation of celestial phenomena and astrophotography, attracting enthusiasts and researchers.
- Astro-Tourism: The reserve fosters astro-tourism, boosting the local economy by creating jobs for guides and supporting infrastructure.
- Preservation of Night Skies: It plays a crucial role in preserving the natural darkness of the sky, curbing light pollution in the region.
- International Attention: The reserve has attracted amateur and professional astronomers from across India and beyond, making it a hub for astronomical events.
| PYQ:
[2018] Consider the following phenomena:
Which of the above is/are the prediction/predictions of Albert Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity, often discussed in media? (a) 1 and 2 only |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
TRISHNA Mission
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: TRISHNA Mission
Why in the News?
Philippe Baptiste, head of the French Space Agency, talked about the joint India-France “TRISHNA Mission.”
TRISHNA Mission:
| Details | |
| Overview | A joint Indo-French Earth observation satellite project developed by ISRO and CNES (French Space Agency).
Acronym for “Thermal infraRed Imaging Satellite for High-resolution Natural resource Assessment” (TRISHNA Mission) |
| Launch Year | Targeted for 2026. |
| Mission Lifespan | Designed for a 5-year operational life. |
| Primary Objectives | • Monitor water and energy budgets of the continental biosphere.
• Assess evapotranspiration for efficient water management. • Improve agricultural water productivity and assist in irrigation water management. • Provide high-resolution observations of water quality in coastal and inland waters. • Assess urban heat islands and detect heat anomalies. |
| Payloads | • Thermal Infrared (TIR) Payload: Provided by CNES, this sensor maps surface temperature and emissivity in high resolution.
• Visible-Near Infrared-Short Wave Infrared (VNIR-SWIR) Payload: Developed by ISRO, this sensor uses seven spectral bands for detailed mapping of surface reflectance. |
| Orbit and Spatial Resolution | • TRISHNA will operate in a sun-synchronous orbit at an altitude of 761 km.
• Spatial resolution: 57 meters for land and coastal areas, 1 km for ocean and polar regions. |
| Application and Significance | • Supports water resource management, agriculture, and urban planning through precise data on water stress, crop productivity, and urban heat islands. • Enhances climate resilience by tracking droughts, evapotranspiration, and permafrost changes. • Contributes to global environmental initiatives like GEOGLAM and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by providing key agricultural and climate variables. |
PYQ:[2016] Discuss India’s achievements in the field of Space Science and Technology. How the application of this technology helped India in its socio-economic development? [2010] In the context of space technology, what is “Bhuvan”, recently in the news? (a) A mini satellite launched by ISRO for promoting the distance education in India (b) The name given to the next Moon Impact Probe, for Chandrayaan-II (c) A geoportal of ISRO with 3D imaging capabilities of India (d) A space telescope developed by India |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Chandrayaan-4, Venus orbiter gets approval from Cabinet
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Chandrayaan 4, Venus Orbiter Mission
Why in the News?
The Union Cabinet approved the expansion of the Chandrayaan-4 mission, Venus Orbiter Mission (Shukrayaan Misison), Gaganyaan, the development of India’s first space station (the Bharatiya Antariksh Station), and NextGen launch vehicles.
About Chandrayaan-4 Mission
- Chandrayaan-4 is the fourth mission in India’s Chandrayaan program (2003).
- The mission is currently under conceptualisation and expected to launch around 2027.
- Aims: To develop technology for a successful moon landing and ensure a safe return to Earth.
- The mission will be launched in two phases onboard two LVM3 rockets.
- It will collect lunar samples for analysis on Earth.
About Venus Orbiter Mission (VOM)
- The VOM, also called Shukrayaan-1, is an upcoming ISRO mission targeting a 2028 launch.
- The mission aims to study Venus’ surface, atmosphere, volcanic activity, and solar wind interactions with its ionosphere.
- It will have a mission duration of 4 years.
- The spacecraft will operate in an elliptical orbit, with distances of 60,000 km at apoapsis and 500 km at periapsis.
- Its payload has a capacity of 100 kg, is powered by 500 watts, and will feature Indian and international instruments for comprehensive analysis.
- For the mission’s payload and technology, collaborations with NASA, CNES (France), and Russia have been established.
PYQ:[2016] The Mangalyaan launched by ISRO:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Study reveals intriguing Magnetic behavior on Mars
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Magnetic Anomalies of Mars
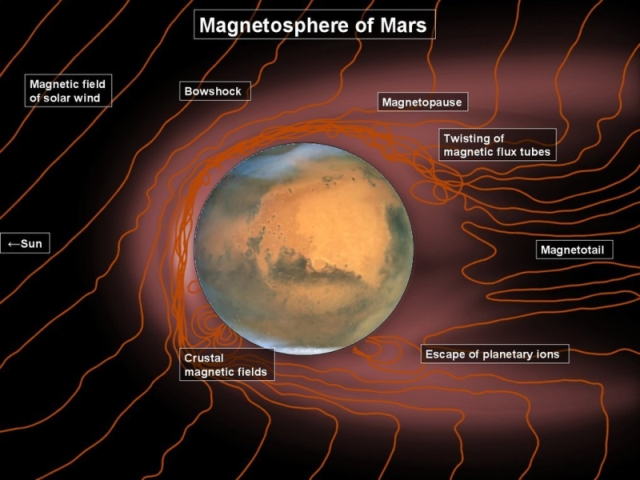
Why in the News?
A study conducted by the Indian Institute of Geomagnetism (IIG) revealed significant variations in the strength of Mars’ crustal magnetic field between day and night.
Notable facts about Mars:
|
Key Findings on Mars’s Magnetic
- Mars’ crustal magnetic field is significantly stronger during the daytime and nearly non-existent at night-time.
- This suggests a diurnal variation in the magnetic field strength on the Martian surface.
- The crustal magnetic field of Mars is primarily located in the southern hemisphere, specifically poleward of 30°S latitude.
- The magnetic fields are scattered within a region between 120° E and 240° E, indicating uneven distribution across the Martian surface.
- The daytime crustal magnetic field plays a crucial role in controlling the ionosphere in Mars’ southern hemisphere.
- This influence impacts communication and navigation systems of future missions.
Data Utilization from MAVEN Satellite:
- The study utilized data from the MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN) Satellite, which has been orbiting Mars since 2014.
- MAVEN’s data on electron density and magnetic field were critical in investigating how Mars’ crustal magnetic field affects its plasma environment and ionosphere.
Significance of the Study
- Understanding Mars’ crustal magnetic field is essential for future robotic and manned missions, as it provides natural magnetic shielding against space radiation.
- The insights from the study can help in developing strategies to mitigate the effects of space weather on spacecraft and astronauts.
PYQ:[2016] The Mangalyaan launched by ISRO
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
A look at ongoing Indian Space Missions
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Various space missions mentioned
Mains level: NA
Why in the News?
Since Chandrayaan 3’s successful moon landing on August 23, 2023 and its declaration of National Space Day, ISRO has remained highly active with several key missions, despite a quieter phase at Sriharikota.
Key Missions and Milestones:
| Details | Date | |
| Chandrayaan 3 |
|
August 23, 2023 |
| Aditya L1 |
|
Launched: September 2, 2023 L1 Orbit: January 6, 2024 |
| Gaganyaan TV-D1 |
|
October 21, 2023 |
| XPoSat |
|
Launched: January 1, 2024 |
| INSAT-3DS |
|
Launched: February 17, 2024 |
| RLV-TD (Pushpak) |
|
LEX-02: March 22, 2024 LEX-03: June 7, 2024 |
| SSLV |
|
August 16, 2024 |
| ISRO Roadmaps |
|
Announced: December 2023 |
| Next-Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV) |
|
Project report submitted: February 2024 |
| NSIL Missions |
|
2024 |
| Private Space Missions |
|
2024 |
| IN-SPACe Initiatives |
|
2024 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO’s SSLV-D3 successfully launches EOS-08 Satellite
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ISRO’s SSLV-D3, EOS-08 Satellite
Why in the News?
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully launched the EOS-08 Earth Observation Satellite using the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV)-D3.
- This marks the third and final development flight of the SSLV.
About EOS-08 Satellite:
| Details | |
| Type | Earth Observation Satellite (EOS) |
| Design Platform | Built on ISRO’s Microsat/IMS-1 bus, known for its compact and efficient design. |
| Orbit | Operates in a Circular Low Earth Orbit (LEO) at an altitude of 475 km with an inclination of 37.4°. |
| Mission Life | 1 year |
| Payloads | – Electro Optical Infrared Payload (EOIR): Captures images in MIR and LWIR bands for surveillance, disaster monitoring, and environmental assessments. – Global Navigation Satellite System-Reflectometry (GNSS-R) Payload: Monitors ocean surface winds, soil moisture, and inland water bodies using GNSS-R-based remote sensing. – SiC UV Dosimeter: Monitors UV irradiance, particularly for ISRO’s Gaganyaan Mission, ensuring safety against UV radiation. |
| Technological Innovations | – Integrated Avionics System: Combines Communication, Baseband, Storage, and Positioning (CBSP) functions into one system. – Embedded Technologies: Includes a Structural Panel Embedded with PCB, Embedded Battery, enhancing structural efficiency and power reliability. – Advanced Antennas: Micro-DGA (Dual Gimbal Antenna) and M-PAA (Phased Array Antenna) for precise control and enhanced signal transmission. – Flexible Solar Panels & Nano Star Sensor: Improves energy efficiency and satellite orientation in space. |
Back2Basics: Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV)-D3
- SSLV is designed to launch Mini, Micro, or Nanosatellites (10 to 500 kg) into a 500 km planar orbit.
- SSLV is a 3-stage launch vehicle with all solid propulsion stages and a liquid propulsion-based Velocity Trimming Module (VTM) as the terminal stage.
- SSLV is designed for low cost and low turn-around time.
- The vehicle offers flexibility in accommodating multiple satellites and is capable of launch-on-demand.
- SSLV requires minimal launch infrastructure, making it a versatile option for satellite deployment.
PYQ:[2018] With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 (c) 1 and 2 (d) 3 only |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
August 23rd declared as National Space Day
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Space Day
Why in the News?
The Centre has officially declared August 23rd as “National Space Day” in honor of the Chandrayaan-3 Mission’s historic achievement.
About the National Space Day:
- It is set to be celebrated on August 23rd every year.
- It marks the successful landing of the Chandrayaan-3 mission’s Vikram Lander and Pragyan Rover on the Moon.
- Theme for 2024:
- “Touching Lives while Touching the Moon: India’s Space Saga” highlights space exploration’s impact on society and technology.
- Significance:
- India became the fourth country to land on the Moon and the first to land near the Moon’s southern polar region.
About Chandrayaan-3 Mission:
| Details | |
| Launch |
|
| Landing Site | Near the Lunar South Pole (Coordinates: 69.373°S 32.319°E) |
| Mission Objectives |
|
| Components |
|
| Major Findings |
|
| Landing Site Name | Named by PM as ‘Shiv Shakti’ (Sanctioned by IAU as “Statio Shiv Shakti”). |
PYQ:[2016] Consider the following statements: The Mangalyaan launched by ISRO
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO has a problem: many rockets, but too few satellites to launch
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Satellite launching vehicles; ISRO;
Mains level: ISRO; Present Scenario of Satellites in India;
Why in the News?
After the ambitious Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV) was finalized in June 2024, ISRO Chairman S. Somanath stated its launch capability exceeded demand threefold, highlighting a need for robust domestic market demand for launch vehicles.
What is the present scenario of Satellites in India?
- India operates a diverse fleet of satellites with applications in Communications, Remote Sensing, Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT), Meteorology, Disaster Management, Space-based internet, Scientific missions, and Experimental missions.
- India currently has four main launch vehicles: the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV), the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV), and the Launch Vehicle Mark-III (LVM-3), capable of launching satellites up to four tonnes to geosynchronous orbit.
- For satellites weighing more than four tonnes, India relies on foreign launch vehicles, such as Europe’s Ariane V and SpaceX’s Falcon 9, to meet its heavy payload requirements.
- India has been actively involved in significant space missions like Chandrayaan 3 (a lunar mission) and Aditya L1 (a mission to study the Sun), showcasing its growing capabilities in space exploration.
Existing Demand-Driven Model in India – Before and After
- Before (Supply-Driven Model)
-
-
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) primarily built and launched satellites based on its assessments and planned missions without waiting for specific customer demands.
- After launching satellites, ISRO would then look for customers who needed the services provided by the satellites, which sometimes led to underutilization or delayed utilization of satellite capabilities.
- The space sector was heavily government-controlled, with limited involvement and investment from private players
- There was less emphasis on educating potential customers about the benefits and applications of space-based services, leading to lower demand from various sectors.
-
- After 2020 (Demand-Driven Model)
-
- The Space sector reforms 2019-2020 encouraged greater private sector participation, fostering innovation, competition, and commercialization in the Indian space industry.
- Satellites are now built and launched based on confirmed customer demands, ensuring that each satellite has a predefined purpose and user base before it is sent into space.
- The market demand for satellite services is validated and secured before the construction and launch phases, leading to better alignment of resources and higher utilization rates.
Major Three Limitations Associated at Present Time:
- Limited Launch Vehicle Capability: Currently, the Indian launch vehicles have restricted payload capacities, necessitating multiple launches for larger missions, increasing costs and complexity.
- Demand-Supply Mismatch: Transitioning from a supply-driven to a demand-driven model faces challenges, including the need to educate potential customers and create a robust private sector ecosystem.
- Economic and Technological Constraints: High costs of developing and maintaining launch vehicles and satellites, coupled with the early stages of implementing cost-effective reusable technologies, and insufficient infrastructure and investment.
Way forward:
- Enhance Launch Vehicle Capacity: Invest in research and development to upgrade existing launch vehicles like GSLV and LVM-3 to increase payload capacity, reducing dependence on foreign launch providers.
- Strengthen Market Engagement and Education: Expand outreach programs to educate potential customers across sectors about the benefits and applications of satellite-based services.
- Promote Private Sector Participation: Facilitate a conducive regulatory environment to attract private investments and foster innovation in satellite manufacturing and launch services.
Mains PYQ:
Q India has achieved remarkable successes in unmanned space missions including the Chandrayaan and Mars Orbiter Mission, but has not ventured into manned space missions. What are the main obstacles to launching a manned space mission, both in terms of technology and logistics? Examine critically. (UPSC IAS/2017)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO’s plans to venture into planetary defence
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Space Objects
Mains level: Challenges related to asteroid Apophis
Why in the news?
Last week, ISRO Chairman S Somanath expressed the possibility of engaging with the asteroid Apophis during its close approach to Earth at a distance of 32,000 km in 2029. However, the specific manner of ISRO’s involvement has not yet been determined.
Space objects:

The asteroid Apophis may pose a threat:
- Initial Concerns: Discovered in 2004, Apophis initially posed a 2.7% chance of colliding with Earth, raising alarms due to its size (about 450 m wide).
- Revised Risk: Subsequent observations ruled out immediate collision risks in 2029, 2036, and 2068, but it will pass close to Earth in 2029 at 32,000 km.
- Potential Impact: Its size could cause significant damage if it were to collide with Earth, though recent observations suggest no imminent danger.
Other possible incoming threats from space:
- Daily Encounters: Thousands of asteroids enter Earth’s atmosphere daily, most burning up due to friction, causing phenomena like fireballs.
- Russian Example: In 2013, a 20-meter asteroid exploded above Russia, releasing significant energy and causing damage and injuries.
- Detection Challenges: Some asteroids are detected only upon entering the atmosphere, especially those coming from the direction of the Sun, which can obscure detection.
ISRO’s plan: From sci-fi to reality:
- Planetary Defense Initiative: ISRO aims to develop capabilities in planetary defense, potentially participating in missions to study and potentially deflect asteroids.
- Collaboration: Considering sending its own spacecraft or collaborating with other space agencies, like NASA, which has already redirected a spacecraft to study Apophis in 2029.
- Evolution of ISRO: Reflects ISRO’s evolution as a space agency, transitioning from aspirations to reality in tackling global space objectives, demonstrating growing confidence and capabilities.
Way forward:
- Form Partnerships: ISRO should actively seek partnerships with leading space agencies like NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), and others involved in asteroid detection and planetary defense.
- Joint Missions: Collaborate on joint missions to study and potentially mitigate asteroid threats. This could include sharing resources, technology, and expertise to maximize effectiveness and minimize costs.
Mains PYQ:
Q What is India’s plan to have its own space station and how will it benefit our space programme? (UPSC IAS/2019)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Lal Crater on Mars
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Mars Craters, IAU
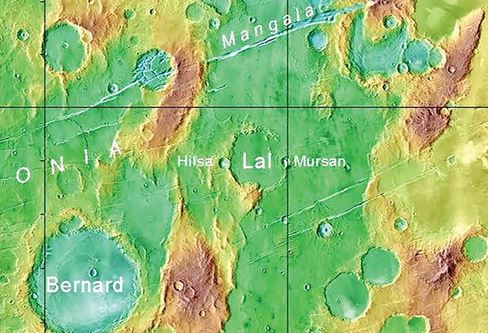
Why in the News?
- Scientists from Ahmedabad-based Physical Research Laboratory (PRL) have identified three new craters on Mars, situated in the Tharsis volcanic region around 21.0 S, 209 W.
- The International Astronomical Union (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature approved the naming of the three craters on Mars, based on PRL’s recommendation.
Back2Basics: International Astronomical Union (IAU)
Major Activities and Initiatives
Membership
|
Crater Names and Significance
- Lal Crater: Named after Prof. Devendra Lal, former director of PRL, this 65 km wide crater is positioned at -20.98° and 209.34°.
- Mursan Crater: Named after a town in Uttar Pradesh, India, this ~10 km wide crater is situated on the eastern side of the Lal crater’s rim.
- Hilsa Crater: Named after a town in Bihar, India, this ~10 km wide crater is positioned on the western side of the Lal crater’s rim.
Scientific Importance of Lal Crater
- Lava Coverage: The entire Lal crater area, located in the Tharsis volcanic region on Mars, is covered with lava.
- Evidence of Water: Geophysical evidence, including a 45-meter thick sedimentary deposit, suggests the presence of water in the subsurface of the Lal crater. This finding supports the theory that Mars once had water flowing on its surface.
- Infilling Process: Mursan and Hilsa craters, positioned on either side of the Lal crater, offer insights into the infilling process of the Lal crater. Their presence indicates that infilling occurred episodically over time.
India’s 2nd Quest for Mars
Other missions to Mars
|
PYQ:[2016] The Mangalyaan launched by ISRO
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
What are Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs)?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Coronal Mass Ejection, Aditya L1 and its various payloads
Why in the News?
- India’s solar mission Aditya-L1 recently captured images of the Sun and it’s Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) during a solar storm in May.
- The Active region AR13664 on the Sun erupted several X-class and M-class flares, which were associated with Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs).
Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs)
|
About Aditya-L1:
- Aditya-L1 mission is India’s first space mission to observe the Sun.
- It is ISRO’s 2nd space-based astronomy mission after AstroSat, which was launched in 2015.
- It was launched on September 2nd 2023 to observe the Sun and the solar corona.
- The L1 point is a location in space where the gravitational forces of two massive objects, such as the Earth and the Sun, balance each other out, allowing a spacecraft to “hover” in a stable orbit.
Launch Details:
- Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) with 7 payloads (instruments) on board.
The 7 payloads include:
-
- Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC): Images of the solar corona in visible light to study its structure and dynamics.
- Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT): Images the solar chromosphere and transition region in ultraviolet light to understand heating and dynamics.
- Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEXS): Measures solar X-ray spectrum to study solar flares and coronal mass ejections.
- High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer (HEL1OS): Measures high-energy solar X-rays to understand particle acceleration.
- Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya (PAPA): Measures solar wind plasma properties to study its interaction with Earth’s magnetosphere.
- Aditya Solar Wind Particle Experiment (ASPEX): Measures energetic particle properties in the solar wind to study their effects on Earth’s atmosphere.
- Solar Irradiance Monitor (SIM): Measures solar irradiance variations and their impact on Earth’s climate.
Objectives:
- Aditya L1 will study the coronal heating, solar wind acceleration, coronal magnetometry, origin and monitoring of near-UV solar radiation and continuously observe the photosphere, chromosphere and corona, solar energetic particles and the magnetic field of the Sun.
Location:
- Aditya is placed in L1 Halo orbit which is about 1.5 million km from the Earth. The orbit allows the mission to look at the Sun continuously.
- L1 refers to Lagrangian/Lagrange Point 1, one of 5 points in the orbital plane of the Earth-Sun system.
- Lagrange Points are positions in space where the gravitational forces of a two-body system like the Sun and Earth produce enhanced regions of attraction and repulsion.
PYQ:[2017] The terms ‘Event Horizon’, ‘Singularity’, ‘String Theory’ and ‘Standard Model’ are sometimes seen in the news in the context of- (a) Observation and understanding of the Universe (b) Study of the solar and lunar eclipses (c) Placing satellites in the orbit of the Earth (d) Origin and evolution of living organisms on the Earth |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
PraVaHa tool for Aerodynamic Design and Analysis
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PraVaHa Tool
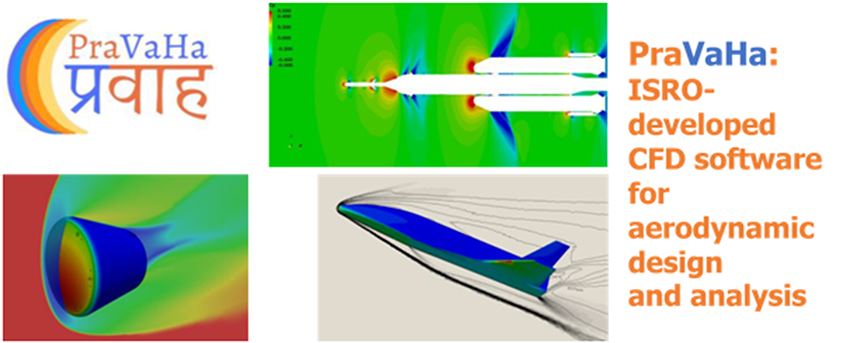
Why in the News?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has launched the Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) software named Parallel RANS Solver for Aerospace Vehicle Aero-thermo-dynamic Analysis (PraVaHa).
About PraVaHa
- PraVaHa was developed at ISRO’s Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), showcasing India’s prowess in aerospace technology.
- It can simulate both external and internal flows on various aerospace vehicles, including launch vehicles, and winged, and non-winged re-entry vehicles.
- It facilitates initial aerodynamic design studies by evaluating numerous configurations, crucial for optimizing vehicle performance and safety.
Role of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
- CFD predicts aerodynamic and aerothermal loads by solving governing equations. It has matured to offer high accuracy and fast simulations, addressing aerospace challenges like high pressure and intense heat flux.
Integration in Gaganyaan Program
- Key Applications: PraVaHa plays a pivotal role in the Gaganyaan program, facilitating aerodynamic analysis of human-rated launch vehicles such as HLVM3, Crew Escape System (CES), and Crew Module (CM).
- Scalability and Collaboration: Designed to leverage both CPU and GPU architectures, PraVaHa ensures compatibility with existing and future supercomputing facilities, fostering collaboration with academic and government institutions.
PYQ:[2010] In the context of space technology, what is “Bhuvan”, recently in the news? (a) A mini satellite launched by ISRO for promoting the distance education in India. (b) The name given to the next Moon Impact Probe, for Chandrayaan-II. (c) A geoportal of ISRO with 3D imaging capabilities of India. (d) A space telescope developed by India. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Agnibaan Sub Orbital Technology Demonstrator (SOrTeD)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Agnibaan SOrTeD, PS4 Engine
Why in the News?
Agnikul Cosmos Private Limited, a space start-up from Chennai, made history by launching the world’s first rocket with a single-piece 3D-printed engine, named Agnibaan Sub Orbital Technology Demonstrator (SOrTeD), from Sriharikota.
About 3D Printed PS4 Engine
|
What is Agnibaan SOrTeD (Suborbital Tech Demonstrator)?
- Agnibaan SOrTeD is a single-stage launch vehicle powered by Agnikul’s patented Agnilet semi-cryogenic engine.
- In contrast to traditional sounding rockets, Agnibaan SOrTeD’s vertical take-off and precise trajectory enable orchestrated manoeuvres during flight.
PYQ:[2018] With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
EU activated Copernicus EMS to Locate Crashed Iranian Helicopter
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Copernicus Programme
Mains level: NA
Why in the News?
- In response to the helicopter crash involving Iranian President Ebrahim Raisi, the European Union had activated its Copernicus Emergency Management Service (EMS) to aid in search and rescue efforts.
About the Copernicus Programme
- This Programme was launched in 1998 by the European Union’s earth observation
- Named for Copernicus, it uses satellites and ground systems for environmental data.
- It is implemented by EU member states with support from entities like the European Space Agency (ESA) and the European Environment Agency (EEA).
Utility of GMES: Rapid Response Mapping Service
- The Copernicus EMS offers rapid response mapping, a crucial component activated during emergencies like natural disasters or accidents.
How Rapid Mapping Works?
- Rapid mapping involves acquiring, processing, and analyzing satellite images and relevant data to provide timely information.
- It offers several products, including pre-event reference and post-event assessments like first estimates, delineation, and grading of the impacted area.
Application in the Iranian President’s Case
- In the case of the Iranian President’s helicopter crash, the EU activated the rapid response mapping service to aid search and rescue operations.
- This technology helps locate the crash site and assess the extent of the impact, facilitating swift response efforts.
PYQ:[2018] With reference to the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 1 and 2 only (c) 2 and 3 only (d) None |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
NISAR Satellite will be able to monitor Tectonic Movements: ISRO chief
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NISAR and its features
Mains level: NA

Why in the News?
The ISRO Chief has confirmed that the NISAR Satellite would be able to monitor the Tectonic Movements of Earth with high precision with a centimeter accuracy.
- Originally planned for July, the NISAR launch may be delayed to October-November due to issues on the U.S. spacecraft side.
About NISAR Satellite:
- NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) is a joint satellite mission between NASA and ISRO.
- It would be a Low Earth Orbit observatory.
- This mission is aimed at enhancing our understanding of Earth’s natural processes and environmental changes.
Features of NISAR Satellite:
- L-band and S-band Radar Frequencies:
-
-
- NASA is responsible for the L-band radar, while ISRO provides the S-band radar.
- This dual-band capability allows the satellite to monitor and measure Earth’s surface with high precision in all weather conditions and throughout both day and night.
-
- Large Deployable Antenna:
-
-
- It is equipped with a large deployable antenna that measures 12 meters in diameter.
- This large antenna enhances the satellite’s ability to capture detailed radar images with high resolution.
- It will have a 39-foot stationary antenna reflector, made of a gold-plated wire mesh to focus radar signals emitted and received by the upward-facing feed on the instrument structure.
-
- Rapid Coverage:
-
-
- NISAR is designed to scan the entire Earth every 12 days.
- This rapid revisiting is crucial for observing and understanding temporal changes in the environment, such as shifting vegetation patterns, ice dynamics, and other critical parameters.
-
- Versatile Monitoring Capabilities:
-
- It will monitor Earth’s ecosystems and dynamics, including forest biomass, ice sheet collapses, and natural hazards such as earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions.
- Its radar system can penetrate vegetation and soil to provide three-dimensional reconstructions of structures and changes.
PYQ:[2015] The term ‘IndARC’ sometimes seen in the news, is the name of? (a) An indigenously developed radar system inducted into Indian Defence. (b) India’s satellite to provide services to the countries of Indian Ocean Rim. (c) A scientific establishment set up by India in Antarctic region. (d) India’s underwater observatory to scientifically study the Arctic region. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Moon occulting the Antares (Jyeshtha)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Antares (Jyeshtha), Occultation
Mains level: NA
Why in the news?
- The Bengaluru-based Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) captured the moon passing in front of Antares, a bright red star.
- Moon occasionally occults bright stars such as Antares and planets as it orbits the Earth once a month.
About Antares (Jyeshtha)

- Antares is a red supergiant star also called ‘Alpha Scorpii,’ located in the constellation of Scorpius.
- It is visible in the southern sky during the summer months in the northern hemisphere.
- It is often referred to as the “heart of the scorpion” due to its location within the Scorpius constellation and its striking red color.
- It is a massive star, with a diameter estimated to be around 700 times that of the Sun.
- It has a relatively low surface temperature compared to other stars, which gives it its distinctive red color.
- The distance to Antares from Earth is approximately 550 light-years, making it one of the closest red supergiant stars to our solar system.
What is Occultation?
|
PYQ:[2012] A person stood alone in a desert on a dark night and wanted to reach his village, which was situated 5 km East of the point where he was standing. He had no instruments to find the direction, but he located the pole-star. The most convenient way now to reach his village is to walk in the _______. (a) Direction facing the pole-star (b) Direction opposite to the pole-star (c) Direction keeping the pole-star to his left (d) Direction keeping the pole-star to his right |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Studies Suggest More Water Ice on Moon: ISRO
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Water Ice on Moon
Mains level: NA

Why in the news?
A study has revealed evidence for enhanced possibility of sub-surface water ice occurrence in the polar craters of the Moon, according to ISRO.
Water Ice on Moon: ISRO’s Findings
- The research indicates that the amount of sub-surface ice within the first few meters is significantly greater, about 5-8x more, than that found on the lunar surface.
- Moreover, the study reveals that the Northern Polar region harbors twice as much water ice as the southern polar region.
- It highlights the necessity of drilling to access this ice for future missions and sustained human presence on the Moon.
Origin of Water Ice:
- The study validates the hypothesis that sub-surface water ice in lunar poles originated from out-gassing during volcanic activity in the Imbrian period.
- It suggests that Lunar Mare Volcanism and preferential impact cratering govern the distribution of water ice on the Moon.
Methodology:
- The research team utilized seven instruments aboard the NASA robotic spacecraft Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO), including radar, laser, optical, neutron spectrometer, ultra-violet spectrometer, and thermal radiometer. LRO hovers over Lunar South Pole.
- These instruments provided crucial data to understand the origin and distribution of water ice on the lunar surface.
Significance of the findings
- Accurate knowledge of water ice distribution and depth is vital for identifying suitable landing and sampling sites for future lunar missions.
- The study supports ISRO’s future plans for in-situ volatile exploration on the Moon, aligning with its broader lunar exploration objectives.
PYQ:Q. Discuss India’s achievements in the field of Space Science and Technology. How the application of this technology helped India in its socio-economic development? (2016) |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
POEM-3: ISRO’s ‘Zero Orbital Debris’ Milestone
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PSLV-C58/XPoSat , POEM-3
Mains level: NA
Why in the news?
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has said its PSLV-C58/XPoSat mission has practically left zero debris in earth’s orbit.
About PSLV Orbital Experimental Module-3 (POEM-3)
- Launched on January 1, 2024, POEM-3 utilized the spent PS4 stage of the PSLV-C58 vehicle, which initially launched XPoSat.
- It is a three-axis-altitude controlled platform with power generation and tele-command & telemetry capabilities, for supporting Payloads.
- The XPoSat mission aimed to leave no debris in space, demonstrating ISRO’s commitment to responsible space practices.
- Upon deployment into its orbit at 650 km, POEM-3 was maneuvered to a 350 km circular orbit to minimize orbit decay time after the experiment’s completion.
- After completing 400 orbits, POEM-3 re-entered Earth’s atmosphere after 73 days in space.
Significance of this achievement
- With the rise in the number of satellites in orbit around the earth, space debris has become a pressing issue.
- Space debris in the low earth orbit (LEO) mainly comprises pieces of spacecraft, rockets, and defunct satellites, and the fragments of objects that have deteriorated explosively as a result of anti-satellite missile tests.
- This debris often flies around at high speeds of up to 27,000 kilometres per hour.
- Due to their sheer volume and momentum, they pose a risk to several space assets.
Threats posed by Space Debris
- Space debris also leads to two major risks:
- It creates unusable regions of the orbit due to excessive debris, and
- Leads to the ‘Kessler syndrome’ – creation of more debris due to cascading collisions resulting from one collision.
Various Initiatives to mitigate the Space Debris Issue
| Description | |
| Project NETRA | ISRO initiative for early warning system in space to detect debris and hazards to the Indian satellites.
It can spot, track and catalogue objects as small as 10 cm, up to a range of 3,400 km and equal to a space orbit of around 2,000 km. |
| Space Debris Mitigation Guidelines | Established in 2002 by the Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC) and endorsed by the United Nations in 2007. |
| Zero Debris Charter by ESA | Adopted by the European Space Agency (ESA) with the goal of achieving zero space debris by 2030. |
| NASA’s Orbital Debris Program | NASA’s initiative since 1979, focusing on reducing orbital debris creation, tracking existing debris, and exploring debris removal technologies. |
| Space Force Tracking System | Implemented by the U.S. Space Force to monitor space debris and assess collision risks in low Earth orbit (LEO). |
| Chinese Debris Removal Initiatives | China’s efforts include deploying spacecraft for debris removal with innovative technologies like solar sails. |
| Japanese CRD2 Demonstration | Partnership between Japan’s Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and Astroscale to develop debris removal technologies. |
Practice MCQ:ISRO’s PSLV Orbital Experimental Module-3 (POEM-3) recently re-entered Earth’s Orbit. What is so significant about this re-entry? (a) It practically left zero debris in earth’s orbit. (b) It facilitated groundbreaking research on the effects of microgravity on biological organisms. (c) It paved the way for the development of reusable spacecraft technology, reducing the cost of future space missions. (d) None of these. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
AgniKul ‘Agnibaan SOrTeD’ Mission
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Agnibaan SOrTeD
Mains level: NA

Why in the news?
- For the second time, the launch of AgniKul ‘Agnibaan SOrTeD’ has been postponed.
- The IIT Madras-based Agnikul Cosmos was to test-fire an Agnibaan rocket with 3D-printed engine, aiming for suborbital flight trajectory control.
What is Agnibaan SOrTeD (Suborbital Tech Demonstrator)?
- Agnibaan SOrTeD is a single-stage launch vehicle powered by Agnikul’s patented Agnilet semi-cryogenic engine.
- In contrast to traditional sounding rockets, Agnibaan SOrTeD’s vertical take-off and precise trajectory enable orchestrated maneuvers during flight.
Distinct Features of Agnibaan:
- Customizability: The rocket offers custom launch configurations, either single or two-stage launches.
- Dimensions: Standing at 18 meters and weighing 14,000 kg, Agnibaan SOrTeD is a powerful presence.
- Payload Capacity: With a capacity for payloads of up to 100 kg, it can reach altitudes of 700 km in five different Lower Earth Orbits (LEOs).
- Engine Configuration: The first stage can house up to seven Agnilet engines, powered by Liquid Oxygen and Kerosene, dependent on the mission’s requirements.
- Launch Pedestal ‘Dhanush’: AgniKul’s built ‘Dhanush’ supports the rocket’s mobility across configurations, ensuring compatibility with multiple launch ports.
- Agnilet Engine: Agnilet engine, a 3D-printed, single-piece, 6 kN semi-cryogenic marvel, drives Agnibaan’s propulsion. The engine employs a novel blend of liquid kerosene and supercold liquid oxygen as propellants.
PYQ:[2011] Satellites used for telecommunication relay are kept in a geostationary orbit. A satellite is said to be in such an orbit when: 1. The orbit is geosynchronous. 2. The orbit is circular. 3. The orbit lies in the plane of the Earth’s equator. 4. The orbit is at an altitude of 22,236 km Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1, 2 and 3 only (b) 1, 3 and 4 only (c) 2 and 4 Only (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
India among countries mulling telescopes on, around the moon
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PRATUSH;
Mains level: Lunar Missions;
Why in the news?
Astronomers are looking forward to opening a new window on the universe by posting high-resolution telescopes on the moon and in orbit around it.
Why Astronomers are looking forward to opening telescopes on the moon?
- Radio telescopes launched into orbit around Earth exacerbated the problem of receiving radio noise from the entire planet, along with signals from outer space.
- The moon’s far side offers pristine, airless conditions ideal for optical telescopes, providing crystal-clear seeing conditions during the two-week lunar night.
Global Initiatives to Install Telescope on the Moon:
- NASA’s LuSEE Night Project: LuSEE Night, a joint NASA-Berkeley Lab project scheduled for launch in December 2025, aims to study the Dark Ages period by landing on the far side of the moon, shielded from radio frequency noise from Earth.
- ESA’s Projects: ESA is preparing to launch a radio telescope to the moon’s far side aboard its lunar lander, ‘Argonaut’, by 2030, along with other projects focused on gravitational wave detection and infrared observations.
- China’s Initiatives: China is also actively involved in lunar exploration, with plans to launch a moon-orbiting radio telescope in 2026 and deploy the Queqiao-2 satellite, which includes a radio telescope payload, to serve as a communications relay between Earth and future missions.
Indian Initiative
- PRATUSH: Indian scientists plan to deploy the radio telescope PRATUSH on the moon’s far side, built by the Raman Research Institute (RRI) in collaboration with the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- Deployment Process: Initially, ISRO will place PRATUSH into orbit around the Earth, then fine-tune it before launching it towards the moon. Operating in Earth orbit will offer advantages such as free space operation and reduced ionosphere impact compared to ground-based experiments.
- Observational Advantages: PRATUSH in lunar orbit will have ideal observing conditions, operating in free space with minimal radio frequency interference (RFI) and no ionosphere, essential for studying the signal from the Dark Ages.
- Instrument Features: PRATUSH will carry a wideband frequency-independent antenna, a self-calibrating analog receiver, and a digital correlator to capture radio noise in the signal from the Dark Ages.
Conclusion: The global initiative to deploy telescopes on and around the moon aims to overcome Earth’s radio noise and capitalize on the lunar far side’s pristine conditions for groundbreaking astronomical observations, including studying the universe’s early Dark Ages.
Mains question for practice
Q Discuss the global initiatives to deploy telescopes on the moon.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Ozone found on Jupiter’s moon Callisto
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ozone, Jupiter's Compositions, Its moon
Mains level: NA
Why in the news?
PRL Ahmedabad researchers has uncovered evidence of ozone presence on Jupiter’s moon Callisto, offering profound insights into celestial chemical processes.
About Jupiter and its Moons
| Description | |
| Discovery | Known since ancient times;
Galileo Galilei observed Jupiter and its moons through a telescope in 1610 |
| Composition | Mostly composed of hydrogen and helium, with traces of other gases such as ammonia, methane, and water vapor |
| Diameter | 139,822 kilometers |
| Mass | 1.898 × 10^27 kilograms (317.8 Earth masses) |
| Orbital Period | Approximately 11.86 Earth years |
| Average Distance from Sun | Approximately 778 million kilometers |
| Surface Temperature | Approximately -145°C (-234°F) |
| Magnetic Field | Strong magnetic field, the strongest in the solar system |
| Moons | Jupiter has 79 known moons, including the four largest Galilean moons: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto.
Other notable moons include Amalthea, Himalia, Elara, Leda, Thebe, Metis, Adrastea, and more. The moons vary significantly in size, composition, and orbital characteristics. |
| Great Red Spot | Enormous storm system, known to exist for at least 400 years |
| Exploration | Explored by spacecraft such as Pioneer, Voyager, Galileo, Juno, and more |
Callisto and its Unique Environment
- Composition: Callisto’s predominantly icy surface, interspersed with rocky materials, sulphur dioxide, and organic compounds, positions it as a compelling candidate for extraterrestrial life exploration.
- Geological Stability: Despite extensive cratering, Callisto’s surface exhibits geological inactivity, suggesting long-term stability conducive to preserving subsurface oceans or potential habitats.
Significance of Ozone Findings
- Life-Sustaining Component: Ozone, a molecule composed of three oxygen atoms, plays a vital role in shielding celestial bodies from harmful ultraviolet radiation, fostering conditions conducive to life.
- Earthly Parallel: Just as the Earth’s ozone layer protects against harmful UV radiation, the presence of ozone on Callisto hints at stable atmospheric conditions and potential habitability, sparking scientific intrigue.
PYQ:What is the difference between asteroids and comets? 1. Asteroids are small rocky planetoids, while comets are made of ice, dust and rocky material. 2. Asteroids are found mostly between the orbits of Jupiter and Mars, while comets are found mostly between Venus and Mercury. 3. Comets show a perceptible glowing tail, while asteroids do not. Which of the statements given above is/ are correct? (2011) (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 1 and 3 only (c) 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO’s NICES Programme Combatting Climate Change
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NICES Programs
Mains level: NA

Why in the news?
The National Information System for Climate and Environment Studies (NICES) Program has extended invitations to Indian researchers to contribute to climate change mitigation efforts.
What is NICES Program?
- The NICES Programme is operated by the ISRO and the Department of Space.
- It was launched in 2012.
- It operates within the framework of the National Action Plan on Climate Change.
- NICES aims to enhance the participation of Indian researchers in addressing climate change-related challenges through multidisciplinary scientific investigations.
- Focus Areas: Potential areas for project submission include Space-based Essential Climate Variables (ECVs) and Climate Indicators, Climate Change Challenges, Weather Extremes, and Climate Services.
Activities held under NICES Program
- NICES invites project proposals from Indian scientists, academicians, and researchers affiliated with various governmental organizations, recognized institutions, universities, and departments.
- Project proposals should address climate change-related challenges.
- These projects are expected be completed within 3 years from the date of sanction.
Objective and Functionality
- The primary objective of the NICES Programme is to generate and disseminate long-term Essential Climate Variables (ECVs) derived from Indian and other Earth Observation (EO) satellites.
- These variables, spanning terrestrial, oceanic, and atmospheric domains, are crucial for characterizing Earth’s climate and monitoring changes over time.
Achievements and Impact:
- Since its inception in 2012, NICES has developed over 70 geophysical products meeting stringent quality standards.
- These products have been instrumental in documenting climate change and its impacts, contributing to scientific understanding and evidence-based decision-making.
PYQ:2021: Describe the major outcomes of the 26th session of the Conference of the Parties (COP) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). What are the commitments made by India in this conference?
Practice MCQ:The NICES Program is an initiative of: (a) Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) (b) Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) (c) Department of Science and Technology (DST) (d) None of the above. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
IAU approves ‘Statio Shiv Shakti’ as name for Chandrayaan-3 Landing Site
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: International Astronomical Union (IAU), Statio Shiv Shakti, Jawahar Point
Mains level: NA

What is the news?
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) working group for Planetary System Nomenclature recently sanctioned the name ‘Statio Shiv Shakti’ for the landing site of Chandrayaan-3’s Vikram lander, marking a significant milestone in planetary nomenclature.
About International Astronomical Union (IAU)
- The IAU was founded on July 28, 1919, during the Constitutive Assembly held in Brussels, Belgium.
- Its creation was prompted by the need for international collaboration in astronomy, especially after the devastation caused by World War I.
- It aims for promoting and safeguarding astronomy in all its aspects through international cooperation.
- IAU is now headquartered in Paris, France.
Major Activities and Initiatives
- General Assembly: The IAU holds a general assembly every three years in varying parts of the world at which professional astronomers meet to discuss research, new cooperative ventures, and similar matters of professional interest.
- Astronomical Nomenclature: IAU standardizes the nomenclature of celestial bodies, features, and phenomena. It maintains several working groups dedicated to naming conventions for stars, planets, asteroids, and other objects.
- Research and Collaboration: It promotes international cooperation in astronomical research and supports initiatives such as observational campaigns, data sharing, and joint projects.
- Education and Outreach: It is actively involved in promoting astronomy education and public outreach efforts worldwide. It supports educational programs, workshops, and resources for students, teachers, and the general public.
Membership
- IAU membership spans 92 countries. Out of those countries, 85 are National Members.
- India is represented by the Astronomical Society of India (ASI).
- Its members are professional astronomers from all over the world, at the D. level and beyond, who are active in professional research, education, and outreach in astronomy.
IAU Nomenclature Criteria
|
About Statio Shiv Shakti’
- Prime Minister announced the name ‘Shiv Shakti’ for the Chandrayaan-3 landing site in August, 2023, reflecting the significance of Indian mythology and cultural heritage.
- It is located at the co-ordinates 69.373°S 32.319°E and lies between the lunar craters Manzinus C and Simpelius N.
- The name ‘Shiv Shakti’ symbolizes the masculine-feminine duality of nature, embodying strength and resolution, with a profound connection to India’s diverse cultural landscape.

| PM previously named the Chandrayaan-2 crash site ‘Tiranga point’, while former President A.P.J. Abdul Kalam suggested ‘Jawahar Point’ for the Chandrayaan-1 impact probe landing site, reflecting a tradition of honoring national figures and symbols. |
PYQ:
2021: Which one of the following is a reason why astronomical distances are measured in light-years?
- Distances among stellar bodies do not change.
- Gravity of stellar bodies does not change.
- Light always travels in straight line.
- Speed of light is always same.
Practice MCQ:
Consider the following statements about International Astronomical Union (IAU):
- It aims for promoting and safeguarding astronomy in all its aspects through international cooperation.
- India is represented by the ISRO in the IAU.
Which of the given statements are correct?
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO successfully conducts ‘Pushpak’ Reusable Landing Vehicle Landing
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Pushpak Reusable Landing Vehicle (RLV), Low Earth Orbits, Gaganyaan
Mains level: NA

What is the news?
- The ISRO has conducted the Pushpak Reusable Landing Vehicle (RLV) LEX 02 landing experiment at the Aeronautical Test Range in Chitradurga. It was lifted by an Indian Air Force Chinook helicopter and released from an altitude of 4.5 km.
- This experiment marks a significant milestone in ISRO’s pursuit of reusable space technology.
About Pushpak Reusable Landing Vehicle (RLV)
- The Pushpak RLV is a winged vehicle, equipped with aerodynamic surfaces that enable controlled flight during re-entry into the Earth’s atmosphere.
- The RLV is designed to autonomously land on a designated runway after completing its mission in space, thereby demonstrating India’s capability in autonomous space vehicle landing.
- It is equipped with sophisticated navigation, control, and landing gear systems that allow it to autonomously navigate and land on a predefined runway.
Key Features
- The RLV is a space plane with a low lift-to-drag ratio, requiring an approach at high glide angles that necessitates landing at high velocities of 350 km/h.
- This design allows it to transport payloads to Low Earth orbits and return to Earth for future use.
Future Prospects
- Iterative Testing: ISRO conducts a series of experiments, such as the RLV LEX 02 landing experiment, to test and validate the performance of the RLV in various scenarios.
- Orbital Re-entry Missions: The successful demonstration of the Pushpak RLV’s capabilities paves the way for future orbital re-entry missions, where reusable vehicles can be deployed for various scientific and commercial purposes.
PYQ:
2018: With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements:
- PSLVs launch the satellites useful for Earth resources monitoring whereas GSLVs are designed mainly to launch communication satellites.
- Satellites launched by PSLV appear to remain permanently fixed in the same position in the sky, as viewed from a particular location on Earth.
- GSLV Mk III is a four-stage launch l vehicle with the first and third stages l using solid rocket motors; and the second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 2
- 3 only
Practice MCQ:
Consider the following statements about the ‘Pushpak’ Reusable Landing Vehicle (RLV):
- It is a winged vehicle.
- It can transport payloads to Low Earth orbits and return to Earth with the help of a parachute.
Which of the given statements are correct?
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Multi-purpose app SAKHI to assist Gaganyaan Crew
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SAKHI App, Progress tracking of Gaganyaan Mission.
Mains level: Not Much
What is the news-
- The Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), an ISRO facility located at Thumba in Thiruvananthapuram, has developed a multi-purpose app ‘SAKHI’ to assist Gaganyaan Crew.
About SAKHI
- The Space-borne Assistant and Knowledge Hub for Crew Interaction (SAKHI) is equipped to monitor astronauts’ health, maintain communication with Earth, and manage dietary schedules.
- It serves as an essential tool for the crew, offering real-time assistance and access to necessary data.
- It would assist astronauts during the Gaganyaan space flight mission, facilitating tasks such as accessing vital technical information and communication.
- Strapped to astronauts’ space suits, it allows for easy access and facilitates the maintenance of mission logs in various formats.
Utility offered by SAKHI
- Health Monitoring: SAKHI provides comprehensive health monitoring, including parameters like blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation. It also reminds astronauts about hydration, dietary schedules, and sleep patterns, enhancing their mission efficiency.
- Communication: SAKHI maintains communication between the crew, onboard computers, and ground-based stations, ensuring seamless connectivity.
Gaganyaan Mission Timeline:
- ISRO aims to launch the Gaganyaan human spaceflight mission in 2025.
- The identities of the four astronaut-designates, all IAF test pilots, were revealed at a high-profile event attended by PM at the VSSC on February 27.
- The final crew for the mission will be selected from among the four astronaut-designates.
Also read:
PYQ:
Which of the following is/are cited by the scientists as evidence/evidences for the continued expansion of the universe? (2012)
- Detection of microwaves in space
- Observation of redshift phenomenon in space
- Movement of asteroids in space
- Occurrence of supernova explosions in space
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 1, 3 and 4
- None of the above can be cited as evidence
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Kulasekarapattinam: ISRO’s New Rocket Launchport
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Kulasekarapattinam, SHAR
Mains level: NA

In the news
- Prime Minister recently laid the foundation stone of ISRO’s second rocket launchport at Kulasekarapattinam.
- Costing Rs 986 crore, this facility, strategically located in Tamil Nadu’s Thoothukudi district, will primarily serve commercial, on-demand, and small satellite launches in the future.
About Kulasekarapattinam
- It will be second after Satish Dhawan Space Centre (Sriharikota Range (SHAR)), founded in Andhra Pradesh’s Sriharikota in 1971, with two launch pads.
- It will focus on the launch of Small Satellite Launch Vehicles (SSLVs) on a commercial basis.
- It would have the capacity to launch 24 satellites per year using a mobile launch structure.
- It strategic location helps save fuel for small rocket launches as the port can launch rockets directly south over the Indian Ocean without requiring crossing landmasses.
Need for such Facility
- Fuel Saving: This is unlike the existing launch site at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, which adds more fuel requirements for launching into a polar orbit as rockets need to follow a curved path to the south to avoid Sri Lanka’s landmass.
- Unburdening SHAR: The opening of the space sector to private players necessitates a rise in commercial launches, prompting ISRO to build a second launchport to alleviate the burden on the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) SHAR in Sriharikota.
- Dedicated Launch for Small Payloads: While SHAR handles larger missions, Kulasekarapattinam launchport will cater exclusively to smaller payloads, including those for commercial purposes and on-demand launches.
Geographical Advantages
- Strategic Location: Kulasekarapattinam provides a natural advantage for ISRO’s future launches, especially for the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV), due to its geographical, scientific, and strategic positioning.
- Optimized Trajectory: The launch trajectory from Kulasekarapattinam enables a direct southward path for SSLVs, minimizing fuel consumption compared to launches from SHAR, which currently follow longer trajectories.
SSLVs: Purpose and Development
- Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV): SSLV is designed to launch small satellites weighing between 10 to 500kg into Low Earth Orbit, catering to commercial and on-demand launches.
- Mission Successes: SSLV-D1’s launch in August 2022 failed to achieve the intended orbit, but SSLV-D2’s success in February 2023 marked a significant milestone for ISRO’s SSLV program.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
4 IAF Gaganyaan Astronaut-designates named
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Gaganyaan Mission
Mains level: Significance of manned space mission for India

In the news
- Prime Minister announced the astronaut designates for India’s inaugural crewed spaceflight, Gaganyaan, slated for a 2025 launch.
About Gaganyaan Mission
- The Gaganyaan Mission is India’s initiative to demonstrate human spaceflight capabilities by sending a crew of 4 members into a 400 km Low Earth Orbit.
- It aims to demonstrate India’s indigenous capability in undertaking human space flights, with an immediate goal of executing a manned mission.
- GSLV Mk III, also known as LVM-3, will be used as a launch vehicle in Gaganyaan mission.

Technological Requirements
- Human-Rated LVM3: A modified version of ISRO’s LVM3 serves as the launch vehicle, equipped with Crew Escape System (CES) and an Orbital Module to ensure crew safety.
- Orbital Module (OM):
-
- Crew Module (CM): Provides a habitable space for crew members, featuring a double-walled rigid construction and essential life support systems.
- Service Module (SM): Supports the Crew Module in orbit, housing propulsion, thermal, and power systems.
- Crew Escape System (CES): Facilitates emergency escape mechanisms for astronauts during critical phases of the mission, ensuring their safety.
- Life Support System: Ensures a conducive environment for crew members in space, addressing physiological needs and emergency provisions.
Phases of Gaganyaan Mission
- Testing Phase: Included Integrated Air Drop Test (IADT) and Pad Abort Test (PAT), crucial for validating safety mechanisms and system performance.
- Unmanned Missions: Technology demonstration and safety verification precede the manned mission, involving advanced tests and flight trials. Vyommitra AI humanoid underwent tests for this mission.
- Manned Mission: Culminates in executing the human spaceflight module of Gaganyaan, following successful unmanned missions.
Significance of the Mission
- Technological Advancement: Propels India towards future technological capabilities, fostering affordable space programs and scientific exploration.
- Youth Inspiration: Inspires youth towards careers in science and technology, igniting innovation and creativity in space science.
- Diplomatic Collaboration: Opens avenues for international cooperation in space exploration, enhancing diplomatic ties and knowledge exchange.
- Scientific Breakthrough: Enables groundbreaking discoveries in medicine, material science, and biology through microgravity experiments.
- Economic Growth: Stimulates economic development, technology spin-offs, and job creation, contributing to India’s overall progress.
Challenges Associated
- Indigenous Technology: Reliance on indigenous technology necessitates complex research and development efforts, ensuring program safety.
- Space Transportation Vehicle: Development of customized launch vehicles poses challenges due to payload constraints and weight limitations.
- Training and Simulation: Lack of critical space training facilities necessitates dependence on other space agencies, augmenting challenges.
- Regenerative Environment: Creation of self-sustaining life support systems in space remains a daunting task, requiring innovative solutions.
- Crew Safety: Mitigating risks associated with crew safety, including psychological and physiological effects of space travel, is imperative.
Conclusion
- The Gaganyaan Mission epitomizes India’s leap towards space exploration, encapsulating aspirations of scientific discovery, technological innovation, and international collaboration.
- Amidst challenges and complexities, India stands poised to script a new chapter in its space odyssey, inspiring generations and propelling towards the frontiers of the cosmos.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
PAPA: Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya L1
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PAPA, Aditya L1, CMEs
Mains level: NA

Introduction
- India’s pioneering solar mission, Aditya-L1, has achieved a significant milestone as advanced sensors onboard successfully detected the impact of coronal mass ejections (CMEs), marking a leap forward in space exploration.
Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs)
|
About Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya (PAPA)
- Purpose: PAPA is an energy and mass analyser tailored for in-situ measurements of solar wind electrons and ions within the low energy range.
- Sensor Composition: PAPA comprises two sensors—Solar Wind Electron Energy Probe (SWEEP) and Solar Wind Ion Composition Analyser (SWICAR)—facilitating comprehensive observations of solar phenomena.
- Functionalities: Sensors not only measure electrons and ions’ energy but also ascertain their direction of arrival, enabling a holistic understanding of solar wind dynamics.
CME Detection and Analysis
- Observations: PAPA detected CME events, notably on December 15, 2023, and during February 10-11, 2024.
- December 15, 2023: Single CME event marked by a sudden increase in electron and ion counts, aligning with solar wind parameters and magnetic field measurements.
- February 10-11, 2024: Multiple minor CME events observed, showcasing nuanced variations in electron and ion counts over time.
Performance Evaluation and Continuous Observations
- PAPA sensors are currently operational in default mode, demonstrating adherence to design specifications across all operational modes.
- Continuous observations underscore PAPA’s efficacy in monitoring space weather conditions and its adeptness in detecting and analyzing solar phenomena.
Back2Basics: Aditya-L1
- Launched successfully by ISRO on September 2.
- Orbits around the Lagrangian Point 1 (L1), maintaining a stable position 1.5 million km from Earth in the direction of the Sun.
- Hosts seven payloads dedicated to studying various aspects of the Sun, encompassing both remote observations and in-situ measurements.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO’s CE20 Cryogenic Engine ready for Gaganyaan Missions
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CE20, Working of Cryogenic Engine
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has achieved a significant breakthrough in its quest for human spaceflight with the successful human rating of its CE20 cryogenic engine.
- The ground qualification tests, conducted at the High Altitude Test Facility at ISRO Propulsion Complex, Mahendragiri, have been successfully completed, validating the CE20 engine for the Gaganyaan programme.
What is Cryogenic Engine?
|
About CE20 Cryogenic Engine
- It has been designed and developed by the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC), a subsidiary of ISRO.
- It is the first Indian cryogenic engine to feature a gas-generator cycle.
- It is one of the most powerful upper-stage cryogenic engines in the world.
- This engine develops a nominal thrust of 186.36 kN in vacuum.
Key Highlights of Ground Qualification Tests
- Thorough Evaluation: The CE20 engine underwent extensive testing, including evaluation under nominal and off-nominal conditions related to thrust, mixture ratio, and propellant tank pressure.
- Hot Firing Tests: Four engines underwent a total of 39 hot firing tests, accumulating a cumulative duration of 8,810 seconds, surpassing the minimum human rating qualification standard requirement of 6,350 seconds.
Update on First Unmanned Gaganyaan (G1) Mission
- Mission Objectives: The Gaganyaan project aims to demonstrate India’s human spaceflight capabilities by launching a crew of three members into a 400 km orbit for a 3-day mission, followed by a safe return to Earth with a landing in Indian sea waters.
- Acceptance Tests: ISRO has completed the acceptance tests of the flight engine designated for the first unmanned Gaganyaan (G1) mission, scheduled tentatively for the second quarter of 2024.
- Engine Specifications: The flight engine, which will power the upper stage of the human-rated LVM3 vehicle, boasts a thrust capability of 19 to 22 tonnes and a specific impulse of 442.5 seconds.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
INSAT-3DS launch: The Naughty Boy of ISRO
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: INSAT-3DS
Mains level: NA

Introduction
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is set to launch its meteorological satellite INSAT-3DS aboard the spacecraft GSLV F14.
INSAT-3DS: Mission Objectives
- Continuity of Services: The mission seeks to continue and enhance the services provided by existing operational satellites like INSAT-3D and INSAT-3DR.
- Meteorological Observations: INSAT-3DS will facilitate advanced meteorological observations, land and ocean surface monitoring, and weather forecasting.
- Disaster Warning: It will play a critical role in disaster warning systems, aiding in timely alerts and response efforts.
- Satellite-aided Research and Rescue Services (SAR): Additionally, the satellite will support SAR operations, contributing to enhanced search and rescue capabilities.
Significance
- This marks the 16th space mission for the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV), emphasizing India’s progress in space technology.
- INSAT-3DS aims to be deployed into the Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO), funded entirely by the Ministry of Earth Sciences, signifying a significant step in India’s space advancements.
- After around 18 minutes of launch, the satellite will be injected in a 36,647 km x 170 km elliptical orbit.
Why called as Naughty Boy?
- Failure: GSLV F14 has faced challenges in the past, earning the moniker “naughty boy” within the Indian space programme due to its history of encountering problems.
- Probability: With a failure rate of 40%, GSLV F14 has experienced issues in six out of its fifteen missions to date.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Aditya-L1 successfully placed in a Halo Orbit around L1 Point
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Aditya L1 Mission
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has achieved a significant milestone by placing the Aditya-L1 spacecraft in a halo orbit around the Lagrangian point (L1).
- Launched on September 2, 2023, Aditya-L1 reached the L1 point on January 6, after a 127-day journey covering 1.5 million km.
What is a Halo Orbit?
- Halo orbits are three-dimensional, periodic orbits around Lagrange points in a two-body system like Earth-Sun or Earth-Moon.
- It is commonly linked with L1, L2, and L3 Lagrange points, where the gravitational forces of two large bodies and centrifugal force balance each other.
- It provides a stable line of sight to Earth and the Sun, beneficial for continuous communication and solar power.
- Unlike typical two-dimensional orbits, halo orbits form a 3D loop, resembling a halo around Lagrange points.
- These orbits, especially around L1 and L2 points, require periodic adjustments for a spacecraft to maintain its trajectory.
- It offers energy-efficient positions in space due to balanced gravitational forces, requiring minimal propulsion for orbit maintenance.
- James Webb Space Telescope utilizes a halo orbit around the Earth-Sun L2 point for a stable observation position.
Aditya-L1’s Mission Objectives and Operations
- Orbit Characteristics: Aditya-L1 is in a periodic halo orbit around L1, approximately 1.5 million km from Earth, with an orbital period of about 177.86 days.
- Mission Life and Goals: With a mission life of five years, Aditya-L1 aims to study the sun’s photosphere, chromosphere, and corona, along with in-situ studies of particles and fields at L1.
- Continuous Solar Observation: The satellite’s position allows for uninterrupted solar observation, crucial for understanding solar activities and space weather dynamics.
Understanding Lagrange Points and L1
- Lagrange Points Explained: Lagrange Points are positions in space where a small object can maintain its position relative to two larger bodies due to the gravitational balance.
- L1 Point Advantage: The L1 point, located about 1.5 million km from Earth, offers continuous solar viewing without occultation or eclipse, providing a strategic advantage for solar observation.
Aditya-L1’s Journey Timeline
- Launch and Initial Orbits: Following its launch, ISTRAC conducted four earth-bound maneuvers to position Aditya-L1 in progressively higher orbits.
- Trans-Lagrangian1 Insertion: The spacecraft underwent a crucial manoeuvre on September 19, marking the start of its 110-day journey to L1.
Why Study the Sun?
- Understanding Solar Dynamics: Studying the sun is crucial for comprehending its energy production, temperature variations, and radiation emissions.
- Monitoring Solar Activities: Continuous monitoring of solar flares and coronal mass ejections is vital for predicting space weather and mitigating its impact on space-reliant technologies.
Conclusion
- Unprecedented Solar Study: Aditya-L1’s unique position and advanced instruments enable an unparalleled study of the sun, contributing significantly to our understanding of solar phenomena.
- ISRO’s Achievement: This successful mission underscores ISRO’s expertise in navigating complex space missions and reinforces India’s position as a leading player in space exploration and research.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO Successfully Tests Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell in Space
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cells
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully tested a 100 W class Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell based Power System (FCPS) in space.
- The FCPS was part of the POEM3 orbital platform, launched onboard PSLV-C58 on January 1, 2024.
About FCPS Experiment
- Primary Goal: The experiment aimed to assess the operation of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel cells in space and gather data for future mission designs.
- Power Generation: During the test, 180 W power was generated using Hydrogen and Oxygen gases, providing valuable data on the performance of the power system.
About Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cells
| Details | |
| Basic Principle | Converts chemical energy from hydrogen into electrical energy, producing water and heat as byproducts. |
| Key Components | Membrane Electrode Assembly (MEA)
Platinum-based catalyst Gas Diffusion Layers (GDLs) Bipolar Plates |
| Operation | Hydrogen Oxidation: At the anode, hydrogen molecules (H2) are split into protons (H+) and electrons (e-).
Proton Conduction: The PEM allows only protons to pass through to the cathode, blocking electrons. Electron Flow: Electrons travel through an external circuit to the cathode, creating an electric current. Oxygen Reduction: At the cathode, oxygen molecules (O2) from the air combine with the protons and electrons to form water (H2O). Heat Production: The reaction generates heat, which can be used for heating purposes in some applications. |
| Types of Membranes | Perfluorosulfonic acid (PFSA) membranes (common)
Hydrocarbon-based membranes (alternative) |
| Advantages | High power density
Low operating temperatures (60-80°C) Zero emissions with pure hydrogen |
Applications in Space and Society
- Multipurpose Space Use: Fuel cells are particularly suitable for human space missions, providing essential power, water, and heat from a single system.
- Societal Benefits: They have significant potential for societal applications, including as replacements for conventional vehicle engines and in standby power systems.
- Advantages over Batteries: Fuel cells offer range and refuelling times comparable to conventional engines and are expected to enable emission-free transportation.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Cabinet approves Prithvi Vigyan Scheme for Earth Sciences
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Prithvi Vigyan Scheme
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- The Union Cabinet, led by Prime Minister, has sanctioned the “Prithvi Vigyan (Prithvi)” scheme, a significant project of the Ministry of Earth Sciences.
- With a budget of Rs 4,797 crore, the scheme is planned for the period from 2021 to 2026.
About Prithvi Vigyan Scheme
- Consolidation of Programs: The Prithvi scheme unifies five existing sub-schemes:
- Atmosphere & Climate Research-Modelling Observing Systems & Services (ACROSS),
- Ocean Services, Modelling Application, Resources and Technology (O-SMART),
- Polar Science and Cryosphere Research (PACER),
- Seismology and Geosciences (SAGE),
- Research, Education, Training and Outreach (REACHOUT).
- Aim: This integration is designed to enhance our understanding of Earth’s systems and apply scientific knowledge for societal, environmental, and economic benefits.
Objectives and Focus Areas
- Comprehensive Observations: The scheme emphasizes long-term monitoring across the atmosphere, ocean, geosphere, cryosphere, and solid earth to track Earth System’s vital signs and changes.
- Development of Predictive Models: It focuses on creating models for weather, ocean, and climate hazards and advancing climate change science.
- Exploration Initiatives: Exploration of Polar Regions and high seas is a key aspect, aiming to discover new phenomena and resources.
- Technological Advancements: The scheme also stresses the development of technology for the sustainable exploitation of oceanic resources for societal applications.
Role of the Ministry of Earth Sciences
- Provision of Critical Services: The Ministry is responsible for delivering crucial services related to weather, climate, ocean and coastal states, hydrology, seismology, and natural hazards.
- Support in Disaster Management: These services are essential for issuing forecasts and warnings for natural disasters, thereby aiding in disaster preparedness and risk mitigation.
Holistic Approach to Earth System Sciences
- Broad Scope of Study: Earth System Sciences involve studying the atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere, cryosphere, and biosphere, and their complex interactions.
- Integrated Research Efforts: The Prithvi scheme aims to address these components comprehensively, enhancing understanding and providing reliable services for India.
Impact and Future Prospects
- Addressing Major Challenges: The scheme’s integrated research and development efforts will tackle significant challenges in various fields like weather, climate, oceanography, cryospheric studies, and seismology.
- Harnessing Resources Sustainably: It explores sustainable methods to utilize both living and non-living resources, contributing to national development and environmental conservation.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Crucial Role of Karman Line in Space Defense Strategies
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Karman Line
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- The Karman line, the theoretical boundary between Earth’s atmosphere and outer space, plays a crucial role in space defense and satellite communications.
Understanding the Karman Line
- The Karman Line is an abstract boundary positioned at an altitude of 100 kilometers above sea level.
- Its primary function is to establish the separation between Earth’s atmosphere and the vast expanse of space.
- Although not universally accepted by all scientists and space explorers, the majority of countries and space organizations acknowledge this demarcation.
- It was formally established in 1960s by the Federation Aeronautique Internationale (FAI), a body responsible for record-keeping.
- Crossing the Karman Line designates an individual as an astronaut.
Potential Threats from Dominating the Karman Line
- Anti-Satellite Weapons: Control over the Karman line could enable adversaries to deploy weapons targeting satellites, disrupting communication links.
- Jamming and Interference: Adversaries might use systems to disrupt satellite communications, causing blackouts or degraded performance.
- Hacking and Cyber-attacks: Unauthorized access to satellite systems could lead to data breaches or manipulation of communication signals.
- Physical Interception or Tampering: The ability to physically reach satellites could allow adversaries to alter orbits, damage components, or eavesdrop on communications.
- Space Debris and Kinetic Kill Vehicles: Creating debris or deploying kinetic kill vehicles could disrupt satellite networks.
- Electromagnetic Pulse (EMP) Weapons: EMPs could damage satellite electronics, rendering them inoperable.
- Denial of Access to Space: Dominating the Karman line could enable adversaries to deny space access to certain countries or entities.
- Spoofing and Deception: Manipulating satellite communication signals could mislead or deceive users.
- Space-based Cyber-Physical Attacks: Combining cyber and physical methods could disrupt or manipulate satellite operations.
- Policy and Regulatory Challenges: Dominance could lead to geopolitical challenges and affect international agreements related to space activities.
Historical Context and Recent Developments
- First Breach by V-2 Missile: On June 20, 1944, the V-2 became the first object to breach the Karman line, marking a significant milestone in space exploration.
- Superpower Dominance: Both the United States and the Soviet Union have historically sought to dominate space for military and reconnaissance purposes, leading to the development of anti-satellite weapons and ballistic missiles.
India’s Evolving Space Program
- Shift in Focus: India’s space program has transitioned from a developmental focus to incorporating space for national security objectives, particularly in response to China’s counter-space capabilities.
- Military and Security Considerations: India’s approach now includes robust launch capabilities, military satellites, and an emphasis on self-reliance and situational awareness.
Conclusion
- Strategic Importance: The Karman line’s significance extends beyond scientific understanding to encompass crucial defense strategies in space.
- Need for Vigilance and Cooperation: Nations must protect their space-based assets and collaborate internationally to address the multifaceted threats associated with dominating this critical boundary.
- Future of Space Defense: As space becomes increasingly contested, understanding and securing the Karman line is vital for maintaining and defending capabilities in outer space.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Meet ISRO’s new X-ray eye in the sky
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: POLIX’s beryllium disc
Mains level: detection of lower-energy X-rays
Central idea
Key Highlights:
- ISRO successfully launched XPoSat, an X-ray Polarimeter Satellite, on New Year’s Day in 2024.
- The indigenous instrument, POLIX, built at Raman Research Institute, is a crucial step for Indian astronomers.
- POLIX aims to study X-ray polarization, providing insights into celestial magnetic fields.
Key Challenges:
- Collecting X-rays from space is challenging due to their high energy, making traditional focusing methods impossible.
- Earth’s atmosphere absorbs most X-rays, complicating the study of cosmic X-rays.
Key Terms and Phrases:
- XPoSat: X-ray Polarimeter Satellite.
- POLIX: Indian X-ray Polarimeter.
- Pulsars: Exotic stars emitting X-rays with strong magnetic fields.
- IXPE: NASA’s X-ray Polarimeter Explorer.
- XSPECT: Instrument on XPoSat for studying timing and spectral properties.
Key Quotes:
- “The instrument, totally indigenous in design and fabrication, will herald yet another milestone for Indian astronomers.”
- “Measuring the polarisation of X-rays would enable astronomers to gauge the directions of magnetic fields in celestial objects.”
Key Statements:
- POLIX, a cubical cylinder with a beryllium disc, detects X-rays and works on the principle of polarization after scattering.
- XPoSat, complementing NASA’s IXPE, will provide valuable information about pulsars and black holes.
Key Examples and References:
- Pulsars, city-sized stars with immense mass, often shine in X-rays and have powerful magnetic fields.
- POLIX’s beryllium disc allows the probing of lower energy X-rays compared to NASA’s instrument.
Key Facts and Data:
- POLIX measures roughly half a meter and weighs nearly 200 kilograms.
- XPoSat focuses on studying the timing and spectral properties of X-ray-emitting objects.
Critical Analysis:
- POLIX’s unique design using beryllium enhances the detection of lower-energy X-rays, providing a significant advantage.
- The launch of XPoSat signifies a major advancement in Indian X-ray astronomy, offering a valuable complement to NASA’s efforts.
Way Forward:
- Anticipation surrounds XPoSat’s data collection, expected to deepen our understanding of pulsars and black holes.
- Ongoing collaboration and advancements in X-ray astronomy will likely lead to further discoveries.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO launches X-Ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) Mission
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: X-Ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat)
Mains level: Read the attached story
Central Idea
- The Indian Space Research Organisation has rang in the new year with the launch of the PSLV-C58 X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) mission on January 1, 2024.
About XPoSat Mission
- Orbital Details: XPoSat will operate in a Low Earth Orbit at an altitude of about 650 km, with a low inclination of around 6 degrees.
- Dual Scientific Payloads: The satellite is equipped with two payloads, enabling comprehensive studies of X-ray sources, including their temporal, spectral, and polarization characteristics.
- Mission Goals: XPoSat’s primary objectives include measuring X-ray polarization in the 8-30 keV energy band and conducting long-term studies in the 0.8-15 keV band.
- Mission Lifespan: The satellite is expected to be operational for approximately 5 years.
- Observation Strategy: Observations by XPoSat will primarily occur during the Earth’s eclipse period to maximize efficiency.
Payloads aboard XPoSat
- POLIX – Primary Payload: The Polarimeter Instrument in X-rays (POLIX), developed by Bengaluru’s Raman Research Institute (RRI) with ISRO’s collaboration, is tailored to assess the degree and angle of polarization in medium X-ray energy ranges.
- XSPECT – Secondary Payload: The X-ray Spectroscopy and Timing (XSPECT) payload, created by ISRO’s U.R. Rao Satellite Centre (URSC), will gather spectroscopic data in the 0.8-15 keV range.
Significance of XPoSat
- Polarization refers to the orientation of light waves. X-rays, a form of electromagnetic radiation, can also be polarized.
- Studying it from cosmic sources provides valuable information about the physical conditions and processes occurring in extreme environments, such as around black holes, neutron stars, and supernova remnants.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
India set to launch its first X-Ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: X-Ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat)
Mains level: Read the attached story
Central Idea
- The Indian Space Research Organisation, following a landmark 2023, will ring in the new year with the launch of the PSLV-C58 X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) mission on January 1, 2024.
About XPoSat Mission
- Orbital Details: XPoSat will operate in a Low Earth Orbit at an altitude of about 650 km, with a low inclination of around 6 degrees.
- Dual Scientific Payloads: The satellite is equipped with two payloads, enabling comprehensive studies of X-ray sources, including their temporal, spectral, and polarization characteristics.
- Mission Goals: XPoSat’s primary objectives include measuring X-ray polarization in the 8-30 keV energy band and conducting long-term studies in the 0.8-15 keV band.
- Mission Lifespan: The satellite is expected to be operational for approximately 5 years.
- Observation Strategy: Observations by XPoSat will primarily occur during the Earth’s eclipse period to maximize efficiency.
Payloads aboard XPoSat
- POLIX – Primary Payload: The Polarimeter Instrument in X-rays (POLIX), developed by Bengaluru’s Raman Research Institute (RRI) with ISRO’s collaboration, is tailored to assess the degree and angle of polarization in medium X-ray energy ranges.
- XSPECT – Secondary Payload: The X-ray Spectroscopy and Timing (XSPECT) payload, created by ISRO’s U.R. Rao Satellite Centre (URSC), will gather spectroscopic data in the 0.8-15 keV range.
Significance of XPoSat
- Polarization refers to the orientation of light waves. X-rays, a form of electromagnetic radiation, can also be polarized.
- Studying it from cosmic sources provides valuable information about the physical conditions and processes occurring in extreme environments, such as around black holes, neutron stars, and supernova remnants.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Private: Chandrayaan-3 Propulsion Module retraces Steps to Earth Orbit
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Chandrayaan-3 Propulsion Module
Mains level: NA
Central Idea
- The Propulsion Module (PM) of Chandrayaan-3 successfully returned to Earth’s orbit, marking a significant step in lunar exploration.
- This maneuvers was not part of the original mission plan but capitalized on the mission’s logistical advantages, including excess fuel.
Propulsion Module’s Role and Features
- Difference from Chandrayaan-2: Unlike Chandrayaan-2, which had a full-fledged orbiter, Chandrayaan-3 featured a lighter PM solely for lunar transit.
- Communication: The mission utilized the Chandrayaan-2 orbiter for Earth communications.
- Payload: The PM carried the Spectro Polarimetry of Habitable Planet Earth (SHAPE) instrument, aimed at studying Earth to identify habitable exoplanets.
- Separation and Operation: The PM separated from the lander on August 17 and was initially expected to orbit the Moon for six months with SHAPE operational.
Seizing the Opportunity
- Extended Mission Life: The precise orbit injection and efficient maneuvers led to over 100 kg of fuel savings, extending the PM’s operational life.
- Adapted Mission Plan: This fuel surplus allowed ISRO to demonstrate capabilities for future lunar sample return missions.
Return to Earth Orbit
- Manoeuvres Planning: ISRO designed an optimal Earth return trajectory for October 2023.
- Execution: The PM underwent a series of maneuvers, including orbit elevation around the Moon and a Trans-Earth injection, followed by Moon fly-bys before exiting the Moon’s sphere of influence.
- Current Status: The PM is now in an Earth orbit with a period of nearly 13 days, operating safely without posing threats to other satellites.
Significance of the Maneuver
- Trajectory and Maneuver Execution: The mission provided insights into planning and executing trajectories for small spacecraft to return from the Moon to Earth.
- Software Development: This experience will aid in developing software modules for future mission planning.
- Gravity-Assisted Flybys: The experiment paves the way for planning gravity-assisted flybys across celestial bodies.
- End-of-Life Management: It also helps in avoiding uncontrolled crashes on the Moon’s surface at the end of the PM’s life.
- SHAPE Payload: SHAPE continues to operate, including during a special operation on October 28 during a Solar Eclipse, and will remain active when Earth is in its field of view.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
NASA-ISRO NISAR Mission Prepares for Launch
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) missionv
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- The NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) mission, a collaborative effort between NASA and ISRO, is on track for its scheduled launch in the first quarter of 2024.
About the NISAR Mission
- Collaboration: NISAR is a Low Earth Orbit observatory developed jointly by NASA and ISRO, highlighting international collaboration in space exploration.
- Launch Vehicle: The mission is set to launch from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota onboard ISRO’s GSLV Mark-II launch vehicle.
- Data Utility: NISAR data will offer unprecedented detail and assist researchers in various ways, including monitoring volcanic activity, tracking groundwater use effects, measuring ice sheet melt rates, and observing changes in global vegetation distribution.
- Mission Duration: The $1.5-billion NISAR mission has a planned mission life of three years and will survey Earth’s land and ice-covered surfaces every 12 days following a 90-day commissioning period.
Advanced SAR Technology
- Dual-Band SAR: NISAR carries L and S dual-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) using the Sweep SAR technique, providing both wide coverage and high-resolution data.
- Observatory Structure: The SAR payloads are mounted on the Integrated Radar Instrument Structure (IRIS) along with the spacecraft bus, forming an observatory.
- Contributions: NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) provides the L-band SAR and several key components, while ISRO’s U R Rao Satellite Centre contributes the spacecraft bus, S-band SAR electronics, launch vehicle, and mission operations.
Key milestones achieved
- Thermal Vacuum Testing: The thermal vacuum testing, a critical system-level test, was successfully completed in Bengaluru. This test ensures that the spacecraft can operate effectively under extreme temperature conditions.
- EMI and EMC Testing: Electromagnetic interference (EMI) and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing have also been successfully accomplished.
- Upcoming Vibration Tests: The next phase involves conducting vibration tests to simulate the harsh launch environment. This test will subject the satellite to intense vibrations while mimicking the conditions of a rocket launch.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
What is Stable Auroral Arc?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Stable Aurora Arc
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- Recently, the Indian Astronomical Observatory (IAO) in Ladakh has astounded the world with mesmerizing images of a rare red-colored aurora, known as a Stable Auroral Arc (SAR).
What is Stable Auroral Arc (SAR)?
- Rare Phenomenon: SAR is a unique atmospheric occurrence witnessed during a potent G3-class geomagnetic storm.
- Unconventional Origins: Unlike typical auroras resulting from space borne charged particles colliding with the atmosphere, SAR arcs have a distinct genesis.
- Sign of Energy Flow: SAR arcs signify the transfer of heat energy into the upper atmosphere from Earth’s ring current system, a circular pathway carrying massive electrical currents encircling our planet.
- Geomagnetic Storm Influence: During the recent geomagnetic storm, the ring current was dynamically charged due to prolonged intense geomagnetic activity, leading to the manifestation of SAR arcs.
- Global Impact: This celestial event left its celestial mark across several regions worldwide.
How is it formed?
- Solar Wind Interaction: Aurora formation begins when the sun emits charged particles from its corona, creating solar wind. Upon colliding with Earth’s ionosphere, the mesmerizing aurora takes shape.
- Northern and Southern Counterparts: In the Northern Hemisphere, it’s recognized as the northern lights (aurora borealis), while in the Southern Hemisphere, it’s referred to as the southern lights (aurora australis).
- Magnetic Dance: The varying appearance of auroras in different hemispheres is attributed, in part, to the intricate interplay between the sun’s magnetic field and Earth’s magnetic field.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Gaganyaan: Flight Test Vehicle Abort Mission-1
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: TV-D1 Mission
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- ISRO detailed about Gaganyaan mission’s Test Vehicle-Demonstration 1 (TV-D1) Mission which is scheduled for tomorrow.
- TV-D1 will demonstrate the performance of the crew escape system.
Flight Test Vehicle Abort Mission
- Objective: The mission involves launching a rocket to an altitude of approximately 17 km, followed by a simulated abort signal, resulting in the separation of the crew module.
- Safety Test: The crew module will descend safely using a parachute, ultimately splashing down in the Bay of Bengal.
- Duration: This comprehensive test mission is scheduled to last 532 seconds, from liftoff at 8 am to the crew module’s splashdown, situated about 10 km from the Sriharikota coast.
- Empty Module: It’s important to note that the crew module will remain uncrewed during this test.
What will be tested?
- New Test Vehicle: This mission introduces the new Test Vehicle, aptly named Test Vehicle-Demonstration 1 (TV-D1), and designed specifically for testing systems and procedures.
- Crew Module Functionality: A basic version of the crew module, the capsule in which astronauts will eventually journey into space, will be tested for functions such as mid-flight emergency crew module separation and astronaut escape.
- Technical Terminology: ISRO’s technical definition of the mission is “In-flight Abort Demonstration of Crew Escape System (CES),” which simulates abort conditions during ascent corresponding to a Mach number of 1.2, a critical aspect of the Gaganyaan mission.
About the New Test Vehicle
- Cost-Effective Testing: The TV-D1 mission employs a low-cost Test Vehicle, optimized for system testing, instead of the more expensive GSLV Mk III rocket used in previous tests.
- Innovations: It uses existing liquid propulsion technology but includes innovations such as the throttleable and restartable L110 Vikas engine.
Key Feature: Crew Escape System
- Safety Precedence: The TV-D1 mission underscores ISRO’s unwavering commitment to astronaut safety, particularly in emergencies.
- Environmental Control Systems: ISRO is actively developing environmental control and life support systems for the crew module.
- Integrated Vehicle Health Management: The program includes an integrated system to monitor the vehicle’s health and initiate mission-abort procedures when necessary.
- Testing Milestones: Some of these systems were previously assessed in the Crew module Atmospheric Re-Entry Experiment (CARE) and the Pad Abort Test-PAT in 2018.
Stages of TV-D1 Mission
- Critical Phases: The mission involves key stages, including the separation of the Crew Escape System from the Test Vehicle and the subsequent separation of the crew module.
- Parachute Deployment: Parachutes will be deployed for a safe descent over approximately seven minutes.
- Navy’s Involvement: The Indian Navy will play a crucial role in recovering the crew module from the Bay of Bengal.
- Milestone Setting: The TV-D1 mission serves as a significant milestone, marking the integration of a near-complete system for flight testing.
Status of Preparations
- Unmanned Mission: An unmanned mission is scheduled for early next year, followed by abort missions, with the manned mission targeted for late 2024 or early 2025.
- Technical Readiness: The human-rated LVM 3 rocket has successfully undergone testing, and essential components such as solid rocket boosters and liquid propellant engines are ready.
- Training: Four astronauts from the Indian Air Force have undergone training in Russia and will receive further training to prepare for the final mission.
Conclusion
- ISRO’s relentless pursuit of space exploration reaches a pivotal juncture with the TV-D1 mission.
- As India inches closer to sending its astronauts into space, these planned tests and safety measures underscore ISRO’s commitment to ensuring a safe and successful Gaganyaan mission.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Indian-Built ARTIP Technology Revolutionizes Astronomy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ARTIP
Mains level: NA
Central Idea
- India’s Automated Radio Telescope Image Processing Pipeline (ARTIP) technology has been instrumental in facilitating remarkable discoveries from distant galaxies observed by South Africa’s MeerKAT Telescope.
- MeerKAT acts as a precursor to the Square Kilometre Array (SKA) Telescope, known for its outstanding sensitivity and sky survey capabilities.
- ARTIP’s cutting-edge image data processing is vital for harnessing MeerKAT’s potential for groundbreaking research.
What is ARTIP?
- Development by Thoughtworks: ARTIP was developed by global technology consultancy firm Thoughtworks at its India offices in Bengaluru and Pune.
- Automation of Data Processing: Since 2017, this collaboration has aimed to automate various critical processes, including data processing, flagging, calibration, and imaging.
How ARTIP operates?
- Configurability: ARTIP is highly configurable and customizable, designed to process MeerKAT-generated data. While initially configured for MeerKAT, its adaptability allows it to process data from uGMRT and VLA class telescopes.
- Pipeline Components: It consists of four individual sub-pipelines, including calibration, cube imaging, continuum imaging, and diagnostics, each serving different stages of the data processing workflow.
- Calibration (ARTIP-CAL): This component calibrates data against known astronomical sources and extracts the target source of interest.
- Cube Imaging (ARTIP-CUBE): The calibrated target is then used to generate sky images using this component.
- Continuum Imaging (ARTIP-CONT): This pipeline focuses on generating images from the calibrated data.
- Diagnostics (ARTIP-DIAGNOSTICS): Providing analysis insights into data processing and quality, it functions as a quality assurance pipeline.
Impactful Discoveries by ARTIP
- Hydroxyl Radical (OH) Detection: ARTIP has contributed to significant discoveries, including the detection of the hydroxyl radical (OH), an essential chemical species found throughout the atmosphere in a distant galaxy.
- Identification of Hydrogen Atoms: It has also played a crucial role in identifying massive hydrogen atoms (Rydberg atoms) in another distant galaxy.
- Scientific Recognition: The MALS data processing with ARTIP has received recognition in the international astronomical journal, Proceedings of Science, for its contributions to these discoveries.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Chandrayaan 3 success: India’s role in democratising space
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ISRO missions
Mains level: Rapid commercialization of Space and governance, India's role
What’s the news?
- Chandrayaan 3’s landing on August 23 is a significant development in India’s space exploration efforts. This event prompts reflection on recent developments in outer space activities and their implications for peaceful purposes.
Central idea
- The year 2023 has seen India make significant strides in the realm of outer space activities. From becoming a signatory to the US Artemis Accords, which focus on the responsible use of outer space, to deepening engagements with the United States through initiatives like the US-India Civil Space and Commercial Space Working Groups, India has emerged as a key player in the global space arena.
Evolution of Outer Space Governance
- Historical Initiatives: The journey of outer space governance began with the historic launch of Sputnik in 1957. This event spurred the adoption of UN General Assembly Resolutions 1721 A and B in 1961. These resolutions marked the early acknowledgment of the need for international collaboration in space exploration.
- Consolidation of Principles: Over the years, space-faring nations consistently upheld the principles enshrined in the Outer Space Treaty of 1967. These principles have gradually evolved into customary international laws. This evolution signifies the transformation of outer space into an inclusive and democratized domain.
- Widespread Participation: Presently, outer space is accessible to more than 80 countries, each deriving various advantages from space-based satellite services. This widespread participation reflects the successful international cooperation that has expanded access to space resources.
Outer Space as a Global Common
- The concept of a global common traditionally applies to areas beyond the sovereignty of any single nation, inspired by ideas like Grotius’s Mare Liberum (free sea).
- In the United Nations framework, outer space is recognized as one of the global commons alongside the high seas, the atmosphere, and Antarctica.
Two Perspectives on Global Commons
- Enabling Perspective:
- From a geopolitical and military standpoint, considering outer space as a global common facilitates international cooperation and security.
- Nations worldwide recognize that areas beyond their jurisdiction, such as outer space, are vital for maintaining international order and regional security.
- Rejecting the idea of outer space as a global common could undermine the freedom of navigation, a fundamental principle upheld by initiatives like the QUAD.
- Constraining Perspective:
- Alternatively, viewing outer space as a global common can limit the economic and commercial exploitation of its resources.
- It implies shared ownership, public governance, and restrictions on usage, aligning with the concept of the common heritage of mankind concept as expressed in the Moon Agreement of 1979.
- This concept extends beyond outer space, applying to the high seas and deep-sea beds, emphasizing the need for responsible resource management.
Challenges and Complexity in Outer Space Governance
- Commercial Planetary Resource Extraction: Private companies and nations are exploring the potential for mining resources from celestial bodies such as the moon and asteroids. This raises complex questions about property rights, resource allocation, and environmental concerns in outer space.
- Resource Management: As commercial interests grow, the management of outer space resources becomes increasingly intricate. Determining how to allocate resources fairly and sustainably while avoiding overuse or exploitation poses a significant challenge. Balancing the interests of different nations and entities in resource-rich areas like the Moon adds to the complexity.
- Environmental Concerns: Space debris and orbital congestion pose environmental risks to space activities. With an increasing number of satellites and space missions, managing space debris and ensuring the long-term sustainability of space activities have become pressing challenges.
- Security and Militarization: The militarization of outer space and concerns about security in space have grown. Nations are developing space-based capabilities for defense and surveillance, raising questions about the potential weaponization of space and the need for arms control measures.
- International Collaboration: Ensuring effective international collaboration in space governance can be challenging due to differing national interests, technological disparities, and political tensions.
- Technological Advancements: Rapid technological advancements in space exploration, including the development of reusable rockets and miniaturized satellites, change the landscape of space activities. Keeping regulatory frameworks up-to-date with these advancements is a constant challenge.
India’s Crucial Role in Space Resource Management
- Involvement in International Agreements: India is both a signatory to the Moon Agreement of 1979 and the Artemis Accords. This dual commitment places India in a unique position to influence and contribute to the development of international frameworks for space governance.
- Complex Decision-Making: The complexity arises from the fact that while India has signed the Artemis Accords, it has not yet ratified the Moon Agreement. This highlights India’s need to carefully evaluate its stance on these agreements and the implications for its future space activities and resource management.
- Global Impact: India’s decisions and actions in the realm of space resource management have global implications. As one of the major space-faring nations, India’s approach will significantly influence the international framework for managing space resources, including lunar and celestial bodies.
- International Cooperation: India’s robust international cooperation in space programs, including multilateral and bilateral engagements, positions it as a key collaborator with advanced space powers and emerging space nations.
- Balancing Competing Objectives: India’s role is vital in striking a balance between competing objectives in the use of outer space for peaceful purposes. This involves ensuring responsible resource utilization, promoting equitable access, and upholding international law and principles.
Conclusion
- India’s growing prominence in the field of outer space activities requires a thoughtful approach to its role in shaping the future of space resource management. Balancing competing objectives, promoting peaceful use of outer space, and contributing to the development of an international framework are essential steps to ensure the responsible and equitable exploration and utilization of space resources for the benefit of all humankind.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Chandrayaan-3 Update: Pragyan put to Sleep Mode
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Chandrayan-3
Mains level: Not Much
Central Idea
- Chandrayaan-3 accomplished India’s historic achievement of soft landing on the Lunar South Pole.
- Its mission success marked by several noteworthy observations since touchdown on August 23.
Chandrayaan-3’s: Key Achievements
- Pragyan rover’s Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) instrument identified elements like aluminium, sulphur, calcium, iron, and more.
- Vikram lander recorded a ‘moonquake’ and detected an ultra-thin layer of plasma in the lunar atmosphere.
- These findings hint at distinct characteristics of the moon’s atmosphere compared to Earth.
Significance of Observations
- Sulphur discovery carries paramount importance in comprehending the moon’s origin and past surface (explosiveness) conditions.
- The presence of significant sulphur amounts can provide insights into lunar volcanic activity, potentially indicating the presence of subterranean water.
- Sulphur’s presence could offer clues about past lunar life support and constructing structures for human habitation.
Exploring Lunar Water
- Chandrayaan-3’s findings, particularly sulphur and oxygen on the moon’s surface, play a crucial role in narrowing down possible water sources.
- The presence of sulphur and oxygen enhances the prospects of water detection.
- ISRO was actively pursuing information about lunar hydrogen, another potential indicator of water.
Other mission Lunar Discoveries
- China’s Chang’e 5 mission unveiled a new lunar mineral, Changesite-(Y), and identified water in glass beads.
- Chandrayaan-3’s sulphur detection aligns with the quest for similar glass beads.
- NASA previously confirmed lunar water presence in shadowed craters and sunlit regions.
Present status of Ch-3 Mission
- Chandrayaan-3’s core objectives attained; Pragyan rover placed in ‘sleep’ mode.
- The rover’s solar panels will recharge during the next lunar sunrise.
- Plans to reactivate the rover for further observations remain underway.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Unveiling the Sun’s Secrets: ISRO’s Aditya-L1 Mission
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Adiitya L1 Mission
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- India’s maiden solar observatory mission, Aditya-L1, was successfully launched by ISRO on September 2.
- Carried by the PSLV in its 59th flight, the spacecraft’s mission aims to study the sun’s behaviour and phenomena.
- Aditya-L1 will spend 16 days orbiting Earth, undergoing five manoeuvres for required velocity.
- Subsequent Trans-Lagrangian insertion will begin a 110-day journey towards L1 Lagrange point.
- Aditya-L1 will orbit around L1, a balanced position between Earth and the sun, 1.5 million km away from Earth.
Aditya-L1 Mission

- ISRO introduces the Aditya-L1 mission, a novel space-based observatory designated for studying the Sun.
- The spacecraft will be positioned in a halo orbit around the Lagrange point 1 (L1) in the Sun-Earth system, approximately 1.5 million km from Earth.
- The L1 point’s strategic location enables continuous solar observation devoid of eclipses, furnishing invaluable insights into solar activities and their real-time effects on space weather.
- Once Aditya exits Earth’s sphere of influence, it will head towards the Lagrange point L1, a distance of 1.5 million km.
Significance of Lagrange Point 1
- Lagrange points are equilibrium positions where gravitational forces counteract centripetal forces, offering a stable environment for satellites.
- The spacecraft will be positioned around L1, affording an unobstructed view of the Sun for unhindered observation.
- Different Lagrange points offer unique advantages, such as L1’s consistent view of the Sun, as demonstrated by the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory Satellite (SOHO).
Aditya-L1’s Scientific Endeavors
- Aditya-L1 carries seven payloads to investigate the photosphere, chromosphere, and corona using a range of detectors.
- The payloads encompass instruments like Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC), Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT), Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEXS), and more.
- Payloads examining solar dynamics in the interplanetary medium contribute to a better understanding of phenomena like coronal heating, mass ejections, and space weather.
Significance of Solar Study
- Solar Influence on the System: The Sun significantly shapes planetary evolution and weather, extending its impact to satellites, electronics, power systems, and even Earth’s climate.
- Predicting Solar Storms: Continuous solar observations are essential for tracking Earth-bound solar storms and predicting their potential impacts.
- Gateway through L1: All solar storms heading towards Earth pass through L1, making it a crucial point for monitoring.
Key Feature: Mighty LAM Engine
- The Liquid Apogee Motor (LAM) engine, developed by ISRO’s Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC), is vital to the Aditya-L1 mission’s success.
- LAM has played pivotal roles in missions like Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan) and Chandrayaan-3.
- LAM engines facilitate satellite and spacecraft orbital adjustments, conserving fuel and ensuring optimal positioning.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Nabhmitra: Satellite-Based Safety Device for Fishermen
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Nabhmitra
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- The ISRO Space Applications Centre (Ahmedabad) has developed ‘Nabhmitra,’ a groundbreaking device designed to enhance the safety of fishermen during their maritime activities.
About Nabhmitra
- Nabhmitra employs satellite-based communication for seamless messaging services while at sea.
- Weather alerts, cyclone warnings, and other critical information will be conveyed in the local language.
- Fishermen can send distress messages during emergencies, such as capsizing or fires.
- The device features an emergency button that enables direct communication with the control center.
- Upon pressing the emergency button, the control center receives the alert along with the boat’s location. Simultaneously, the boat’s crew receives a response message from the control center.
Benefits of Nabhmitra
- Nabhmitra enhances the safety of fishermen by providing swift communication during emergencies.
- Fishermen receive timely weather and cyclone alerts, aiding them in making informed decisions.
- The device provides information about shipping channels, maritime boundaries, and fishing fields.
- In the event of accidents or crises, the device streamlines communication between boats and authorities.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Chandrayaan-3 landing site called ‘Shiv Shakti’

Central Idea
- PM’s recent announcement of naming the Chandrayaan-3 lunar lander’s touch-down site as “Shiv Shakti” highlights the tradition of assigning names to significant points on celestial bodies.
- The lunar landscape is peppered with such nomenclature, each reflecting a rich history of exploration and achievement.
Lunar Ownership and the Outer Space Treaty
- Global Exploration: The Moon, as a celestial body, remains beyond the jurisdiction of any single country. The Outer Space Treaty of 1966 declares that outer space, including celestial bodies like the Moon, cannot be claimed under national sovereignty.
- Cooperation over Competition: The Treaty fosters international cooperation in space exploration while discouraging exclusive claims. It was developed during the Cold War to promote shared achievements and limit conflicts arising from superpower rivalry.
Role of the International Astronomical Union (IAU)
- Global Naming Authority: The IAU, with 92 member countries, plays a pivotal role in naming planetary features, including the Moon’s surface points.
- Established Conventions: The IAU has overseen planetary and satellite nomenclature since its founding in 1919, aiming to standardize naming practices for better astronomical understanding.
Nomenclature Process for Lunar Landmarks
- Initiation: Initial naming suggestions for planetary features arise from IAU task group members or investigators involved in mapping or describing specific surfaces.
- Review and Approval: Proposed names undergo review by task groups and the Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN). Successful names become official IAU nomenclature and are entered into the Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature.
- Considerations and Limitations: IAU’s guidelines emphasize simple and unambiguous names, avoiding political, military, or religious significance. Honouring individuals is acceptable after a three-year posthumous period.
Legacy of Lunar Naming
- Influential Factors: The quality of images from spacecraft has driven naming. Far-side craters were often named after scientists and engineers. Informal names given during missions eventually received official status.
- Variability and Symbolism: Not all notable figures are honored with prominent crater names. The selection can seem arbitrary, with scientific prominence not guaranteeing crater-endowed immortality.
- Cultural Inspirations: The IAU permits names from Greco-Roman mythology for Jupiter and Saturn’s satellites. Giants, monsters, and descendants of mythological figures have been added to the allowable source of names.
India’s earlier Lunar Naming
- Jawahar Sthal: India’s Chandrayaan-1 mission’s probe impact site was named “Jawahar Sthal” in honor of Jawaharlal Nehru, India’s first Prime Minister. His advocacy for scientific development and research in India inspired the gesture.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
After Chandrayaan-3, what has ISRO planned?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ISRO Missions
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- ISRO’s triumphant landing of the Chandrayaan-3 lander on the moon’s South Polar Region marks a significant achievement in space exploration.
- As India emerges as a key player in the field, the focus now shifts to its multifaceted activities, upcoming missions, and technological advancements.
Diverse ISRO Activities
- Multifaceted Endeavors: ISRO’s operations span research, satellite development, rocket production, satellite tracking infrastructure maintenance, and more, catering to diverse space-related needs.
- Key Focus Areas: Prominent areas of focus include the ‘Gaganyaan’ human spaceflight mission, Reusable Launch Vehicle Technology Demonstrator (RLV-TD), SCE-200 engine development, and the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV).
Glimpses of Upcoming Missions
- Aditya L1: Scheduled for September 2023, Aditya L1 is a scientific mission to study the sun in detail, providing critical insights into solar activities.
- NISAR Satellite: In January 2024, the joint ISRO-NASA NISAR satellite will study earth’s surface processes using advanced radar technology.
- Gaganyaan G1 and G2 Flights: 2024 witnesses test flights of human-rated rockets, a prelude to India’s ambitious Gaganyaan human spaceflight.
Beyond Launches: Technology Innovations
- Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV-TD): Resembling the NASA Space Shuttle, RLV-TD’s design enables air propulsion or gliding, capable of lifting 20,000 kg to low-earth orbit.
- Advanced Propulsion: ISRO explores advanced rocket fuels like methalox propellant and electric propulsion systems, enhancing efficiency and safety.
Moon Missions and Lunar Exploration
- Chandrayaan-3 and Beyond: Chandrayaan-3 paves the way for further lunar exploration, with plans for missions like LUPEX (Lunar Polar Exploration) in collaboration with JAXA.
- LUPEX’s Ambitions: LUPEX aims to deploy a sophisticated lander and rover to study the moon’s South Polar Region, including subsurface sample extraction and night survival.
Expanding Collaborations and Global Partnerships
- Alternative Space Service Providers: ISRO fills gaps left by sanctions on Russia, launching OneWeb satellites and expectedly launching the European Space Agency’s PROBA-3 satellites.
- Lunar Exploration with JAXA: Collaborating with JAXA for LUPEX showcases ISRO’s commitment to global partnerships in space exploration.
Mars and Venus Missions
- Mars Return Mission: ISRO plans a return to Mars, building on its previous successful Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan).
- Venus Exploration: ‘Shukrayaan’: Ambitious plans to study Venus through the ‘Shukrayaan’ mission demonstrate ISRO’s expanding horizons in planetary exploration.
Conclusion
- ISRO’s remarkable accomplishments and future undertakings illuminate its stature as a global space powerhouse.
- From lunar landings to solar studies, human spaceflight to interplanetary missions, ISRO continues to shape the landscape of space exploration.
- By pushing boundaries, fostering innovation, and fostering international cooperation, ISRO cements its role in humanity’s journey to unravel the mysteries of the cosmos.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Unraveling the Lunar Landscape: Near, Far, and Dark Sides
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Near, Far, and Dark Sides, KREEP
Mains level: Lunar study by Chandrayaan 3

Central Idea
- The Chandrayaan-3 mission’s recent lunar landing has sparked curiosity about the moon’s various sides – near, far, and even the intriguing ‘dark’ side.
- Delving into these distinctions sheds light on the moon’s enigmatic nature and how space exploration helps us unravel its mysteries.
Facts for PrelimsImpact/Landing point names on Moon: 1. Chandrayaan 1: Jawahar Point 2. Chandrayaan 2: Tiranga Point 3. Chandrayaan 3: Shivshakti Point |
Moon’s Visible and Hidden Faces
- Near and Far Sides: The moon’s ‘near side,’ visible from Earth, covers around 60% of its surface. In contrast, the ‘far side’ remained hidden from us until modern spacecraft brought it into view.
- Clarifying the ‘Dark’ Side: Often misconstrued as constantly dark, the ‘dark side’ simply refers to the unseen side. It gets illuminated during the ‘new moon’ phase, challenging the misconception of its perpetual darkness.
Why is their composition different?
- The composition of the Moon’s near and far sides is different, and scientists believe they have identified the reasons behind this discrepancy.
- A study published in the journal Nature Geoscience reveals that the presence of KREEP, a rock enriched in potassium (K), rare-earth elements (REE), and phosphorus (P), plays a crucial role.
Key Points from the Study:
- Moons Near and Far Sides: The Moon’s near side, always facing Earth, has visible dark and light patches known as “maria.” Telescopic observations showed that these were not seas as early astronomers thought, but rather craters or volcanic features. The far side of the Moon has fewer maria than the near side.
- Moon’s Formation: The uneven distribution of volcanism and the KREEP signature between the near and far sides of the Moon puzzled scientists.
- Radioactive Unstable Elements: Potassium (K), thorium (Th), and uranium (U) are unstable, radioactive elements that have various isotopes with different numbers of neutrons. The radioactive decay of these elements generates heat that can melt rocks and contribute to volcanic activity.
- Heat and Melting: The study found that the inclusion of KREEP in rocks not only enhances heating but also lowers their melting temperature. This combination increases volcanic activity beyond what is predicted by radiogenic decay models.
- Geological Record: The Moon’s surface preserves geological events from the early history of the Solar System due to the absence of erosion processes. Concentrations of radioactive elements like uranium (U) and thorium (Th) on the near side provide insights into the Moon’s formation and early Earth conditions.
Phases and Illumination
- New Moon Phase: The ‘new moon’ phase unveils the moon’s ‘far side,’ exposing it to sunlight for about two weeks.
- Historic Revelation: In 1968, astronauts aboard Apollo 8 became the first humans to observe the ‘far side,’ demystifying its hidden features.
Chandrayaan-3’s Approach
- Closest South Pole Landing: Chandrayaan-3’s landing at coordinates 69.36 S and 32.34 E marks the closest approach to the lunar South Pole.
- Exploring Permanently Shadowed Regions: The strategic landing aimed to study regions that never receive sunlight, potentially containing frozen water ice and other lunar resources.
- Sunlight Necessity: Vikram’s nearness to the South Pole ensures sunlight for solar battery recharging, crucial for its operation.
- Choice of Landing Site: The decision to land on the ‘near side’ was driven by mission objectives, including real-time communication with Earth. Landing on the ‘far side’ would have required relay satellites and introduced delays.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
K Kasturirangan explains: Chandrayaan-3 and India’s Evolving Space Ambitions
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Chandrayaan-3 Mission
Mains level: Chandrayaan 3 Success and its Implications
Central Idea
- The successful Chandrayaan-3 mission not only marks a significant achievement for India’s space program but also signifies the nation’s attainment of a pivotal capability: direct physical access to another celestial body.
- This accomplishment propels India into an elite group of spacefaring nations and affords participation in shaping future planetary exploration endeavors and resource extraction from space.
Who is Dr. K. Kasturirangan?
|
India’s Integration into Planetary Exploration and Decision-Making
- Access to Celestial Bodies: Chandrayaan-3 provides India with a tangible gateway to planetary bodies, elevating its status in space exploration.
- Frontiers of Technology: India’s pioneering capabilities place it at the forefront of space technology, enabling participation in shaping future planetary explorations and resource extraction policies.
- A Seat at the Table: India’s involvement in this realm positions it naturally within the club of nations that influence and formulate space-related policies, ending a history of exclusion.
Now, India’s stature in Global Space Dynamics
- Historical Context: India’s past exclusion from technological clubs has driven its pursuit of self-reliance and global influence, transforming from a dependent to a self-sufficient nation.
- Space Diplomacy: Space capabilities will play a pivotal role in shaping global equations in the 21st century, and India’s active participation will bolster its international standing.
- Equitable Contributions: Chandrayaan-3 bolsters India’s potential to play a decisive role in space-related international decision-making, strengthening its voice on equal terms.
Chandrayaan-3’s Significance for ISRO
- Planetary Exploration Strategy: Chandrayaan-3 showcases ISRO’s comprehensive planetary exploration capabilities, encompassing satellite deployment, lunar orbits, surface study, and landing.
- Direct Lunar Access: The mission grants India direct physical access to the Moon, offering new avenues for lunar exploration and resource utilization.
- Kasturirangan’s Vision: The vision of Dr. K. Kasturirangan, former ISRO chairman, harmonizes with Sarabhai’s principles, building upon a foundation of technological self-sufficiency.
- Progressive Continuation: ISRO’s pursuits of planetary exploration and Chandrayaan missions align with the trajectory Kasturirangan initiated, enhancing the nation’s profile on the global stage.
Completing the Transformation: From Development to Exploration
- Sequential Alignment: ISRO’s evolution from developmental needs to commercial launches and now to scientific and planetary exploration reflects its responsiveness to India’s evolving requirements.
- Government Support: ISRO’s consistent success has been underpinned by unwavering government backing, which has enabled the organization to expand its horizons.
- Strategic Role: Space technology’s growing influence necessitates robust capabilities, and ISRO’s achievements foster meaningful international partnerships, enhancing India’s global prestige.
Conclusion
- Chandrayaan-3 is more than a singular event; it signifies India’s ascendancy as a formidable force in space exploration.
- As the nation transitions from a developing to a developed status, its capabilities to explore, innovate, and collaborate extend far beyond Earth’s boundaries.
- Chandrayaan-3’s impact extends beyond the Moon’s surface, fostering diplomatic connections, winning allies, and amplifying India’s influence on the global stage under the visionary guidance of Dr. K. Kasturirangan.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Chandrayaan-3’s Success: Future Objectives
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Chandrayaan-3 Mission
Mains level: Read the attached story
Central Idea
- As Chandrayaan-3 succeeded on its lunar soft landing, its six-wheeled rover begins a journey to unravel the mysteries of the Moon.
- With its payloads and instruments, the mission aims to build on the knowledge gained from its predecessors, investigating lunar quakes, mineral compositions, and water-ice presence.
Chandrayaan-3 Mission: Journey post soft landing
- Rover’s Arrival: The 26-kg rover, launched from the Chandrayaan-3 lander, is poised to cover up to 500 meters, commencing its lunar exploration.
- Duration: The lander and rover, equipped with six payloads, are primed to collect valuable data during the single lunar day (equivalent to 14 Earth days) of operation.
- Studying Lunar Quakes: The Chandrayaan-3 mission seeks to deepen insights into lunar quakes, expanding on the knowledge gained from its predecessors.
- Mineral Composition: The rover’s endeavors include examining the mineral compositions of the Moon’s surface, shedding light on its geological history.
- Electrons and Ions Study: The Radio Anatomy of Moon Bound Hypersensitive ionosphere and Atmosphere (RAMBHA) payload aims to study the behavior of electrons and ions near the lunar surface over time.
- Thermal Properties: Chandra’s Surface Thermo physical Experiment (ChaSTE) will explore the thermal characteristics of the Moon’s Polar Regions.
- Lunar Seismic Activity: The Instrument for Lunar Seismic Activity (ILSA) endeavors to measure lunar quakes and study the Moon’s crust and mantle composition.
- Laser Retroreflector Array: A passive experiment by NASA, the LASER Retroreflector Array (LRA), will serve as a target for precise laser measurements in future missions.
- Chemical Insights: The LASER Induced Breakdown Spectroscope (LIBS) aboard the rover is designed to identify the chemical and mineral composition of the lunar surface.
- Elemental Analysis: The Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) aims to analyze elements such as magnesium, aluminium, silicon, potassium, calcium, titanium, and iron in lunar soil and rocks.
- Mineral Mapping: The CLASS X-ray Fluorescence experiment, covering nearly 95% of the lunar surface, offers detailed mineral mapping. Oxygen-rich minerals hold potential for future missions as fuel resources.
Earlier Chandrayaan: Pioneering discoveries
- Water Unveiled: Chandrayaan-1 played a pivotal role in uncovering the presence of water and hydroxyl molecules in the Moon’s atmosphere and surface, particularly in its southern polar regions.
- Subsurface Water-Ice: Payloads like mini-SAR and Moon Mineralogy Mapper (M3) detected subsurface water-ice deposits within craters near the lunar South Pole.
- Lava Tubes for Habitability: Terrain mapping on Chandrayaan-1 unveiled buried lava tubes that could provide protective habitats for humans, shielding against radiation and extreme lunar conditions.
- Magma Ocean Hypothesis: M3 payload data suggested the possibility of a past magma ocean on the Moon, pointing to its formation and evolution.
- Active Moon: Contrary to previous notions of lunar inactivity, Chandrayaan-1 revealed dynamic lunar processes, including volcanic activity evidenced by lava channels and vents less than 100 million years old.
- Surface-Exosphere Interaction: Measurements indicated that the lunar surface interacts with the exosphere, evident in the emission of carbon dioxide and other gases.
- Solar Mysteries: The Solar X-Ray Monitor on Chandrayaan-2’s orbiter observed solar microflares outside active regions, providing insights into coronal heating mysteries.
Conclusion
- Chandrayaan-3’s scientific journey exemplifies India’s dedication to unraveling the Moon’s mysterious nature.
- As data pours in from its payloads and instruments, the mission builds upon its predecessors, propelling our understanding of lunar geology, composition, and mysteries.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO gears up for Aditya-L1 Mission
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Aditya L1 mission
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- Although the mission launch date is yet to be announced, the Aditya-L1 satellite has arrived at the Satish Dhawan Space Center (SDSC) in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh, for integration with the launch vehicle, PSLV.
Aditya-L1 Mission
- Aditya-L1’s primary objective is to closely observe the Sun and gather insights into its corona, solar emissions, flares, solar winds, and Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs).
- The satellite is equipped with seven advanced payloads for these scientific endeavors.
- The mission promises round-the-clock imaging of the Sun, enabling an unprecedented understanding of its behavior and impacts.
Significance of the mission
- Solar Influence: The evolution of every celestial body, including Earth and distant exoplanets, is intricately linked to its parent star. The Sun’s weather and environment have a profound impact on the entire solar system.
- Space Weather Impact: Variations in solar activity can disrupt satellite orbits, damage electronics, trigger power blackouts, and induce disturbances on Earth. Accurate knowledge of solar events is essential for comprehending and predicting space weather phenomena.
L1 Lagrange Point Advantage
- Continuous Solar Observations: Positioned at the Lagrangian Point 1 (L1) — about 1.5 million km from Earth — Aditya-L1 will be uniquely positioned to observe the Sun without the interference of occultation or eclipses. L1 is an orbital location where gravitational forces create stable regions of attraction and repulsion.
- L1’s Significance: The Solar and Heliospheric Observatory Satellite (SOHO) is stationed at L1 and has facilitated groundbreaking solar research. Aditya-L1’s observations will contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of solar behavior.
Comparison with International Missions
- Closer than Ever: While NASA’s Parker Solar Probe has ventured closer to the Sun, Aditya-L1 will focus on direct solar observations from a greater distance.
- Technical Challenges: Many instruments and components for Aditya-L1 are being developed in India for the first time, representing both a challenge and an opportunity for the nation’s scientific and engineering communities.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO Rocket Debris on Australian Shore
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Liability Convention
Mains level: Space Debris Issue

Central Idea
- A couple of weeks ago, a large object discovered on the shores of Western Australia has been confirmed to be the debris of an ISRO rocket used for IRNSS constellation.
- The incident raises concerns about space debris and its potential impact on Earth and its inhabitants.
Frequency and Risks of Space Junk
- Common Occurrences: Incidents of space debris falling back to Earth are not uncommon. Most instances involve relatively small fragments that survive atmospheric friction, typically not making significant news.
- Publicized Instances: However, there have been a few highly publicized falls, such as a 25-tonne Chinese rocket chunk falling into the Indian Ocean in May 2021 and the disintegration of the Skylab space station in 1979, with some fragments landing in Western Australia.
How did ISRO debris land in Australia?
- Probable Re-entry and Ocean Drift: The debris likely remained unburnt while dropping back into the atmosphere during re-entry and eventually fell into the ocean. Ocean currents may have carried it towards the Australian shores.
- Move for disposal: The Australian Space Agency is working with ISRO to determine the next steps, including considering obligations under the United Nations space treaties.
Potential Hazards and Impact
- Threat to Life and Property: The threat to life and property from falling space junk cannot be ignored. Even objects falling into oceans can pose risks to marine life and contribute to pollution.
- Recorded Incidents: So far, there are no recorded incidents of falling space objects causing significant damage on Earth. Instances of debris falling over land have generally occurred in uninhabited areas.
International Regulations and Liability
- Convention on International Liability for Damage Caused by Space Objects: International regulations, such as this Convention, govern issues related to space debris falling back to Earth.
- Absolute Liability: The launching country is “absolutely liable” to pay compensation for any damage caused by its space object on Earth or to a flight in the air.
- Compensation Provision: In the current case, if the PSLV debris had caused any damage in Australia, India could have been liable to pay compensation, regardless of it falling into the ocean first.
- Past Compensation: The Convention has resulted in compensation payment only once when Canada sought damages from the Soviet Union for a satellite with a radioactive substance falling into its uninhabited northern territory in 1978. The Soviet Union paid 3 million Canadian dollars as compensation.
Liability Convention, 1972
|
ISRO’s Efforts to Mitigate Space Debris
- Unique Scientific Experiment: ISRO successfully conducted a dedicated commercial mission, placing seven Singaporean satellites into intended orbits on board a PSLV rocket.
- Orbit-lowering Experiment: During this mission, ISRO performed a unique experiment, lowering the fourth stage of the rocket into a 300 km high orbit after placing customer satellites at an altitude of 536 km to mitigate space debris concerns.
- Reducing Debris Duration: Thanks to the orbit-lowering experiment, the duration of the stage in space has been significantly reduced to “two months.”
- Objectives of the Experiment: The experiment aims to address space debris mitigation problems and preserve valuable orbits for future satellite deployments.
Conclusion
- The incident of India’s space debris washing ashore in Australia highlights the importance of managing space debris to ensure the safety of Earth and its inhabitants.
- ISRO’s efforts to mitigate space debris through conscious measures demonstrate responsible space exploration practices.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Counting down: Launch of Chandrayaan-3 Mission
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Chandrayaan-3
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is set to launch the Chandrayaan 3 mission on July 14 from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota.
- This mission follows the Chandrayaan 2, which encountered technical issues and crash-landed on the moon in September 2019.
Chandrayaan-3: Mission Details and Landing
- Launch Vehicle: Chandrayaan 3 will be launched aboard the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III (GSLV Mk III) rocket.
- Landing Site: The spacecraft is expected to land near the moon’s South Pole.
- Operational Duration: Chandrayaan 3 will operate on the lunar surface for one lunar day, equivalent to 14 Earth days.
Significance of the Lunar South Pole
- Scientific Interest: The lunar South Pole is a compelling location due to the presence of towering massifs and permanently shadowed craters that may contain volatile compounds and water-ice deposits.
- Planetary Formation Insights: Studying the South Pole-Aitken Basin’s age and impact melt could provide insights into planetary formation.
- Valuable Resource: Volatile deposits at the South Pole could serve as a valuable resource for future exploration and astrobiology investigations.
- Solar Power Potential: Some mountain peaks near the pole receive extended periods of sunlight, making them potential sites for continuous solar power supply.
- Fossil Record: Craters at the South Pole may contain a fossil record of the early Solar System, providing valuable scientific data.
Choosing the South Pole over the North Pole
|
Trajectory and Landing Procedure
- Similar to Chandrayaan 2: Chandrayaan 3 will follow a trajectory similar to Chandrayaan 2, utilizing a propulsion module to orbit Earth before heading to the moon.
- Lunar Orbit and Landing: Once within the moon’s gravitational pull, the module will lower itself to a 100 x 100 km circular orbit. The lander will then detach and descend to the lunar surface.
Scientific Payloads
- The Lander: The lander, named ‘Vikram,’ will deploy four scientific payloads to study the moon’s surface temperature and subterranean characteristics.
- The Rover: The rover, named ‘Pragyan,’ will conduct chemical and visual tests as it roves around the lunar surface.
Objectives of Chandrayaan 3
- Safe Landing Demonstration: Chandrayaan 3 aims to demonstrate safe and soft landing on the lunar surface.
- Rover Roving Capability: The mission will showcase the capability of the rover to traverse the lunar surface.
- In-situ Scientific Experiments: Chandrayaan 3 will conduct in-situ scientific experiments on the moon.
Development and Delay
- Development Phase: The development phase for Chandrayaan 3 began in January 2020, with scientists and engineers working on the spacecraft’s design and assembly.
- Manufacturing Delays: The COVID-19 pandemic caused delays in the manufacturing and testing of the propulsion systems.
- Launch Schedule: The launch, initially planned for early 2021, was postponed due to the pandemic. The spacecraft is now set to launch in July 2023.
Importance of Chandrayaan 3
- India’s Third Lunar Mission: Chandrayaan 3 is India’s third lunar mission and the second attempt at a soft landing on the moon.
- Renewed Interest in Lunar Exploration: In recent years, there has been a renewed interest in exploring the moon following Chandrayaan-1’s discovery of water on the lunar surface.
Conclusion
- Chandrayaan 3 represents India’s continuous efforts to explore the moon and achieve a soft landing.
- The mission’s success will contribute to scientific advancements and further our understanding of the lunar surface.
- As space agencies around the world plan future lunar missions, humanity’s return to the moon seems imminent after more than five decades.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
LVM-3: the ISRO Rocket
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: LVM3
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- ISRO is scheduled to launch the Chandrayaan 3 mission on July 14.
- The mission will be carried out using the LVM-3 configuration.
- The GSLV is used for heavier payloads and higher orbits, with the most powerful configuration known as LVM-3.
| Soon a comprehensive article about Chandrayaan 3 would be released! |
LVM3: Unlocking New Frontiers of Space Exploration
- Expendable Space Launch Vehicle: LVM3 is an expendable space launch vehicle meticulously crafted by ISRO.
- Purpose: Its primary objective is to deploy satellites and space objects into Geosynchronous Transfer Orbits (GTO).
- Launch History: ISRO successfully launched the first LVM3 on April 18, 2001, and has accomplished a total of 13 launches to date.
- Impressive Specifications: With a lift-off mass of 420 tonnes, LVM3 demonstrates its robustness in handling complex missions.
Stages of LVM3: Powering the Journey to Orbit
First Stage:
- S139 Solid Booster: The initial stage of LVM3 features the S139 solid booster, armed with 138 tonnes of propellant.
- Liquid Strap-on Motors: Additionally, it incorporates four liquid strap-on motors, each carrying 40 tonnes of propellant.
Second Stage:
- Liquid Engine: The second stage of LVM3 is equipped with a liquid engine, propelling the vehicle with 40 tonnes of liquid propellant.
Third Stage:
- Cryogenic Upper Stage (CUS): LVM3 showcases its technological prowess with the indigenously built CUS, capable of accommodating 15 tonnes of cryogenic propellants.
Back2Basics: Sattelite Launch Vehicles

Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Sun’s Magnetic Field and its Influence on Interplanetary Space
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Solar Mean Magnetic Field (SMMF)
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- Scientists from the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) have conducted a study to better understand the relationship between the sun’s magnetic field and the interplanetary magnetic space.
- It is said to play a crucial role in space weather.
- The findings provide valuable insights into the Solar Mean Magnetic Field (SMMF) and its connection with the Interplanetary Magnetic Field (IMF).
Sun’s Magnetic Field and Its Generation
- The sun’s magnetic field is generated by electrical currents acting as a magnetic dynamo within the sun.
- The corona, photosphere, and chromosphere of the sun contain the magnetic field, with the chromosphere being a near-transparent layer just above the photosphere.
What is Solar Mean Magnetic Field (SMMF)?
- The SMMF represents the mean value of the line-of-sight component of the solar vector magnetic field averaged over the visible hemisphere of the sun.
- Understanding the SMMF’s effect on the IMF is crucial for better space weather forecasting and response.
Investigating the SMMF at Chromospheric Heights
- IIA scientists aimed to explore the relationship between the SMMF at chromospheric and photospheric heights.
- Their analysis revealed a strong similarity between the two, with the chromospheric SMMF being lower than the photospheric SMMF.
- This suggests that the primordial magnetic field inside the sun could be a source of the SMMF.
Data and Methodology
- The scientists utilized magnetic field measurements from the Synoptic Optical Long-term Investigations of the Sun (SOLIS)/Vector Spectromagnetograph (VSM) instrument from 2010 to 2017.
- They cross-verified the data with measurements from the Wilcox Solar Observatory.
Significance and Future Implications
- Understanding the source and driving parameters of the SMMF contributes to a better understanding of how it influences the IMF.
- This knowledge can aid in improved space weather prediction and response.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Nearing the launch of Chandrayaan-3 Mission
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Chandrayaan 3
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- India’s upcoming moon exploration mission, Chandrayaan-3, is set to launch in mid-July.
- In a significant decision, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) plans to retain the names of the lander and rover from the previous mission, Chandrayaan-2.
Chandrayaan-3 Mission
- Chandrayaan-3 is a follow-on mission to Chandrayaan-2 to demonstrate end-to-end capability in safe landing and roving on the lunar surface.
- It consists of Lander and Rover configuration. It will be launched by LVM3 from SDSC SHAR, Sriharikota.
- The propulsion module will carry the lander and rover configuration till 100 km lunar orbit.
- The propulsion module has Spectro-polarimetry of Habitable Planet Earth (SHAPE) payload to study the spectral and Polari metric measurements of Earth from the lunar orbit.
Retaining the Names: A Tribute to Chandrayaan-2
- ISRO Chairman confirmed that the names Vikram and Pragyan will be carried over to the Chandrayaan-3 mission.
- This decision pays homage to the 2019 Chandrayaan-2 lunar adventure while symbolizing India’s commitment to its space exploration legacy.
Overcoming Past Challenges: Learning from Chandrayaan-2:
- The Chandrayaan-2 mission faced setbacks when the lander-rover configuration, along with the payloads, was lost during a failed soft landing attempt.
- Undeterred by the previous mission’s outcome, ISRO announced its plans for Chandrayaan-3, aiming for a successful lunar landing.
Mission Details: Exploring the Moon’s Surface and Atmosphere
- Chandrayaan-3 will be launched aboard the LVM3 rocket from Sriharikota using a propulsion module.
- The lander-rover configuration will be transported to a 100-km lunar orbit by the propulsion module.
- The Vikram lander module will deploy Pragyan, which will conduct in-situ chemical analysis of the lunar surface.
[A] Scientific Payloads: Unravelling Lunar Mysteries
- Radio Anatomy of Moon Bound Hypersensitive Ionosphere and Atmosphere (RAMBHA): Studying the moon’s ionosphere and atmosphere.
- Chandra’s Surface Thermo physical Experiment (ChaSTE): Analyzing the thermal characteristics of the lunar surface.
- Instrument for Lunar Seismic Activity (ILSA): Investigating seismic activities on the moon.
- LASER Retroreflector Array (LRA): Enabling precise measurements of the lunar distance.
[B] Rover Payloads
- Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS): Analyzing the elemental composition of the lunar surface.
- LASER Induced Breakdown Spectroscope (LIBS): Studying the elemental abundance and characteristics of lunar rocks.
[C] Propulsion Module Payload:
- Spectro-polarimetry of HAbitable Planet Earth (SHAPE): Collecting data related to Earth’s habitability.
Conclusion
- India’s Chandrayaan-3 mission signifies the nation’s determination to explore the moon further and overcome past challenges.
- By retaining the names Vikram and Pragyan, ISRO honors its space program’s pioneers while embarking on a new lunar adventure.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
India discovers TOI 4603b Exoplanet
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Exoplanet TOI4603b
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- A new Jupiter-size exoplanet with the highest density known till this date has been discovered by an international team of scientists at the Exoplanet Research Group of the Physical Research Laboratory (PRL), Ahmedabad.
- Massive giant exoplanets are defined as those with a mass greater than four times that of Jupiter.
About the Exoplanet TOI4603b
- The exoplanet is found around the star called TOI4603 or HD 245134.
- It has a mass 13 times greater than that of Jupiter and a density of approximately 14 g/cm3.
- Initially, NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) declared TOI4603 as a possible candidate to host a secondary body of unknown nature.
- Using PARAS, scientists confirmed the secondary body as a planet, and it was named TOI 4603b or HD 245134b.
- The exoplanet is located 731 light years away and orbits a sub-giant F-type star TOI4603 every 7.24 days.
Note: An exoplanet, short for “extra-solar planet,” is a planet that orbits a star other than our Sun. These planets are located outside of our solar system and are not part of our planetary system.
Unprecedented Density and Proximity
- TOI 4603b is one of the most massive and densest giant planets discovered to date.
- It orbits very close to its host star at a distance less than 1/10th the distance between our Sun and Earth.
- Comparisons between the TOI-4603 star-planet system and the Sun-Mercury and Sun-Jupiter systems highlight the close proximity of TOI-4603 b to its star.
- The exoplanet is situated more than 50 times closer to its star than Jupiter is to the Sun.
- TOI-4603b is 13 times more massive than Jupiter.
Utilization of Indigenous Technology
- The discovery of this massive exoplanet was made using the indigenously made PRL Advanced Radial-velocity Abu-sky Search spectrograph (PARAS) at the 1.2 m telescope of PRL at its Gurushikhar Observatory in Mt. Abu.
- The mass of the planet was measured precisely using PARAS.
Uniqueness of the Discovery
- The planet falls into the transition mass range of massive giant planets and low-mass brown dwarfs, with masses ranging from 11 to 16 times the mass of Jupiter.
- Only fewer than five exoplanets are currently known in this mass range.
- The rarity of such discoveries makes this finding significant.
Insights into Formation and Evolution
- The exoplanet has a surface temperature of 1670 K and is likely undergoing high-eccentricity tidal migration with an eccentricity value of approximately 0.3.
- The detection of such systems provides valuable insights into the formation, migration, and evolution mechanisms of massive exoplanets.
India’s Contribution to Exoplanet Discoveries
- This marks the third exoplanet discovery by India and the PRL scientists using the PARAS spectrograph and the PRL 1.2m telescope.
- Previous discoveries include K2-236b in 2018 and TOI-1789b in 2021.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO successfully deploys NavIC NVS-1 Satellite
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NAVIC
Mains level: Indigenous GPS

Central Idea
- The Indian Space Research Organisation has successfully launched its fifth satellite of 2023.
- A 2,232-kilogram satellite named NVS-1 was launched into space as part of the NavIC
What is NAVIC?
- NavIC is a regional satellite navigation system consisting of seven satellites in orbit that provide positioning, navigation, and timing services to various sectors, including civil aviation and the military.
(1) Origins and Motivation:
- The idea of NAVIC emerged in the early 2000s as IRNSS (Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System) to address India’s need for an independent navigation system for strategic and civilian purposes.
- The motivation behind NAVIC was to reduce dependence on foreign systems like GPS and enhance national security, sovereignty, and economic growth.
(2) Satellite Deployment:
- The NAVIC constellation consists of a total of 7* satellites.
- The first satellite, IRNSS-1A, was launched in July 2013, followed by subsequent launches of IRNSS-1B, 1C, 1D, 1E, 1F, and IRNSS-1I.
- Each satellite is placed in a geostationary orbit or an inclined geosynchronous orbit, providing continuous coverage over the Indian landmass and surrounding regions.
(3) Renaming to NAVIC:
- In 2016, the system was officially named NAVIC, which stands for Navigation with Indian Constellation.
- The name change aimed to create a distinct brand identity for the Indian regional navigation system.
Key Features and Technical Details
(1) Coverage Area:
- NAVIC provides coverage within India and extends up to 1,500 kilometres beyond its borders.
- The system covers the Indian landmass, as well as the Indian Ocean region.
(2) Satellite Configuration:
- The NAVIC satellites are equipped with atomic clocks to provide accurate timing signals.
- They transmit signals on different frequencies, including L5 and S bands, for enhanced accuracy and reliability.
(3) Applications and Services:
- NAVIC has a wide range of applications, including terrestrial, aerial, and marine navigation.
- It is utilized in various sectors such as transportation, agriculture, disaster management, surveying, and geodetic applications.
- The system supports position determination, velocity measurement, and time synchronization services.
About NVS-1 Satellite
- NVS-1 is part of the second-generation NavIC satellite series and ensures continuity of existing services while introducing new services in the Li band.
- The satellite features two solar arrays generating up to 2.4 kW of power, a lithium-ion battery for eclipse support, and thermal management and propulsion systems.
- Notably, NVS-1 includes a Rubidium atomic clock developed in-house by the Space Applications Centre, showcasing India’s technical expertise in this advanced technology.
India’s launch capabilities and recent missions
- The NVS-1 launch marks the second successful mission in a month and the fifth launch of the year for ISRO.
- In April, ISRO completed the PSLV-C55 mission, deploying two satellites, including TeLEOS-2 with a synthetic aperture radar payload.
- The PSLV-C55 mission highlighted collaboration between India and Singapore in space exploration and technology.
*Note: The numbers of satellites in this constellation is disputed. It is given as 7 and 8 on different sources. Total Nine satellites were launched out of which the very first (IRNSS-1A) is partially failed because of some issue in its Atomic Clock. Another and the last satellite had a launch failure. Hence the number 7/8.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
XPoSat: India’s first Polarimetry Mission
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: XPOSAT, Polarimetry
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is partnering with the Raman Research Institute (RRI) in Bengaluru to develop the X-Ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat), set to launch later this year.
What is XPoSat?
- XPoSat aims to study various dynamics of bright astronomical X-ray sources in extreme conditions.
- It is India’s first polarimetry mission and the world’s second, with NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) being the other major mission launched in 2021.
- IXPE carries three state-of-the-art space telescopes to observe polarized X-rays from neutron stars and supermassive black holes, providing insights into the geometry and inner workings of the light source.
XPoSat Payloads
- XPoSat will carry two scientific payloads in a low Earth orbit.
- The primary payload, POLIX, will measure the polarimetry parameters of X-rays, observing approximately 40 bright astronomical sources across different categories during the mission’s planned five-year lifetime.
- The XSPECT (X-ray Spectroscopy and Timing) payload will provide spectroscopic information on how light is absorbed and emitted by objects, allowing observations of X-ray pulsars, black hole binaries, low-magnetic field neutron stars, and more.
X-Rays in Space
- X-rays in space have higher energy and shorter wavelengths, ranging from 0.03 to 3 nanometers.
- X-rays are emitted by objects with temperatures in the millions of degrees Celsius, such as pulsars, galactic supernova remnants, and black holes.
- Polarized light, consisting of organized moving electric and magnetic waves, plays a role in X-ray observations, and polarized lenses are used by fishermen to reduce glare from sunlight.
Significance of Polarimetry
- Polarimetry involves measuring the angle of rotation of the plane of polarized light as it passes through certain transparent materials.
- XPoSat’s primary payload, POLIX (Polarimeter Instrument in X-rays), developed by RRI and UR Rao Satellite Centre, will measure the degree and angle of polarization in X-rays from astronomical sources.
- The emission mechanisms of various astronomical sources are complex, and understanding them poses challenges that polarimetry can help address.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Private: NAVIC (Navigation by Indian Constellation)
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Private: Space Science and Technology Awareness Training
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Indian Space Policy 2023: A Vision that Needs Legislative Support
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Indian Space Policy 2023 and its features, IN-SPACe and NSIL
Mains level: Indian Space Policy 2023, Policy gaps and steps to address these gaps
Central Idea
- India’s new space policy released in 2023 is a promising move towards a flourishing commercial presence in space. However, the policy needs to be accompanied by clear rules and regulations and suitable legislation to create a conducive environment for private sector participation in the Indian space industry.
The Indian Space Policy 2023
- The Indian Space Policy 2023 is a short 11-page document that includes a vision to enable, encourage and develop a flourishing commercial presence in space.
- It recognizes the private sector as a critical stakeholder in the entire value chain of the space economy.
- It makes five key points and outlines the roles of various entities, including the Department of Space, ISRO, Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe), and the NewSpace India Limited (NSIL).
- The policy lays out a strategy and spells out the roles of the entities mentioned above.
What is mean by The Second Space Age and its features?
- The Second Space Age refers to a period in the space industry following the early 1990s when private sector involvement in space technology began to increase.
- The Second Space Age is characterized by the following features:
- Increased private sector involvement: The Second Space Age has seen private sector companies take a more prominent role in the space industry. This shift has led to innovation and growth, with private companies investing in space tourism, satellite-based services, and other commercial applications of space technology.
- Commercial applications of space technology: The Second Space Age is marked by a shift towards commercial applications of space technology. Private sector companies are investing in satellite-based services such as broadband, OTT, and 5G, which promise a double-digit annual growth rate.
- Increased global competition: The Second Space Age has led to increased global competition in the space industry. Countries such as China, India, and private companies like SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic are competing for a share of the space industry’s market.
- Increased collaboration: The Second Space Age has seen increased collaboration between government agencies and private sector companies. This collaboration has led to the development of new technologies and innovative solutions to problems faced in space exploration.

Facts for prelims
IN-SPACe
New Space India Limited (NSIL)
|
Gaps in Indian Space Policy 2023
- Lack of legislative framework: The policy provides a broad framework for promoting private sector participation in the Indian space industry but lacks a legislative framework to support it. A regulatory body like IN-SPACe needs legislative authority to be effective.
- Lack of clear rules and regulations: The policy framework envisaged will need clear rules and regulations pertaining to FDI and licensing, government procurement to sustain the new space start-ups, liability in case of violations, and an appellate framework for dispute settlement.
- Ambiguity in IN-SPACe’s position: IN-SPACe currently functions under the purview of the Department of Space, and its position is ambiguous. The Secretary (Space) is also the Chairman of ISRO, the government entity to be regulated by IN-SPACe. This ambiguity could create conflicts of interest and undermine IN-SPACe’s effectiveness.
- Lack of timelines: The policy sets out an ambitious role for IN-SPACe but provides no timeline for the necessary steps ahead. There is no indicative timeline for ISRO’s transitioning out of its current practices, nor is there a schedule for IN-SPACe to create the regulatory framework.
Way ahead: Steps to implement the policy effectively
- Enactment of a new Space Activities Bill: The draft Space Activities Bill, which lapsed in 2019 with the outgoing Lok Sabha, needs to be reintroduced and enacted. The Bill will provide a comprehensive legislative framework to support the Indian Space Policy 2023 and regulate space activities carried out by government and non-government entities.
- Establishment of a clear regulatory framework: IN-SPACe needs to create a clear regulatory framework that sets out the rules and regulations for private sector participation in the Indian space industry. This will ensure a level playing field and promote the growth and development of the industry.
- Timely implementation of the policy: The Indian government needs to work closely with ISRO and other stakeholders to ensure the timely implementation of the policy. This will require setting clear timelines for the necessary steps ahead and ensuring their effective implementation.
- Promotion of private sector participation: The Indian government needs to promote private sector participation in the Indian space industry by providing incentives, facilitating technology transfer, and creating a conducive environment for innovation and growth.
- Collaboration with international partners: The Indian government needs to collaborate with international partners to share knowledge, expertise, and resources in the space domain. This will help in promoting innovation and growth in the Indian space industry and enhancing India’s global competitiveness.
Conclusion
- The Indian Space Policy 2023 is a promising move towards creating a conducive environment for private sector participation in India’s space industry. However, it needs legislative support to create a stable and predictable regulatory framework and ensure a level playing field for the private sector. A vision that needs legislative support to launch India into the Second Space Age.
Also read:
| The Indian Space Policy 2023 and The Role of Private Sector |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
The Indian Space Policy 2023 and The Role of Private Sector
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Private sector startups and recent developments
Mains level: Indian Space Policy 2023, Role of private sector, advantages and potential drawbacks
Central Idea
- The Indian Space Policy 2023 has been approved by the Indian Cabinet Committee on Security. The policy has opened up the Indian space sector, facilitating an enhanced role for the private sector to augment the development and competitiveness of the Indian space program.
All you need to know about Indian Space Policy 2023
- Clear roles and responsibilities: The Indian Space Policy 2023 policy clarifies the roles and responsibilities of the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), NewSpace India Limited (NSIL), and the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center (IN-SPACe), as well as that of the private players in the Indian space sector.
- Opportunities for private sector players: One of the key aspects of the new policy is to open up the Indian space sector to provide opportunities for private sector players to play an active role in augmenting the development and competitiveness of the Indian space program. This will allow ISRO to focus on non-commercial missions, such as research and development of advanced space technologies and space exploration.
- Enhance overall ISRO missions: The policy is expected to enhance overall ISRO missions with greater participation of non-government entities, including academia, the research community, startups, and industry.
- Institutional setups: Strategic activities within the space sector will be handled by NSIL, an institutional set up within the Department of Space that will address these activities in a demand-driven mode. The other recent institutional set up that will be critical in coordination between the public sector and the private players is IN-SPACe.
- Framework for use of ISRO facilities: The policy outlines a framework under which the private sector can use ISRO facilities for a small fee.
- Making Indian space programme competitive: The private players are also expected to create new infrastructure in the space sector. This will be critical in ensuring that the Indian space program becomes more competitive and developed.
- ISRO will focus on research and development: In a significant move, ISRO has stated that it will not do any operational and production work for the space sector and will instead focus its energies on developing new technologies, new systems, and research and development. This essentially means that the routine production and launches that the ISRO was involved in until now will be handled by the private sector completely.
What is mean by Open Space Policy?
- An Open Space Policy refers to a policy that allows for open and transparent participation in space activities.
- It involves the collaboration between public and private entities in the exploration and use of space.
- The goal of an open space policy is to promote innovation, competition, and the growth of the space industry while ensuring the safety and security of space activities.
- This policy allows for the development of new technologies, research and development, and increased cooperation and collaboration between different countries and organizations.

Facts for prelims: Private space sector startups in India
|
Company Name |
Area of Specialization |
Recent Developments |
| Skyroot Aerospace, Hyderabad | Launch Vehicles for Small Satellites | Successfully launched their first indigenously designed and developed launch vehicle, Vikram I. Vikram S (Mission Prarambh) rocket recently launched as first privately built Indian rocket to make it to space |
| Agnikul Cosmos, Chennai | Launch Vehicles for Small Satellites | Successfully tested their fully 3D printed rocket engine, the Agnilet, in January 2021. |
| Bellatrix Aerospace, Bangalore | Electric Propulsion Systems | Signed an agreement with Skyroot Aerospace for the use of electric propulsion technology in their launch vehicles. |
| Pixxel, Bangalore | Earth Observation Satellites | Launched their first satellite, Anand, in February 2021, and plans to launch a constellation of 30 satellites by 2023. |
| Kawa Space, Mumbai | Space-Related Technologies | Developed a ground station in collaboration with the Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay, to track and receive data from satellites. |
| Skylo, Bangalore | Low-Cost Satellite-Connected Devices for IoT | Raised $103 million in Series B funding round led by SoftBank Group Corp in August 2021. |
| SatSure, Bangalore | Data Analytics Services for Agriculture Industry | Launched their new product, SatSure Agri, in May 2021 to provide crop yield forecasting services to farmers. |
| Dhruva Space, Bangalore | Satellite-Based Communication Solutions | Signed a Memorandum of Understanding with Ananth Technologies in October 2021 to provide satellite-based communication services to the aviation industry. |
Benefits of having an open space policy
- Messaging tool: An open space policy can be used as a messaging tool, both for friends and potential foes. It can demonstrate India’s commitment to the peaceful use of outer space and build confidence among other nations.
- Moderating fears and concerns: An open space policy can help to moderate fears and concerns about India’s space activities, by providing greater clarity on India’s space objectives and priorities.
- Rebuilding confidence: An open space policy can help to rebuild confidence among other nations that India is committed to the peaceful use of outer space.
- Outlining objectives: An open space policy can provide a clear outline of India’s short-term and long-term space objectives and priorities.
- Better resource allocation: An open space policy can help to ensure better resource allocation for India’s space program, by providing a clear framework for decision-making and prioritization.
Potential drawbacks of open space policy
- Increased competition: An open space policy could lead to increased competition among countries and private entities to gain access to space and its resources. This could lead to a potential arms race in space and increased tensions between countries.
- Security concerns: Open access to space could also create security concerns, as countries may develop space weapons or use space to conduct surveillance on other countries.
- Environmental impact: An open space policy could also have environmental consequences, as increased space activity could lead to more space debris and pollution, potentially harming the Earth’s orbit and its environment.
- Lack of regulation: Without proper regulation, an open space policy could lead to the exploitation of space resources, such as minerals and water, which could negatively impact the environment and lead to unfair distribution of resources.
- Cost: Increased space activity and access could also lead to higher costs for countries and private entities, which may not be sustainable in the long run.
Conclusion
- The new policy is expected to bring about significant changes in the Indian space ecosystem, including greater private sector participation, better resource allocation, and institutional clarity. This is an important step towards an open space policy that integrates both commercial and national security requirements in a balanced fashion.
Mains Question
Q. The Indian Space Policy 2023 has been approved by the Indian Cabinet Committee on Security. Note down some of its key aspects. What do you understand by mean open space policy? Discuss its advantages and potential drawbacks.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO to launch TeLEOS-2 Satellite
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: TeLEOS-2 Satellite, PSLV
Mains level: NA

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) will launch Singapore’s TeLEOS-2 satellite this week, from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota.
What is TeLEOS-2?
- TeLEOS-2 is a Singaporean Earth Observation satellite built by ST Electronics (Satellite Systems).
- It carries a made-in-Singapore Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) capable of providing 1 m resolution data.
- It will be equipped with a 500 GB onboard recorder for recording the data captured and a high speed 800 Mbps downlink.
- In 2015, ISRO launched TeLEOS-1, the first Singapore commercial Earth Observation Satellite, which was launched into a low Earth orbit for remote sensing applications.
- ISRO has so far launched nine satellites belonging to Singapore.
About the launch vehicle: PSLV-CA
- The PSLV-CA was manufactured by ISRO with the first launch on 2007-04-23.
- CA means “Core Alone”, model premiered on 23 April 2007.
- PSLV-CA has 15 successful launches and 0 failed launches with a total of 15 launches.
- The CA model does not include the six strap-on boosters used by the PSLV standard variant.
- The fourth stage of the CA variant has 400 kg less propellant when compared to its standard version.
- It currently has the capability to launch 1,100 kg to a 622 km Sun-synchronous orbit.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
NISAR to map Himalayas’ Seismic Zones
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NISAR, Seismic Zones
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central idea
- The ISRO and the NASA have jointly developed a forthcoming satellite called NISAR.
- It will map the most earthquake-prone regions in the Himalaya.
What is NISAR?
- NISAR stands for NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar.
- The mission aims to provide global measurements of the causes and consequences of land surface changes using advanced radar imaging.
- The satellite is equipped with two types of synthetic aperture radars (SAR): L-band and S-band, which will allow for high-resolution, all-weather imaging of the Earth’s surface.
- The NISAR satellite is expected to be launched in January 2024.
How it will be used for earthquake monitoring?
- It will generate data that can potentially give advance warning of land subsidence and identify places that are at greatest risk from earthquakes.
- The geoscience community can use this to determine how strain is building up in various parts of the Himalayas.
- Strain refers to the deformation that occurs in rocks when it is under pressure from other rocks.
- Movements of continental plates that are sliding, colliding, or subducting against each other cause strain.
- With a frequency of 12 days and the ability to provide images even under cloudy conditions, NISAR would be a valuable tool to study deformation patterns, such as in Joshimath.
Strain Map already in place
- In 2021, scientists from the Geological Survey of India published a “strain map” of the Himalayas based on data from 1,252 GPS stations along the Himalayas.
- It identified regions that had the greatest odds of generating earthquakes of magnitude above 8 and their extent.
- However, these many stations are still too few, and there’s only one satellite (Sentinel) that we rely on.
- With NISAR, the costliest space mission ever, we can have a game-changer in earth-science observation.
Seismic Zones of India
India is divided by Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) into 4 seismic zones based on the level of seismicity and the frequency of earthquakes that occur in that particular region. These zones are as follows: 1. Zone 2: This is a low seismic zone comprising of areas with the lowest risk of earthquakes. It includes regions like the northeastern states of India, parts of J&K, Himachal Pradesh, and Uttarakhand. 2. Zone 3: This is a moderate seismic zone comprising of areas that are at moderate risk of earthquakes. It includes regions like Gujarat, Haryana, Delhi, parts of UP, Bihar, West Bengal, and parts of Jharkhand. 3. Zone 4: This is a high seismic zone comprising of areas that are at high risk of earthquakes. It includes regions like the A&N Islands, parts of Himachal Pradesh, J&K, Uttarakhand, and the entire northeastern region. 4. Zone 5: This is a very high seismic zone comprising of areas that are at the highest risk of earthquakes. It includes regions like the entire state of J&K, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, the entire northeastern region, parts of Gujarat, Rajasthan, Maharashtra, and the A&N Islands. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
India’s Space Industry: Enormous Potential
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Private Space companies in news
Mains level: India's space sector and role pf private companies and startups
Central Idea
- India needs an enabling policy and regulatory environment to tap into the potential of the Second Space Age and its rapidly growing space economy.
What is mean by the Second Space Age?
- Commercialization: The Second Space Age refers to the recent era of increased commercialization and private sector involvement in space exploration, which began in the early 2000s.
- Emergence of private space companies: This period has been marked by the emergence of private space companies like SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic, who are investing heavily in space technology and infrastructure.
- Today’s space domain has many more actors once dominated by US and USSR: Compared to the First Space Age dominated by the US and the USSR, today’s space domain has many more actors, with a majority being private companies. Private companies account for 90% of global space launches since 2020, and India is no exception
- Increasing involvement of non-spacefaring nations: The Second Space Age is also characterized by the increasing involvement of non-spacefaring nations in space exploration and the development of technologies that enable greater access to space for both commercial and scientific purposes.
- Exploration: The hope is that this new era will lead to breakthroughs in areas like space tourism, asteroid mining, and Mars colonization, among others.
India’s Space Journey
- India’s journey in space began modestly in the 1960s.
- Societal objectives: Over the decades, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) prioritized societal objectives and benefits, such as developing satellite technology for mass communication, remote sensing for weather forecasting, resource mapping of forests, agricultural yields, groundwater and watersheds, fisheries and urban management, and satellite-aided navigation.
- Enhanced launch capabilities: ISRO also developed satellite launch capabilities, beginning with the SLV-1 in the 1980s, followed by the PSLV series, which has become its workhorse with over 50 successful launches.
Facts for prelims
| Steps taken to promote the space industry in India |
Resulting Outcome |
| Creation of Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) in 1969 | Establishment of a strong foundation for space research and exploration in India |
| Launch of Aryabhata satellite in 1975 | First satellite successfully launched by India |
| Establishment of the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) in 1972 | Development of technologies for rocket and satellite launch |
| Launch of Rohini satellite in 1983 | First satellite launched using an Indian-made launch vehicle |
| Launch of Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) in 1993 | Capability to launch smaller satellites into orbit |
| Launch of Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) in 2001 | Capability to launch larger and heavier satellites into orbit |
| Successful Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) in 2014 | India became the first country to successfully launch a spacecraft to Mars in its first attempt |
| Formation of NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) in 2019 | Increased involvement of private sector in space activities and commercialization of space technologies |
| Announcement of Gaganyaan mission in 2018 | Development of human spaceflight capabilities in India |
India’s Space Potential
- Economy and employment: India’s space economy, estimated at $9.6 billion in 2020, is expected to be $13 billion by 2025. However, with an enabling policy and regulatory environment, the Indian space industry could exceed $60 billion by 2030, directly creating more than two lakh jobs.
- Downstream activities: Downstream activities such as satellite services and associated ground segment are dominant, accounting for over 70% of India’s space economy.
- Media and entertainment segment: Media and entertainment account for 26% of India’s space economy, with consumer and retail services accounting for another 21%.
The Growing Role of the Private Sector
- Increasing space start ups: The Indian private sector is responding to the demands of the Second Space Age, with over 100 space start-ups today. From less than $3 million in 2018, investment in the sector has doubled in 2019 and crossed $65 million in 2021.
- Potential of multiplier effect on economy: The sector is poised for take-off, as a transformative growth multiplier like the IT industry did for the national economy in the 1990s.
Way ahead: Creating an Enabling Environment
- ISRO needs to focus on research and collaborate with the Indian private sector, which has different needs and demands.
- To create an enabling environment for the private sector, India needs a space activity act that provides legal grounding, sets up a regulatory authority, and enables venture capital funding into the Indian space start-up industry.
- Although a series of policy papers have been circulated in recent years, legislation is needed to provide legal backing and create an enabling environment for private sector growth.
Conclusion
- India’s space industry has enormous potential, but realizing it requires an enabling policy and regulatory environment that encourages private sector growth. With a space activity act that provides legal backing, sets up a regulatory authority, and enables venture capital funding, India can take advantage of the Second Space Age and become a major player in the global space economy.
Mains Question
Q. What do you understand by mean Second Space Age? Highlight potential of India’s space industry and growing role of private sector
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Union Cabinet gives nod to Indian Space Policy, 2023
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Indian Space Policy, 2023
Mains level: Not Much
Central idea: The Union Cabinet has approved the Indian Space Policy, 2023.
Indian Space Policy, 2023
- It aims to enhance the role of the Department of Space, boost the activities of ISRO missions, and encourage participation from research, academia, startups, and industry.
Salient features
(1) Outlining roles and responsibilities
- The Indian Space Policy, 2023 outlines the roles and responsibilities of various organizations in the space sector.
- The policy includes the responsibilities of ISRO, NewSpace India Limited, and private sector entities.
- This clarity in roles will help in the efficient functioning of the components set up in recent times.
(2) Multistakeholder participation
- The policy aims to boost the space sector by enhancing the role of the Department of Space and encouraging participation from research, academia, startups, and industry.
- This will help in the development of the space segment and create more opportunities for the private sector.
(3) Boosting ISRO Missions
- The Indian Space Policy, 2023 aims to boost the activities of ISRO missions.
- This will help ISRO achieve its objectives more efficiently and effectively.
- It will also help in the development of new technologies and innovative solutions.
(4) Involvement of Private Sector
- The Policy, 2023 recognizes the importance of the private sector in the development of the space sector.
- It encourages the involvement of private sector entities in various aspects of the space segment.
- This will create more opportunities for the private sector and help in the growth of the Indian space industry.
(5) Research and development
- The policy aims to involve research, academia, and startups in the development of the space sector.
- This will help in the development of new technologies, innovative solutions, and talent pool.
- It will also help in the growth of the Indian space industry and create more opportunities for research and development in the sector.
Conclusion
- The Indian Space Policy, 2023 is a comprehensive policy that provides clarity in the roles and responsibilities of various organizations in the space sector.
- The policy aims to boost the space segment, encourage private sector involvement, and involve research, academia, and startups in the development of the sector.
- The policy will help in achieving the objectives of ISRO more efficiently and effectively, and create more opportunities for the private sector and research and development in the space sector.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
What is Dhawan II Engine?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Dhawan II engine
Mains level: Privatization of space activities

In Telangana, private space vehicle company Skyroot Aerospace has test-fired its 3D-printed Dhawan II engine.
Dhawan II Engine
- The Dhawan II engine is a cryogenic engine developed by Skyroot Aerospace for use as the upper stage of the updated version of their Vikram II rocket.
- The engine was recently test-fired for a duration of 200 seconds and demonstrated impressive performance results.
- Cryogenic engines use extremely cold liquid propellants, which can provide greater thrust and enhance the payload-carrying capacity of a rocket.
- The engine was developed using advanced technologies like 3D printing and green propellants.
- Its successful testing marks a significant milestone for Skyroot Aerospace in their efforts to become the first private launcher from South Asia.
Stipulated use
- The Dhawan II engine will be used as the upper stage of the updated version Vikram-2.
- Using a cryogenic upper stage instead of a solid fuel stage enhances the payload carrying capacity of a rocket.
- The updated Vikram II rocket is scheduled to become launch-ready by next year, making Skyroot the first private launcher from South Asia.
Skyroot’s other sub-orbital and orbital flights
- Skyroot carried out its first sub-orbital flight in November 2021, using a single-stage solid fuel Vikram S rocket.
- The company plans to carry out its first orbital flight by the end of this year using the updated Vikram II rocket.
- The Vikram-1 rocket, the first in the series of rockets being developed by Skyroot, will use three solid-fuel stages to take satellites to orbit.
Impressive performance results and advanced technologies
- The endurance test of Dhawan-II demonstrated impressive performance results.
- The company is proud to be at the forefront of developing cutting-edge cryogenic technologies in the private space sector of India.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO’s Reusable Launch Vehicle Mission RLV LEX
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: RLV
Mains level: Read the attached story

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) conducted a successful autonomous landing mission experiment for a Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) at the Aeronautical Test Range in Chitradurga, Karnataka.
What is a Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV)?
- RLV is a type of spacecraft that is designed to be reused multiple times for launching payloads into space, instead of being discarded after a single launch like traditional rockets.
- They are seen as a more cost-effective and sustainable option for space launches, as they reduce the need for manufacturing new rockets for each mission.
- They typically consist of a reusable orbiter, similar to a space shuttle, and a reusable booster that provides the initial thrust needed to lift the orbiter and payload into space.
- After the payload is released into orbit, the orbiter and booster return to Earth and land back on a runway, where they can be refurbished and reused for future launches.
Why developing RLV is a big feat?
Developing RLVs requires advanced technologies, including-
- Heat-resistant materials for protecting the spacecraft during re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere
- Advanced guidance and control systems for landing and
- Reliable propulsion systems for launching and landing
ISRO’s RLV-TD project
- ISRO is developing essential technologies for a fully reusable launch vehicle to enable low-cost access to space.
- The RLV-TD is being used to develop technologies like hypersonic flight (HEX), autonomous landing (LEX), return flight experiment (REX), powered cruise flight, and Scramjet Propulsion Experiment (SPEX).
- It looks like an aircraft and consists of a fuselage, a nose cap, double delta wings, and twin vertical tails.
Development of RLV
(1) First RLV experiment:
- In 2016, the RLV-TD was launched into space on a rocket powered by a conventional solid booster (HS9) engine.
- The spacecraft travelled at a speed of Mach 5 when re-entering the earth’s orbit and travelled a distance of 450 km before splashdown in the Bay of Bengal.
- Critical technologies such as autonomous navigation, guidance and control, reusable thermal protection system, and re-entry mission management were successfully validated.
(2) Second RLV experiment:
- The RLV LEX test on April 2, 2023, involved a Chinook Helicopter lifting the RLV LEX to a height of 4.5 km and releasing the RLV.
- After midair release, the RLV carried out an autonomous landing on the Aeronautical Test Range airstrip, under the exact conditions of a Space Re-entry vehicle’s landing.
- It achieved landing parameters as might be experienced by an orbital re-entry space vehicle in its return path.
Advantages of RLVs
- Reusable launch vehicles are considered a low-cost, reliable, and on-demand mode of accessing space.
- The cost of a launch can be reduced by nearly 80 percent of the present cost by using RLVs.
Global RLV technologies
- NASA space shuttles have been carrying out dozens of human space flight missions.
- The private space launch services provider SpaceX demonstrated partially reusable launch systems with its Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy rockets since 2017.
- SpaceX is also working on a fully reusable launch vehicle system called Starship.
- Several private launch service providers and government space agencies are working on developing reusable launch systems.
Significance
- RLVs have the potential to significantly reduce the cost of space launches, as a significant portion of the cost of traditional rockets comes from the need to manufacture new rockets for each mission.
- By reusing spacecraft, the cost per launch can be significantly reduced.
- Additionally, RLVs can provide greater flexibility and reliability for space launches, as they can be launched on-demand instead of needing to be manufactured and assembled for each mission.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Starberry-Sense: A low cost Star Sensor
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Starberry-Sense
Mains level: Not Much

Researchers at the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) have developed a low-cost star sensor for astronomy and small CubeSat class satellite missions.
What is Starberry-Sense?
- Based on commercial/off-the-shelf components, this star sensor costs less than 10% of those available in the market.
- It is made from a single-board Linux computer called Raspberry Pi, which is widely used among electronics hobby enthusiasts.
Benefits of Starberry-Sense
- Starberry-Sense can help small CubeSat class satellite missions find their orientation in space.
- The instrument can be used for CubeSats and other small satellite missions in the future.
- The position of stars in the sky is fixed relative to each other and can be used as a stable reference frame to calculate the orientation of a satellite in orbit.
Successful test
- The star sensor has successfully undergone the vibration and thermal vacuum test that qualifies it for a space launch and operations.
- These tests were conducted in-house at the environmental test facility located at the CREST Campus of IIA in Hosakote.
Are you an IAS Worthy Aspirant? Get a reality check with the All India Smash UPSC Scholarship Test
Get upto 100% Scholarship | 900 Registration till now | Only 100 Slots Left
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
In news: Megha Tropiques Satellite
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Megha Tropiques Satellite, Controlled re-entry
Mains level: Space junk clearing

ISRO attempted a controlled re-entry of the Megha Tropiques-1 satellite with leftover fuel to lower the orbit and reduce space debris.
Megha Tropiques Satellite
- The weather satellite Megha Tropiques-1 was developed as a joint mission by Indian and French space agencies.
- It was launched aboard a PSLV by the space agency in 2011.
- And, although the planned mission life of the satellite was only three years, it continued providing data on water cycle and energy exchanges in the tropics for nearly a decade.
How was the satellite brought down?
- With over 120kgs of fuel remaining in the satellite even after being decommissioned.
- ISRO determined that there was enough to attempt a controlled re-entry.
- When the satellites re-enter the atmosphere, the friction causes it to heat up to extreme high temperatures of thousands of degrees Celsius.
- Without a heat shield, 99% of a satellite gets burnt up whether in a controlled re-entry or an uncontrolled one.
Significance of the move
- This was the first time that ISRO attempted such a manoeuvre to clear out space debris despite the satellite not being built to do so.
- Usually, satellites are left in their orbit and because of the gravitational pull of the earth, they come down to the atmosphere over years and years.
Why did ISRO attempt a controlled re-entry?
- ISRO attempted the control re-entry to demonstrate and understand the process of doing so.
- Keeping space clean is crucial with multiple spacefaring nations and private entities launching satellites.
- Thousands of objects are flying around in low earth orbits, including old satellites, parts, and rocket stages.
- Even small debris can destroy active satellites due to high speeds.
- Kessler syndrome is a scary scenario where space debris collisions create more debris.
What happens to satellites usually?
- A controlled re-entry like the one attempted by Isro earlier this week is possible only for satellites in the low-earth orbit – at about 1,000 kms over the surface of the earth.
- These manoeuvres, however, are not usually attempted because fuel reserves have to be maintained in the satellite after mission life is over.
- And, this is impossible for satellites placed in geo-stationary or geosynchronous orbit – where time taken by the satellite to orbit the earth matches Earth’s rotation.
- Such satellites are at altitudes of nearly 36,000 kms.
- For attempting to bring down a satellite from such as orbit, a huge fuel reserve would be needed. This will only make the satellite heavier and costlier at launch.
Also read-
Are you an IAS Worthy Aspirant? Get a reality check with the All India Smash UPSC Scholarship Test
Get upto 100% Scholarship | 900 Registration till now | Only 100 Slots Left
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Kodaikanal Solar Observatory
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Kodaikanal solar observatory
Mains level: NA

The Kodaikanal Solar Observatory (KoSO) has been observing the Sun for over a century.
Why in news?
- Kodaikanal Solar Observatory (KoSO) has been observing the Sun for over a century
- KoSO has captured images of sunspots and recorded changes in the Sun’s behavior
- Solar physicists at the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) and Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences (ARIES) have digitized 1.48 lakh solar images captured since 1904
A Brief History of Kodaikanal Solar Observatory
- KoSO is one of the world’s oldest observatories studying the Sun.
- Norman Pogson, astronomer and Government Astronomer of the Madras Observatory, proposed the idea of taking pictures of the Sun using a 20-inch telescope.
- The Madras Observatory was set up as the private effort of an official of the British East India Company in 1786.
- The decision to establish a solar observatory was taken in 1893, and Kodaikanal in present-day Tamil Nadu was chosen for its high altitude and dust-free environment.
- The Solar Physics Observatory opened on April 1, 1899, and was later named KoSO.
- The Bhavnagar Telescope, named after the Maharaja of Bhavnagar, was one of the more famous instruments at KoSO during the early decades of its operation.
- A 15cm telescope was used to capture solar images onto a photographic film or plate.
- Solar magnetic plages and prominences were recorded since 1911, taken on photographic films and plates.
Solar Observations, One Every Day: How They Are Taken
- White light images of the Sun have been captured every day since 1904 using a 6-inch telescope
- Visible light images reveal sunspots on the surface of the Sun.
- One image is taken daily around 8 am, which has been a fixed routine for over a century now
- Each observation accompanies the corresponding date and time, which is key for calibration purposes later.
- These plates or films are sent to the darkroom and developed either the same day or the next day
- Once the film has been developed, the date and time of observation are written on the plate and entered in the logbook.
- These plates or films are kept in an envelope with the handwritten date and time of observation and stored carefully in humidity-controlled rooms.
Arrival of New Technology and the Process of Digitization
- Between 1904 and 2017, all solar observations were traced onto photographic films and plates
- A new telescope mounted with CCD cameras has taken over and, since 2017, continued to observe the Sun.
- Digitization of the records was initiated in 1984 by Prof J C Bhattacharyya, and others continued the effort.
- In 2018, digitized solar observations for the period 1921-2011 were made available to the scientific community.
- Raw and calibrated data for the period of 1904 to 2017 were added, and the digitization process is nearly complete.
- KoSO is now home to a digital repository of a whopping 1.48 lakh solar images adding up to 10 terabyte of data.
- These include 33,500 white-light images (showing sunspots), 45,000 images of the Ca II K spectral line (which reveals plages), and 70,000 H-alpha photographic plates that show prominences.
Are you an IAS Worthy Aspirant? Get a reality check with the All India Smash UPSC Scholarship Test
Get upto 100% Scholarship | 900 Registration till now | Only 100 Slots Left
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Space Debris: India’s Contribution and Efforts to Tackle the Problem
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Space debries
Mains level: Space updates
Central Idea
- Space debris, particularly in Low Earth Orbit (LEO), is becoming an increasingly urgent problem due to the rising number of rocket launches and payloads, as well as anti-satellite missile tests and collisions. On March 7, 2023, ISRO successfully carried out a controlled re-entry for the decommissioned Megha-Tropiques-1 (MT1).
ISRO’s controlled re-entry of the decommission
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully carried out a controlled re-entry of the decommissioned Megha-Tropiques-1 (MT1) satellite.
- MT1 was launched over a decade ago with the objective of studying clouds in the tropical regions of the world.
- As the satellite had reached the end of its operational life, ISRO brought it down in a controlled manner to reduce space debris in the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and limit the potential risks associated with it.
Space debris
- Space debris refers to any human-made object that is in orbit around the Earth but no longer serves any useful purpose. This can include pieces of spacecraft, rocket stages, and other materials that have been left in space after they have completed their missions or have been discarded.
- Space debris can vary in size, from small paint flecks and bolts to larger objects like satellites and old rocket bodies.
- There are currently more than 26,000 objects larger than 10 cm in orbit around the Earth, and many smaller objects that are too small to be tracked.
Surge in Space Debris
- Increasing number of payloads: The surging number of rocket launches and the increasing number of payloads carried in recent years have made the space junk problem acute, especially after private companies such as SpaceX launched thousands of satellites to provide Internet access.
- For instance: In 2022, over 2,160 objects were launched into space, about 300 more than 2021 and 900 more than 2020.
- Data on fragmented debris: The number of satellites in space has crossed the 10,000 mark, including active and defunct ones still orbiting Earth, and the number of fragmentation debris is hurtling towards the 14,000-mark.
- Smaller debris poses a bigger challenge: While satellite launches are the reason for the rise in rocket bodies orbiting Earth, fragmented debris are mostly a consequence of collisions and Anti-Satellite (ASAT) missile tests. The fragmented junk poses a bigger challenge as tracking debris smaller than 10 centimetres is tough.
Countries responsible
- Russia: Close to 35% originated from the Soviet Union/Russia,
- US: 31% from the U.S.,
- China: 29% from China, over 2,700 pieces of debris from a Chinese anti-satellite test in 2007, marked as the single worst contamination of space in history, are still in orbit.
- India: India’s contribution is 0.5%.
- India added to the problem in 2019 by testing an ASAT missile which targeted a live satellite in LEO which resulted in 400 pieces of orbital debris
- While all the trackable debris from India’s test have re-entered Earth in subsequent years, over 50 pieces from a break-up event of the 4th stage of PSLV-C3 in 2001 are still in orbit.
The cost of avoiding collision
- High cost: While debris has the potential to cause serious accidents, the cost of manoeuvres to avoid collisions is high.
- For instance: In 2022, ISS had to conduct two such collision avoidance manoeuvres due to threats posted by debris from Russia’s ASAT test in 2021.
- Challenges: Such manoeuvres are costly as they require hours of monitoring, fuel for movement, and also result in loss of data as instruments are turned off during such operations.
- India’s honest efforts:
- India conducted 21 such corrections for its satellites in 2022, the highest ever for the country.
- Also, in 2021, ISRO monitored 4,382 events in LEO and 3,148 events in geostationary orbit (GEO) in which debris or other space objects came close to India’s space assets.
Conclusion
- Small debris orbiting Earth pose threats to space assets, the immediate need is that the countries must acknowledge the responsibility. India’s continues efforts towards controlled decommission set the bar high.
Mains Question
Q. Discuss the challenges posed by increasing space debris and the potential risks associated with it.
Are you an IAS Worthy Aspirant? Get a reality check with the All India Smash UPSC Scholarship Test
Get upto 100% Scholarship | 900 Registration till now | Only 100 Slots Left
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
NASA hands over NISAR satellite to ISRO
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NISAR
Mains level: NA

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has received the NASA-ISRO SAR (NISAR) satellite.
What is NISAR?
- NISAR has been built by space agencies of the US and India under a partnership agreement signed in 2014.
- The 2,800 kilograms satellite consists of both L-band and S-band synthetic aperture radar (SAR) instruments, which makes it a dual-frequency imaging radar satellite.
- While NASA has provided the L-band radar, GPS, a high-capacity solid-state recorder to store data, and a payload data subsystem, ISRO has provided the S-band radar, the GSLV launch system and spacecraft.
- Another important component of the satellite is its large 39-foot stationary antenna reflector.
- Made of a gold-plated wire mesh, the reflector will be used to focus the radar signals emitted and received by the upward-facing feed on the instrument structure.
Objectives of NISAR
- Once launched into space, NISAR will observe subtle changes in Earth’s surfaces, helping researchers better understand the causes and consequences of such phenomena.
- It will spot warning signs of natural disasters, such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes and landslides.
- The satellite will also measure groundwater levels, track flow rates of glaciers and ice sheets, and monitor the planet’s forest and agricultural regions, which can improve our understanding of carbon exchange.
- By using synthetic aperture radar (SAR), NISAR will produce high-resolution images.
- SAR is capable of penetrating clouds and can collect data day and night regardless of the weather conditions.
Are you an IAS Worthy Aspirant? Get a reality check with the All India Smash UPSC Scholarship Test
Get upto 100% Scholarship | 900 Registration till now | Only 100 Slots Left
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO successful in key test for Chandrayaan-3 Mission
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Chandrayaan
Mains level: Chandrayaan-3 Mission

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully conducted a crucial test for its upcoming Chandrayaan-3 mission.
What was the test?
- The test involved the high-thrust cryogenic engine, which will be used to power the rocket that carries the Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft.
- The engine was tested for its endurance and performance under various conditions.
About Chandrayaan-3 Mission
- The Chandrayaan-3 mission is the third lunar exploration mission by the Indian Space Research Organisation.
- The mission follows the successful Chandrayaan-1 and Chandrayaan-2 missions, which were launched in 2008 and 2019 respectively.
- The Chandrayaan-3 mission is designed to further explore the Moon’s South Pole region and conduct various scientific experiments, including studying the lunar surface, mineralogy, and the presence of water.
Significance of the recent test
- With the successful test of the high-thrust cryogenic engine, ISRO is now one step closer to launching the Chandrayaan-3 mission.
- The mission is expected to be a significant step forward in India’s space exploration efforts and will further our understanding of the Moon and its potential for future exploration and exploitation.
Chandrayaan-2: A quick recap
- Chandrayaan-2 consisted of an Orbiter, Lander and Rover, all equipped with scientific instruments to study the moon.
- The Orbiter would watch the moon from a 100-km orbit, while the Lander and Rover modules were to be separated to make a soft landing on the moon’s surface.
- ISRO had named the Lander module as Vikram, after Vikram Sarabhai, the pioneer of India’s space programme, and the Rover module as Pragyaan, which crash-landed.
Inception of Chandrayaan 3
- The subsequent failure of the Vikram lander led to the pursuit of another mission to demonstrate the landing capabilities needed for the Lunar Polar Exploration Mission proposed in partnership with Japan for 2024.
Its design
- The lander for Chandrayaan-3 will have only four throttle-able engines.
- Unlike Vikram on Chandrayaan-2 which had five 800N engines with a fifth one being centrally mounted with a fixed thrust.
- Additionally, the Chandrayaan-3 lander will be equipped with a Laser Doppler Velocimeter (LDV).
Back2Basics: Chandrayaan-1 Mission
- The Chandrayaan-1 mission was launched in October 2008 was ISRO’s first exploratory mission to the moon, in fact to any heavenly body in space.
- The mission was designed to just orbit around the moon and make observations with the help of the instruments onboard.
- The closest that the Chandrayaan-1 spacecraft came to the moon was in an orbit 100 km from its surface.
Attempt UPSC 2024 Smash Scholarship Test | FLAT* 100% OFF on UPSC Foundation & Mentorship programs

Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
India-US Space Cooperation
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NISAR
Mains level: US- India space collaboration
Context
- India and the United States agreeing to advance space collaboration in several areas, under the ‘initiative on critical and emerging technology’ umbrella, including human space exploration and commercial space partnership, comes at a crucial time for both countries. This follows from the eighth meeting of the U.S.-India Civil Space Joint Working Group (CSJWG), that was held on January 30-31, 2023.
Crack Prelims 2023! Talk to our Rankers
Limiting factors in India-U.S. space cooperation
- Mismatch in the two nations interests in outer space: The first structural factor that limits long-term India-U.S. space cooperation is the mismatch in the two nations interests in outer space.
- American ambitions beyond earth orbits: Although the U.S. and its partners stress the importance of maintaining capabilities in low-earth orbit, their ambitions are firmly set on the moon.
- India’s current focus is on increasing its satellite launch capabilities: India’s scientific community focuses on building the nation’s capability in and under earth orbits. The Gaganyaan human space flight programme hopes to sustain India’s human presence in space for the long term. This is not to say that India does not aim for the moon, Mars or beyond. But India’s top priority is to substantially increase its satellite and launch capabilities in earth orbits and catch up with other spacefaring nations such as China.
- The asymmetry in capabilities: The U.S. has the highest number of registered satellites in space. It also has a range of launch vehicles serving both commercial and national-security needs.
- Private sector, for instance: Private entity SpaceX, for example, managed to achieve a record 61 launches in 2022, far higher than the number of launches undertaken by any other commercial entity or country. The American private sector has also assumed the challenge of replacing the International Space Station by 2030 with many smaller stations.
- The greatest challenge for India here is lack of capacity: The country has just over 60 satellites in orbit and cannot undertake double-digit launches annually. The Indian government also opened the space industry to the private sector only in 2020. Since the U.S. already has an extensive network of partners for space cooperation, it has few technical incentives to cooperate with India.
- Disagreements on govern space activities: Compounding these problems are disagreements on how best to govern space activities on the moon and other celestial bodies. Even though countries have a mindset to collaborate, the structural factors overpower diplomatic incentives to pursue long-term cooperation.
Have you read about “NISAR”?
- NISAR has been built by space agencies of the US and India under a partnership agreement signed in 2014.
- The 2,800 kilograms satellite consists of both L-band and S-band synthetic aperture radar (SAR) instruments, which makes it a dual-frequency imaging radar satellite.
- While NASA has provided the L-band radar, GPS, a high-capacity solid-state recorder to store data, and a payload data subsystem, ISRO has provided the S-band radar, the GSLV launch system and spacecraft.
- Another important component of the satellite is its large 39-foot stationary antenna reflector.
- Made of a gold-plated wire mesh, the reflector will be used to focus the radar signals emitted and received by the upward-facing feed on the instrument structure.
Some novel solutions
- Sustained engagement: The standard solution to induce long-term cooperation is to sustain the engagement between academics, the private sector and state-led entities in the two countries. Sustained engagement could also take the form of collaborating on highly specialised projects such as the NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) mission.
- Cooperation and collaboration between state and private entities: One form of cooperation is a partnership between state and private entities; or, as agreed in the most recent meeting, a convention of American and Indian aerospace companies to advance collaboration under the National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) programme. Such an arrangement could be taken further.
- Reducing dependence: India could send its astronauts to train at American private companies. This could help India reduce its dependence on Russia while ISRO builds its own astronaut training centre.
- Government-owned New Space India Limited: Another novel arrangement could be a consortium led by the government-owned New Space India Limited which involves private companies in the U.S. This setup could accelerate India’s human spaceflight programme and give the U.S. an opportunity to accommodate Indian interests in earth orbits.
Conclusion
- The US and India have taken significant strides in advancing the private space sector. Together, these endeavors have the capability to shape and impact U.S. and Indian space policies and programmes over the next decade.
Mains question
Q. The US and India have taken significant strides in space cooperation. Discuss the limiting factors and suggest probable solutions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
In news: Agasthyarkoodam Observatory
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Agasthyarkoodam Observatory
Mains level: NA

Agasthyarkoodam was once home to a forgotten and long-lost 19th-century observatory established by Scottish meteorologist John Allan Broun.
Agasthyarkoodam Observatory
- The Agasthyarkoodam Observatory is an astronomical research observatory located in the state of Kerala.
- The observatory is situated at an altitude of 1600 meters above sea level and is owned and operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA).
- The observatory is equipped with a 1-meter optical telescope and various other instruments for studying the night sky.
- The observatory is used for research and educational purposes and is open to the public for viewing night-sky objects.
Why in news?
- Agasthyarkoodam in the Western Ghats once housed a magnetic observatory that was established by Scottish meteorologist John Allan Broun.
- Broun used it to record magnetic and meteorological observations in tandem with the Thiruvananthapuram astronomical observatory.
- Broun’s astronomical research in India began after he was invited by the ruler of the erstwhile Travancore Uthram Tirunal Marthanda Varma to helm the Thiruvananthapuram observatory following the death of its first director John Caldecott in 1849.
- The observatory started recording observations in July 1855.
- However, it was closed in 1881 by the then Madras Governor Sir William Denison.
What are magnetic observatories?
- Magnetic observatories continuously measure and record Earth’s magnetic field at a number of locations.
- In an observatory of this sort, magnetized needles with reflecting mirrors are suspended by quartz fibres.
- Light beams reflected from the mirrors are imaged on a photographic negative mounted on a rotating drum.
- Variations in the field cause corresponding deflections on the negative.
- Their magnetograms are photographed on microfilm and submitted to world data centres, where they are available for scientific or practical use.
Crack Prelims 2023! Talk to our Rankers
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO’s SSLV-D2 launched successfully
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PSLV, SSLV, GSLV
Mains level: Not Much

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) will undertake the second development flight of the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV –D2).
Payload details
The SSLV-D2 is intended to inject ISRO’s EOS-07, U.S.-based firm Antaris’ Janus-1 and Chennai-based space start-up Space Kidz’s AzaadiSAT-2 satellites into a 450-km circular orbit in its 15 minutes flight.
- EOS-07: is a 156.3 kg satellite designed, developed and realized by the ISRO. Its mission objective is to design and develop payload instruments compatible with microsatellite buses and new technologies that are required for future operational satellites.
- Janus-1: Weighing around 10.2 kg, Janus-1 is a technology demonstrator, smart satellite mission based on Antaris software platform.
- AzaadiSAT-2: A 8.7-kg satellite, AzaadiSAT-2 is a combined effort of about 750 girl students across India guided by Space Kidz India, Chennai.
What is SSLV?
- The SSLV is a small-lift launch vehicle being developed by the ISRO with payload capacity to deliver:
- 600 kg to Low Earth Orbit (500 km) or
- 300 kg to Sun-synchronous Orbit (500 km)
- It would help launching small satellites, with the capability to support multiple orbital drop-offs.
- In future a dedicated launch pad in Sriharikota called Small Satellite Launch Complex (SSLC) will be set up.
- A new spaceport, under development, near Kulasekharapatnam in Tamil Nadu will handle SSLV launches when complete.
- After entering the operational phase, the vehicle’s production and launch operations will be done by a consortium of Indian firms along with NewSpace India Limited (NSIL).
Vehicle details
(A) Dimensions
- Height: 34 meters
- Diameter: 2 meters
- Mass: 120 tonnes
(B) Propulsion
- It will be a four stage launching vehicle.
- The first three stages will use Hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene (HTPB) based solid propellant, with a fourth terminal stage being a Velocity-Trimming Module (VTM).
SSLV vs. PSLV: A comparison
- The SSLV was developed with the aim of launching small satellites commercially at drastically reduced price and higher launch rate as compared to Polar SLV (PSLV).
- The projected high launch rate relies on largely autonomous launch operation and on overall simple logistics.
- To compare, a PSLV launch involves 600 officials while SSLV launch operations would be managed by a small team of about six people.
- The launch readiness period of the SSLV is expected to be less than a week instead of months.
- The SSLV can carry satellites weighing up to 500 kg to a low earth orbit while the tried and tested PSLV can launch satellites weighing in the range of 1000 kg.
- The entire job will be done in a very short time and the cost will be only around Rs 30 crore for SSLV.
Significance of SSLV
- SSLV is perfectly suited for launching multiple microsatellites at a time and supports multiple orbital drop-offs.
- The development and manufacture of the SSLV are expected to create greater synergy between the space sector and private Indian industries – a key aim of the space ministry.
Crack Prelims 2023! Talk to our Rankers
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
NASA-ISRO partnership’s NISAR and its Mission
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NISAR
Mains level: Not Much

An earth-observation satellite NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) jointly developed by NASA and ISRO is all set to be shipped to India later this month for a possible launch in September.
What is NISAR?
- NISAR has been built by space agencies of the US and India under a partnership agreement signed in 2014.
- The 2,800 kilograms satellite consists of both L-band and S-band synthetic aperture radar (SAR) instruments, which makes it a dual-frequency imaging radar satellite.
- While NASA has provided the L-band radar, GPS, a high-capacity solid-state recorder to store data, and a payload data subsystem, ISRO has provided the S-band radar, the GSLV launch system and spacecraft.
- Another important component of the satellite is its large 39-foot stationary antenna reflector.
- Made of a gold-plated wire mesh, the reflector will be used to focus the radar signals emitted and received by the upward-facing feed on the instrument structure.
What is the mission?
- Once launched into space, NISAR will observe subtle changes in Earth’s surfaces, helping researchers better understand the causes and consequences of such phenomena.
- It will spot warning signs of natural disasters, such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes and landslides.
- The satellite will also measure groundwater levels, track flow rates of glaciers and ice sheets, and monitor the planet’s forest and agricultural regions, which can improve our understanding of carbon exchange.
- By using synthetic aperture radar (SAR), NISAR will produce high-resolution images.
- SAR is capable of penetrating clouds and can collect data day and night regardless of the weather conditions.
Crack Prelims 2023! Talk to our Rankers
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Aditya-L1: India’s first mission to Sun to be launched soon
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Aditya L1 mission
Mains level: Read the attached story

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is planning to launch the Aditya-L1 mission by June or July this year.
What is Aditya-L1 Mission?
- ISRO categorizes Aditya L1 as a 400 kg-class satellite that will be launched using the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) in XL configuration.
- It will observe the Sun from a close distance, and try to obtain information about its atmosphere and magnetic field.
- The space-based observatory will have seven payloads (instruments) on board to study the Sun’s corona, solar emissions, solar winds and flares, and Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs), and will carry out round-the-clock imaging of the Sun.
L1: Behind the name
- L1 refers to Lagrangian/Lagrange Point 1, one of five points in the orbital plane of the Earth-Sun system.
- Lagrange Points, named after Italian-French mathematician Josephy-Louis Lagrange, are positions in space where the gravitational forces of a two-body system (like the Sun and the Earth) produce enhanced regions of attraction and repulsion.
- The L1 point is about 1.5 million km from Earth, or about one-hundredth of the way to the Sun.
Major payloads
- In total Aditya-L1 has seven payloads, of which the primary payload is the Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC), designed and fabricated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Bengaluru.
- The satellite carries additional six payloads-
- SUIT, the solar ultraviolet imaging telescope
- ASPEX (Aditya Solar Wind Particle Experiment),
- PAPA (Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya),
- SoLEXS (Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer),
- HEL1OS (High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray spectrometer) and
- Magnetometer — with enhanced science scope and objectives possible by extensive remote and in-situ observation of the sun.
Why is studying the Sun important?
(1) To understand space weather
- To learn about and track Earth-directed storms, and to predict their impact, continuous solar observations are needed.
- Every storm that emerges from the Sun and heads towards Earth passes through L1, and a satellite placed in the halo orbit around L1 of the Sun-Earth system has the major advantage of continuously viewing the Sun without any occultation/eclipses.
(2) Observing corona
- The VELC payload will be able to observe the corona continuously and the data provided by it is expected to answer many outstanding problems in the field of solar astronomy.
- No other solar coronagraph in space has the ability to image the solar corona as close to the solar disk as VELC can.
- It can image it as close as 1.05 times the solar radius.
- It can also do imaging, spectroscopy, and polarimetry at the same time, and can take observations at a very high resolution (level of detail) and many times a second.
Why are solar missions challenging?
- Distance: What makes a solar mission challenging is the distance of the Sun from Earth (about 149 million km on average, compared to the only 3.84 lakh km to the Moon).
- Heat: More importantly the super-hot temperatures and radiations in the solar atmosphere make it difficult to study.
Major missions to Sun till now
- NASA’s Parker Solar Probe has already gone far closer — but it will be looking away from the Sun.
- The earlier Helios 2 solar probe, a joint venture between NASA and space agency of erstwhile West Germany, went within 43 million km of the Sun’s surface in 1976.
Crack Prelims 2023! Talk to our Rankers
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
[pib] First evidence of Solitary Waves near Mars
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Solitary Waves, Mars
Mains level: Not Much
In a first-of-its-kind discovery, a team of Indian scientists from the Indian Institute of Geomagnetism (IIG) reported the first evidence of the presence of solitary waves around Mars.
Mars
|
What are Solitary Waves?
- Solitary waves are distinct electric field fluctuations (bipolar or monopolar) that follow constant amplitude-phase relations.
- Their shape and size are less affected during their propagation.
- Solitary waves are known to be responsible for the plasma energization and its transport in Earth’s magnetosphere.
Unveiling the undercover solitary waves
- Earth is a giant magnetic entity, wrapped in a magnetosphere generated by the motion of molten iron in its core.
- This magnetosphere casts a protective layer around our home planet, shielding us from the solar winds coughed towards us by the Sun.
- But unlike Earth, Mars lacks a robust intrinsic magnetic field, which effectively allows the high-speed solar wind to interact directly with the Martian atmosphere.
- This interaction suggests that even with a weak and flimsy magnetosphere, the frequent occurrences of solitary waves on Mars remain a possibility.
Why this is a significant feat for India?
- Despite several missions to Mars, their presence has never been detected — until now.
- However, Indian Scientists have successfully identified and reported the first-ever solitary waves detected on Mars.
- They arrived at this result by analyzing about 450 solitary wave pulses observed by the Langmuir Probe and Waves instrument on NASA’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) spacecraft.
Decoding the data
- Their analysis revealed distinct electric field fluctuations, which lasted for about 0.2-1.7 milliseconds.
- Such signals were predominant during dawn or between afternoon to dusk at an altitude of 1000-3500 km from Mars’ surface.
- Further investigation is needed to determine exactly why these waves are dominant during a fixed time of the day.
Significance of such waves on Mars
- These pulses are dominantly seen in the dawn and afternoon dusk sectors at an altitude of 1000–3500 km around Mars.
- Researchers are further exploring their role in the particle dynamics in the Martian magnetosphere and whether such waves play any role in the loss of atmospheric ions on Mars.
- The study of these waves is crucial as they directly control particle energization, plasma loss, transport, etc., through wave-particle interactions.
Crack Prelims 2023! Talk to our Rankers
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO pushing Venus Mission ‘Shukrayaan’ to 2031
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Shukrayaan I
Mains level: Not Much

ISRO said that it is yet to receive approval from the Indian government for the Venus mission and that the mission could as a result be postponed to 2031.
Shukrayaan I: Venus Orbiter Mission
- Shukrayaan-I is a planned orbiter to Venus by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) to study the surface and atmosphere of Venus.
- The idea was born in 2012; five years later, ISRO commenced preliminary studies after the Department of Space received a 23% hike in the 2017-2018 budget.
- The orbiter, depending on its final configuration, would have a science payload capability of approximately 100 kilograms (220 lb) with 500 W available power.
- The launch will involve GSLV Mark II.
Expected launch
- ISRO had originally hoped to launch Shukrayaan I in mid-2023 but cited the pandemic when it pushed the date to December 2024.
- Optimal launch windows from Earth to Venus occur once around every 19 months.
- This is why ISRO has ‘backup’ launch dates in 2026 and 2028 should it miss the 2024 opportunity.
- But even more optimal windows, which further reduce the amount of fuel required at liftoff, come around every eight years.
Other missions to Venus
- The US and the European space agencies have Venus missions planned for 2031 — referring to VERITAS and EnVision, respectively.
Crack Prelims 2023! Talk to our Rankers
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
What are Globular Clusters?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Globular Cluster, Omega Centurari
Mains level: Not Much

Astronomers and scientists at the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) while studying the Omega Centauri have found that hot stars and white dwarfs emitted less ultraviolet radiation than expected.
Omega Centauri
|
What is a globular cluster?
- A globular cluster is a spheroidal conglomeration of stars.
- Globular clusters are bound together by gravity, with a higher concentration of stars towards their centres.
- They can contain anywhere from tens of thousands to many millions of member stars.
- They orbit mostly in the extended stellar halos surrounding most spiral galaxies.
How are they formed?
- No one knows precisely how globular clusters formed. Or what role, if any, they played in the development of galaxies.
- We know globular clusters are the oldest, largest and most massive type of star cluster. And globular clusters contain the oldest stars.
- Their age is determined by their almost complete lack of what astronomers call metals, the heavier elements forged in star interiors.
Our Milky Way has over 150 globular clusters
- Our own Milky Way has over 150 globular clusters, with perhaps more, hidden by galactic dust.
- The Andromeda galaxy (M31), our neighboring spiral galaxy, appears to have around 300 globular clusters.
Difference between a globular cluster and an open cluster
- Globular clusters are big, symmetric and old. They can reach 300 light-years in diameter and contain 10 million stars. On the other hand, open star clusters, contains sibling stars, scattered through the disk of our galaxy and presumably other galaxies.
- Globular star cluster are very symmetrical in shape, and are densest toward their centers. Open star clusters are irregular in shape and loosely grouped together.
- Globular clusters orbit in the halo of our galaxy. Plus, center around the galaxy’s core and expanding above and below the galactic disk. Open star clusters tend to orbit within the disk.
- Globular star clusters contain million of stars. Yet some globular clusters, like Omega Centauri, contain millions of stars. Open star clusters contain only hundreds of stars.
Click and get your FREE Copy of CURRENT AFFAIRS Micro Notes
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Uncontrolled Re-entries of Satellites
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Uncontrolled re-entry, Liability Convention, 1972
Mains level: Not Much

Many dignitaries have signed an open letter published by the Outer Space Institute (OSI) calling for both national and multilateral efforts to restrict uncontrolled re-entries of Satellites back to earth.
About Open Space Institute (OSI)
- OSI is a conservation organization that seeks to preserve scenic, natural and historic landscapes for public enjoyment, conserve habitats while sustaining community character, and help protect the environment.
- It uses policy initiatives and ground-level activism to help accomplish its goals.
What are the stages of a rocket launch?
- Rockets have multiple stages.
- Once a stage has increased the rocket’s altitude and velocity by a certain amount, the rocket sheds it.
- Some rockets jettison all their larger stages before reaching the destination orbit; a smaller engine then moves the payload to its final orbit.
- Others carry the payload to the orbit, then perform a deorbit manoeuvre to begin their descent.
- In both cases, rocket stages come back down — in controlled or uncontrolled ways.
What is an uncontrolled re-entry?
- It is the phenomenon of rocket parts falling back to earth in unguided fashion once their missions are complete.
- In an uncontrolled re-entry, the rocket stage simply falls.
- Its path down is determined by its shape, angle of descent, air currents and other characteristics.
- It will also disintegrate as it falls.
How many satellites are there in space?
- The Soviet Union launched the first artificial satellite in 1957.
- Today, there are more than 6,000 satellites in orbit, most of them in low-earth (100-2,000 km) and geostationary (35,786 km) orbits, placed there in more than 5,000 launches.
- The number of rocket launches have been surging with the advent of reusable rocket stages.
Why is this hazardous?
- As the smaller pieces fan out, the potential radius of impact will increase on the ground.
- Some pieces burn up entirely while others don’t.
- But because of the speed at which they’re travelling, debris can be deadly.
- If re-entering stages still hold fuel, atmospheric and terrestrial chemical contamination is another risk.
Why are we discussing this?
|
Damage control mechanism for uncontrolled re-entry
- There is no international binding agreement to ensure rocket stages always perform controlled re-entries nor on the technologies with which to do so.
- The Liability Convention, 1972 requires countries to pay for damages, not prevent them.
- These technologies include wing-like attachments, de-orbiting brakes, and extra fuel on the re-entering body, and design changes that minimise debris formation.
Click and get your FREE Copy of CURRENT AFFAIRS Micro Notes
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
[pib] Vainu Bappu Observatory
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Vainu Bappu Observatory
Mains level: Not Much

The several stellar discoveries of the 40-inch telescope at the Vainu Bappu Observatory in Kavalur, Tamil Nadu, were highlighted at the celebration of its 50 years of its operation.
Vainu Bappu Observatory
- The Vainu Bappu Observatory is an astronomical observatory owned and operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics.
- It is located at Kavalur in the Javadi Hills, near Vaniyambadi in Tirupathur district in Tamil Nadu.
- The 40-inch telescope was installed in 1972 and started producing important astronomical discoveries soon after.
- More than a generation of astronomers were trained at this telescope as well.
Significant feats achieved by VBO
The telescope set up by Professor Vainu Bappu has played a significant role in astronomy with major discoveries like-
- Presence of rings around the planet Uranus,
- New satellite of Uranus,
- Presence of an atmosphere around Ganymede which is a satellite of Jupiter
- Discovery and study of many ‘Be stars’, Lithium depletion in giant stars, optical variability in Blazars, the dynamics of the famous supernova SN 1987A and so on.
Click and get your FREE Copy of CURRENT AFFAIRS Micro Notes
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO successfully conducts test of Scramjet Engine
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ramjet, Scramjet Engine
Mains level: Not Much

The ISRO successfully conducted test for credible next-generation air-breathing scramjet engines, in order to launch satellites in a predetermined orbit at a low cost.
What is a jet engine?
- A jet engine is a machine that converts energy-rich, liquid fuel into a powerful pushing force called thrust.
- The thrust from one or more engines pushes a plane forward, forcing air past its scientifically shaped wings to create an upward force called lift that powers it into the sky.
Ramjet vs. Scramjet Engine
- Both scramjet and Ramjet are types of jet engines.
- A ramjet is an air breathing jet engine which is usually associated with supersonic transport.
- Ramjets can start at supersonic speeds only, so as a result they cannot be started at zero velocity and cannot produce thrust as there is a lack of airspeed.
- Hence assisted take off flights or rockets are needed to or accelerate it to a supersonic speed from which it starts producing thrust.
- This makes ramjet engine to be efficient only at supersonic speeds as it can accelerate to speeds of about Mach 6.
- Ramjet has revolutionized Rocket Propulsion and Missile Technology over the years.
How different is Scramjet?
- The Scramjet or the Supersonic Combustion Ramjet is a further complex model and is efficient at hypersonic speeds, usually upwards of Mach 6.
- They do not have any moving parts to compress the air as the air entering is already at high pressure.
- Scramjets have a very similar working to that of the ramjet except the fact that combustion also takes place at supersonic speed.
- This means that the air being compressed does not slow down as it enters the combustion chamber.
Click and get your FREE Copy of CURRENT AFFAIRS Micro Notes
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
What is a Trisonic Wind Tunnel?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Trisonic Wind Tunnel
Mains level: Not Much

The new trisonic wind tunnel at the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) was inaugurated by conducting the first blow-down test successfully.
What is a Wind Tunnel?
- Wind tunnels are large tubes with air moving inside.
- The tunnels are used to copy the actions of an object in flight.
- Researchers use wind tunnels to learn more about how an aircraft will fly.
- Space agencies uses wind tunnels to test scale models of aircraft and spacecraft. Some wind tunnels are big enough to hold full-size versions of vehicles.
- The wind tunnel moves air around an object, making it seem like the object is really flying.
How do Wind Tunnels work?
- Most of the time, powerful fans move air through the tube.
- The object to be tested is fastened in the tunnel so that it will not move.
- The object can be a small model of a vehicle. It can be just a piece of a vehicle.
- It can be a full-size aircraft or spacecraft. It can even be a common object like a tennis ball.
- Smoke or dye can be placed in the air and can be seen as it moves. Threads can be attached to the object to show how the air is moving.
- Special instruments are often used to measure the force of the air on the object.
About Trisonic Wind Tunnel at VSCC
- ‘Trisonic’ refers to the tunnel’s capability to test in three speed regimes—below the speed of sound (subsonic), at the speed of sound (transonic), and above the speed of sound (supersonic).
- Its parts include air storage vessels, a settling chamber where the airflow is ‘smoothened’ out, and nozzles for releasing the air into the test section.
- It is about 160 metres long and measures 5.4 metres at its widest part.
- In a ‘blow down test’, stored gases are released and blown through the tunnel’s test section, simulating flight conditions.
- The tunnel can simulate flight conditions from 0.2 times the speed of sound (68 metres per second) to four times the speed of sound (1,360 metres per second), according to the space agency.
- Commissioned in 2017, this tunnel can simulate flow speeds up to Mach 12.
Click and get your FREE Copy of CURRENT AFFAIRS Micro Notes
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO to establish SpaceTech Innovation Network (SpIN)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SpaceTech Innovation Network (SpIN)
Mains level: Commercial space activities in India

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has signed a MoU with Social Alpha, a multistage innovation curation and venture development platform, to launch SpaceTech Innovation Network (SpIN).
SpaceTech Innovation Network (SpIN)
- SpIN is India’s first dedicated platform for innovation, curation, and venture development for the burgeoning space entrepreneurial ecosystem.
- SpIN will primarily focus on facilitating space tech entrepreneurs in three distinct innovation categories:
- Geospatial Technologies and Downstream Applications;
- Enabling Technologies for Space & Mobility; and
- Aerospace Materials, Sensors, and Avionics.
Key initiative
- SpIN has launched its first innovation challenge for developing solutions in areas of maritime and land transportation, urbanization, mapping, and surveying.
- The selected start-ups and innovators will be able to access both Social Alpha’s and ISRO’s infrastructure and resources as per the prevailing guidelines.
- They will be provided active hand-holding in critical areas, including access to product design, testing and validation infrastructure, and intellectual property management.
Click and get your FREE Copy of CURRENT AFFAIRS Micro Notes
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
SARAS 3 Telescope gives clues to first stars, galaxies of universe
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Saras 3
Mains level: Not Much

India’s SARAS radio telescope has helped scientists determine the properties of the earliest radio luminous galaxies formed 200 million years after the Big Bang, a period known as the Cosmic Dawn.
SARAS 3 Telescope
- SARAS stands for Shaped Antenna measurement of the background Radio Spectrum 3 (SARAS) telescope.
- It is an indigenously designed and built at Raman Research Institute and was deployed over Dandiganahalli Lake and Sharavati backwaters, located in Northern Karnataka, in early 2020.
What have the researchers found?
- Researchers have been able to determine properties of radio luminous galaxies formed just 200 million years post the Big Bang, a period known as the Cosmic Dawn.
- These are the masses of the first generation of galaxies that are bright in radio wavelengths.
- This helps provide an insight into the properties of the earliest radio loud galaxies that are usually powered by supermassive black holes.
What is Cosmic Dawn?
- The ignition of the first stars marks the end of the Dark Ages and the beginning of our “Cosmic Dawn,” some 100 million years after the Big Bang.
- For the first time, our universe began shining with a light other than the afterglow of the Big Bang.
- SARAS 3 had improved the understanding of astrophysics of Cosmic Dawn by telling astronomers that less than 3% of the gaseous matter within early galaxies was converted into stars.
- It found that the earliest galaxies that were bright in radio emission were also strong in X-rays, which heated the cosmic gas in and around the early galaxies.
Click and get your FREE Copy of CURRENT AFFAIRS Micro Notes
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO to attempt 200th consecutively successful launch of RH-200 sounding rocket
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ISRO's 200th launch
Mains level: Not Much

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has attempted the 200th consecutively successful launch of the Rohini RH-200 sounding rocket from Thumba.
RH-200 (Rohini )
- RH-200 is a two-stage rocket capable of climbing to a height of 70 km bearing scientific payloads.
- The first and second stages of RH-200 are powered by solid motors. The ‘200’ in the name denotes the diameter of the rocket in mm.
- Other operational Rohini variants are RH-300 Mk-II and RH-560 Mk-III.
- For years, the RH-200 rocket had used a polyvinyl chloride (PVC)-based propellant.
- The first RH-200 to use a new propellant based on hydroxyl-terminated Polybutadiene (HTPB) was successfully flown from the TERLS in September 2020.
- The first and second stages of RH200 rocket are powered by solid motors.
- Since inception of RH200 rocket, both solid stages are processed using polyvinyl chloride (PVC) based propellant.
- As compared to PVC based propellants, HTPB based propellant is more energetic, higher mechanical & interface properties and has less defects due to lower processing temperature.
What basically is a Sounding Rocket?
- A sounding rocket is an instrument-carrying rocket designed to take measurements and perform scientific experiments during its sub-orbital flight.
- The rockets are used to launch instruments from 48 to 145 km above the surface of the Earth, the altitude generally between weather balloons and satellites.
- The maximum altitude for balloons is about 40 km and the minimum for satellites is approximately 121 km.
History of sounding rockets in India
- Sounding rockets have an important place in the ISRO story.
- The first sounding rocket to be launched from Thumba was the American Nike-Apache — on November 21, 1963.
- After that, two-stage rockets imported from Russia (M-100) and France (Centaure) were flown. The ISRO launched its own version — Rohini RH-75 — in 1967.
- The ISRO has launched more than 1,600 RH-200 rockets so far.
- Currently, the RH200, RH300 MkII and RH560 Mk-III rockets are operational which were developed during the early phase of our journey in rocketry.
Click and get your FREE Copy of CURRENT AFFAIRS Micro Notes
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Vikram-S: India’s first private sector rocket
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Vikram-S
Mains level: Privatization of space activities

India’s first privately developed rocket, Vikram-S, is set for launch between November 12 and 16.
Vikram-S
- Vikram-S is India’s first privately developed rocket and is all set to be launched as part of the Prarambh space mission.
- It is a single-stage sub-orbital launch vehicle which would carry three customer payloads and help test and validate the majority of the technologies in the Vikram series of space launch vehicles.
- It was developed by the Hyderabad-based Skyroot Aerospace.
- The Prarambh mission is aimed at carrying three payloads into space, including a 2.5-kilogram payload that has been developed by students from several countries.
- Skyroot’s launch vehicles are named ‘Vikram’ as a tribute to the founder of the Indian space program and renowned scientist Vikram Sarabhai.
Significance of the mission
- With this mission, Skyroot is set to become the first private space company in India to launch a rocket into space.
- It is heralding a new era for the space sector which was opened up in 2020 to facilitate private sector participation.
- The Prarambh mission was extensively supported from ISRO and IN-SPACe (Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre).
Back2Basics: IN-SPACE
- The establishment of IN-SPACe was announced in June 2020.
- It is an autonomous and single window nodal agency in the Department of Space for the promotion, encouragement and regulation of space activities of both government and private entities.
- It also facilitates the usage of ISRO facilities by private entities.
- It comprises technical experts for space activities along with safety expert, academic experts and legal and strategic experts from other departments.
- It also comprises members from PMO and MEA of Government of India.
Roles and Responsibilities
- Space activities including building of launch vehicles and satellites and providing space based services as per the definition of space activities.
- Sharing of space infrastructure and premises under the control of ISRO with due considerations to on-going activities.
- Establishment of temporary facilities within premises under ISRO control based on safety norms and feasibility assessment
How is it different from ANTRIX?
- Antrix Corporation Limited (ACL), Bengaluru is a wholly-owned Government of India Company under the administrative control of the Department of Space.
- It is as a marketing arm of ISRO for promotion and commercial exploitation of space products, technical consultancy services and transfer of technologies developed by ISRO.
- Antrix is engaged in providing Space products and services to international customers worldwide.
What about New Space India Limited (NSIL)?
- It functions under the administrative control of the Department of Space (DOS).
- It aims to commercially exploit the research and development work of ISRO Centres and constituent units of DOS.
- The NSIL would enable Indian Industries to scale up high-technology manufacturing and production base for meeting the growing needs of the Indian space program.
- It would further spur the growth of Indian Industries in the space sector.
Click and get your FREE Copy of CURRENT AFFAIRS Micro Notes
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO launches 36 satellites through its heaviest rocket LVM3
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: LVM3 (GSLV MK3), PSLV
Mains level: Satellite program of Indi

The ISRO’s heaviest rocket, Launch Vehicle Mark 3 (LVM3 or GSLV Mark 3) has successfully put into orbit 36 satellites of the U.K.-based OneWeb.
Also in news
- The ISRO has renamed the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) Mark -III as Launch Vehicle Mark-III, mainly to identify its task of placing satellites into a variety of orbits.
What is LVM3?
- LVM3 (erstwhile GSLV) is an expendable space launch vehicle designed, developed, and operated by the ISRO to launch satellites and other space objects into Geosynchronous Transfer Orbits.
- It is 49.13 m tall and tallest among all other vehicles of ISRO.
- It is a three-stage vehicle with a lift-off mass of 420 tonnes.
- ISRO first launched LVM3 on April 18, 2001 and has made 13 launches since then.
Stages in LVM3
- The first stage comprises S139 solid booster with 138-tonne propellant and four liquid strap-on motors, with 40-tonne propellant.
- The second stage is a liquid engine carrying 40-tonne of liquid propellant.
- The third stage is the indigenously built Cryogenic Upper Stage (CUS) carrying 15-tonne of cryogenic propellants.
Difference between PSLV and LVM3
- LVM3 has the capability to put a heavier payload in the orbit than the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV).
- PSLV can carry satellites up to a total weight of 2000 kg into space and reach up to an altitude of 600-900 km.
- LVM3 can carry weight up to 5,000 kg and reach up to 36,000 km.
- PSLV is designed mainly to deliver earth observation or remote sensing satellites, whereas, LVM3 has been designed for launching communication satellites.
- LVM3 delivers satellites into a higher elliptical orbit, Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) and Geosynchronous Earth Orbit (GEO).
Upgrades brought by LVM3
- The LVM3 is capable of lifting much heavier satellites than the GSLV Mk II with a bigger cryogenic upper stage and a larger first stage.
- Both GSLV Mk II and LVM3 are three-stage vehicles, while the PSLV, which launches to low earth polar orbits, is a four-stage vehicle.
- The GSLV Mk-II can place up to 2,500kg in geosynchronous orbits and up to 5,000kg to low earth orbit.
- By comparison, the LVM3 can lift 4,000kg to GTO and up to 8,000 kg to LEO.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO proposes Bharat Krishi Satellite Programme Copy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Krishi Satellite Program
Mains level: Space applications for agriculture

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has proposed dedicated satellites for supporting the country’s agriculture sector.
Bharat Krishi Satellite Programme
- Minimum of two satellites are stipulated to guarantee adequate coverage of the entire agricultural area of the country.
- They will aid a gamut of farm-related activities related to crop forecasting, pesticide application, irrigation, soil data, and generation of critical data related to drought.
- The satellites will be owned by the Department of Agriculture and not by ISRO. The ISRO will provide the technical support.
- An ‘Earth Observation Council’ be created for addressing the current deficiencies in earth observation capabilities and data utilisation.
- Such a council can tackle shortcomings in this area in a centralised manner.
Why need such program?
Current deficiencies include:
- Discontinuity in earth observation missions
- Low utilisation of available remote sensing data
- Technology gaps and
- Absence of a streamlined mechanism for data processing and dissemination as required by the industry
Applications of space for agriculture

Satellites in use
| Satellite Type | Satellite | Objectives |
| Multispectral imaging satellite | Resourcesat-2 & Resourcesat-2A | Multispectral imaging for crop production forecast, land, water and natural resource inventory and management, and disaster management support |
| Cartography satellite | Cartosat-1 | High resolution cartographic mapping, digital elevation mapping – drainage and irrigation networks, topographic mapping and contouring |
| Radar imaging | RISAT-1 | All weather imaging capability targeted for kharif crop (June to November) during south-west and north-east monsoon seasons. Flood and natural disaster management |
| Meteorological forecasting | Kalpana-1 | Comprehensive weather status reporting and forecasting |
| Meteorological observation | INSAT-3D & INSAT-3DR | Improved meteorological observations including vertical – temperature and humidity–atmosphere weather forecasting and disaster warning |
Issues in harmonizing space technology
- India’s satellite data is sequestered within the government.
- The private sector has limited access to it, even though it plays an increasing role in the country’s agriculture value chain.
Various govt programs
- Following are some of the programs that are functioning in full spirit-
- In 2017, these insular projects were integrated into a single entity, the National Programme on use of Space Technology for Agriculture (NPSTA).
| NPSTA Constituent Programmes | Goals of the constituent Programme | |
| National Programme on use of Space Technology for Agriculture (NPSTA) | Forecasting Agricultural output using Space, Agro-meteorology and Land-based observations (FASAL) | Crop Forecasting |
| National Agricultural Drought Assessment and Monitoring Systems (NADAMS) | Drought Assessment | |
| Coordinated programme on Horticulture Assessment and Management using Geoinformatics (CHAMAN) | Horticulture assessment and development | |
| C(K)rop Insurance using Space technology and Geoinformatics (KISAN) now incorporated into Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojna | Crop Insurance |
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO proposes Bharat Krishi Satellite Programme Copy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Krishi Satellite Program
Mains level: Space applications for agriculture

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has proposed dedicated satellites for supporting the country’s agriculture sector.
Bharat Krishi Satellite Programme
- Minimum of two satellites are stipulated to guarantee adequate coverage of the entire agricultural area of the country.
- They will aid a gamut of farm-related activities related to crop forecasting, pesticide application, irrigation, soil data, and generation of critical data related to drought.
- The satellites will be owned by the Department of Agriculture and not by ISRO. The ISRO will provide the technical support.
- An ‘Earth Observation Council’ be created for addressing the current deficiencies in earth observation capabilities and data utilisation.
- Such a council can tackle shortcomings in this area in a centralised manner.
Why need such program?
Current deficiencies include:
- Discontinuity in earth observation missions
- Low utilisation of available remote sensing data
- Technology gaps and
- Absence of a streamlined mechanism for data processing and dissemination as required by the industry
Applications of space for agriculture

Satellites in use
| Satellite Type | Satellite | Objectives |
| Multispectral imaging satellite | Resourcesat-2 & Resourcesat-2A | Multispectral imaging for crop production forecast, land, water and natural resource inventory and management, and disaster management support |
| Cartography satellite | Cartosat-1 | High resolution cartographic mapping, digital elevation mapping – drainage and irrigation networks, topographic mapping and contouring |
| Radar imaging | RISAT-1 | All weather imaging capability targeted for kharif crop (June to November) during south-west and north-east monsoon seasons. Flood and natural disaster management |
| Meteorological forecasting | Kalpana-1 | Comprehensive weather status reporting and forecasting |
| Meteorological observation | INSAT-3D & INSAT-3DR | Improved meteorological observations including vertical – temperature and humidity–atmosphere weather forecasting and disaster warning |
Issues in harmonizing space technology
- India’s satellite data is sequestered within the government.
- The private sector has limited access to it, even though it plays an increasing role in the country’s agriculture value chain.
Various govt programs
- Following are some of the programs that are functioning in full spirit-
- In 2017, these insular projects were integrated into a single entity, the National Programme on use of Space Technology for Agriculture (NPSTA).
| NPSTA Constituent Programmes | Goals of the constituent Programme | |
| National Programme on use of Space Technology for Agriculture (NPSTA) | Forecasting Agricultural output using Space, Agro-meteorology and Land-based observations (FASAL) | Crop Forecasting |
| National Agricultural Drought Assessment and Monitoring Systems (NADAMS) | Drought Assessment | |
| Coordinated programme on Horticulture Assessment and Management using Geoinformatics (CHAMAN) | Horticulture assessment and development | |
| C(K)rop Insurance using Space technology and Geoinformatics (KISAN) now incorporated into Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojna | Crop Insurance |
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO proposes Bharat Krishi Satellite Programme
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Krishi Satellite Program
Mains level: Space applications for agriculture

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has proposed dedicated satellites for supporting the country’s agriculture sector.
Bharat Krishi Satellite Programme
- Minimum of two satellites are stipulated to guarantee adequate coverage of the entire agricultural area of the country.
- They will aid a gamut of farm-related activities related to crop forecasting, pesticide application, irrigation, soil data, and generation of critical data related to drought.
- The satellites will be owned by the Department of Agriculture and not by ISRO. The ISRO will provide the technical support.
- An ‘Earth Observation Council’ be created for addressing the current deficiencies in earth observation capabilities and data utilisation.
- Such a council can tackle shortcomings in this area in a centralised manner.
Why need such program?
Current deficiencies include:
- Discontinuity in earth observation missions
- Low utilisation of available remote sensing data
- Technology gaps and
- Absence of a streamlined mechanism for data processing and dissemination as required by the industry
Applications of space for agriculture

Satellites in use
| Satellite Type | Satellite | Objectives |
| Multispectral imaging satellite | Resourcesat-2 & Resourcesat-2A | Multispectral imaging for crop production forecast, land, water and natural resource inventory and management, and disaster management support |
| Cartography satellite | Cartosat-1 | High resolution cartographic mapping, digital elevation mapping – drainage and irrigation networks, topographic mapping and contouring |
| Radar imaging | RISAT-1 | All weather imaging capability targeted for kharif crop (June to November) during south-west and north-east monsoon seasons. Flood and natural disaster management |
| Meteorological forecasting | Kalpana-1 | Comprehensive weather status reporting and forecasting |
| Meteorological observation | INSAT-3D & INSAT-3DR | Improved meteorological observations including vertical – temperature and humidity–atmosphere weather forecasting and disaster warning |
Issues in harmonizing space technology
- India’s satellite data is sequestered within the government.
- The private sector has limited access to it, even though it plays an increasing role in the country’s agriculture value chain.
Various govt programs
- Following are some of the programs that are functioning in full spirit-
- In 2017, these insular projects were integrated into a single entity, the National Programme on use of Space Technology for Agriculture (NPSTA).
| NPSTA Constituent Programmes | Goals of the constituent Programme | |
| National Programme on use of Space Technology for Agriculture (NPSTA) | Forecasting Agricultural output using Space, Agro-meteorology and Land-based observations (FASAL) | Crop Forecasting |
| National Agricultural Drought Assessment and Monitoring Systems (NADAMS) | Drought Assessment | |
| Coordinated programme on Horticulture Assessment and Management using Geoinformatics (CHAMAN) | Horticulture assessment and development | |
| C(K)rop Insurance using Space technology and Geoinformatics (KISAN) now incorporated into Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojna | Crop Insurance |
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Next-Gen Launch Vehicle- NGLV to assume PSLV’s role
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NGLV, PSLV, SSLV, GSLV
Mains level: Not Much
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is developing a Next-Gen Launch Vehicle (NGLV), which will one day replace operational systems like the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV).
What is the news?
- PSLV, often dubbed the ‘trusted workhorse’, “will have to retire” one day, said ISRO chairman.
What is NGLV?
- NGLV will feature a simple, robust design that allows bulk manufacturing, modularity in systems, sub-systems and stages and minimal turnaround time.
- Potential uses will be in the areas of launching communication satellites, deep space missions, future human spaceflight and cargo missions.
What all modifications would be required?
- In NGLV, ISRO is understood to be looking at a cost-efficient, three-stage, reusable heavy-lift vehicle with a payload capability of 10 tonnes to Geostationary Transfer Orbit (GTO).
- NGLV will feature semi-cryogenic propulsion for the booster stages which is cheaper and efficient.
- For that, at least 10 tonne capability to GTO is needed.
- Correspondingly, the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) capability will be twice that.
- However, payload capability will be lower when the rocket is reusable.
Back2Basics: Various satellite launch vehicles in India

UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
India’s Space economy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: INSPACE, NSIL
Mains level: India's space economy
India’s space economy is likely to be worth nearly $13 billion by 2025, with the satellite launch services segment set to witness the fastest growth due to increasing private participation.
About the report
- The report is released by the Indian Space Association (ISpA) and Ernst & Young.
- It says that the growing demand for smaller satellites is set to boost satellite manufacturing in the country.
- It will attract global start-ups in the sector to help incubate space tech companies to India.
Key highlights
- India’s space economy was pegged at $9.6 billion in 2020 and is expected to touch $12.8 billion by 2025.
- In dollar terms, the satellite services and applications segment would be the largest with a turnover of $4.6 billion by 2025, followed by the ground segment at $4 billion.
- Satellite manufacturing stands at $3.2 billion and launch services at $1 billion.
- The launch services segment was pegged at $600 million in 2020 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 13 percent to reach $1 billion by 2025.
Key drivers of this demand
- India has of over 100 space tech start-ups with investments in the segment touching $68 million in 2021.
- The availability of low-cost satellite launch vehicles coupled with mass production will lead to demand from customers around the world.
- Several companies are utilising cutting-edge technologies to develop innovative launch solutions in India.
Where does India stand in the global space market?
- As per SpaceTech Analytics, India is the sixth-largest player in the industry internationally having 3.6% of the world’s space-tech companies (as of 2021).
- US holds the leader’s spot housing 56.4% of all companies in the space-tech ecosystem.
- Other major players include UK (6.5%), Canada (5.3%), China (4.7%) and Germany (4.1%).
- The Indian Space Industry was valued at $7 billion in 2019 and aspires to grow to $50 billion by 2024.
Why does India matter in the global space-tech market?
- The country’s standout feature is its cost-effectiveness.
- India holds the distinction of being the first country to have reached the Mars’ orbit in its first attempt and at $75 million — way cheaper than Western standards.
Future prospects of India’s private ‘Space’
Ans. India may lead in space junk management
- Almost 60-odd start-ups had registered with the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) this year.
- A majority of them were dealing in projects related to space debris management.
- As space becomes more congested with satellites, the technology would thus help in managing ‘space junk’ (debris of old spacecraft and satellites).
How is the private sector’s involvement regulated in India?
- In June 2020, the Union government announced reforms in the space sector enabling more private players to provide end-to-end services.
- The central idea was to bring forth a predictable policy and regulatory environment for them and additionally provide access to ISRO facilities and assets to improve their capacities.
(1) Establishment of IN-SPACe
- An announcement for the establishment of the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) was made.
- It was mandated the task of promoting, authorising and licensing private players to carry out space activities.
- As an oversight and regulatory body, it is responsible for devising mechanisms to offer sharing of technology, expertise, and facilities free of cost to promote non-government private entities (NGPEs).
- IN-SPACe’s Monitoring and Promotion Directorate oversees NGPE’s activities as per prescribed regulations and reports back in case any corrective actions or resolutions are required.
- ISRO shares its expertise in matters pertaining to quality and reliability protocols, documentation, and testing procedure through IN-SPACe’s ‘interface mechanism’.
(2) Establishment of NSIL
- Additionally, constituted in March 2019, New Space India Ltd (NSIL), is mandated to transfer the matured technologies developed by the ISRO to Indian industries.
- All of them are under the purview of the Ministry of Defence.
- Private sector’s involvement in the long term, as with other commercial sectors, is believed to help spur investment and expertise in the realm which is capital-intensive and demands high technology.
Where does India lack?
Ans. Undisputedly, it is the finances
- The US and Canada were the highest receivers of space-related investment in 2021.
- The US’s space budget was $41 billion in 2021, $23.3 billion of which was focused on NASA.
- India’s total budgetary allocation for FY2022-23 towards the Department of Space was ₹13,700 crore ($172 million).
- Further, as per Tracxn data, funding into the sector’s start-ups (in India) nearly tripled to $67.2 million on a year-over-year basis in 2021.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Private: Chandrayaan-2 gauges sodium content on Moon’s surface
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Chandrayaan-2
Mains level: Not Much

Scientists from ISRO have mapped out the global distribution of sodium on the Moon’s surface using the CLASS instrument (Chandrayaan-2 large area soft X-ray spectrometer) onboard of the Chandrayaan-2 mission.
Why in news now?
- This is the first effort to provide a global-scale measurement of sodium on the lunar surface using X-ray fluorescent spectra.
Chandrayaan-2: A quick recap
- Chandrayaan-2 consisted of an Orbiter, Lander and Rover, all equipped with scientific instruments to study the moon.
- The Orbiter would watch the moon from a 100-km orbit, while the Lander and Rover modules were to be separated to make a soft landing on the moon’s surface.
- ISRO had named the Lander module as Vikram, after Vikram Sarabhai, the pioneer of India’s space programme, and the Rover module as Pragyaan, meaning wisdom.
- The Orbiter part of the mission has been functioning normally. It is carrying eight instruments.
- Each of these instruments has produced a handsome amount of data that sheds new light on the moon and offers insights that could be used in further exploration.
What is X-Ray Fluorescence?
- It is commonly used to study the composition of materials in a non-destructive manner.
- When the sun gives out solar flares, a large amount of X-ray radiation falls on the moon, triggering X-ray fluorescence.
- The CLASS measures the energy of the X-ray photons coming from the moon and counts the total number.
- The energy of the photons indicates the atom (for instance, sodium atoms emit X-ray photons of 1.04 keV) and the intensity is a measure of how many atoms are present.
How is it related to the history of moon?
- Sodium can be used as a tracer of the volatile history of the moon.
- When compared to Earth, the moon is significantly depleted of volatile elements such as sodium.
- The amount of volatiles on the moon today can be used to test formation scenarios of the Earth-Moon system.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
India’s Dark Sky Reserve
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Dark Sky Reserve
Mains level: Science tourism
 Context
Context
- The union territory of Ladakh will host India’s first Dark Sky Reserve which will be set up in Hanle area in the next three months. The Dark Sky Reserve is being built as part of Ladakh’s high-altitude Changthang Wildlife Sanctuary.
What is Dark Sky Reserve (DSR)?
- Definition of Dark Sky Reserve: The International Dark Sky Association (IDSA) defines an international dark sky reserve (IDSR) as “a public or private land of substantial size (at least 700 km², or about 173,000 acres) possessing an exceptional or distinguished quality of starry nights and nocturnal environment, and that is specifically protected for its scientific, natural, educational, cultural heritage, and/or public enjoyment.
What is Core Area of Dark Sky Reserve?
- A dark sky reserve requires a “core” area that has clear sky without any light pollution, which can enable telescopes to see the sky in its natural darkness.
Why Ladakh is chosen as ideal location for DSR?
- Ladakh is ideal for long-term observatories and dark-sky sites because of its large arid area, high elevation, and sparse population, extreme cold and minimum temperature drops to minus 40 degree celcius.
- The Changthang wildlife Sanctuary, the DSR site is situated around 4,500 metres above sea level, which makes it a perfect host for telescopes.
Who is managing India’s DSR?
- The Department of Science and Technology and Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) in Bengaluru are providing support for the facility. The IIA already manages the Indian Astronomical Observatory (IAO) complex in Hanle, Ladakh.
What are the International standards for DSR?
- International Dark Sky Association’s Recognition: The IDSA recognizes and accredits dark-sky areas worldwide, in three categories. The Mont Mégantic Observatory in Quebec is the first such site to be recognized (in 2007) as an International Dark Sky Reserve.
- Categorical Certification: Individuals or groups can nominate a site for certification to the International Dark Sky Association (IDSA). There are five designated categories, namely International Dark Sky parks, communities, reserves, sanctuaries and Urban Night Sky Places.
- Global Recognition: The certification process is similar to that of a site being awarded the UNESCO World Heritage Site tag or getting recognised as a Biosphere Reserve. Between 2001 and January 2022, there have been 195 sites recognised as International Dark Sky Places globally, the IDSA said.
- Dark Sky Park: IDSA recognized Natural Bridges National Monument in Utah as the world’s first International Dark Sky Park.
- Dark Sky Sanctuary: In 2015, the IDSA introduced the term “Dark Sky Sanctuary” and designated the Elqui Valley of northern Chile as the world’s first International Dark Sky Sanctuary. The Gabriela Mistral Dark Sky Sanctuary is named after a Chilean poet.
 What is India’s objective with DSR?
What is India’s objective with DSR?
- To promote AstroTourism: The primary objective of the proposed Dark Sky Reserve is to promote astronomy tourism in a sustainable and environment-friendly manner. Scientific methods will be used here to preserve the night sky from ever-increasing light pollution.
- To offer clear skies for observations: With metros, cities and peripheral areas experiencing light pollution and remaining constantly lit up, there are diminishing areas that offer a view of clear skies on cloudless nights.
- For training purpose: In the pilot phase, the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA),has procured ten small and easy-to-handle telescopes and light-reflecting shields. IIA’s scientists and outreach experts will identify locals and train them to use these telescopes.
- Sky gazing and a boost for village economy: This will include basic sky gazing, identification of constellations, and locating the pole star, among others. These telescopes will be installed at the homestays, which is a popular option for tourist accommodation in Ladakh.
 Conclusion
Conclusion
- The Dark Sky Reserve is likely to boost Astro tourism in India where there has been no such reserve. Once set up, the reserve will be the highest-located site in the country for infrared, gamma-ray, and optical telescopes.
Mains Question
Q. What are the Dark Sky Reserves? How DRS will help in astronomical research and observations in India?
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Vyommitra Humanoid to undergo pre-flight tests
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Vyommitra, Gaganyaan Mission
Mains level: Not Much

Vyommitra, the humanoid designed and developed by the ISRO to fly aboard unmanned test missions ahead of the Gaganyaan human space-flight mission, is undergoing pre-flight ground tests at the ISRO Inertial Systems Unit (IISU).
Vyommitra
- The AI-based robotic system is developed at a robotics lab at the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) at Thumba, Thiruvananthapuram.
- Vyommitra will be used for an unmanned flight of ISRO’s GSLV III rocket in December 2020, which, along with a second unmanned flight in July 2021.
- This will serve as the test of ISRO’s preparedness for its maiden manned space mission, Gaganyaan, being targeted for 2022 to mark 75 years of India’s independence.
Functions of the humanoid
- Vyommitra, equipped with a head, two arms and a torso, is built to mimic crew activity inside the crew module of Gaganyaan.
- Attaining launch and orbital postures, responding to the environment, generating warnings, replacing carbon dioxide canisters, and operating switches, monitoring of the crew module, receiving voice commands, and responding via speech (bilingual) are among the functions listed.
- It will have a human-like face, with lips synchronized for movement to mimic speech.
- Once it is fully developed, Vyommitra will be able to use the equipment on board the spacecraft’s crew module, like safety mechanisms and switches, as well as receive and act on commands sent from ground stations.
What is the recent development?
- The IISU has successfully integrated it with a computer “brain”, which enables it to “read” control panels aboard the unmanned test flights and communicate with the ISRO ground stations.
- It has a certain level of intelligence.
- It is intended to operate and read the display panels and communicate back to ground station using its own voice.
Back2Basics: Gaganyaan Mission
- Gaganyaan is crewed orbital spacecraft intended to be the formative spacecraft of the Indian Human Spaceflight Programme (IHSP).
- The IHSP was initiated in 2007 by ISRO to develop the technology needed to launch crewed orbital spacecraft into low Earth orbit.
- ISRO had been working on related technologies and it performed a Crew Module Atmospheric Re-entry Experiment and a Pad Abort Test for the mission.
- If completed in meantime, India will become the fourth nation to conduct independent human spaceflight after Russia, US, and China.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Satellite Broadband Services in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Satellite broadband
Mains level: Read the attached story

The race for providing satellite broadband connectivity in India is heating up as companies like Jio, Oneweb, Hughes and Tata-backed Nelco are preparing to provide these services.
Recent developments on satellite broadband
- Earlier last month, Hughes Communications India (HCI), a satellite internet service provider launched India’s first high throughput satellite (HTS) broadband service powered by ISRO satellites.
- It used Ku-band capacity from ISRO GSAT-11 and GSAT-29 satellites with Hughes JUPITER Platform ground technology to deliver high-speed broadband.
What is a Satellite Broadband Service?
- Broadband essentially means a wide bandwidth, high-capacity data transmission technique, using a broad range of frequencies.
- In the case of a satellite broadband service, broadband services are delivered directly via satellites instead of optical fibre or mobile networks.
How is it different from existing broadband services?
(1) Transmission of data over space
- The main difference is that aggregation of all the data generated and transmitted by users accessing the internet happens in the sky or space that is in the satellite.
- In contrast to this, if we take a look at cellular networks, aggregation happens on the ground, in the base stations through optical fibre, cable, etc.
(2) Access to the services
- Another key difference is that to access satellite services, we will need a dish antenna just like we do in the case of TV services, so a normal mobile handset cannot directly access satellite broadband.
- For a user to access satellite broadband a clear line of sight to the satellite is needed.
Advantages offered
- Speed: The main advantage of satellite services is that you can provide high-speed internet services in remote areas, where terrestrial networks cannot be set up.
- Eliminating terrain shortcomings: For instance in the middle of the ocean, in rugged unreachable terrain such as the Himalayas — even as remote as on top of Mt. Everest, satellite broadband will work.
- Curbing the divide: In a country with a wide range of geographies such as India, 20-25 per cent of the Indian population resides in areas where it is extremely hard for terrestrial operators to install internet facilities.
Present scope in India
- Currently, VSAT operators offer satellite broadband services at a very limited capacity in India in a few remote locations.
- The utilisation of satellite services for broadband services is restricted to minimal applications — such as disaster management, defence, scientific locations, etc.
How India (undoubtedly, the ISRO) has geared up for adapting to this?
- ISRO’s high throughput GEO (Geostationary Equatorial Orbit) satellites – GSAT-11 and GSAT-29 a few years ago, can beam high-speed internet up to 300 gigabytes per second.
- Apart, many global players look to provide satellite broadband services in India by deploying low earth orbit (LEO) satellites.
- They are launching a constellation of satellites very close to the earth’s surface in order to reduce the latency of satellite broadband.
- Presently, Elon Musk’s Starlink, Sunil Bharti Mittal-backed OneWeb and the Canadian satellite major Telesat are eyeing the Indian market.
When will these services be available in India?
- If things go as planned and the players get the necessary regulatory clearance, these services could become operational in India as soon as next year.
- OneWeb wants to provide backhaul services to telcos by mid-next year, while Starlink wants to provide direct broadband services by December 2022, aiming at 2 lakh terminals.
- Telesat, on the other hand, is eyeing an India launch by 2024.
How much will it cost?
- The provision of direct broadband services through satellites will be pricey.
- According to a user guide for India, provided by Starlink, the first-year cost of a Starlink terminal will be ₹1,58,000 after which it will cost around ₹1,15,000 every year.
Has it been rolled out in other parts of the world?
- Starlink is operational in 14 countries, with 1 lakh terminals shipped to North America and Europe.
- Starlink and OneWeb are still launching satellites that will be a part of their LEO constellation.
What are the major hurdles?
- Latency: Additionally, satellite Internet latency can be a significant problem. This can be a matter of only a second or two, but a delay on that scale can seriously affect real-time applications like video chats.
- Spatial hurdles: Users might not be able to connect to a satellite at all if they are located under heavy foliage or surrounded by other obstructions.
- Limited bandwidth: Satellite data transfer provides very slow Internet speeds and limited satellite bandwidth because of the distances the signals have to travel and all the potential obstacles in between.
- Connection times: This can also be impacted by your surroundings, the length of your message, and the status and availability of the satellite network.
- High input cost: This along with the complex equipment like satellite dishes being used to avail these services makes the service expensive.
Perspective analysis: Why is India itself lagging in this race?
- Globally, companies are striving to build and deploy “mega-constellations” of hundreds or thousands of satellites for this.
- Despite India’s impressive achievements in the space sector, growth has been at snail’s pace.
- Satellite broadband services in India remains primarily for the B2B sector with a market size of roughly $100 million.
Reason’s for India’s slow pace
- Upgrade issues: The Indian networks are still using conventional satellites despite the proliferation of high throughput satellites world-over.
- Lack of domestic industries: There is a lack of domestic participation for building space infrastructure despite ‘Make in India’ mission.
Way forward
- An urgent re-look at deregulation and privatization is required.
- Advanced space-faring nations have privatized most of these blocks in the value chain.
- There is a need for building systems to help nurture the industry and create an extensive ecosystem to generate a ‘Space 2.0’ in India.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Rohini RH-200: ISRO eyeing 200th successful launch of Rohini RH-200
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Rohini
Mains level: Not Much

In a few weeks’ time, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) hopes to achieve a remarkable feat — the 200th successful launch of the Rohini RH-200 sounding rocket in a row.
Rohini RH-200
- RH-200 is a two-stage rocket capable of climbing to a height of 70 km bearing scientific payloads.
- The first and second stages of RH-200 are powered by solid motors. The ‘200’ in the name denotes the diameter of the rocket in mm.
- Other operational Rohini variants are RH-300 Mk-II and RH-560 Mk-III.
- For years, the RH-200 rocket had used a polyvinyl chloride (PVC)-based propellant.
- The first RH-200 to use a new propellant based on hydroxyl-terminated Polybutadiene (HTPB) was successfully flown from the TERLS in September 2020.
- The first and second stages of RH200 rocket are powered by solid motors.
- Since inception of RH200 rocket, both solid stages are processed using polyvinyl chloride (PVC) based propellant.
- As compared to PVC based propellants, HTPB based propellant is more energetic, higher mechanical & interface properties and has less defects due to lower processing temperature.
What basically is a Sounding Rocket?
- A sounding rocket is an instrument-carrying rocket designed to take measurements and perform scientific experiments during its sub-orbital flight.
- The rockets are used to launch instruments from 48 to 145 km above the surface of the Earth, the altitude generally between weather balloons and satellites.
- The maximum altitude for balloons is about 40 km and the minimum for satellites is approximately 121 km.
History of sounding rockets in India
- Sounding rockets have an important place in the ISRO story.
- The first sounding rocket to be launched from Thumba was the American Nike-Apache — on November 21, 1963.
- After that, two-stage rockets imported from Russia (M-100) and France (Centaure) were flown. The ISRO launched its own version — Rohini RH-75 — in 1967.
- The ISRO has launched more than 1,600 RH-200 rockets so far.
- Currently, the RH200, RH300 MkII and RH560 Mk-III rockets are operational which were developed during the early phase of our journey in rocketry.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Centre’s push for NavIC System
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NAVIC, IRNSS, GPS
Mains level: Read the attached story

The Union government is pushing tech giants to make smartphones compatible with its home-grown navigation system ‘NavIC’.
What is NavIC?
- NavIC, or Navigation with Indian Constellation, is an independent stand-alone navigation satellite system developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- NavIC was originally approved in 2006 at a cost of $174 million.
- It was expected to be completed by late 2011, but only became operational in 2018.
- NavIC consists of eight satellites and covers the whole of India’s landmass and up to 1,500 km (930 miles) from its boundaries.
Note: The numbers of satellites in this constellation is disputed. It is given as 7 and 8 on different sources. Total Nine satellites were launched out of which the very first (IRNSS-1A) is partially failed because of some issue in its Atomic Clock. Another and the last satellite had a launch failure. Hence the number 7/8.
Why is the Centre pushing for NavIC?
- Currently, NavIC’s use is limited.
- It is being used in public vehicle tracking in India.
- It helps providing emergency warning alerts to fishermen venturing into the deep sea where there is no terrestrial network connectivity, and for tracking and providing information related to natural disasters.
- Enabling it in smartphones is the next step India is pushing for.
- India’s 2021 satellite navigation draft policy stated the government will work towards expanding the coverage from regional to global to ensure availability of NavIC signal in any part of the world.
How does NavIC compare?
- The main difference is the serviceable area covered by these systems.
- GPS caters to users across the globe and its satellites circle the earth twice a day, while NavIC is currently for use in India and adjacent areas.
- Like GPS, there are three more navigation systems that have global coverage – Galileo from the European Union, Russia-owned GLONASS and China’s Beidou.
- QZSS, operated by Japan, is another regional navigation system covering Asia-Oceania region, with a focus on Japan.
Strategic significance of NavIC
- India says NavIC is conceived with the aim of removing dependence on foreign satellite systems for navigation service requirements, particularly for “strategic sectors.”
- Relying on systems like GPS and GLONASS may not always be reliable, India says, as those are operated by the defence agencies of respective nations.
- It is possible that civilian services can be degraded or denied.
- NavIC is an indigenous positioning system that is under Indian control.
- There is no risk of the service being withdrawn or denied in a given situation.
Try this PYQ:
Q. With reference to the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), consider the following statements:
- IRNSS has three Satellites in geostationary and four satellites the geosynchronous orbits.
- IRNSS covers entire India and about 5500 sq. km beyond its borders.
- India will have its own satellite navigation system with full global coverage by the middle of 2019.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) None
Answer:
(Post it here.)
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO tests system recoverable rocket ‘Inflatable Aerodynamic Decelerator (IAD)’
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Inflatable Aerodynamic Decelerator (IAD)
Mains level: Not Much

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully tested a technology that could aid the cost-effective recovery of spent rocket stages and safely land payloads on other planets.
What is IAD?
- IAD is a technique used for an atmospheric entry payload.
- An inflatable envelope and an inflatant (anything that inflates the envelope, like air or helium) make up the inflatable aerodynamic decelerator.
- While entering the atmosphere, it inflates like a balloon and decelerates the lander.
- The inflatant is designed to fill the inflatable envelope to a condition such that it surrounds the payload meant to enter the atmosphere of a planet or satellite and causes aerodynamic forces to slow it down.
- In simpler words, IAD is designed to increase drag upon entering the atmosphere of any planetary body, like Earth, Mars, or even Moon.
- Its shape is maintained by a closed, gas-pressured body and the inflatant gas is also generated internally. Some versions also use ram air or both.
How significant is this IAD?
- Some space agencies, including NASA, have already successfully tested advanced versions of the technology, including the supersonic and hypersonic variants.
- However, for near future missions of ISRO, the current version that it tested is perfect.
- Its use was first proposed by NASA more than 50 years ago for planetary entries.
Minuscule of ISRO’s IAD
- The IAD tested by ISRO was inflated at an altitude of around 84 km and the sounding rocket’s cargo dropped through the atmosphere on it.
- It is fitted with a booster motor. It also has a spin rocket that is ejectable.
- The inflatable structure is made out of Kevlar fabric, which is a very strong synthetic fibre and also heat resistant to withstand atmospheric pressure and temperature changes.
- On top of it, it’s coated with polychloroprene, an oil and wax resistant rubber, to withstand extreme temperatures.
- In the inflation system, it uses compressed nitrogen stored in a bottle.
- It has consistently decreased the payload’s velocity through aerodynamic drag while maintaining the expected trajectory during the test flight.
Where does ISRO intend to use it?
- The IAD will help ISRO in performing many space tasks effectively including recovery of spent stages of rockets, for landing payloads on missions to other planetary bodies.
- This is the first instance where an IAD has been specially created for spent stage recovery.
- So inter-planetary missions are certainly one aspect that ISRO wishes to explore.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
India’s first Dark Sky Reserve to come up in Ladakh
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Dark Sky Reserve
Mains level: Not Much

In a first-of-its-kind initiative, the Department of Science & Technology (DST) has announced the setting up of India’s first dark sky reserve at Hanle in Ladakh in the next three months.
What is a Dark Sky Reserve?
- A dark-sky reserve is an area, usually surrounding a park or observatory that is kept free of artificial light pollution.
- The purpose of a dark sky preserve is generally to promote astronomy.
- Because different national organizations have worked independently to create their programs, different terms have been used to describe the areas.
How is it designated?
- A dark sky reserve is a designation given to a place that has policies in place to ensure that a tract of land or region has minimal artificial light interference.
- The International Dark Sky Association is a US-based non-profit that designates sites as international dark sky places, parks, sanctuaries and reserves, depending on the criteria they meet.
- Several such reserves exist around the world but none so far in India.
Dark Sky Reserve at Hanle
- Hanle, which is about 4,500 metres above sea level, hosts telescopes and is regarded as one of the world’s most optimal sites for astronomical observations.
- However, ensuring that the site remains well-suited for astronomy implies keeping the night sky pristine, or ensuring minimal interference to the telescopes from artificial light sources such as electric lights and vehicular lights from the ground.
- The site will have activities to help in boosting local tourism and economy through interventions of science and technology.
The Himalayan Chandra Telescope, High Energy Gamma Ray Telescope, Major Atmospheric Cherenkov Experiment Telescope and GROWTH-India are the prominent telescopes located at the Hanle observatory.
Ideal conditions in India
- The Indian Astronomical Observatory, the high-altitude station of the IIA, is situated to the north of Western Himalayas, at an altitude of 4,500 metres above mean sea level.
- Located atop Mt. Saraswati in the Nilamkhul Plain in the Hanle Valley of Changthang, it is a dry, cold desert with sparse human population.
- The cloudless skies and low atmospheric water vapour make it one of the best sites in the world for optical, infrared, sub-millimetre, and millimetre wavelengths.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) launched into wrong Orbit
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SSLV, PSLV, GSLV
Mains level: Not Much

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has said that the satellite onboard its’ maiden Small Satellite Launch Vehicle “are no longer usable” after the SSLV-D1 placed them in an elliptical orbit instead of a circular one.
What is SSLV?
- The SSLV is a small-lift launch vehicle being developed by the ISRO with payload capacity to deliver:
- 600 kg to Low Earth Orbit (500 km) or
- 300 kg to Sun-synchronous Orbit (500 km)
- It would help launching small satellites, with the capability to support multiple orbital drop-offs.
- In future a dedicated launch pad in Sriharikota called Small Satellite Launch Complex (SSLC) will be set up.
- A new spaceport, under development, near Kulasekharapatnam in Tamil Nadu will handle SSLV launches when complete.
- After entering the operational phase, the vehicle’s production and launch operations will be done by a consortium of Indian firms along with NewSpace India Limited (NSIL).
Vehicle details
(A) Dimensions
- Height: 34 meters
- Diameter: 2 meters
- Mass: 120 tonnes
(B) Propulsion
- It will be a four stage launching vehicle.
- The first three stages will use Hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene (HTPB) based solid propellant, with a fourth terminal stage being a Velocity-Trimming Module (VTM).
SSLV vs. PSLV: A comparison
- The SSLV was developed with the aim of launching small satellites commercially at drastically reduced price and higher launch rate as compared to Polar SLV (PSLV).
- The projected high launch rate relies on largely autonomous launch operation and on overall simple logistics.
- To compare, a PSLV launch involves 600 officials while SSLV launch operations would be managed by a small team of about six people.
- The launch readiness period of the SSLV is expected to be less than a week instead of months.
- The SSLV can carry satellites weighing up to 500 kg to a low earth orbit while the tried and tested PSLV can launch satellites weighing in the range of 1000 kg.
- The entire job will be done in a very short time and the cost will be only around Rs 30 crore for SSLV.
Significance of SSLV
- SSLV is perfectly suited for launching multiple microsatellites at a time and supports multiple orbital drop-offs.
- The development and manufacture of the SSLV are expected to create greater synergy between the space sector and private Indian industries – a key aim of the space ministry.
Back2Basics: Various Orbits of Satellites
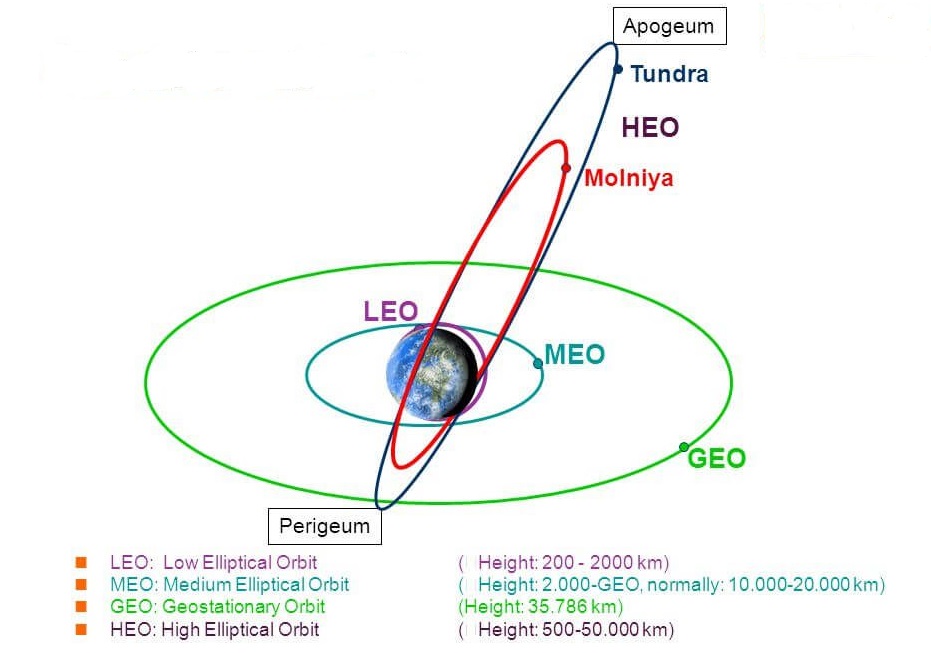
[1] Geostationary orbit (GEO)
- Satellites in geostationary orbit (GEO) circle Earth above the equator from west to east following Earth’s rotation – taking 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds – by travelling at exactly the same rate as Earth.
- This makes satellites in GEO appear to be ‘stationary’ over a fixed position.
- In order to perfectly match Earth’s rotation, the speed of GEO satellites should be about 3 km per second at an altitude of 35 786 km.
- This is much farther from Earth’s surface compared to many satellites.
- GEO is used by satellites that need to stay constantly above one particular place over Earth, such as telecommunication satellites.
- Satellites in GEO cover a large range of Earth so as few as three equally-spaced satellites can provide near-global coverage.
[2] Low Earth orbit (LEO)
- A low Earth orbit (LEO) is, as the name suggests, an orbit that is relatively close to Earth’s surface.
- It is normally at an altitude of less than 1000 km but could be as low as 160 km above Earth – which is low compared to other orbits, but still very far above Earth’s surface.
- Unlike satellites in GEO that must always orbit along Earth’s equator, LEO satellites do not always have to follow a particular path around Earth in the same way – their plane can be tilted.
- This means there are more available routes for satellites in LEO, which is one of the reasons why LEO is a very commonly used orbit.
- It is most commonly used for satellite imaging, as being near the surface allows it to take images of higher resolution.
- Satellites in this orbit travel at a speed of around 7.8 km per second; at this speed, a satellite takes approximately 90 minutes to circle Earth.
[3] Medium Earth orbit (MEO)
- Medium Earth orbit comprises a wide range of orbits anywhere between LEO and GEO.
- It is similar to LEO in that it also does not need to take specific paths around Earth, and it is used by a variety of satellites with many different applications.
- It is very commonly used by navigation satellites, like the European Galileo system of Europe.
- It uses a constellation of multiple satellites to provide coverage across large parts of the world all at once.
[4] Polar Orbit
- Satellites in polar orbits usually travel past Earth from north to south rather than from west to east, passing roughly over Earth’s poles.
- Satellites in a polar orbit do not have to pass the North and South Pole precisely; even a deviation within 20 to 30 degrees is still classed as a polar orbit.
- Polar orbits are a type of low Earth orbit, as they are at low altitudes between 200 to 1000 km.
[5] Sun-synchronous orbit (SSO)
- SSO is a particular kind of polar orbit. Satellites in SSO, travelling over the polar regions, are synchronous with the Sun.
- This means they are synchronised to always be in the same ‘fixed’ position relative to the Sun.
- This means that the satellite always visits the same spot at the same local time.
- Often, satellites in SSO are synchronised so that they are in constant dawn or dusk – this is because by constantly riding a sunset or sunrise, they will never have the Sun at an angle where the Earth shadows them.
- A satellite in a Sun-synchronous orbit would usually be at an altitude of between 600 to 800 km. At 800 km, it will be travelling at a speed of approximately 7.5 km per second.
[6] Transfer orbits and geostationary transfer orbit (GTO)
- Transfer orbits are a special kind of orbit used to get from one orbit to another.
- Often, the satellites are instead placed on a transfer orbit: an orbit where, by using relatively little energy from built-in motors, the satellite or spacecraft can move from one orbit to another.
- This allows a satellite to reach, for example, a high-altitude orbit like GEO without actually needing the launch vehicle.
- Reaching GEO in this way is an example of one of the most common transfer orbits, called the geostationary transfer orbit (GTO).
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Russia to leave International Space Station (ISS)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: International Space Station (ISS)
Mains level: Implications of Russia-Ukraine War

Russia will pull out of the International Space Station (ISS) after 2024 and focus on building its own orbiting outpost.
Why in news?
- Russia will end a symbolic two-decade orbital partnership between Moscow and the west.
International Space Station (ISS)
- The ISS was launched in 1998 as part of joint efforts by the U.S., Russia, Japan, Canada and Europe.
- The idea of a space station originated in the 1984 State of the Union address by former U.S. President Ronald Reagan.
- The space station was assembled over many years, and it operates in low-earth orbit.
- Since its inception, it has served as a laboratory suspended in space and has aided multiple scientific and technological developments.
- The ISS was originally built to operate for 15 years.
Why was ISS launched?
- A space station permits quantum leaps in research in science, communications, and in metals and lifesaving medicines which could be manufactured only in space.
- ISS has consistently maintained human presence for the past 21 years, providing astronauts with sophisticated technologies for scientific research.
What is Russia’s role in maintaining the ISS?
- The ISS is built with the cooperation of scientists from five international space agencies — NASA of the U.S., Roscosmos of Russia, JAXA of Japan, Canadian Space Agency and the European Space Agency.
- Each agency has a role to play and a share in the upkeep of the ISS.
- Both in terms of expense and effort, it is not a feat that a single country can support.
- Russia’s part in the collaboration is the module responsible for making course corrections to the orbit of the ISS.
- They also ferry astronauts to the ISS from the Earth and back.
- Until SpaceX’s dragon spacecraft came into the picture the Russian spacecraft was the only way of reaching the ISS and returning.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Outer Space
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Outer Spaces and its utility

Recently, the UK hosted the fourth summit for Space Sustainability in London in collaboration with the Secure World Foundation.
What does Sustainability in Outer Space mean?
- One of the hot issues when it comes to space sustainability is orbital crowding.
- With the emergence of large constellations and complex satellites, there is a risk of collisions and interference with radio frequencies.
- It poses a direct threat to the operations and safety of a mission and is likely to cause legal and insurance-related conflicts.
- Space debris is another prominent issue.
- After the completion of a mission, an ‘end-of-life protocol’ requires space objects to be moved to the graveyard orbit or to a low altitude.
- Other causes of concern are solar and magnetic storms which potentially damage communication systems.
- Such space weather threats need to be addressed along with the efforts to identify the terrestrial carbon footprint of outer space missions.
Why was a conference held in the UK?
- Long-term sustainability looks toward space research and development of technology to ensure the reuse and recycling of satellites at every stage.
- The UK plan proposes active debris removal and in-orbit servicing.
Policy measures so far
- As the outer space is considered a shared natural resource, the United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (COPUOS) in 2019 adopted a set of 21 voluntary, non-binding guidelines.
- They aim to ensure the long-term sustainability of outer space activities.
What does the UK plan for space sustainability entail?
- The UK calls for an “Astro Carta” for space sustainability, based on the Artemis Accords model for sustainable space exploration.
- The UK Space Sustainability plan mentions four primary elements:
- To review the regulatory framework of the UK’s orbital activity
- To work with organisations such as the G-7 and the UN to emphasise international engagement on space sustainability
- To try and develop safety and quality-related metrics that quantify the sustainability of activities; and
- To induce additional funding of $6.1 million on active debris removal
- The UK also confirmed investments in its National Space Surveillance and Tracking Programme, which works on collision assessment services for UK-licenced satellite operators.
Where does India stand on space sustainability?
- India is well on its way to create a subsystem that addresses global sustainability questions.
- The headquarters of the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (In-SPACe) was formally inaugurated last month.
- One can expect an increased role of the private sector in India’s space activities.
- The ISRO has initiated ‘Project NETRA’ to monitor space debris.
- To provide in-orbit servicing, ISRO is developing a docking experiment called ‘SPADEX’.
- It looks at docking a satellite on an existing satellite, offering support in re-fuelling and other in-orbit services while enhancing the capability of a satellite.
Way forward
- Outer space in the 2020s can no longer be considered a ‘space race’ because of the cost, when compared to the beginning of this century.
- Today, any entity (government or private) with the necessary access to resources and technology can invest in outer space.
- Sustainable practices in outer space would directly help reduce orbital crowding and collision risk while nurturing future technologies.
- As the natural course of evolution, the Plan for Space Sustainability, which includes private industries, is a timely move.
- This would serve as a model for other space programmes.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
What is PSLV Orbital Experimental Module (POEM)?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: POEM
Mains level: Not Much

The ISRO has launched three Singaporean satellites in precise orbit through the PSLV Orbital Experimental Module or ‘POEM’.
What is POEM?
- The POEM is a platform that will help perform in-orbit experiments using the final, and otherwise discarded, stage of ISRO’s workhorse rocket, the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV).
- The PSLV is a four-stage rocket where the first three spent stages fall back into the ocean, and the final stage (PS4) — after launching the satellite into orbit — ends up as space junk.
- However, in PSLV-C53 mission, the spent final stage will be utilised as a “stabilised platform” to perform experiments.
- POEM is carrying six payloads, including two from Indian space start-ups Digantara and Dhruva Space.
Features of POEM
- POEM has a dedicated Navigation Guidance and Control (NGC) system for attitude stabilisation, which stands for controlling the orientation of any aerospace vehicle within permitted limits.
- The NGC will act as the platform’s brain to stabilize it with specified accuracy.
- POEM will derive its power from solar panels mounted around the PS4 tank, and a Li-Ion battery.
- It will navigate using four sun sensors, a magnetometer, gyros & NavIC.
- It carries dedicated control thrusters using Helium gas storage. It is enabled with a telecomm and feature.
Has ISRO repurposed and used PS4 rocket junk earlier?
- The Indian space agency first demonstrated the capability of using PSLV-C44 as an orbital platform in 2019.
- It injected Microsat-R and Kalamsat-V2 satellites into their designated orbits.
- The fourth stage in that mission was kept alive as an orbital platform for space-based experiments.
- While in that mission, the fourth stage had Li-Ion batteries, solar panels are an addition this time.
- The latest repurposing and upgrade of the fourth stage of the PSLV rocket involves the stabilization of the orbital platform.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
What is IN-SPACe?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: IN-SPACE
Mains level: Commercial space activities in India
The Prime Minister inaugurated the headquarters of the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) at Bopal, Ahmedabad.
What is IN-SPACe?
- The establishment of IN-SPACe was announced in June 2020.
- It is an autonomous and single window nodal agency in the Department of Space for the promotion, encouragement and regulation of space activities of both government and private entities.
- It also facilitates the usage of ISRO facilities by private entities.
- It comprises technical experts for space activities along with safety expert, academic experts and legal and strategic experts from other departments.
- It also comprises members from PMO and MEA of Government of India.
Roles and Responsibilities
- Space activities including building of launch vehicles and satellites and providing space based services as per the definition of space activities.
- Sharing of space infrastructure and premises under the control of ISRO with due considerations to on-going activities.
- Establishment of temporary facilities within premises under ISRO control based on safety norms and feasibility assessment
How is it different from ANTRIX?
- Antrix Corporation Limited (ACL), Bengaluru is a wholly-owned Government of India Company under the administrative control of the Department of Space.
- It is as a marketing arm of ISRO for promotion and commercial exploitation of space products, technical consultancy services and transfer of technologies developed by ISRO.
- Antrix is engaged in providing Space products and services to international customers worldwide.
What about New Space India Limited (NSIL)?
- It functions under the administrative control of the Department of Space (DOS).
- It aims to commercially exploit the research and development work of ISRO Centres and constituent units of DOS.
- The NSIL would enable Indian Industries to scale up high-technology manufacturing and production base for meeting the growing needs of the Indian space program.
- It would further spur the growth of Indian Industries in the space sector.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
International Liquid Mirror Telescope (ILMT)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: International Liquid Mirror Telescope (ILMT)
Mains level: Not Much

The four-meter International Liquid Mirror Telescope (ILMT) saw the first light recently, gazing out from its vantage on Devasthal, a hill in Uttarakhand.
What is the ILMT?
- The telescope has been built by a collaboration of scientists from Canada, Belgium and India.
- It is located at an altitude of 2,450 metres on the Devasthal Observatory campus of the Aryabhata Research Institute of Observational Sciences (ARIES) in Nainital district.
- A large pool of mercury placed in a vessel is spun around so fast that it curves into a parabolic shape. Since mercury is reflective, this shape helps in focusing the reflected light.
- Nearly 50 litres of mercury, weighing close to 700 kilograms, is spun hard to form a paraboloid mirror of just 4 mm thickness and a diameter of about 4 metres.
- A thin sheet of mylar protects the mercury from the wind.
- Once it starts making observations, the telescope will collect gigabytes of data, which will need to be analysed using artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI and ML) tools.
It’s utility
- The telescope will make sky surveys possible and obtain images that can help observe transient phenomena.
- It will help analyse events such as supernovae and record the presence of space debris or meteorites — basically, watch the skies.
What is the first image?
- The first image made by the telescope consisted of several stars and a galaxy, NGC 4274, which is 45 million light years away.
- The telescope, having a primary mirror that is liquid, cannot be turned and pointed in any direction.
- It “stares” at the zenith and watches the sky as the earth rotates, thereby giving a view of different objects.
- This property can be used to scan and survey the sky, and observe transients and moving objects such as meteorites.
- It will work in tandem with the existing 3.6-metre Devasthal Optical Telescope.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO’s goal for Venus Mission
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Shukrayan Mission
Mains level: Interplanetary missions

India’s Venus mission has been conceived. The project report for ‘Shukrayaan-I’ – the name given to ISRO’s Venus mission
About Venus
- Venus is the second planet from the Sun and is Earth’s closest planetary neighbor.
- It’s one of the four inner, terrestrial (or rocky) planets, and it’s often called Earth’s twin because it’s similar in size and density.
- Venus has a thick, toxic atmosphere filled with carbon dioxide and it’s perpetually shrouded in thick, yellowish clouds of sulphuric acid that trap heat, causing a runaway greenhouse effect.
- It’s the hottest planet in our solar system, even though Mercury is closer to the Sun.
- Surface temperatures on Venus are about 900 degrees Fahrenheit (475 degrees Celsius) – hot enough to melt lead.
- Venus has crushing air pressure at its surface – more than 90 times that of Earth – similar to the pressure you’d encounter a mile below the ocean on Earth.
Do you know?
Venus rotates on its axis backward, compared to most of the other planets in the solar system. This means that, on Venus, the Sun rises in the west and sets in the east, opposite to what we experience on Earth. (It’s not the only planet in our solar system with such an oddball rotation – Uranus spins on its side.)
What is Shukrayaan-I Mission?
- Shukrayaan will be India’s first orbiter mission to Venus after sending similar missions to the Moon and Mars.
- The mission aims to study the surface of the hottest planet in our solar system and unravel the mysteries under the Sulphuric Acid clouds enveloping it.
- The orbiter is the third mission announced to the inferno world of Venus after NASA announced two probes followed by a spacecraft by the European Space Agency.
- The probes will investigate the world looking for clues to understand the destructive past of Earth’s mysterious twin, which scientists believe once had vast reserves of water similar to our planet.
Stated objectives
- Investigation of the surface processes and shallow sub-surface stratigraphy, including active volcanic hotspots and lava flows
- Studying the structure, composition, and dynamics of the atmosphere
- Investigation of solar wind interaction with the Venusian Ionosphere
Delay with the launch
- The ISRO is eyeing the December 2024 window for launch with orbital maneuvers planned for the following year.
- This is when earth and Venus would be so aligned that the spacecraft could be put in the neighboring planet’s orbit using a minimum amount of propellant.
- The next similar window would be available in 2031.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
SSLV ‘development flights’ likely in 2022
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SSLV, PSLV, GSLV
Mains level: Not Much

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is hoping to have all three development flights planned for its ‘baby rocket’ — the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) — in 2022 itself.
What is SSLV?
- The SSLV is a small-lift launch vehicle being developed by the ISRO with payload capacity to deliver:
- 600 kg to Low Earth Orbit (500 km) or
- 300 kg to Sun-synchronous Orbit (500 km)
- It would help launching small satellites, with the capability to support multiple orbital drop-offs.
- In future a dedicated launch pad in Sriharikota called Small Satellite Launch Complex (SSLC) will be set up.
- A new spaceport, under development, near Kulasekharapatnam in Tamil Nadu will handle SSLV launches when complete.
- After entering the operational phase, the vehicle’s production and launch operations will be done by a consortium of Indian firms along with NewSpace India Limited (NSIL).
Vehicle details
(A) Dimensions
- Height: 34 meters
- Diameter: 2 meters
- Mass: 120 tonnes
(B) Propulsion
- It will be a four stage launching vehicle.
- The first three stages will use Hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene (HTPB) based solid propellant, with a fourth terminal stage being a Velocity-Trimming Module (VTM).
SSLV vs. PSLV: A comparison
- The SSLV was developed with the aim of launching small satellites commercially at drastically reduced price and higher launch rate as compared to Polar SLV (PSLV).
- The projected high launch rate relies on largely autonomous launch operation and on overall simple logistics.
- To compare, a PSLV launch involves 600 officials while SSLV launch operations would be managed by a small team of about six people.
- The launch readiness period of the SSLV is expected to be less than a week instead of months.
- The SSLV can carry satellites weighing up to 500 kg to a low earth orbit while the tried and tested PSLV can launch satellites weighing in the range of 1000 kg.
- The entire job will be done in a very short time and the cost will be only around Rs 30 crore for SSLV.
Significance of SSLV
- SSLV is perfectly suited for launching multiple microsatellites at a time and supports multiple orbital drop-offs.
- The development and manufacture of the SSLV are expected to create greater synergy between the space sector and private Indian industries – a key aim of the space ministry.
Back2Basics:

UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Why are blue straggler stars different from the norm?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Blue Straggler Stars
Mains level: Not Much

Researchers from the Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Bengaluru have studied the eccentricities of blue straggler stars.
What are Blue Straggler Stars?
- A blue straggler is a main-sequence star in an open or globular cluster that is more luminous and bluer than stars at the main sequence turnoff point for the cluster.
- Blue stragglers were first discovered by Allan Sandage in 1953 while performing photometry of the stars in the globular cluster M3.
What did the Indian researchers study?
- Eccentricity is the deviation of a planets’ or stars’ orbit from circularity — the higher the eccentricity, the greater the elliptical orbit.
- For this, the researchers also made use of the observations by the UVIT instrument (Ultra Violet Imaging Telescope) of ASTROSAT, India’s first science observatory in space.
(a) Stellar ageing of stars
- To know what blue stragglers are, it is necessary to understand how stars are classified and their evolution, studied.
- Our Sun, for example, is what is called a main sequence star, and, given its mass and age, it is expected that once it has converted all its hydrogen into helium, its core will get denser, while outer layers expand.
- So, it will bloat into a red giant.
- After this phase, its fuel spent, it will shrink, becoming a smaller, cooling star called a white dwarf star at the end of its life.
(b) Sequencing of stars
- To study the behaviour of the star, you could plot a graph of the colour of a star, which is an indication of its surface temperature, against its magnitude, which is related to the total energy given off by it.
- If you do this for all the stars in a globular cluster, a large number of stars are seen to find a place within a band known as the main sequence.
- Our Sun is a main sequence star, too, and the expectation is that all main sequence stars follow a pattern of evolution pretty much like our Sun’s fate, which was described earlier.
- There are a few stars that, just at the stage of their lives, when they are expected to start expanding in size and cooling down, do just the opposite.
- They grow brighter and hotter and blue in colour, thus standing out from the cooler red stars in their vicinity in the colour-magnitude diagram.
- Since they lag behind their peers in the evolution, they are called stragglers, more specifically, blue stragglers, because of their hot, blue colour.
Outcome of the research: Reasons for Blue Stragglers behaviour
- The puzzle of why a blue straggler is more massive, and energetic than expected may be resolved in several ways.
- One that these do not belong to the family of stars in the cluster, and hence are not expected to have the group properties.
- Second, the straggler draws matter from the giant companion and grows more massive, hot and blue, and the red giant ends up as a normal or smaller white dwarf.
- The third possibility is that the straggler draws matter from a companion star, but that there is a third star that facilitates this process.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO develops Space Bricks from Martian Soil
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Space Bricks
Mains level: Not Much

Researchers from the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have developed a way to make bricks from Martian soil with the help of bacteria and urea.
Space Bricks
- ISRO and IISc have collaborated to develop a novel scalable technique of manufacturing space bricks using Martian Simulant Soil (MSS).
- The team first made the slurry by mixing Martian soil with guar gum, a bacterium called Sporosarcina pasteurii, urea and nickel chloride (NiCl2).
- This slurry can be poured into moulds of any desired shape, and over a few days the bacteria convert the urea into crystals of calcium carbonate.
- These crystals, along with biopolymers secreted by the microbes act as cement holding the soil particles together.
- This method ensures that the bricks are less porous, which was a problem with other methods used to make Martian bricks.
- The bacteria seep deep into the pore spaces, using their own proteins to bind the particles together, decreasing porosity and leading to stronger bricks.
Their significance
- In the past, the team had made bricks out of lunar soil using a similar method.
- These ‘space bricks’ can be used to construct building-like structures on Mars that could facilitate human settlement on the red planet.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
GSLV-F10
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SSLV, PSLV, GSLV
Mains level: Read the attached story

The Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) with improvements added to its cryogenic upper stage (CUS) is expected to be ready in the second half of this year.
What is GSLV?
- GSLV is an expendable space launch vehicle designed, developed, and operated by the ISRO to launch satellites and other space objects into Geosynchronous Transfer Orbits.
- GSLV is 49.13 m tall and tallest among all other vehicles of ISRO.
- It is a three-stage vehicle with a lift-off mass of 420 tonnes.
- ISRO first launched GSLV on April 18, 2001 and has made 13 launches since then.
Stages in GSLV
- The first stage comprises S139 solid booster with 138-tonne propellant and four liquid strap-on motors, with 40-tonne propellant.
- The second stage is a liquid engine carrying 40-tonne of liquid propellant.
- The third stage is the indigenously built Cryogenic Upper Stage (CUS) carrying 15-tonne of cryogenic propellants.
Variants in GSLV
- GSLV rockets using the Russian Cryogenic Stage (CS) are designated as the GSLV Mk I while versions using the indigenous Cryogenic Upper Stage (CUS) are designated the GSLV Mk II.
- All GSLV launches have been conducted from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota.
Difference between PSLV and GSLV
- GSLV has the capability to put a heavier payload in the orbit than the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV).
- PSLV can carry satellites up to a total weight of 2000 kg into space and reach up to an altitude of 600-900 km.
- GSLV can carry weight up to 5,000 kg and reach up to 36,000 km.
- PSLV is designed mainly to deliver earth observation or remote sensing satellites, whereas, GSLV has been designed for launching communication satellites.
- GSLV delivers satellites into a higher elliptical orbit, Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) and Geosynchronous Earth Orbit (GEO).
Back2Basics: ISRO’s transportation modules
(1) SLV
- In the space transportation domain, the commissioning of the Satellite Launch Vehicle-3 (SLV-3) project in the early 1970s was the first indigenous experimental satellite launch vehicle.
- As a four stage, all solid, launch vehicle, SLV-3 had its successful launch in July 1980, thrusting India into the select league of six countries with the capability to launch satellites on their own.
- The ASLV- Augmented Satellite Launch Vehicle project, in the early 1980s, was the next step of evolution in launch vehicle technology.
(2) PSLV
- In mid 80s came the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) project. PSLV was successfully launched in 1994.
- The vehicle has proven to be a workhorse of ISRO, logging over 50 successful missions, launching national as well as foreign satellites.
- On 15 February 2017, PSLV created a world record by successfully placing 104 satellites.
- The nation embarked upon a highly challenging quest to master the complex cryogenic technology.
(3) GSLV
Discussed above.
(4) SSLV
- The Small Satellites Launching Vehicles (SSLVs) used for commercial launching of small satellites is under incubation.
- It is a small-lift launch vehicle being developed by the ISRO with payload capacity to deliver:
- 600 kg to Low Earth Orbit (500 km) or
- 300 kg to Sun-synchronous Orbit (500 km)
- It would help launching small satellites, with the capability to support multiple orbital drop-offs.
- In future a dedicated launch pad in Sriharikota called Small Satellite Launch Complex (SSLC) will be set up.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
What is Project NETRA?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Project NETRA
Mains level: Space Debris

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is building up its orbital debris tracking capability by deploying new radars and optical telescopes under the Network for Space Objects Tracking and Analysis (NETRA) project.
Project NETRA
- The project will give India its own capability in space situational awareness (SSA) like the other space powers — which is used to ‘predict’ threats from debris to Indian satellites.
- NETRA’s eventual goal is to capture the GEO, or geostationary orbit, scene at 36,000 km where communication satellites operate.
- The initial SSA will first be for low-earth orbits or LEO which have remote-sensing spacecraft.
- Under NETRA the ISRO plans to put up many observational facilities: connected radars, telescopes; data processing units and a control centre.
- They can, among others, spot, track and catalogue objects as small as 10 cm, up to a range of 3,400 km and equal to a space orbit of around 2,000 km.
- The NETRA effort would make India a part of international efforts towards tracking, warning about and mitigating space debris.
What NETRA consists of?
- In the plans are a high-precision, long range telescope in Leh and a radar in the North East.
- Along with them, we will also use the Multi-Object Tracking Radar (MOTR) that we have put up at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, and the telescopes at Ponmudi and Mount Abu to get a broad SSA picture.
- NORAD, or the North American Aerospace Defense Command, is an initiative of the U.S. and Canada that shares selective debris data with many countries.
- The new SSA centre would consolidate debris tracking activities that are now spread across ISRO centres.
- Currently there are 15 functional Indian communication satellites in the geostationary orbit of 36,000 km; 13 remote sensing satellites in LEO of up to 2,000 km; and eight navigation satellites in medium earth orbits.
Why Space debris matters?
- Space junk or debris consists of spent rocket stages, dead satellites, fragments of space objects and debris resulting from ASAT.
- Hurtling at an average speed of 27,000 kmph in LEO, these objects pose a very real threat as collisions involving even centimetre-sized fragments can be lethal to satellites.
- Last year, ISRO monitored 4,382 events in LEO and 3,148 events in the geostationary orbit where space objects closely approached Indian assets.
- Fragments from the Fengyun-1C satellite (part of the anti-satellite test (ASAT) by China in 2007) and the Cosmos 2251-Iridium satellite collision in 2009 accounted for the maximum number of these threats.
- The observations also covered 84 “close approaches of less than one km” between Starlink satellites and Indian assets.
Enhancing Space situational awareness (SSA)
- India, as a responsible space power, should have SSA as a part of a national capability, as in the U.S. This is a vital requirement for protecting our space assets and a force multiplier.
- The SSA has a military quotient to it and adds a new ring to the country’s overall security.
- It uses satellites, ground and air radars to secure its two countries against attacks from air, space or sea.
- With long-range tracking radars, the SSA also provides us the capability of an early warning system against ballistic missiles coming in at a height.
- Apart from radars and telescopes, he said India should also think of deploying satellites that track other satellites — as the U.S. and other space powers had done.
- Combined with other elements of military intelligence SSA would help us to understand motives behind any suspicious orbit changes of other satellites and to know if they were spying on or harming our spacecraft.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
GSAT 7B and India’s other Military Satellites
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Indias military satellites
Mains level: Not Much
The Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) chaired by Defence Minister Rajnath Singh cleared the Acceptance of Necessity (AoN) for procurement of a GSAT 7B satellite.
What are the GSAT 7 series satellites?
- GSAT 7 satellites are advanced satellites developed by the ISRO to meet the communication needs of the defence services.
- The satellite was injected into a geosynchronous transfer orbit (GTO) of 249 km perigee (nearest point to earth), 35,929 km apogee (farthest point to earth) and an inclination of 3.5 degree with respect to the equator.
- The GSAT 7 satellite was launched in August 2013 from an Ariane 5 ECA rocket from Kourou in French Guiana.
- It is a 2,650 kg satellite which has a footprint of nearly 2,000 nautical miles in the Indian Ocean region.
Utility of this satellite
- This satellite is mainly used by the Indian Navy for its communication needs.
- The GSAT 7 provides a gamut of services for military communication needs, which includes low bit voice rate to high bit rate data facilities, including multi-band communications.
- Named Rukmini, the satellite carries payloads in UHF, C-band and Ku-band, and helps the Navy to have a secure, real time communication link between its land establishments, surface ships, submarines and aircraft.
What will be the role of the GSAT 7B satellite?
- The GSAT 7B will primarily fulfil the communication needs of the Army.
- Currently, the Army is using 30 per cent of the communication capabilities of the GSAT 7A satellite, which has been designed for the Indian Air Force (IAF).
- The GSAT 7B will also help the Army enhance its surveillance in border areas.
- While many features of this satellite are still a closely guarded secret, it is expected that the state of the art, multi-band, military-grade satellite shall be a shot in the arm for the communication and surveillance needs of the Army.
What is the role of the GSAT 7A satellite, which is already operational?
- The GSAT 7A was launched in 2018 from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota.
- It has gone a long way in boosting the connectivity between the ground radar stations, airbases and the airborne early warning and control aircraft (AEW&C) of the IAF.
- It also helps in satellite controlled operations of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) which gives a great deal of reliability to the operations as compared to ground-controlled operations.
- This satellite has 10 channels in Ku band with switchable frequency for mobile users, one fixed Gregorian or parabolic antenna, and four steerable antennae.
Future plans
- A GSAT 7C satellite is on the cards for the IAF, and a proposal to this effect was cleared by the DAC in 2021.
- This satellite would facilitate real time communication with IAF’s software defined radio communication sets.
- It will increase the capability of the IAF to communicate beyond the line of sight in a secure mode.
What other kinds of military satellites does India have?
- An Electromagnetic Intelligence Gathering Satellite (EMISAT), developed by ISRO, was launched in April 2020 through a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV-C45).
- It has an Electronic Intelligence (ELINT) package called Kautilya, which allows the interception of ground-based radar and also carries out electronic surveillance across India.
- The ELINT package provides the capability in direction-finding of radar and fixing their locations.
- It is placed in a 748-km orbit, and is said to be based on the Israeli satellite system.
- This satellite circles the globe pole-to-pole, and is helpful in gathering information from radars of countries that have borders with India.
- India also has a RISAT 2BR1 synthetic aperture radar imaging satellite, which was launched in December 2019 from Sriharikota.
- It has the capability to operate in different modes including very high resolution imaging modes of 1×0.5 metre resolution and 0.5×0.3 m resolution with a swath of 5-10 km.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
What are Earth Observation Satellites (EOS)?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Earth Observation Satellites (EOS)
Mains level: Not Much
After a disappointing 2021 which saw just one successful launch, ISRO is getting back to business with the EOS-04, an earth observation satellite.
What are EOS?
- An EOS or Earth remote sensing satellite is a satellite used or designed for Earth observation (EO) from orbit.
- It includes spy satellites and similar ones intended for non-military uses such as environmental monitoring, meteorology, cartography, and others.
- The most common type is Earth-imaging satellites that take satellite images, analogous to aerial photographs.
- Some EOS may perform remote sensing without forming pictures, such as in GNSS radio occultation.
What is EOS-04 all about?
- The EOS-04 is fourth in a series of earth observation satellites that are being launched under a new generic name.
- It is designed to provide high-quality images for applications such as agriculture, forestry, and plantations, flood mapping, soil moisture, and hydrology.
- It will complement the data from Resourcesat, Cartosat and RISAT-2B series of satellites that are already in orbit.
Why such different nomenclature?
- Two years ago, ISRO had moved to a new naming system for its earth observation satellites which till then had been named thematically, according to the purpose they were meant for.
- The Cartosat series of satellites were meant to provide data for land topography and mapping, while the Oceansat satellites were meant for observations overseas.
- Some INSAT-series, Resourcesat series, GISAT, Scatsat, and a few other earth observation satellites were named differently for the specific jobs they were assigned to do, or the different instruments that they.
- All these would now become part of the new EOS series of satellites.
What other satellites are being launched?
- Besides EOS-04, two other small satellites —INSPIREsat-1 and INS-2TD — will ride on the heaviest version of the PSLV rocket in the early hours from the Sriharikota launch range.
- The other co-passenger, INS-2TD, is a technology demonstrator for the first India-Bhutan joint satellite that is scheduled to be launched next month.
- The two countries had signed a space agreement last year, and its first outcome would be the launch of Bhutan-Sat, or INS-2B, on a PSLV rocket.
How many satellites does India have in space?
- India currently has 53 operational satellites, of which 21 are earth observation ones and another 21 are communication-based.
- EOS-4 launch would be the 54th flight of the PSLV rocket, and the 23rd of its most powerful XL-version that has six strap-on boosters.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Chandrayaan-3 set for launch in August
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Chandrayaan-3
Mains level: Not Much
ISRO plans to execute the Chandrayaan-3 mission in August this year.
What is Chandrayaan-3 Mission?
- The Chandrayaan-3 mission is a follow-up of Chandrayaan-2 of July 2019, which aimed to land a rover on the lunar South Pole.
Chandrayaan-2: A quick recap
- Chandrayaan-2 consisted of an Orbiter, Lander and Rover, all equipped with scientific instruments to study the moon.
- The Orbiter would watch the moon from a 100-km orbit, while the Lander and Rover modules were to be separated to make a soft landing on the moon’s surface.
- ISRO had named the Lander module as Vikram, after Vikram Sarabhai, the pioneer of India’s space programme, and the Rover module as Pragyaan, meaning wisdom.
Utility of the Orbiter
- The Orbiter part of the mission has been functioning normally. It is carrying eight instruments.
- Each of these instruments has produced a handsome amount of data that sheds new light on the moon and offers insights that could be used in further exploration.
Inception of Chandrayaan 3
- The subsequent failure of the Vikram lander led to the pursuit of another mission to demonstrate the landing capabilities needed for the Lunar Polar Exploration Mission proposed in partnership with Japan for 2024.
Its design
- The lander for Chandrayaan-3 will have only four throttle-able engines.
- Unlike Vikram on Chandrayaan-2 which had five 800N engines with a fifth one being centrally mounted with a fixed thrust.
- Additionally, the Chandrayaan-3 lander will be equipped with a Laser Doppler Velocimeter (LDV).
Back2Basics: Chandrayaan-1 Mission
- The Chandrayaan-1 mission was launched in October 2008 was ISRO’s first exploratory mission to the moon, in fact to any heavenly body in space.
- The mission was designed to just orbit around the moon and make observations with the help of the instruments onboard.
- The closest that Chandrayaan-1 spacecraft came to the moon was in an orbit 100 km from its surface.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SSLV, PSLV, GSLV
Mains level: Commercial space activities in India

The new chairman of the ISRO Dr S Somanath has indicated inauguration of indigenous new launch rockets, called the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV).
What is SSLV?
- The SSLV is a small-lift launch vehicle being developed by the ISRO with payload capacity to deliver:
- 600 kg to Low Earth Orbit (500 km) or
- 300 kg to Sun-synchronous Orbit (500 km)
- It would help launching small satellites, with the capability to support multiple orbital drop-offs.
- In future a dedicated launch pad in Sriharikota called Small Satellite Launch Complex (SSLC) will be set up.
- A new spaceport, under development, near Kulasekharapatnam in Tamil Nadu will handle SSLV launches when complete.
- After entering the operational phase, the vehicle’s production and launch operations will be done by a consortium of Indian firms along with NewSpace India Limited (NSIL).
Vehicle details
(A) Dimensions
- Height: 34 meters
- Diameter: 2 meters
- Mass: 120 tonnes
(B) Propulsion
- It will be a four stage launching vehicle.
- The first three stages will use Hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene (HTPB) based solid propellant, with a fourth terminal stage being a Velocity-Trimming Module (VTM).
SSLV vs. PSLV: A comparison
- The SSLV was developed with the aim of launching small satellites commercially at drastically reduced price and higher launch rate as compared to Polar SLV (PSLV).
- The projected high launch rate relies on largely autonomous launch operation and on overall simple logistics.
- To compare, a PSLV launch involves 600 officials while SSLV launch operations would be managed by a small team of about six people.
- The launch readiness period of the SSLV is expected to be less than a week instead of months.
- The SSLV can carry satellites weighing up to 500 kg to a low earth orbit while the tried and tested PSLV can launch satellites weighing in the range of 1000 kg.
- The entire job will be done in a very short time and the cost will be only around Rs 30 crore for SSLV.
Significance of SSLV
- SSLV is perfectly suited for launching multiple microsatellites at a time and supports multiple orbital drop-offs.
- The development and manufacture of the SSLV are expected to create greater synergy between the space sector and private Indian industries – a key aim of the space ministry.
Back2Basics:

Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Gaganyaan and other new Missions in 2022
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Gaganyaan Mission
Mains level: Indian Human Spaceflight Programme (IHSP)
After a rather muted 2021 in terms of satellite launches, Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) is gearing up for a number of missions in 2022 including the launch of the first unmanned mission of Gaganyaan.
Gaganyaan Mission
- Gaganyaan is crewed orbital spacecraft intended to be the formative spacecraft of the Indian Human Spaceflight Programme (IHSP).
- The IHSP was initiated in 2007 by ISRO to develop the technology needed to launch crewed orbital spacecraft into low Earth orbit.
- The first uncrewed flight, named Gaganyaan 1, is scheduled to launch no earlier than June 2022 on a GSLV Mark III rocket.
- ISRO had been working on related technologies and it performed a Crew Module Atmospheric Re-entry Experiment and a Pad Abort Test for the mission.
- If completed in meantime, India will become the fourth nation to conduct independent human spaceflight after the Russia, US and China.
Details of the project
- The spacecraft is being designed to carry three people, and a planned upgraded version will be equipped with rendezvous and docking capability.
- In its maiden crewed mission, this capsule will orbit the Earth at 400 km altitude for up to seven days with a two or three-person crew on board.
- This Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) manufactured crew module had its first un-crewed experimental flight in 2014.
- DRDO will provide support for critical human-centric systems and technologies like space-grade food, crew healthcare, radiation measurement and protection, parachutes for the safe recovery of the crew module and fire suppression system.
Other missions this year
- Earth Observation Satellites: EOS-4 and EOS-6
- Flights for Crew Escape System of Gaganyaan
- Chandrayaan-03
- Aditya Ll
- XpoSat
New projects
- Venus mission
- DISHA –a twin aeronomy satellite mission
- TRISHNA, an ISRO-CNES [Centre national d’études spatiales] mission
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Dhawan-1: India’s first privately developed Cryogenic Rocket
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Dhawan-1
Mains level: Space startups in India

Skyroot Aerospace successfully tested Dhawan-1 last month. It became the country’s first privately developed fully cryogenic rocket engine.
Dhawan-1
- The indigenous engine was developed using 3D printing with a superalloy.
- It runs on two high-performance rocket propellants — liquid natural gas (LNG) and liquid oxygen (LoX).
- This was after successfully designing and developing the solid propulsion rocket engine, the first private firm in the country to do so.
Other projects by Skyroot
- Skyroot is working simultaneously on different stages of both solid propulsion and liquid propulsion engines.
- It is named after eminent scientists, like Kalam (Abdul Kalam) series for the former and Dhawan (Satish Dhawan).
- The launch vehicles are named after Vikram Sarabhai.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Katol L6 Chondrite Meteorite
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Katol L6, Interior of Earth
Mains level: Hypothesis of planetary system formation

Last month, researchers from the Geological Survey of India collected some meteorite fragments near the town of Katol in Nagpur in 2012. Studying this, IIT Kgp researchers have unravelled the composition expected to be present in the Earth’s lower mantle which is at about 660 km deep.
Katol L6
- Initial studies revealed that the host rock was mainly composed of olivine, an olive-green mineral.
- Olivine is the most abundant phase in our Earth’s upper mantle.
- Our Earth is composed of different layers including the outer crust, followed by the mantle and then the inner core.
Key findings: Presence of Bridgmanite
- The study reported for the first time, presence of veins of the mineral bridgmanite, which is the most abundant mineral in the interior of the Earth, within the Katol L6 Chondrite meteorite.
- Bridgmanite consists of magnesium, iron, calcium aluminium oxide and has a perovskite structure. It is the most volumetrically abundant mineral of the Earth’s interior.
- It is present in the lower mantle (from 660 to 2700 km), and it is important to understand its formation mechanism to better comprehend the origin and evolution of planetary interiors.
What is the hypothesis of moon-formation?
The discovery of Bridgmanite in Katol L6 adds evidence to the Moon-forming giant impact hypothesis.
- The Moon-forming giant impact hypothesis occurred nearly 4.5 billion years ago.
- The Earth collided with a planet the size of Mars named Thela.
- The force of this impact was so huge as to melt the Earth down from the surface to a depth of 750 km to 1,100 km.
- The hypothesis goes that this caused the Earth to be bathed in a magma ocean, and the ejecta from the collision led to the formation of the Moon.
Note: Earth was an ocean of magma in the past. The heavier iron and nickel went to the core while the lighter silicates stayed in the mantle.
Future prospect of the study
- This finding could help investigations of high-pressure phase transformation mechanisms in the deep Earth.
Back2Basics: Interior of Earth

The earth is made up of three different layers: the crust, the mantle and the core.
The crust
This is the outside layer of the earth and is made of solid rock, mostly basalt and granite. There are two types of crust; oceanic and continental. Oceanic crust is denser and thinner and mainly composed of basalt. Continental crust is less dense, thicker, and mainly composed of granite.
The mantle
The mantle lies below the crust and is up to 2900 km thick. It consists of hot, dense, iron and magnesium-rich solid rock. The crust and the upper part of the mantle make up the lithosphere, which is broken into plates, both large and small.
The core
The core is the centre of the earth and is made up of two parts: the liquid outer core and solid inner core. The outer core is made of nickel, iron and molten rock. Temperatures here can reach up to 50,000 C.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
[pib] Indian Space Association
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Indian Space Association (ISpA)
Mains level: Commercial space exploration in India

The PM has launched the Indian Space Association (ISpA), an industry body consisting of various stakeholders of the Indian space domain.
Indian Space Association (ISpA)
- The ISpA is a premier industry association of space and satellite companies, which aspires to be the collective voice of the Indian space industry.
- It will be headed by retired Lieutenant General AK Bhatt, who will be its Director General.
- It will target to undertake policy advocacy and engage with all stakeholders in the Indian space domain. It will engage with the government and all its agencies.
Why is the formation of ISpA significant?
- Million-dollar industry: Governments across the world have poured millions of dollars to push the envelope in term of exploring the edges of the space.
- Collaborated research: With time, governments and government agencies collaborated to explore newer planets and galaxies in search of life forms that exist outside Earth.
- Private players involvement: In the recent past, private sector companies such as Elon Musk’s SpaceX, Richard Branson’s Virgin Galactic, and Jeff Bezos’ Blue Origin have taken the lead in spaceflight.
- Easing workload on ISRO: Though India too has made significant strides in space exploration over time, state-run ISRO has been at the centre and front of this progress.
What does ISpA aim to achieve?
- Supplementing space research: One of the main goals of the organisation is to supplement the government’s efforts towards making India a global leader in commercial space-based excursions.
- Commercial space exploration: ISpA said it would engage with stakeholders across the ecosystem for the formulation of an enabling policy framework which fulfills the government vision of leading commercial space exploration.
- Establishing global linkages: ISpA will also work towards building global linkages for the Indian space industry to bring in critical technology and investments into the country to create more high skill jobs.
Who are the stakeholders in this organisation? How will they contribute?
- ISpA will be represented by leading domestic and global corporations that have advanced capabilities in space and satellite technologies.
- It has taken off with several Indian and international companies betting on it as the next frontier to provide high-speed and affordable Internet connectivity to inaccessible areas as well.
- This includes SpaceX’s StarLink, Sunil Bharti Mittal’s OneWeb, Amazon’s Project Kuiper, US satellite maker Hughes Communications, etc.
- OneWeb, for example, is building its initial constellation of 648 low-earth orbit satellites and has already put 322 satellites into orbit.
Why is satellite-based Internet important in India?
- The expansion of the Internet in India is crucial to the Modi government’s dream of a digital India where a majority of government services are delivered directly to the customer.
- The government aims to connect all villages and gram panchayats with high-speed Internet over the next 1000 days through BharatNet.
- However, internet connectivity in hilly areas and far-flung places of Northeast India are still a challenge.
- To overcome this, industry experts suggest that satellite Internet will be essential for broadband inclusion in remote areas and sparsely populated locations where terrestrial networks have not reached.
- Satellite communications remain limited to use by corporates and institutions that use it for emergency use, critical trans-continental communications and for connecting to remote areas with no connectivity.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Indian meteorite helps study Earth’s formation
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Olivine, Bridgmanite
Mains level: Formation of Earth

The researchers from the Geological Survey of India collected about 30 meteorite fragments with the largest weighing around a kilogram near the town of Katol in Nagpur in 2012.
Significance of meteor study
- Now, by studying the composition of these meteorite fragments, researchers have unraveled the composition expected to be present in the Earth’s lower mantle which is at about 660 km deep.
- Studying the meteorite could also tell us more about how our Earth evolved from being a magma ocean to a rocky planet.
Key component of the Meteor: Olivine
- Initial studies revealed that the host rock was mainly composed of olivine, an olive-green mineral.
- Olivine is the most abundant phase in our Earth’s upper mantle.
- Our Earth is composed of different layers including the outer crust, followed by the mantle and then the inner core.
How to study a meteorite?
- The researchers took a small sample of the meteorite and examined it using special microscopy techniques.
- The mineralogy was determined using a laser micro-Raman spectrometer.
- These techniques helped the team identify, characterise the crystal structure of the meteorite and determine its chemical composition and texture.
What does the new study show?
- The international team of scientists examined a section of this highly-shocked meteorite. It resembles to the first natural occurrence of a mineral called bridgmanite.
- The mineral was named in 2014 after Prof. Percy W. Bridgman, recipient of the 1946 Nobel Prize in Physics.
- Various computational and experimental studies have shown that about 80% of the Earth’s lower mantle is made up of bridgmanite.
- By studying this meteorite sample, scientists can decode how bridgmanite crystallized during the final stages of our Earth’s formation.
Bridgmanite: On Earth vs. on Meteorite
- Katol meteorite is a unique sample and it is a significant discovery.
- The bridgmanite in the meteorite was found to be formed at pressures of about 23 to 25 gigapascals generated by the shock event.
- The high temperature and pressure in our Earth’s interior have changed over billions of years causing crystallisation, melting, remelting of the different minerals before they reached their current state.
- It is important to study these individual minerals to get a thorough idea of how and when the Earth’s layers formed.
How does it help understand evolution of Earth?
- The inner planets or terrestrial planets or rocky planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars are formed by accretion or by rocky pieces coming together.
- They were formed as a planet by increased pressure and high temperature caused by radioactive elements and gravitational forces.
- Our Earth was an ocean of magma before the elements crystallised and stabilised and the different layers such as core, mantle were formed.
- The heavier elements like iron went to the core while the lighter silicates stayed in the mantle.
- By using the meteorite as an analog for Earth, we can unearth more details about the formation.
Answer this question from our AWE initiative:
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
IAO Hanle: A promising astronomical observatory
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: IAO Hanle
Mains level: NA

A new study shows that the Indian Astronomical Observatory (IAO) located in Hanle is one of the emerging sites for infrared and optical astronomy studies.
About IAO Hanle
- The IAO, located in Hanle at Mount Saraswati near Leh in Ladakh, has one of the world’s highest located sites for optical, infrared and gamma-ray telescopes.
- It was established in 2001 and is operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Bangalore.
- It is currently the ninth highest optical telescope in the world, situated at an elevation of 4,500 meters.
Note: University of Tokyo Atacama Observatory (TAO) located in the Atacama desert of Chile is the highest at an elevation of 5,640 m.
Major telescopes at Hanle include:
- Himalayan Chandra Telescope (An optical-infrared telescope named after India-born Nobel laureate Subrahmanyam Chandrasekhar)
- GROWTH-India Telescope (A robotic optical telescope)
- High Altitude Gamma Ray Telescope
Distinct factors of IAO Hanle
- IAO Hanle offers a clear view of space among all observatories globally.
- This is due to its advantages of more clear nights, minimal light pollution, background aerosol concentration, extremely dry atmospheric condition and uninterrupted monsoon.
- Hanle site is as dry as Atacama Desert in Chile and much drier than Devasthal and has around 270 clear nights in a year and is also one of the emerging sites for infrared and submillimetre optical astronomy.
- This is because water vapor absorbs electromagnetic signals and reduces their strength.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Tasks accomplished by the Chandrayaan-2
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Chandrayaan-3 Mission
Mains level: Accomplishments of India's Lunar Mission
The failure of Chandrayaan-2, India’s second mission to the Moon, to make a soft landing on the lunar surface had led to much disappointment. But that did not mean the entire mission had been wasted.
Chandrayaan-2: A quick recap
- Chandrayaan-2 consisted of an Orbiter, Lander and Rover, all equipped with scientific instruments to study the moon.
- The Orbiter would watch the moon from a 100-km orbit, while the Lander and Rover modules were to be separated to make a soft landing on the moon’s surface.
- ISRO had named the Lander module as Vikram, after Vikram Sarabhai, the pioneer of India’s space programme, and the Rover module as Pragyaan, meaning wisdom.
Utility of the Orbit
- The Orbiter part of the mission has been functioning normally. It is carrying eight instruments.
- Each of these instruments has produced a handsome amount of data that sheds new light on the moon and offers insights that could be used in further exploration.
Some of the most significant results so far:
(a) Water
- The presence of water on the Moon had already been confirmed by Chandrayaan-1, India’s first mission to the Moon that flew in 2008.
- Using far more sensitive instruments, the Imaging Infra-Red Spectrometer (IIRS) onboard Chandrayaan-2 has been able to distinguish between hydroxyl and water molecules and found unique signatures of both.
- This is the most precise information about the presence of H2O molecules on the Moon to date.
- Previously, water was known to be present mainly in the polar regions of the Moon.
- Chandrayaan-2 has now found signatures of water at all latitudes, although its abundance varies from place to place.
(b) Minor elements
- The Large Area Soft X-ray Spectrometer (CLASS) measures the Moon’s X-ray spectrum to examine the presence of major elements such as magnesium, aluminum, silicon, calcium, titanium, iron, etc.
- This instrument has detected the minor elements chromium and manganese for the first time through remote sensing, thanks to a better detector.
- The finding can lay the path for understanding magmatic evolution on the Moon and deeper insights into the nebular conditions as well as planetary differentiation.
- CLASS has mapped nearly 95% of the lunar surface in X-rays for the first time.
- Sodium, also a minor element on the Moon surface, was detected without any ambiguity for the first time.
(c) Study of Sun
- One of the payloads, called Solar X-ray Monitor (XSM), besides studying the Moon through the radiation coming in from the Sun, has collected information about solar flares.
- XSM has observed a large number of microflares outside the active region for the first time.
- This has great implications on the understanding of the mechanism behind the heating of the solar corona, which has been an open problem for many decades.
Utility of this Data
- While the Orbiter payloads build upon existing knowledge of the Moon in terms of its surface, sub-surface and exosphere, it also paves the path for future Moon missions.
- Four aspects — mineralogical and volatile mapping of the lunar surface, surface and subsurface properties and processes involved, quantifying water in its various forms across the Moon surface, and maps of elements present on the moon — will be key for future scope of work.
- A key outcome from Chandrayaan-2 has been the exploration of the permanently shadowed regions as well as craters and boulders underneath the regolith, the loose deposit comprising the top surface extending up to 3-4m in depth.
- This is expected to help scientists to zero in on future landing and drilling sites, including for human missions.
Who is going to use it?
- Some key future Moon missions that hope to make use of such data include the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA)-ISRO collaboration Lunar Polar Exploration (LUPEX) mission scheduled for launch in 2023/2024.
- Its aim is to obtain knowledge of lunar water resources and to explore the suitability of the lunar polar region for setting up a lunar base.
- NASA’s Artemis missions plan to enable human landing on the Moon beginning 2024 and target sustainable lunar exploration by 2028.
- The Chinese Lunar Exploration Programme too plans to establish a prototype of the International Lunar Research Station (ILRS) at the lunar south pole and build a platform supporting large-scale scientific exploration.
What was missed because of the crash-landing?
- The most obvious miss has been the opportunity to demonstrate the technology to make a soft landing in outer space.
- The lander Vikram and rover Pragyaan were carrying instruments to carry out observations on the surface.
- These were supposed to pick up additional information about the terrain, and composition, and mineralogy.
- While the instruments onboard the Orbiter is making “global” observations, those on the lander and rover would have provided much more local information.
- The two diverse sets of data could have helped prepare a more composite picture of the Moon.
Future with the Chandrayaan-3
- ISRO scientists maintain that the accident was caused by a relatively small error that has been identified and corrected.
- But, to demonstrate this technology all over again, ISRO would have to send a fresh mission, Chandrayaan-3, planned for next year.
- It is expected to have only a lander and rover, and no Orbiter.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
[pib] Formation of Blue Straggler
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Blue Stragglers
Mains level: Not Much

Carrying out the first-ever comprehensive analysis of blue stragglers, Indian researchers found that half of the blue stragglers in their sample are formed through mass transfer from a close binary companion star.
What are Blue Stragglers?
- A blue straggler is a main-sequence star in an open or globular cluster that is more luminous and bluer than stars at the main sequence turnoff point for the cluster.
- The most likely explanation is that blue stragglers are the result of stars that come too close to another star or similar mass object and collide.
- The newly-formed star has thus a higher mass and occupies a position on the HR diagram which would be populated by genuinely young stars.
- One-third of them are likely formed through collisions of 2 stars, and the remaining are formed through interactions of more than 2 stars.
How are they formed?
- A bunch of stars born at the same time from the same cloud form a star cluster.
- As time passes, each star evolves differently depending on its mass.
- The most massive and bright stars evolve and move off the main sequence creating a bend in their track, known as the turnoff.
- Stars above this bend or brighter and hotter stars are not expected in a cluster, as they leave the main sequence to become red giants.
- But in 1953, Allan Sandage found that some stars seem to be hotter than the turnoff of the parent cluster.
Behind the nomenclature
- Initially, these blue stars still straggling above the turnoff were not part of these clusters.
- However, later studies confirmed that these stars are indeed cluster members, and they were termed “Blue Stragglers”.
- The only probable way these stars can still be present in these clusters is if they have somehow acquired extra mass along the way while on the main sequence.
- Confirming the mechanisms of the mass gain required a study using a large sample of blue-straggler stars and estimates of the mass they have gained.
What have Indian researchers found?
- Research showed that these stars are primarily present in the older and massive star clusters. And due to their large mass, they are segregated towards the centre of the clusters.
- The researchers compared the mass of the blue stragglers to the mass of the turnoff stars (which are the most massive ‘normal’ stars in the cluster) and predicted the formation mechanisms.
- The study will help improve understanding of these stellar systems to uncover exciting results in studies of large stellar populations, including galaxies.
- Following these findings, the researchers are conducting detailed analyses of individual blue stragglers in the catalog to obtain their stellar properties.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NASA-ISRO SAR
Mains level: Not Much

The NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar satellite, aimed at making global measurement of land surface changes using advanced radar imaging, is proposed to be launched in early 2023, informed Earth Sciences Minister.
Note the key features of the Mission. Every statement has a unique information.
NASA-ISRO SAR
- NISAR is a joint collaboration for a dual-frequency L and S-band SAR for earth observation.
- NASA and Bengaluru-headquartered ISRO signed a partnership on September 30, 2014, to collaborate on and launch NISAR.
- The mission is targeted to launch in early 2022 from ISRO’s Sriharikota spaceport in Andhra Pradesh’s Nellore district, about 100km north of Chennai.
- It is capable of producing extremely high-resolution images for a joint earth observation satellite mission with NASA.
- It will be the first satellite mission to use two different radar frequencies (L-band and S-band) to measure changes in our planet’s surface less than a centimeter across.
Objectives of the NISAR
- NISAR will observe Earth’s land and ice-covered surfaces globally with 12-day regularity on ascending and descending passes, sampling Earth on average every six days for a baseline three-year mission.
- It will measure Earth’s changing ecosystems, dynamic surfaces, and ice masses, providing information about biomass, natural hazards, sea-level rise, and groundwater, and will support a host of other applications.
- It would also provide data on natural hazards including earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanoes, and landslides.
What are L and S Bands?
- L band waves are used for GPS units because they are able to penetrate clouds, fog, rain, storms, and vegetation.
- The S-band is used by airport surveillance radar for air traffic control, weather radar, surface ship radar, and some communications satellites, especially those used by NASA to communicate with the Space Shuttle and the International Space Station.
- NISAR uses a sophisticated information-processing technique known as SAR to produce extremely high-resolution images.
- Radar penetrates clouds and darkness, enabling NISAR to collect data day and night in any weather.
What is collaboration?
- NASA is providing the mission’s L-band SAR, a high-rate communication subsystem for science data, GPS receivers, a solid-state recorder, and payload data subsystem.
- ISRO is providing the spacecraft bus, the S-band radar, the launch vehicle, and associated launch services for the mission, whose goal is to make global measurements of the causes and consequences of land surface changes using advanced radar imaging.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Stellar Mid-life Crisis: What ails the middle-aged Sun?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Stellar Middle Age
Mains level: Not Much

Stars like our Sun can go through a mid-life crisis, according to new research carried out by scientists from IISER Kolkata.
Stellar Middle Age
- At about 4.6 billion years of age, the sun is middle-aged, that is, it will continue to live for roughly the same period.
- There are accurate methods for estimating the age of the Sun, such as by using radioactive dating of very old meteorites that have fallen on the Earth.
- However, for more distant stars which are similar in mass and age to the Sun, such methods are not possible.
- One of the methods used is called gyrochronology.
- There is a relationship between rotation rate and age, that is the rotation rate of a star slows down with age.
How does it occur?
- When the stellar wind escapes from the star, it carries away with it a part of the angular momentum of the star, which results in its slowing down.
- The stellar wind has two drivers: one is the high temperature of the outer atmosphere of stars – the corona – which results in an outward expansion and hence plasma winds that emanate out.
- The other is the magnetic field.
- The magnetic field actually heats the corona and so when magnetic activity is strong the winds are strong and since wind carries away the internal (rotational) angular momentum of the star, it slows down its rotation.
- This is called magnetic braking.
- As the star ages, due to this mechanism, its rotation slows down and this relationship is used in gyrochronology to estimate the age of the star.
Impact
- This can lead to dramatic changes in their activity and rotation rates.
- The study also provides an explanation for the breakdown of the long-established relation between rotation rate and age in middle-aged sunlike stars.
- However, there is a breakdown of the gyrochronology relationship, because, after midlife, a star’s rate of spin does not slow down with age as fast as it was slowing down earlier.
- Another intriguing fact is that the Sun’s activity level has been observed to be much lower than other stars of similar age.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
[pib] Near-Surface Shear Layer (NSSL) of Sun
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Near-Surface Shear Layer
Mains level: NA

Indian astronomers have found a theoretical explanation for the existence of the Near-Surface Shear Layer (NSSL) of the Sun for the first time.
What is a Near-Surface Shear Layer?
- It was long known the Sun’s equator spins faster than the poles.
- However, a peek into the internal rotation of the Sun using sound waves revealed the existence of an intriguing layer where the rotation profile of the Sun changes sharply.
- The layer is called as a near-surface shear layer (NSSL), and it exists very close to the solar surface, where there is an outward decrease in angular velocity.
What have researchers found?
- They have used an equation called the thermal wind balance equation to explain how the slight difference in temperature between solar poles and equator, called thermal wind term.
- It is balanced by the centrifugal force appearing due to solar differential rotation.
- They have noted that if this condition is true near the solar surface, it can explain the existence of NSSL, which is inferred in helioseismology (technique of using sound waves to peek inside the Sun) based observation.
Why study NSSL?
- Understanding NSSL is crucial for the study of several solar phenomena like sunspot formation, solar cycle, and it will also help in understanding such phenomena in other stars.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Geo-imaging satellite EOS-03
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: EOS-03, SSLV
Mains level: Not Much
Geo-imaging satellite for earth observation EOS-03, which would enable near real-time monitoring of natural disasters like floods and cyclones, is scheduled for launch in the third quarter of 2021.
EOS-03
- ISRO has realized a geo-imaging satellite, “EOS-03”, for Earth Observation from Geostationary Orbit.
- EOS-03 is capable of imaging the whole country four-five times daily and would enable near real-time monitoring of natural disasters like floods and cyclones.
- In addition to natural disasters, EOS-03 would also enable monitoring of water bodies, crops, vegetation condition, forest cover changes.
Other developments: Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV)
- The first developmental flight of the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) is scheduled for the fourth quarter of 2021 from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota.
- The SSLV is a cost-effective, three-stage and all-solid launch vehicle with a payload capability of 500 kg to 500 km planar orbit or 300 kg to Sun-Synchronous Polar Orbit.
- It is ideal for the on-demand, quick turn-around launch of small satellites.
- The major technologies developed as part of SSLV are flexible nozzle control with electro-mechanical actuators for all stages, miniaturized avionics, and a velocity trimming module in the upper stage for precise satellite injection.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
[pib] What are Gamma Ray Burst (GRB) Explosion?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: GRB Explosions
Mains level: Various interstellar phenomena

The emission from the most notable Gamma Ray Burst (GRB) explosion away from 4.5 billion light-years has been traced by Indian researchers.
What are GRB Explosions?
- GRBs are immensely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies.
- They are the brightest and most energetic electromagnetic events known to occur in the universe.
- Bursts can last from ten milliseconds to several hours.
- After an initial flash of gamma rays, a longer-lived “afterglow” is usually emitted at longer wavelengths (X-ray, ultraviolet, optical, infrared, microwave and radio).
- The intense radiation of most observed GRBs is thought to be released during a supernova or superluminous supernova as a high-mass star implodes to form a neutron star or a black hole.
What makes GRB special?
- The explosions are both extremely energetic (a typical burst releases as much energy in a few seconds as the Sun will in its entire 10-billion-year lifetime) and extremely rare.
- All observed GRBs have originated from outside the Milky Way galaxy, although a related class of phenomena, soft gamma repeater flares, are associated with magnetars within the Milky Way.
- It has been hypothesized that a gamma-ray burst in the Milky Way, pointing directly towards the Earth, could cause a mass extinction event.
Answer this PYQ in the comment box:
Q.Which of the following is/are cited by the scientists as evidence/evidences for the continued expansion of universe? (CSP 2012)
1. Detection of microwaves in space
2. Observation of red shift phenomenon in space
3. Movement of asteroids in space
4. Occurrence of supernova explosions in space
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4
(d) None of the above can be cited as evidence.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
[pib] 3D distribution of Molecular & Atomic Hydrogen in Galaxies
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Read the attached story
Mains level: Formation of stars
Indian scientists have estimated the three-dimensional distribution of molecular and atomic hydrogen in a nearby galaxy which can help lead to clues to the star formation processes and the evolution of the galaxy.
Study on Hydrogen distribution
- Galaxies like the one we reside in, the Milky Way, consist of discs containing stars, molecular and atomic hydrogen, and helium.
- The molecular hydrogen gas collapses on itself in distinct pockets, forming stars, its temperature was found to be low –close to 10 kelvin, or -263 ºC, and thickness is about 60 to 240 light-years.
- The atomic hydrogen extends both above and below the discs.
- Indian scientists have estimated that molecular hydrogen extends farther from the disc in both directions, up to about 3000 light-years.
- This gaseous component is warmer than the one straddling the disc and has comparatively lesser densities, thus escaping earlier observations.
- They called it the ‘diffuse’ component of the molecular disc.
Answer this PYQ in the comment box:
Q. Which one of the following sets of elements was primarily responsible for the origin of life on the Earth?
(a) Hydrogen, Oxygen, Sodium
(b) Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen
(c) Oxygen, Calcium, Phosphorous
(d) Carbon, Hydrogen, Potassium
Why does this study matter?
- The molecular hydrogen gas converts to individual stars under the pull of gravity, thus holding clues to the star formation processes and the evolution of the galaxy.
- If a significant part of the gas extends beyond the thin disc of a few hundred light-years, it may explain why astronomers also observe stars at a few thousand light-years perpendicular to the galactic disc.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
NASA’s OSIRIS-REx begins journey back from asteroid
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Asteroid Bennu
Mains level: Paper 3- OSIRIS-REx starts journey back to the earth
On May 11, NASA’s Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security, Regolith Explorer (OSIRIS-REx) spacecraft will depart asteroid Bennu, and start its two-year-long journey back to Earth.
About OSIRIS-REx
- OSIRIS-REx is NASA’s first mission to visit a near-Earth asteroid, survey its surface and collect a sample from it.
- The mission was launched in 2016, it reached its target in 2018 and since then, the spacecraft has been trying to match the velocity of the asteroid using small rocket thrusters.
- It also utilised this time to survey the surface and identify potential sites to take samples.
- In October 2020, the spacecraft briefly touched asteroid Bennu, from where it collected samples of dust and pebbles.
- Once the surface was disturbed, the spacecraft’s robotic arm captured some samples.
- The spacecraft’s engineers have also confirmed that shortly after the spacecraft made contact with the surface, it fired its thrusters and “safely backed away from Bennu”.
About Bennu
- Bennu is considered to be an ancient asteroid that has not gone through a lot of composition-altering change through billions of years, which means that below its surface lie chemicals and rocks from the birth of the solar system.
- Around 20-40 percent of Bennu’s interior is empty space and scientists believe that it was formed in the first 10 million years of the solar system’s creation, implying that it is roughly 4.5 billion years old.
- Bennu is a B-type asteroid, implying that it contains significant amounts of carbon and various other minerals.
- Because of its high carbon content, the asteroid reflects about four percent of the light that hits it, which is very low when compared with a planet.
- Bennu is named after an Egyptian deity.
- The asteroid was discovered by a team from the NASA-funded Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research team in 1999.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
[pib] What are Wolf–Rayet Stars?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Wolf–Rayet Stars
Mains level: Not Much
Indian astronomers have tracked a rare supernova explosion and traced it to one of the hottest kind of stars called Wolf–Rayet stars or WR stars.
Space science-related terms these days are often focused on Gravitational waves, Black holes etc. But basic terminologies are very important and need to be taken care of. For example, a layman may hardly find any difference between Novae-Supernovae, Neutron star, Nebula etc. UPSC often tries to bust you with such basic differences.
Wolf–Rayet Stars
- Wolf-Rayet stars represent a final burst of activity before a huge star begins to die.
- These stars, which are at least 20 times more massive than the Sun, “live fast and die hard”.
- Wolf-Rayets stars are divided into 3 classes based on their spectra, the WN stars (nitrogen dominant, some carbon), WC stars (carbon dominant, no nitrogen) and WO where oxygen is in dominant quantities.
- The average temperature of a Wolf-Rayet star is greater than 25,000 Kelvin, and they can have luminosities of up to a million times that of the Sun.
What have Indian researchers studied?
- Indian astronomers have conducted the optical monitoring of one such stripped-envelope supernova called SN 2015dj hosted in the galaxy NGC 7371 which was spotted in 2015.
- They calculated the mass of the star that collapsed to form the supernovae as well as the geometry of its ejection.
Their findings
- The scientists found that the original star was a combination of two stars – one of them is a massive WR star and another is a star much less in mass than the Sun.
- Supernovae (SNe) are highly energetic explosions in the Universe releasing an enormous amount of energy.
- Long-term monitoring of these transients opens the door to understand the nature of the exploding star as well as the explosion properties.
- It can also help enumerate the number of massive stars.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Lunar Polar Exploration (LUPEX) Mission
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: LUPEX Mission
Mains level: Not Much

India and Japan are working together on a joint lunar polar exploration (LUPEX) mission that aims to send a lander and rover to the Moon’s the South Pole around 2024.
Try this PYQ from CSP 2020:
Q.The experiment will employ a trio of spacecraft flying in formation in the shape of an equilateral triangle that has sides one million km long, with lasers shining between the craft.” the experiment in the question refers to?
(a) Voyager-2
(b) New horizons
(c) LISA pathfinder
(d) Evolved LISA
LUPEX Mission
- The LUPEX is a robotic lunar mission concept by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA).
- It would send a lunar rover and lander to explore the South Pole region of the Moon in 2024.
- JAXA is likely to provide the under-development H3 launch vehicle and the rover, while ISRO would be responsible for the lander.
- The mission concept has not yet been formally proposed for funding and planning.
- The Lunar Polar Exploration mission would demonstrate new surface exploration technologies related to vehicular transport and lunar night survival for sustainable lunar exploration in Polar Regions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NASA-ISRO SAR
Mains level: Read the attached story

Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has completed the development of a Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR).
Note the key features of the Mission. Every statement has a unique information.
NASA-ISRO SAR
- NISAR is a joint collaboration for a dual-frequency L and S-band SAR for earth observation.
- NASA and Bengaluru-headquartered ISRO signed a partnership on September 30, 2014, to collaborate on and launch NISAR.
- The mission is targeted to launch in early 2022 from ISRO’s Sriharikota spaceport in Andhra Pradesh’s Nellore district, about 100km north of Chennai.
- It is capable of producing extremely high-resolution images for a joint earth observation satellite mission with NASA.
- It will be the first satellite mission to use two different radar frequencies (L-band and S-band) to measure changes in our planet’s surface less than a centimetre across.
Objectives of the NISAR
- NISAR will observe Earth’s land and ice-covered surfaces globally with 12-day regularity on ascending and descending passes, sampling Earth on average every six days for a baseline three-year mission.
- It will measure Earth’s changing ecosystems, dynamic surfaces and ice masses, providing information about biomass, natural hazards, sea-level rise and groundwater, and will support a host of other applications.
- It would also provide data on natural hazards including earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanoes and landslides.
What are L and S Bands?
- L band waves are used for GPS units because they are able to penetrate clouds, fog, rain, storms, and vegetation.
- The S-band is used by airport surveillance radar for air traffic control, weather radar, surface ship radar, and some communications satellites, especially those used by NASA to communicate with the Space Shuttle and the International Space Station.
- NISAR uses a sophisticated information-processing technique known as SAR to produce extremely high-resolution images.
- Radar penetrates clouds and darkness, enabling NISAR to collect data day and night in any weather.
What is collaboration?
- NASA is providing the mission’s L-band SAR, a high-rate communication subsystem for science data, GPS receivers, a solid-state recorder and payload data subsystem.
- ISRO is providing the spacecraft bus, the S-band radar, the launch vehicle and associated launch services for the mission, whose goal is to make global measurements of the causes and consequences of land surface changes using advanced radar imaging.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
[pib] Devasthal Optical Telescope
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Devasthal Optical Telescope
Mains level: India's astronomical feats

Indian Scientists have indigenously designed and developed a low-cost optical spectrograph called Devasthal Optical Telescope (DOT).
Devasthal Optical Telescope
- The ‘Made in India’ optical spectrograph is named as Aries-Devasthal Faint Object Spectrograph & Camera (ADFOSC).
- It is indigenously designed and developed by Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences (ARIES), Nainital.
- DOT locates sources of faint light from distant quasars and galaxies in a very young universe, regions around supermassive black-holes around the galaxies, and cosmic explosions.
- Such spectroscopes were so far imported from abroad involved high costs.
Try this PYQ:
Q.“Event Horizon” is related to:
(a) Telescope
(b) Black hole
(c) Solar glares
(d) None of the above
Special features
- It is about 2.5 times less costly compared to the imported ones and can locate sources of light with a photon-rate as low as about 1 photon per second.
- It has been successfully commissioned on the 3.6-m Devasthal Optical Telescope (DOT), the largest in the country and in Asia, near Nainital Uttarakhand.
- This instrument uses a complex arrangement of several lenses made of special glasses, polished to better than 5-nanometer smoothness to produce sharp images of the celestial sky.
- Photons coming from distant celestial sources, collected by the telescope, are sorted into different colours by the spectrograph and are finally converted into electronic recordable signals.
- It uses an in-house developed Charge-Coupled Device (CCD) camera cooled to an extremely low temperature of -120 0
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO places Brazil’s Amazonia-1 satellite
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Amazonia satellite
Mains level: Not Much

The successful launch of Brazil’s Amazonia-1 satellite by the Indian Space Research Organisation marks a new high point in space cooperation between the two countries.
Note why Amazonia-1 Satellite is distinct in itself. It paves for statement based MCQs.
Amazonia-1 Satellite
- The Amazônia-1 or SSR- is the first Earth observation satellite entirely developed by Brazil.
- It is optimized to peer at the cloud-covered region of its namesake, the Amazon forest since it has infrared capabilities that allow it to look at the forest cover regardless of the weather.
- Brazil plans to use the satellite to “alert deforestation” in the region, Brazil’s National Institute for Space Research (INPE) said in an Amazonia 1 mission description.
Significance of the launch
- This confirms the infinite potential of the India-Brazil partnership to overcome our development challenges through high technology.
- The launch also marked the first dedicated mission of ISRO’s commercial arm NewSpace India Ltd. (NSIL).
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
[pib] Sun’s Rotation over the Century
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Sun’s Rotation
Mains level: Not Much

Scientists at Kodaikanal Solar Observatory have estimated how the Sun has rotated over a century from data extracted from old films and photographs that have been digitized.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Consider the following phenomena:
- Size of the sun at dusk
- Colour of the sun at dawn
- Moon being visible at dawn
- Twinkle of stars in the sky
- Polestar being visible in the sky
Which of the above are optical illusions?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 3, 4 and 5
(c) 1, 2 and 4
(d) 2, 3 and 5
Sun’s Rotation
- The Sun rotates around an axis that is roughly perpendicular to the plane of the ecliptic; the Sun’s rotational axis is tilted by 7.25° from perpendicular to the ecliptic.
- It rotates in the counterclockwise direction (when viewed from the north), the same direction that the planets rotate (and orbit around the Sun).
- The Sun’s rotation period varies with latitude on the Sun since it is made of gas.
- Equatorial regions rotate faster than Polar Regions.
- The equatorial regions (latitude = 0 degrees) rotate in about 25.6 days. The regions at 60 degrees latitude rotate in about 30.9 days. Polar Regions rotate in about 36 days.
Key observations of the study
- The Sun rotates more quickly at its equator than at its poles.
- Over time, the Sun’s differential rotation rates cause its magnetic field to become twisted and tangled.
- The tangles in the magnetic field lines can produce strong localized magnetic fields.
- When the Sun’s magnetic field gets twisted, there are lots of sunspots.
- The sunspots which form at the surface with an 11-year periodicity are the only route to probe the solar dynamo or solar magnetism inside the Sun and hence measure the variation in solar rotation.
Benefits offered
- This estimation would help study the magnetic field generated in the interior of the Sun, which causes sunspots and results in extreme situations like the historical mini-ice age on Earth (absence of sunspots).
- It could also help predict solar cycles and their variations in the future.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ISRO collaborates to build alternative to Google Maps
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: MapmyIndia, Various tools of ISRO
Mains level: Geospatial data and its utilization
The ISRO has joined hands with MapmyIndia to combine their geospatial expertise and build holistic solutions by leveraging their geoportals.
Note various geo-spatial solutions of ISRO mentioned in the newscard.
What is the Project?
- It combines the power of MapmyIndia’s digital maps and technologies with ISRO’s catalogue of satellite imagery and earth observation data.
- Indian users would not be dependent on foreign organisations for maps, navigation and geospatial services, and leverage made-in-India solutions instead.
Various components
The collaboration will enable them to jointly identify and build holistic geospatial solutions utilising the ISRO’s earth observation datasets such as-
- IRNSS (Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System) called NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation, is India’s own navigation system, developed by ISRO.
- Bhuvan is the national geo-portal developed and hosted by ISRO comprising geospatial data, services and tools for analysis.
- VEDAS (Visualization of Earth observation Data and Archival System) is an online geo-processing platform using an optical, microwave, thermal and hyperspectral EO data covering applications particularly meant for academia, research and problem solving, according to ISRO.
- MOSDAC (Meteorological and Oceanographic Satellite Data Archival Centre)is a data repository for all the meteorological missions of ISRO and deals with weather-related information, oceanography and tropical water cycles.
About MapmyIndia
- MapmyIndia is an Indian technology company that builds digital map data, telematics services, location-based SaaS (Software as a service) and GIS AI services.
- The company was founded in 1992 and is headquartered at New Delhi with regional offices in Mumbai and Bengaluru and smaller offices across India.
- Its map covers all 7.5 lakh villages, 7500+ cities at street and building-level, connected by all 63 lakh kilometres of road network pan India and within cities, in total providing maps for an unparalleled 3+ crore places across India.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Mukundpura CM2
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Meteor terminology
Mains level: Study of asteroids and meteors

An asteroid which made its landfall in Mukundpura village near Jaipur has been named after the same village and is under the study of Geological Survey of India, Kolkata.
Try this question from CSP 2014:
Q.What is a coma, in the content of astronomy?
(a) Bright half of material on the comet
(b) Long tail of dust
(c) Two asteroids orbiting each other
(d) Two planets orbiting each other
Mukundpura CM2
- The meteorite named Mukundpura CM2 was classified to be a carbonaceous chondrite.
- This is a type of stony meteorite, considered the most primitive meteorite and a remnant of the first solid bodies to accrete in the solar system.
- The composition of carbonaceous chondrites is also similar to the Sun.
- Chondrites are silicate-droplet-bearing meteorites, and this Mukundpura chondrite is the fifth carbonaceous meteorite known to fall in India.
Why it is important to study meteorites?
- Meteorites are representative of asteroids.
- Asteroids are the remnant debris of the inner solar system formation process and thus offer the formation history or the building blocks of the planets.
- Therefore, by studying meteorites in the laboratory and asteroids by exploration and sample return mission we try to reconstruct the activity of early solar system events.
- Also, asteroids are often rich in volatiles and other minerals and can be exploited for future planetary exploration.
Do you know?
Meteorites are broadly classified into three groups – stony (silicate-rich), iron (Fe–Ni alloy), and stony-iron (mixed silicate–iron alloy).
Details of its study
- The study revealed that Mukundpura CM2 had experienced varying degrees of alteration during the impact.
- Some minerals like forsterite and FeO olivine, calcium aluminium rich inclusion (CAI) minerals escaped alteration.
- Few magnetites, sulphides and calcites were also found.
- Detailed spectroscopic studies revealed that the meteorite had very high (about 90%) phyllosilicate minerals comprising both magnesium and iron.
- Further X-ray studies showed it also had aluminium complexes.
Relevance to asteroids
- The results of the Mukundpura CM2 study are relevant to the surface composition of near-Earth asteroids Ryugu and Bennu.
- In October 2020, NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission collected samples from Bennu and is expected to return in September 2023.
- Last month, Japan’s Hayabusa-2 mission landed on Earth with samples from Ryugu.
Back2Basics:

Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
CMS-01 Satellite launched by ISRO
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CMS-01
Mains level: Not Much

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully placed into a transfer orbit India’s 42nd communications satellite, CMS-01, carried onboard the PSLV-C50.
CMS-01
- It is a communications satellite envisaged for providing services in extended C Band of the frequency spectrum and its coverage will include the Indian mainland and the Andaman & Nicobar and Lakshadweep islands, the ISRO.
- The satellite is expected to have a life of over seven years.
- It was injected precisely into its pre-defined sub- geostationary transfer orbit (GTO).
- CMS-01 is considered to be a replacement of the aged satellite GSAT-12. It provides services like tele-education, tele-medicine, disaster management support and Satellite Internet access.
What is GTO?

- A geosynchronous transfer orbit or geostationary transfer orbit (GTO) is a type of geocentric orbit.
- Satellites which are destined for geosynchronous (GSO) or geostationary orbit (GEO) are (almost) always put into a GTO as an intermediate step for reaching their final orbit.
- A GTO is highly elliptic.
- Its perigee (closest point to Earth) is typically as high as low Earth orbit (LEO), while its apogee (furthest point from Earth) is as high as geostationary (or equally, a geosynchronous) orbit.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: GMRT
Mains level: Not Much

The Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT) has been selected as a ‘Milestone’ facility by the U.S.-based Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE).
Note: GMRT is not an ISRO mission.
About GMRT
- The GMRT located near Pune is an array of thirty fully steerable parabolic radio telescopes of 45-metre diameter, observing at metre wavelengths.
- It is operated by the National Centre for Radio Astrophysics (NCRA), a part of the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Mumbai.
- It was conceived and built under the direction of Late Prof. Govind Swarup from 1984 to 1996.
- At the time it was built, it was the world’s largest interferometric array offering a baseline of up to 25 kilometres (16 mi).
- Astronomers from all over the world regularly use this telescope to observe many different astronomical objects such as HII regions (interstellar atomic hydrogen that is ionized), galaxies, pulsars, supernovae, and Sun and solar winds.
A significant feat
- IEEE is the world’s largest technical professional organisation dedicated to advancing technology in all areas related to electrical and electronics engineering.
- The IEEE Milestones programme honours significant technical achievements which have a global or regional impact. This is only the third such IEEE ‘Milestone’ recognition for an Indian contribution.
- The previous two Indian IEEE Milestones were for the pioneering work done by Sir J.C. Bose to demonstrate the generation and reception of radio waves in 1895 (recognised in 2012), and for the Nobel Prize-winning (in 1930) ‘scattering of light’ phenomenon observed by Sir C.V. Raman in 1928.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
[pib] IRNSS now part of World Wide Radio Navigation System
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: IRNSS, IMO, NaVIC
Mains level: IRNSS

The Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) has been accepted as a component of the World Wide Radio Navigation System (WWRNS) for operation in the Indian Ocean Region by the International Maritime Organization (IMO).
Try this PYQ:
With reference to the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), consider the following statements:
- IRNSS has three Satellites in geostationary and four satellites the geosynchronous orbits.
- IRNSS covers entire India and about 5500 sq. km beyond its borders.
- India will have its own satellite navigation system with full global coverage by the middle of 2019.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) None
What is IRNSS?
- The IRNSS, with an operational name of NavIC (acronym for Navigation with Indian Constellation) is an Indian regional satellite navigation system that provides accurate real-time positioning and timing services.
- It covers India and a region extending 1,500 km around it, with plans for further extension.
- The system currently consists of a constellation of seven satellites, with two additional satellites on ground as stand-by.
- The constellation is in orbit as of 2018, and the system was expected to be operational from early 2018 after a system check.
- It will provide two levels of service, the “standard positioning service”, which will be open for civilian use, and a “restricted service” (an encrypted one) for authorised users (including the military).
Benefits of the move
- This move will enable merchant vessels to use IRNSS for obtaining position information similar to GPS and GLONASS.
- This will assist in the navigation of ships in Indian ocean waters within the area covered by 50°N latitude, 55°E longitude, 5°S latitude and 110°E longitude (approximately up to 1500 km from Indian boundary).
Back2Basics: International Maritime Organisation (IMO)
- IMO is the UN specialized agency with responsibility for the safety and security of shipping and the prevention of marine pollution by ships.
- Its primary purpose is to develop and maintain a comprehensive regulatory framework for shipping and its remit today includes safety, environmental concerns, legal matters, technical co-operation, maritime security and the efficiency of shipping.
- IMO is governed by an assembly of members and is financially administered by a council of members elected from the assembly.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
EOS-01 Satellite
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: EOS-01
Mains level: Not Much
India would launch its latest earth observation satellite EOS-01 and nine international customer spacecraft onboard it’s PSLV-C49.
Try this PYQ:
Q.The term ‘IndARC’, sometimes seen in the news, is the name of:
(a) An indigenously developed radar system inducted into Indian Defence
(b) India’s satellite to provide services to the countries of Indian Ocean Rim
(c) A scientific establishment set up by India in Antarctic region
(d) India’s underwater observatory to scientifically study the Arctic region
EOS-01
- EOS-01 is intended for applications in agriculture, forestry and disaster management support.
- This is the first launch by the Indian Space Research Organisation since the COVID-19-induced lockdown came into force in March.
- This will be the 51st mission of ISRO’s workhorse, the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle.
What is Earth Observation Satellite (EOS)?
- An EOS or remote sensing satellite is a satellite used or designed for Earth observation (EO) from orbit, including spy satellites and similar ones intended for non-military uses such as environmental monitoring, meteorology, cartography and others.
- Starting with IRS-1A in 1988, ISRO has launched many operational remote sensing satellites.
- Today, India has one of the largest constellations of remote sensing satellites in operation.
- Currently, *thirteen* operational satellites are in Sun-synchronous orbit and *four* in Geostationary orbit.
- The data from these satellites are used for several applications covering agriculture, water resources, urban planning, rural development, mineral prospecting, environment, forestry, ocean resources and disaster management.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Indian Sat: Another satellite made by students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Femto Satellites, Micro-gravity
Mains level: Not Much

An experimental satellite developed by three students of Karur (TN) has been selected for launch in sub-orbital space by NASA.
Try this PYQ:
Q.The term ‘IndARC’, sometimes seen in the news, is the name of:
(a) An indigenously developed radar system inducted into Indian Defence
(b) India’s satellite to provide services to the countries of Indian Ocean Rim
(c) A scientific establishment set up by India in Antarctic region
(d) India’s underwater observatory to scientifically study the Arctic region
Indian Sat
- The Indian Sat is made of reinforced graphene polymer. It is 3 cm in size and weighs 64 gm.
- It has its own radio frequency communication to transmit and receive a signal from earth to outer space. The solar cells attached to the satellite generate power for it.
- The photographic film will absorb and measure the cosmic radiation inside the rocket.
- It would study the effect of reinforced graphene polymers in microgravity. It would be in sub-orbital space flight for a few minutes before landing in the ocean.
What is micro-gravity?
- The term micro-g environment is more or less synonymous with the terms weightlessness and zero-g, but with an emphasis on the fact that g-forces are never exactly zero—it is just very small.
- On the ISS, for example, the small g-forces come from tidal effects, gravity from objects other than the Earth, such as astronauts, the spacecraft, and the Sun, and, occasionally, air resistance.
Back2Basics: Femto-satellites
- Femto-satellites are satellites with a mass lower than 100 grams.
- These new categories of satellites are, by concept, low cost devices if they are based on Commercial-of-the-Shelf (COTS) components.
- Some examples of applications are related to low-cost missions with a short time of development.
Kalamsat
- Kalamsat was a communication satellite with a life span of two months launched in 2017.
- The nanosatellite is a 10cm cube weighing 1.2 kg.
- It will be the first to use the rocket’s fourth stage as an orbital platform.
- The fourth stage will be moved to higher circular orbit so as to establish an orbital platform for carrying out experiments.
- It is named after former Indian president Dr APJ Abdul Kalam and was built by an Indian high school student team, led by Rifath Sharook, an 18-year-old from the Tamil Nadu town of Pallapatti.
- It is the world’s lightest and first-ever 3D-printed satellite.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
[pib] 20 years of Himalayan Chandra Telescope (HCT)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Chandra Telescope, Chandra X Ray Observatory
Mains level: Not Much

In the cold, dry desert of Ladakh, 4500 meters above the mean sea level, for two decades, the 2-m diameter optical-infrared Himalayan Chandra Telescope (HCT) at the Indian Astronomical Observatory (IAO) has been scanning the night sky for 20 years in search of stellar explosions, comets, asteroids, and exo-planets.
Chandra X-Ray observatory and now, it is Himalayan Chandra Telescope. Do you the key difference? The former is a NASA project while the HCT is the Indian one.
Himalayan Chandra Telescope
- The HCT is a 2.01 meters (6.5 feet) diameter optical-infrared telescope named after India-born Nobel laureate Subrahmanyam Chandrasekhar.
- It contains a modified Ritchey-Chretien system with a primary mirror made of ULE ceramic which is designed to withstand low temperatures it experiences.
- The telescope was manufactured by Electo-Optical System Technologies Inc. at Tucson, Arizona, USA.
- It is mounted with 3 science instruments called Himalaya Faint Object Spectrograph (HFOSC), the near-IR imager and the optical CCD imager.
- It is remotely operated from Hosakote, about 35 km northeast of Bangalore via an INSAT-3B satellite link which allows operation even in sub-zero temperatures in winter.
Significant feats
- The telescope has been used in many coordinated international campaigns to monitor stellar explosions, comets, and exo-planets, and has contributed significantly to these studies.
- Some of the thrust research areas are the study of solar system bodies like; comets, asteroids, the study of star formation processes and young stellar objects, the study of open and globular clusters and variable stars in them.
- It has helped in analysis of elements in the atmosphere of evolved stars, star formation in external galaxies, Active Galactic Nuclei, stellar explosions like novae, supernovae, gamma-ray bursts and so on.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
[pib] UVIT: India’s first multi-wavelength astronomical observatory
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: UVIT
Mains level: Not Much

The satellite that detected the first extreme-UV rays in the Universe from the cosmic noon celebrated its 5th birthday today.
Try this PYQ:
Q.“Event Horizon” is related to:
(a) Telescope
(b) Black hole
(c) Solar glares
(d) None of the above
Ultra-Violet Imaging Telescope (UVIT)
- The UVIT is a remarkable 3-in-1 imaging telescope.
- Weighing all of 230 kg, the UVIT can simultaneously observe in the visible, the near-ultraviolet (NUV) and the far-ultraviolet (FUV).
- UVIT comprises of two separate telescopes. One of them works in the visible (320-550 nm) and the NUV (200-300 nm).
- The second works only in the FUV (130-180 nm).
Its achievement
- It has carried out 1166 observations of 800 unique celestial sources proposed by scientists both from India and abroad.
- It has explored stars, star clusters, mapping of the large and small satellite galaxies nearby to our own Milky Way galaxy called the Magellanic Clouds.
- It is an energetic phenomenon in the Universe such as the ultra-violet counterparts to gamma-ray bursts, supernovae, active galactic nuclei, and so on.
- Its superior spatial resolution capability has enabled astronomers to probe star formation in galaxies as well as resolve the cores of star clusters (3 times better than the last NASA mission, GALEX).
- Observations from UVIT has recently led to the discovery of a galaxy located at a distance of about 10 billion light-years from Earth and emitting extreme ultraviolet radiation that can ionize the intergalactic medium.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Space industry and challenges
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 3- Opportunities and challenges in outer space
The article analyses opportunities and challenges the outer space technology offers to us.
Emerging trends in space industry
- The price for reaching low Earth orbit has declined by a factor of 20 in a decade.
- It enhances human space travel possibilities by leveraging new commercial capabilities.
- According to a Bank of America Report, the $350 billion space market today will touch $2.7 trillion by 2050.
- Starlink, the constellation being constructed by SpaceX to provide global Internet access, plans more than 10,000 mass-produced small satellites in low Earth orbit.
- In a decade, 80,000 such satellites could be in space compared to less than 3,000 at present.
- Companies such as Planet, Spire Global and Iceye are using orbital vantage points to collect and analyse data to deliver fresh insights in weather forecasting, global logistics, crop harvesting and disaster response.
- Space could prove attractive for high-tech manufacturing too.
- In short, an exciting new platform is opening up for entrepreneurs.
3 Challenges
1) Governance of outer space
- Framework for governance of outer space as it becomes democratised, commercialised and crowded is becoming obsolescent.
- The Outer Space Treaty of 1967 enshrines the idea that space should be “the province of all mankind” and “not subject to national appropriation by claims of sovereignty”.
- The Rescue Agreement, Space Liability Convention, and the Space Registration Convention expanded provisions of the Outer Space Treaty.
- The Moon Treaty of 1979 was not ratified by major space-faring nations.
- Space law does not have a dispute settlement mechanism, is silent on collisions and debris, and offers insufficient guidance on interference with others’ space assets.
- These gaps heighten the potential for conflict in an era of congested orbits and breakneck technological change.
2) Acknowledging role of non-state entities
- The legal framework related to outre space is state-centric, placing responsibility on states alone.
- However, non-state entities are now in the fray for commercial space exploration and utilisation.
- Some states are providing frameworks for resource recovery through private enterprises.
- Some scholars and governments view this as against the principle of national non-appropriation, violating the spirit if not the letter of the existing space law.
- The lack of alignment of domestic and international normative frameworks risks a damaging free-for-all competition for celestial resources involving actors outside the space framework.
3) The arms race in outer space
- The space arms race is difficult to curb, especially since almost all space technologies have military applications.
- For example, satellite constellations are commercial but governments could acquire their data to monitor military movements.
- Investment in technologies that can disrupt or destroy space-based capabilities is under way.
- Despite concerns about military activity in outer space for long, not much progress has been made in addressing them.
- The UN General Assembly passes a resolution on Prevention of an Arms Race in Outer Space since 1982.
- The current geopolitical situation does not hold hope for addressing concerns of a space arms race.
Need for space legislation in India
- India has invested enormous resources in its space programme through the Indian Space Research Organisation.
- More importantly, our space assets are crucial for India’s development.
- The proposed involvement of private players and the creation of an autonomous body IN-SPACe for permitting and regulating activities of the private sector are welcome efforts.
- However, the space environment that India faces requires us to go beyond meeting technical milestones.
- We need a space legislation enabling coherence across technical, legal, commercial, diplomatic and defence goals.
Consider the question “Outer space technology is expanding its horizon day by day. However, there are certain challenges the expansion of the space technology faces. What are these challenges and suggest ways to deal with such challenges.”
Conclusion
Our space vision also needs to address global governance, regulatory and arms control issues. As space opens up our space vision needs broadening too.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
ASTROSAT Satellite
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ASTROSAT; Space missions of ISRO and NASA
Mains level: NA
ASTROSAT, India’s first multi-wavelength satellite observatory, has detected an extreme ultraviolet (UV) light from a galaxy which is 9.3 billion light-years away from Earth.

Try out:
Consider the following statements regarding the AstroSat:
1)AstroSat is India’s multi-wavelength space telescope.
2)ASTROSAT mission is that enables the simultaneous multi-wavelength observations of various astronomical objects with a single satellite.
3)ASTROSAT observes the universe in the optical and high energy X-ray regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.Which of the following above statements is true?
a.1 and 2
b.2 and 3
c.1 and 3
d.1, 2 and 3
AUDFs01
- AstroSat has detected extreme-UV light from a galaxy, called AUDFs01, 9.3 billion light-years away from Earth.
- The galaxy is located in the Hubble Extreme Deep field, through AstroSat.
- This is a very important clue to how the dark ages of the universe ended and there was light in the universe.
About ASTROSAT
- AstroSat is India’s first dedicated multi-wavelength space telescope. It was launched on a PSLV-XL on 28 September 2015.
It is the first dedicated Indian astronomy mission aimed at studying celestial sources in X-ray, optical and UV spectral bands simultaneously.
————–//—————-
Find some time to scroll through recent ISRO missions and discoveries.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
[pib] Sarabhai Crater
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Sarabhai Crater
Mains level: Chandrayaan 2 Mission

The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) has named a crater captured by Chandrayaan 2 Orbiter after Vikram Sarabhai.
Try this PYQ:
What do you understand by the term Aitken Basin? (CSP 2012)
(a) It is a desert in southern Chile which is known to be the only location on earth where no rainfall takes place
(b) It is an impact crater on the far side of the Moon
(c) It is a Pacific coast basin, which is known to house large amounts of oil and gas
(d) It is a deep hypersaline anoxic basin where no aquatic animals are found
Sarabhai Crater
- “Sarabhai” Crater is named after Dr Vikram Sarabhai and around 250 to 300 kilometres east of this Crater is where the Apollo 17 and Luna 21 Missions had landed.
- The crater captured in 3D images shows that the Crater has a depth of around 1.7 Kms taken from its raised rim and the slope of Crater walls is in between 25 to 35 degree.
- These findings will help the Space Scientists to understand further the process of the lunar region filled with lava.
Who was Vikram Sarabhai?
- Sarabhai was an Indian physicist and astronomer who initiated space research and helped develop nuclear power in India.
- He is internationally regarded as the Father of the Indian Space Program.
- Known as the cradle of space sciences in India, the Physical Research Laboratory (PRL) was founded in 1947 by him. He was the founder of ISRO.
- He started a project for the fabrication and launch of an Indian satellite.
- As a result, the first Indian satellite, Aryabhata, was put in orbit in 1975 from a Russian cosmodrome.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Lithium Nucleosynthesis in Stars
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Lithium, Nucleosynthesis, Big Bang
Mains level: Formation of stars
A forty-year-old puzzle regarding the production of lithium in stars has been solved by Indian researchers.
Try this question from CSP 2013:
Q.Consider the following phenomena:
- Size of the sun at dusk
- Colour of the sun at dawn
- Moon being visible at dawn
- Twinkle of stars in the sky
- Polestar being visible in the sky
Which of the above are optical illusions?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 3, 4 and 5
(c) 1, 2 and 4
(d) 2, 3 and 5
Lithium nucleosynthesis in Stars
- Stars, as per known mechanisms of evolution, actually destroy lithium as they evolve into red giants.
- Planets were known to have more lithium than their stars — as is the case with the Earth-Sun pair.
- However, leading to a contradiction, some stars were found that were lithium-rich.
- The new work by an Indian researcher shows that when stars grow beyond their Red Giant stage into what is known as the Red Clump stage, they produce lithium.
- This is known as a Helium Flash and this is what enriches them with lithium.
Studying lithium-rich stars
- About 40 years ago, a few large stars were spotted that were lithium-rich.
- This was followed by further discoveries of lithium-rich stars, and that posed a puzzle — if stars do not produce lithium, how do some stars develop to become lithium-rich.
- The planet engulfment theory was quite popular. For example, Earth-like planets may increase the star’s lithium content when they plunge into [their] star’s atmosphere when the latter become Red Giants.
Findings of the Indian research
- Indian researchers have been working on this puzzle for nearly 20 years to devise a method of measuring lithium content using low-resolution spectra in a large number of stars.
- The study demonstrated that lithium abundance enhancement among low mass giant stars is common.
- Until now, it was believed that only about 1% of giants are lithium-rich.
- Secondly, the team has shown that as the star evolves beyond the Red Giant stage, and before it reaches the Red Clump stage, there is a helium flash which produces an abundance of lithium.
Back2Basics: Lithium
- Lithium is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the lightest metal and the lightest solid element.
- S light element commonly used today in communication device technology, it has an interesting story.
- It was first produced in the Big Bang, around 13.7 billion years ago when the universe came into being, along with other elements.
- While the abundance of other elements grew millions of times, the present abundance of lithium in the universe is only four times the original [Big Bang] value. It is actually destroyed in the stars.
- The Sun, for instance, has about a factor of 100 lower amount of lithium than the Earth.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Phobos: The closest and biggest moon of Mars
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: MOM, Phobos
Mains level: Quest for Mars and its possibility to host life

The Mars Colour Camera (MCC) onboard ISRO’s Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) has captured the image of Phobos, the closest and biggest moon of Mars.
Try this question from CSP 2017:
Q.Which region of Mars has a densely packed river deposit indicating this planet had water 3.5 billion years ago?
(a) Aeolis Dorsa (b) Tharsis (c) Olympus Mons (d) Hellas
About Phobos
- Phobos is the innermost and larger of the two natural satellites of Mars, the other being Deimos.
- Both moons were discovered in 1877 by American astronomer Asaph Hall.
- Phobos is a small, irregularly shaped object with a mean radius of 11 km and is seven times as massive as the outer moon, Deimos.
- Phobos is largely believed to be made up of carbonaceous chondrites.
- The violent phase that Phobos has encountered is seen in the large section gouged out from a past collision (Stickney crater) and bouncing ejecta.
Back2Basics: Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM)
- The MOM also called Mangalyaan is a space probe orbiting Mars since 24 September 2014. It was launched on 5 November 2013 by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- It aims at studying the Martian surface and mineral composition as well as scans its atmosphere for methane (an indicator of life on Mars).
- It is India’s first interplanetary mission and it made it the fourth space agency to reach Mars, after Roscosmos, NASA, and the European Space Agency.
- It made India the first Asian nation to reach Martian orbit and the first nation in the world to do so on its maiden attempt.
- It was initially meant to last six months, but subsequently, ISRO had said it had enough fuel for it to last “many years.”
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
IN-SPACe: Future forerunner for India’s space economy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: IN-SPACE, ANTRIX, NSIl
Mains level: ISRO and India's space economy
- The government approved the creation of Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) to ensure greater private participation in India’s space activities.
- This decision is described as historic being part of an important set of reforms to open up the space sector and make space-based applications and services more widely accessible to everyone.
Practice question for mains:
Q. What is IN-SPACe? Discuss how it would benefit ISRO and contribute to India’s space economy.
What is IN-SPACe?
- IN-SPACe is supposed to be a facilitator, and also a regulator.
- It will act as an interface between ISRO and private parties and assess how best to utilise India’s space resources and increase space-based activities.
- IN-SPACe is the second space organisation created by the government in the last two years.
- In the 2019 Budget, the government had announced the setting up of a New Space India Limited (NSIL), a public sector company that would serve as a marketing arm of ISRO.
Confusion over NSIL and ANTRIX
- NSIL’s main purpose is to market the technologies developed by ISRO and bring it more clients that need space-based services.
- That role, incidentally, was already being performed by Antrix Corporation, another PSU working under the Department of Space, and which still exists.
- It is still not very clear why there was a need for another organisation with overlapping function.
- The government now had clarified the role of NSIL that it would have a demand-driven approach rather than the current supply-driven strategy.
- Essentially, what that means is that instead of just marketing what ISRO has to offer, NSIL would listen to the needs of the clients and ask ISRO to fulfil those.
Then, why was IN-SPACe needed?
(1) ISRO and its limited resources
- It is not that there is no private industry involvement in India’s space sector.
- In fact, a large part of the manufacturing and fabrication of rockets and satellites now happens in the private sector. There is increasing participation of research institutions as well.
- Indian industry, however, is unable to compete, because till now its role has been mainly that of suppliers of components and sub-systems.
- Indian industries do not have the resources or the technology to undertake independent space projects of the kind that US companies such as SpaceX have been doing or provide space-based services.
(2) India and the global space economy
- Indian industry had a barely three per cent share in a rapidly growing global space economy which was already worth at least $360 billion.
- Only two per cent of this market was for rocket and satellite launch services, which require fairly large infrastructure and heavy investment.
- The remaining 95 per cent related to satellite-based services, and ground-based systems.
(3) Catering to domestic demands
- The demand for space-based applications and services is growing even within India, and ISRO is unable to cater to this.
- The need for satellite data, imageries and space technology now cuts across sectors, from weather to agriculture to transport to urban development and more.
- If ISRO is to provide everything, it would have to be expanded 10 times the current level to meet all the demand that is arising.
(4) Promoting other private players
- Right now, all launches from India happen on ISRO rockets, the different versions of PSLV and GSLV.
- There were a few companies that were in the process of developing their own launch vehicles, the rockets like ISRO’s PSLV that carry the satellites and other payloads into space.
- Now ISRO could provide all its facilities to private players whose projects had been approved by IN-SPACe.
How ISRO gains from all these?
- There are two main reasons why enhanced private involvement in the space sector seems important.
- One is commercial, and the other strategic. And ISRO seems unable to satisfy this need on its own.
- Of course, there is a need for greater dissemination of space technologies, better utilization of space resources, and increased requirement of space-based services.
- The private industry will also free up ISRO to concentrate on science, research and development, interplanetary exploration and strategic launches.
- Right now too much of ISRO’s resources are consumed by routine activities that delay its more strategic objectives.
A win-win situation for all
- ISRO, like NASA, is essentially a scientific organisation whose main objective is the exploration of space and carrying out scientific missions.
- There are a number of ambitious space missions lined up in the coming years, including a mission to observe the Sun, a mission to the Moon, a human spaceflight, and then, possibly, a human landing on the Moon.
- And it is not that private players will wean away from the revenues that ISRO gets through commercial launches.
- The space-based economy is expected to “explode” in the next few years, even in India, and there would be more than enough for all.
- In addition, ISRO can earn some money by making its facilities and data available to private players.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Centre (IN-SPACe)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: IN-SPACE, ANTRIX
Mains level: ISRO and the scope for its commercial operations
The Union Cabinet has approved the creation of the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Centre (IN-SPACe) to provide a level playing field for private companies to use Indian space infrastructure.
Note the key differences between IN-SPACe, ANTRIX and NSIL. We can expect a prelims question with shuffled objectives of these organisations.
IN-SPACe
- The creation of IN-SPACe is part of reforms aimed at giving a boost to private sector participation in the entire range of space activities.
- The IN-SPACe is expected to hand-hold, promote and guide the private industries in space activities through encouraging policies and a friendly regulatory environment.
- It would endeavour to reorient space activities from a ‘supply-driven’ model to a ‘demand-driven’ one, thereby ensuring optimum utilization of the nation’s space assets.
Why need IN-SPACe?
- India is among a handful of countries with advanced capabilities in the space sector.
- Space sector can play a major catalytic role in the technological advancement and expansion of our Industrial base.
- The proposed reforms will enhance the socio-economic use of space assets and activities, including through improved access to space assets, data and facilities.
Back2Basics: New Space India Limited (NSIL)
- It functions under the administrative control of Department of Space (DOS).
- It aims to commercially exploit the research and development work of ISRO Centres and constituent units of DOS.
- The NSIL would enable Indian Industries to scale up high-technology manufacturing and production base for meeting the growing needs of the Indian space programme.
- It would further spur the growth of Indian Industries in the space sector.
ANTRIX
- Antrix Corporation Limited (ACL), Bengaluru is a wholly-owned Government of India Company under the administrative control of the Department of Space.
- It is as a marketing arm of ISRO for promotion and commercial exploitation of space products, technical consultancy services and transfer of technologies developed by ISRO.
- Antrix is engaged in providing Space products and services to international customers worldwide.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Detection of Fluorine in hot Extreme Helium (EHe) Stars
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Extreme Helium (EHe) Stars
Mains level: NA
A study by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) has detected the presence of singly ionized fluorine for the first time in the atmospheres of hot Extreme Helium Stars.
UPSC may ask a simple statement-based question considering the following points:
If there is the presence of hydrogen, their abundance in universe and how it is different from neutron stars etc.
What are EHe stars?
- An extreme helium star or EHe is a low-mass supergiant that is almost devoid of hydrogen, the most common chemical element of the universe.
- There are 21 of them detected so far in our galaxy.
- The origin and evolution of these Hydrogen deficient objects have been shrouded in mystery.
- Their severe chemical peculiarities challenge the theory of well-accepted stellar evolution as the observed chemical composition of these stars do not match with that predicted for low mass evolved stars.
Why is the study significant?
- Clues to the evolution of extreme helium stars require accurate determinations of their chemical composition, and the peculiarities, if any, become very important.
- Fluorine plays a very crucial role in this regard to determine the actual evolutionary sequence of these hydrogen deficient objects.
- The scientists explored the relationship of hot EHes with the cooler EHes, based on their fluorine abundance and spotted it in the former, thus establishing an evolutionary connection across a wide range of effective temperature.
- This makes a strong case that the main form of these objects involves a merger of a carbon-oxygen (CO) and a Helium (He) white dwarf.
- The detection of enhanced fluorine abundances in the atmospheres of hot EHes solves a decade-old mystery about their formation.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
[pib] Earth’s Magnetosphere and its dynamics
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Earths magnetosphere
Mains level: Earths magnetosphere and its significance for space missions

Scientists at the Indian Institute of Geomagnetism (IIG) have developed a generalized one-dimensional fluid simulation code capable of studying a wide spectrum of coherent electric field structures of earth’s magnetosphere which can be useful in the planning of future space missions.
The newscard talks of not so new phenomenon but a basic terminology of space sciences. Kindly make a note of what the Magnotesphere is, how it is formed, role of solar winds, Geodynamo etc.
Earth’s Magnetosphere
- The magnetosphere is the region of space surrounding Earth where the dominant magnetic field is the magnetic field of Earth, rather than the magnetic field of interplanetary space.
- It is generated by the interaction of the solar wind with Earth’s magnetic field.
Features of the Earth’s magnetosphere
1) Bow shock,
2) Magnetosheath,
3) Magnetopause,
4) Northern tail lobe,
5) Southern tail lobe,
6) Plasmasphere,
7) Solar wind.
How is it formed?
- Sun is the major source of plasma deposition in space around the Earth. Sun forces some of its plasma towards the earth in the form of the solar wind.
- The speed of this wind varies between 300 to 1500 km/s, which carries with it solar magnetic field, called as Interplanetary Magnetic Field (IMF).
- The magnetic field is generated by electric currents due to the motion of convection currents of a mixture of molten iron and nickel in the Earth’s outer core.
- These convection currents are caused by heat escaping from the core, a natural process called a geodynamo.
Why study the magnetosphere?
- The Earth’s magnetosphere is a vast region which has a finite number of satellites hurtling through this realm.
- The morphology of the plasma processes around the satellite can be understood quite well.
- However, when they leave the observational domain of one satellite to enter into another, a vast blind arena is created.
- How the morphology of these processes changes over space and time can be ideally deciphered only through computer simulations.
Outcome of the study
- Almost 99% of matter in the universe is in the form of plasma, Earth’s magnetosphere, too, contains this material and the plasma.
- They have the ability to hamper the working of a number of satellites that have been placed in orbit in the magnetospheric region.
Significance
- Apart from the well being of these expensive satellites, the academic understanding of this region is quite essential to comprehend the cosmos in its entirety.
- The study will help advance the knowledge of plasma waves, instabilities, and coherent effects associated with wave-particle interactions that are useful in planning of future space missions.
- It can also lead to precisely controlled fusion laboratory experiments for ever-expanding energy needs of humanity.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
[pib] Super-luminous Supernova SN 2010kd
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Supernovae
Mains level: Not Much
Indian researchers have found that SN 2010kd, a super-luminous supernova stands out with the amount of mass as well as Nickel ejected during explosion.
Space science-related terms these days are often focused on Gravitational waves, Black holes etc. But basic terminologies are very important and need to be taken care of. For example, a layman may hardly find any difference between Novae-Supernovae, Neutron star, Nebula etc. UPSC often tries to bust you with such basic differences.
What are Supernovae?
- Supernovae are kind of energetic explosions were the core of massive stars (a few times to that of the mass of our Sun) goes to a catastrophic phase of explosion liberating huge amounts of energy and mass.
- These events are visible through very far away distances much beyond our own solar system.
- Super-luminous supernovae are a special type of stellar explosions having energy output 10 or more times higher than that of standard supernovae.
What is so distinct about SN 2010kd?
- The mass ejection from SN 2010kd is metallic and is much more than seen in case of normal core-collapse supernovae.
- The scientists found that SN 2010kd exploded with a larger velocity but decayed slower than other similar supernovae.
- The observations show that parameters like rotation and metallicity play a crucial role in stellar explosions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
[pib] What is Big Bang Nucleosynthesis (BBN)?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Big Bang Nucleosynthesis (BBN)
Mains level: BBN and its significance in the formation of our solar system
Indian researchers have discovered hundreds of Li-rich giant stars produced during BBN indicating that Li is being produced in the stars and accounts for its abundance in the interstellar medium.
Most of the space based theories and missions are focussed on the formation of our solar system. BBN is the most basic auxillary among them.
What is Big Bang Nucleosynthesis (BBN)?
- BBN is the production of nuclei other than those of the lightest isotope of hydrogen during the early phases of the Universe.
- Primordial nucleosynthesis is believed by most cosmologists to have taken place in the interval from roughly 10 seconds to 20 minutes after the Big Bang.
- It is calculated to be responsible for the formation of most of the universe’s helium in various isotopic forms.
- Essentially all of the elements that are heavier than lithium were created much later, by stellar nucleosynthesis in evolving and exploding stars.
Lithium in space
- Lithium (Li), is one of the three primordial elements, apart from Hydrogen and Helium (He), produced in the Big Bang Nucleosynthesis (BBN).
- However, the present measurement of Li in the interstellar medium and very young stars is about 4 times more than the primordial value.
- Thus, identifying sources of Li enrichment in our Galaxy has been a great interest to researchers to validate BBN as well as a stellar mixing process.
- In general, stars are considered as Li sinks. This means that the original Li, with which stars are born, only gets depleted over stars’ life-time as Li burns at relatively very low temperatures.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
[pib] What are Blazars?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Blazars
Mains level: Black Holes, Blazars

Researchers from the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA), Bangalore have conducted the first systematic study on the gamma-ray flux variability nature on different types of Blazars.
Strange terminologies from space-based studies are very important from prelims point of view. We can expect a statement based question seeking to identify the term which is being referred to in the paragraph.
What are Blazars?
- At the center of most galaxies, there’s a massive black hole that can have mass of millions or even billions of Suns that accrete gas, dust, and stellar debris around it.
- As these material falls towards the black hole, their gravitational energy gets converted to light forming active galactic nuclei (AGN).
- A minority of AGN (~15%) emit collimated charged particles called jets travelling at speeds close to the speed of light.
- Blazars are AGN whose jets are aligned with the observer’s line of sight.
- Some blazars are thought to host binary black holes in them and could be potential targets for future gravitational-wave searches.
Studying blazars
- Blazars are the most luminous and energetic objects in the known universe were found to be emitters of gamma-rays in the 1990s.
- It is only with the capability of Fermi Gamma-ray space telescope (launched in 2008) to scan the entire sky once in three hours one is able to probe the flux variability characteristics of blazars on a range of time scales.
- Gamma-ray band is one of the bands of the electromagnetic spectrum on which there is limited knowledge on the flux variability of blazars.
- Major problem while studying them is to localize the site for the production of gamma-rays.
Significance
- The study of blazars could provide clues to the processes happening close to the black hole, not visible through direct imaging.
- Exploring blazars will provide key inputs to constrain the high energy production site as well as the high energy emission processes.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Aditya L1 Mission
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Parker Probe. Aditya L1 Mission, Lagranges points
Mains level: Read the attached story

NASA’s Parker Solar Probe launched on August 12, 2018 has completed its fourth close approach — called perihelion very recently, whizzing past at about 3.93 lakh km/h, at a distance of only 18.6 million km from the Sun’s surface.
Aditya L1: Exciting ahead
- The ISRO is preparing to send its first scientific expedition to study the Sun.
- Named Aditya-L1, the mission, expected to be launched early next year, will observe the Sun from a close distance, and try to obtain information about its atmosphere and magnetic field.
- ISRO categorizes Aditya L1 as a 400 kg-class satellite that will be launched using the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) in XL configuration.
- The space-based observatory will have seven payloads (instruments) on board to study the Sun’s corona, solar emissions, solar winds and flares, and Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs), and will carry out round-the-clock imaging of the Sun.
- Aditya L1 will be ISRO’s second space-based astronomy mission after AstroSat, which was launched in September 2015.
What is L1?
- L1 refers to Lagrangian/Lagrange Point 1, one of five points in the orbital plane of the Earth-Sun system.
- Lagrange Points, named after Italian-French mathematician Josephy-Louis Lagrange, are positions in space where the gravitational forces of a two-body system (like the Sun and the Earth) produce enhanced regions of attraction and repulsion.
- These can be used by spacecraft to reduce fuel consumption needed to remain in position.
- The L1 point is home to the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory Satellite (SOHO), an international collaboration project of NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA).
- The L1 point is about 1.5 million km from Earth, or about one-hundredth of the way to the Sun.
But why is studying the Sun important?
- Every planet, including Earth and the exoplanets beyond the Solar System, evolves — and this evolution is governed by its parent star.
- The solar weather and environment, which is determined by the processes taking place inside and around the sun, affects the weather of the entire system.
- Variations in this weather can change the orbits of satellites or shorten their lives, interfere with or damage onboard electronics, and cause power blackouts and other disturbances on Earth.
- Knowledge of solar events is key to understanding space weather.
- To learn about and track Earth-directed storms, and to predict their impact, continuous solar observations are needed.
- Every storm that emerges from the Sun and heads towards Earth passes through L1, and a satellite placed in the halo orbit around L1 of the Sun-Earth system has the major advantage of continuously viewing the Sun without any occultation/eclipses.
Why are solar missions challenging?
- What makes a solar mission challenging is the distance of the Sun from Earth (about 149 million km on average, compared to the only 3.84 lakh km to the Moon).
- More importantly the super hot temperatures and radiations in the solar atmosphere make it difficult to study.
- NASA’s Parker Solar Probe has already gone far closer — but it will be looking away from the Sun.
- The earlier Helios 2 solar probe, a joint venture between NASA and space agency of erstwhile West Germany, went within 43 million km of the Sun’s surface in 1976.
Problem of Heat
- The Parker Solar Probe’s January 29 flyby was the closest the spacecraft has gone to the Sun in its planned seven-year journey so far.
- Computer modelling estimates show that the temperature on the Sun-facing side of the probe’s heat shield, the Thermal Protection System, reached 612 degrees Celsius, even as the spacecraft and instruments behind the shield remained at about 30°C, NASA said.
- During the spacecraft’s three closest perihelia in 2024-25, the TPS will see temperatures around 1370°C.
Hurdles for Aditya L1
- It will stay much farther away, and the heat is not expected to be a major concern for the instruments on board. But there are other challenges.
- Many of the instruments and their components for this mission are being manufactured for the first time in the country, presenting as much of a challenge as an opportunity for India’s scientific, engineering, and space communities.
- One such component is the highly polished mirrors which would be mounted on the space-based telescope.
- Due to the risks involved, payloads in earlier ISRO missions have largely remained stationary in space; however, Aditya L1 will have some moving components, scientists said.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
NavIC navigation system
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NAVIC, IRNSS
Mains level: Utility of NAVIC
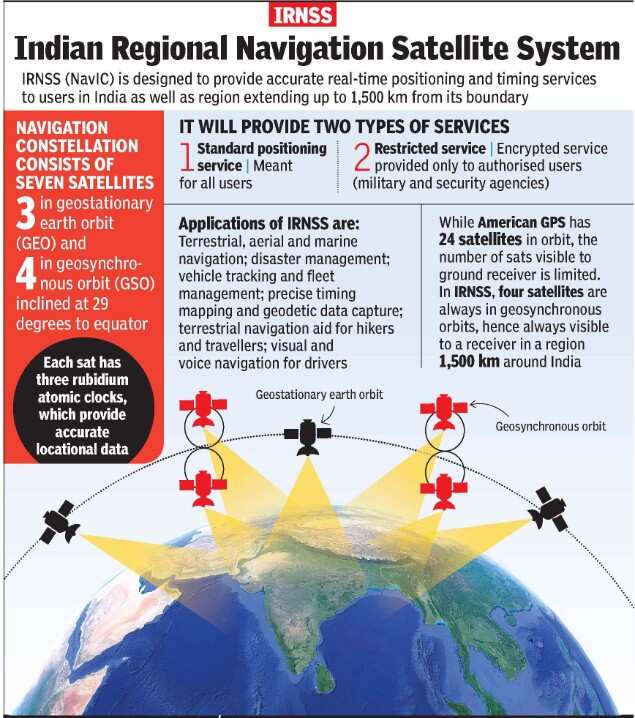
Qualcomm Technologies has released chipsets, supporting India’s own GPS system ‘Navigation with Indian Constellation’ (NavIC).
New androids to be equipped with NavIC
- The Qualcomm chipsets now supports up to 7 satellite constellations at the same time, including the use of all of NavIC’s operating satellites.
- These enhancements will enable select mobile, automotive and IoT platforms to better serve key industries and technology ecosystems in the region.
- It will help improve user experience for location-based applications especially in dense urban environments where geolocation accuracy tends to degrade, said the company earlier.
About NavIC
- The name NavIC was given by Prime Minister Narendra Modi after successful launch of the seventh navigation satellite, in April, 2016.
- To date, ISRO has built a total of nine satellites in the IRNSS series, of which eight are currently in orbit.
- The constellation is designed to provide accurate position information service to users in India as well as the region extending up to 1,500 km from its boundary, which is its primary service area.
- It is designed to provide two types of services – Standard Positioning Service (SPS), which is provided to all users and Restricted Service (RS), which is an encrypted service provided only to the authorised users.
- The system is expected to provide a position accuracy of better than 20 m in the primary service area.
For more readings about NAVIC, navigate to the page:
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
[op-ed of the day] Lady Gaganaut
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Skybot F-850: Robot sent by Russia to dock with the International Space Station.
Mains level: Paper 3-Vyommitra, India's human spaceflight in 2022.
Context
The first gaganaut-Vyomamitra- to head for space in an Indian craft will not be human, but humanoid.
What Vyomamitra would do on spaceflight?
- Test the technological environment: Vyomamitra unveiled by ISRO will fly two missions to test the technological environment which human gaganauts will inhabit on India’s first demonstration of human spaceflight in 2022.
- She will test the systems and instruments that they would use.
- Vyomamitra cannot test the cabin ecosystem, as she would not be able to breathe the air.
- Other functions: Vyomamitra is perfectly capable of issuing commands, activating switches and, obviously, communicating with earth.
- Give company to human travellers: Her prototype has already chatted with people at the Isro event where she was introduced to the public, and future iterations will be able to give company to human travellers at the loneliest frontier.
A shift from sending animals to humanoids
- Performing roles previously performed by animals: Vyomamitra will be executing the pioneering role which has traditionally been given to animals – testing systems for survivability.
- Fruit flies and monkeys were the first beings to lift off, riding V2 rockets with devices monitoring their vital signs.
- Why using humanoid is more useful: Using a humanoid robot is more useful because it can be used to replicate the behavioural and operational responses of a human.
- Indeed, robots need not remain pioneers testing survivability, or assistants to the human crew, but are expected to crew missions that are too prolonged or too dangerous for a human pilot.
Opportunities and the future of AI-powered humanoid
- Russian robot in space: As India prepared for human flight, in August 2019, the Russian space agency Roscosmos sent up the anthropomorphic robot Skybot F-850 to dock with the International Space Station.
- The mission has been halted because of technical issues.
- Goals beyond survivability testing: If the nation which pioneered human spaceflight with Yuri Gagarin’s mission in 1961 is sending humanoid robots into space, survivability testing is not the only legitimate goal of missions powered by artificial intelligence and robotics.
- Opportunity to develop new technologies: Humanoid in space also provide opportunities to test and develop these technologies under circumstances that do not prevail on earth.
- The inputs, goals and skills learned are different and while AI on earth specifically focuses on creating systems which do not think like humans,
- Human-like AI system need of industry: The space industry would value systems that are human-like, to stand in for crew.
Conclusion
Vyomamitra represents the very first iteration of AI in space, and later generations could prove to be as essential for spaceflight as cryogenic engines.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Vyom Mitra: ISRO’s half-humanoid
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Vyoma Mitra
Mains level: Various functions of Vyoma Mitra in ISRO's unmanned missions

ISRO unveiled its first ‘woman’ astronaut during the event ‘Human Spaceflight and Exploration’.
Vyom Mitra
- The AI-based robotic system is being developed at a robotics lab at the VSSC in Thiruvananthapuram.
- Vyom Mitra will be used for an unmanned flight of ISRO’s GSLV III rocket in December 2020, which, along with a second unmanned flight in July 2021.
- This will serve as the test of ISRO’s preparedness for its maiden manned space mission, Gaganyaan, being targeted for 2022 to mark 75 years of India’s independence.
Functions of the humanoid
- Vyommitra, equipped with a head, two arms and a torso, is built to mimic crew activity inside the crew module of Gaganyaan.
- Attaining launch and orbital postures, responding to the environment, generating warnings, replacing carbon dioxide canisters, operating switches, monitoring of the crew module, receiving voice commands, responding via speech (bilingual) are among its functions listed.
- It will have a human-like face, with lips synchronised for movement to mimic speech.
- Once it is fully developed, Vyommitra will be able to use equipment on board the spacecraft’s crew module, like safety mechanisms and switches, as well as receive and act on commands sent from ground stations.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
GSAT-30 successfully launched
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: GSAT-30 and its applications
Mains level: Not Much
India’s first satellite of 2020, the GSAT-30 was successfully launched. The launch vehicle Ariane 5 VA-251 lifted off from Kourou Launch Base, French Guiana.
GSAT-30
- GSAT-30 derives its heritage from ISRO’s earlier INSAT/GSAT satellite series and will replace INSAT-4A in
- In the days ahead, orbit-raising manoeuvres will be performed to place the satellite in Geostationary Orbit (36,000 km above the equator) by using its onboard propulsion
- During the final stages of its orbit raising operations, the two solar arrays and the antenna reflectors of GSAT-30 will be
- Following this, the satellite will be put in its final orbital . The satellite will be operational after the successful completion of all in-orbit tests.
Utility of the satellite
- GSAT-30 will provide DTH Television Services, connectivity to VSATs for ATM, Stock-exchange, Television unlinking and Teleport Services, Digital Satellite News Gathering (DSNG) and e-governance applications.
- The satellite will also be used for bulk data transfer for a host of an emerging telecommunication
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
ISRO Missions and Discoveries
Indian Data Relay Satellite System (IDRSS)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Indian Data Relay Satellite System (IDRSS)
Mains level: Significance of IDRSS
India plans to ring in its own era of space-to-space tracking and communication of its space assets this year by putting up a new satellite series called the Indian Data Relay Satellite System.
Indian Data Relay Satellite System (IDRSS)
- The IDRSS is planned to track and be constantly in touch with Indian satellites, in particular those in low-earth orbits which have limited coverage of earth.
- In the coming years, it will be vital to ISRO whose roadmap is dotted with advanced LEO missions such as space docking, space station, as well as distant expeditions to moon, Mars and Venus.
- It will also be useful in monitoring launches.
- The first beneficiary would be the prospective crew members of the Gaganyaan mission of 2022 who can be fully and continuously in touch with mission control throughout their travel.
- IDRSS satellites of the 2,000 kg class would be launched on the GSLV launcher to geostationary orbits around 36,000 km away.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Let’s cover the entire gamut of projects concluded by ISRO in these 2 years.
IRNSS will be covered in a separate article.
GSAT Series
#1. GSAT-6
- GSAT-6 is the twenty fifth geostationary communication satellite of India built by ISRO and twelfth in the GSAT series
- Five of GSAT-6’s predecessors were launched by GSLV during 2001, 2003, 2004, 2007 and 2014 respectively
- After its commissioning, GSAT-6 has joined the group of India’s other operational geostationary satellites
- GSAT-6 Satellite provides communication through five spot beams in S-band and a national beam in C-band for strategic users
- It was launched using GSLV-D6 (Explained below in GSLV Missions)
#2. GSAT-15
- It is a high power satellite being inducted into the INSAT/ GSAT system
- It carries a total of 24 communication transponders in Ku-band as well as a GPS
- Aided GEO Augmented Navigation (GAGAN) payload operating in L1 and L5 bands
- It is the third satellite to carry GAGAN payload after GAST-8 and GSAT-10, which are already providing navigation services from orbit
- It carries a Ku-band beacon as well to help in accurately pointing ground antennas towards the satellite
- It was launched by Ariane-5 VA-227 launch vehicle from Kourou, French Guiana on early morning of November 11, 2015
#3. GSAT-16
- GSAT-16, an advanced communication satellite, weighing 3181.6 kg at lift-off, is being inducted into the INSAT-GSAT system
- GSAT-16 is configured to carry a total of 48 communication transponders, the largest number of transponders carried by a communication satellite developed by ISRO so far, in normal C-band, upper extended C-band and Ku-band
- GSAT-16 carries a Ku-band beacon as well to help accurately point ground antennas towards the satellite
- The designed on-orbit operational life of GSAT-16 is 12 years
- The communication transponders on-board GSAT-16 together ensure continuity of various services currently provided by INSAT-GSAT system and serve as on-orbit spares to meet contingency requirements or for the augmentation of such services
- GSAT-16 was launched into a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) by Ariane-5 VA-221 launch vehicle from Kourou, French Guiana
- GSAT-16 was positioned at 55 deg East longitude in the Geostationary orbit and co-located with GSAT-8, IRNSS-1A and IRNSS-1B satellites
PAYLOADS OF GSAT-16
- 12 Ku-band transponders each with 36 MHz usable bandwidth with footprint covering Indian mainland and Andaman & Nicobar islands
- 24 C-band transponders each with 36 MHz usable bandwidth with footprint covering Indian mainland and island territories
- 12 Upper Extended C-band transponders each with 36 MHz usable bandwidth with footprint covering Indian mainland and island territories
PSLV Missions
#1. PSLV C28/ DMC3 Mission: Heaviest commercial mission ever undertaken by ISRO
- PSLV in its 30th flight (PSLV-C28) launched three identical DMC3 optical earth observation satellites built by Surrey Satellite Technology Limited (SSTL), UK
- PSLV-C28 was the ninth flight of PSLV in ‘XL’ configuration
- With the overall lift-off mass of the five satellites amounting to about 1440 kg, this mission becomes the heaviest commercial mission ever undertaken by Antrix/ISRO
- The three DMC3 satellites, each weighing 447 kg, were launched into a 647 km Sun-Synchronous Orbit (SSO) using the high-end version of PSLV (PSLV-XL) from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota (SDSC-SHAR), the spaceport of India
DMC3
- The DMC3 constellation comprises of three advanced mini-satellites DMC3-1, DMC3-2 and DMC3-3
- It is designed to address the need for simultaneous high spatial resolution and high temporal resolution optical Earth Observation
- Launched into a single Low-Earth Orbit plane and phased with a separation of 120° between them, these satellites can image any target on the Earth’s surface every day
- Major application areas include surveying the resources on earth and its environment, managing urban infrastructure and monitoring of disasters
It also carried two auxiliary satellites from UK:
- CBNT-1, an optical technology demonstrator earth observation micro satellite built by SSTL
- De-OrbitSail, a technology demonstrator nano satellite built by Surrey Space Centre
#2. PSLV C30/ Astrosat
- PSLV, in its 31st flight (PSLV-C30), launched Astrosat into a 650 km orbit of 6 deg inclination to the equator
- Along with Astrosat, six satellites from international customers viz. LAPAN-A2 of Indonesia, NLS-14 (Ev9) of Canada and four identical LEMUR satellites of USA were launched
- PSLV-C30 is the tenth flight of PSLV in its ‘XL’ Configuration
#3. PSLV C29/ TeLEOS-1 Mission/ 6 Singapore satellites
- PSLV, in its 32nd flight (PSLV-C29), launched six satellites of Singapore into a 550 km circular orbit inclined at 15 degrees to the equator
- This is the eleventh flight of PSLV in ‘core-alone’ configuration (without the use of solid strap-on motors)
- Of these six satellites, TeLEOS-1 is the primary satellite weighing 400 kg
- The other five are co-passenger satellites which include two micro-satellites and three nano-satellites:
- VELOX-CI, micro-satellite
- VELOX-II, 6U-Cubesat technology demonstrator
- Athenoxat-1, a technology demonstrator nano-satellite
- Kent Ridge-1, a micro-satellite
- Galassia, 2U-Cubesat
IRNSS Constellation
The recent launches in this series are:
#1. PSLV C-27/ IRNSS-1D
#2. PSLV C-31/ IRNSS-1E
#3. PSLV C32/ IRNSS-1F
#4. PSLV C33/ IRNSS-1G
IRNSS-1G was the 7th and last satellite in the IRNSS constellation.
With this, India has achieved the milestone of being one the very few countries to have its own Positioning System.
[IRNSS will be dealt with in detail in a separate story]
GSLV Missions
#1. GSLV-D6/ GSAT-6
- GSLV-D6 is the ninth flight of India’s Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV)
- It is also the fifth developmental flight of GSLV
- This is the third time the indigenously developed Cryogenic Upper Stage (CUS) is being carried on-board during a GSLV flight
- GSLV-D6 flight is significant since it intends to continue the testing of CUS
- GSLV is designed to inject 2 ton class of communication satellites into Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO)
- GSAT-6 is explained above
#2. GSLV-Mk III: Launching humans into space
- ISRO killed two birds with one stone when the GSLV Mk3 test with an inert cryogenic stage took off with the CARE (Crew Module Atmospheric Re-entry Experiment)
- The module reached an altitude of 80 km and made a successful splash down in the sea using the largest parachutes ever made in the country
- Once operational, the crew module will host up to three Indian astronauts for orbital missions lasting up to a week in space
- It will make India only the fourth nation in the world after Russia, US and China to have the ability to send humans into space; maybe even to the moon one day
- According to ISRO the schedule for sending the first Indian on an Indian rocket is planned for 2021
- For this, the GSLV Mk3 will have to be man-rated – it has to demonstrate a set number of continuous successful launches
Reusable Launch Vehicle- Technology Demonstrator (RLV-TD)
The cost of access to space is the major deterrent in space exploration and space utilization. A reusable launch vehicle is the unanimous solution to achieve low cost, reliable and on-demand space access
Reusable Launch Vehicle-Technology Demonstration Program or RLV-TD is a series of technology demonstration missions that have been considered as a first step towards realizing a Two Stage To Orbit (TSTO) fully re-usable vehicle.
A Winged Reusable Launch Vehicle technology Demonstrator (RLV-TD) has been configured to act as a flying test bed to evaluate various technologies, namely, hypersonic flight, autonomous landing, powered cruise flight and hypersonic flight using air-breathing propulsion.
2015 Space Pioneer Award
- Space Pioneer award for the year 2015 was presented to Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) in the Science and Engineering category during the 34th Annual International Space Development Conference held at Toronto in Canada during May 20 -24, 2015
- National Space Society (NSS) of USA presented this award in recognition of ISRO’s efforts in accomplishing Mars Mission in its very first attempt
- In 2009, NSS has presented similar award to ISRO in recognition of the great accomplishment they have made in the success of the Lunar Probe, Chandrayaan-1
- National Space Society (NSS) is an independent nonprofit educational membership organisation dedicated to the creation of a space faring civilisation




























