Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Data trends in economic survey;
Mains level: Major five issues with the Indian Economy;
Why in the News?
The 2023-24 Economic Survey highlights realistic challenges for India’s growth, projecting GDP growth at 6.5%-7% for FY 2024-25 despite 8% growth in FY 2023-24.
What are the major five issues with the Indian Economy?
- Weak Demand: In India, an unfavourable environment for FDI growth is due to high interest rates in developed countries, which increases the cost and opportunity cost of investment in India.
- Dependence on China: Due to over-reliance on China for imports, particularly in key sectors like renewable energy, limits India’s manufacturing capabilities and increases vulnerability to geopolitical tensions.
- Tepid Private Investment: Despite tax cuts aimed at stimulating capital formation, the corporate sector has not significantly increased investment, leading to a lack of job creation and economic dynamism.
- Employment Challenges: The need to generate approximately 78.5 lakh jobs annually in the non-farm sector until 2030 to accommodate the growing workforce, coupled with insufficient data on job creation, complicates labour market analysis.
- Infrastructure Deficiencies: Inadequate infrastructure, such as roads, railways, and sanitation, continues to hinder economic development and efficiency, requiring substantial investment and reform to improve productivity.
What are the suggestions given in the Economic Survey?
- Private Sector’s Role in Job Creation: The corporate sector should take responsibility for creating jobs, as it is in their enlightened self-interest.
- Embracing Healthy Lifestyle: Indian businesses should learn from India’s traditional lifestyle, food, and recipes to live healthily and in harmony with nature.
- Focusing on Agriculture: The farm sector can generate higher value addition, boost farmers’ income, create opportunities for food processing and exports, and make the sector attractive to urban youth.
- Removing Regulatory Bottlenecks: Licensing, inspection, and compliance requirements imposed by various levels of government are an onerous burden on businesses, especially MSMEs.
- Improving Data Quality: The lack of availability of timely data on the absolute number of jobs created in various sectors precludes an objective analysis of the labour market situation.
Way forward:
- Enhance Infrastructure Development: Need to prioritize investments in essential infrastructure such as roads, railways, and sanitation to boost economic efficiency and productivity.
- Strengthen Data Collection and Analysis: The government should develop robust mechanisms for timely and accurate data collection on employment and other key economic indicators.
Mains PYQ:
Q Do you agree with the view that steady GDP growth and low inflation have left the Indian economy in good shape? Give reasons in support of your arguments. (2019)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bordering countries of India;
Mains level: Neighbourhood First Policy;
Why in the News?
The Union Budget presented by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman prioritized India-funded projects in neighbouring countries, receiving the majority of the Ministry of External Affairs’ allocation.
What are the India-funded projects in the neighbourhood?
- India has provided significant aid to Nepal, including funding for hydroelectric power plants like Pardi, Trishuli and Devighat.
- In Afghanistan, India has provided over $3 billion in assistance and was involved in over 400 projects across 34 provinces, including major infrastructure projects like the Salma Dam and the Zaranj-Dalaram Highway.
- In Myanmar, Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Projects is $484 million project aims to connect the northeastern Indian state of Mizoram to the Sittwe port in Myanmar’s Rakhine state.
- In the 2024-25 budget, India allocated ₹700 crore to Nepal (up from ₹550 crore), ₹245 crore to Sri Lanka (up from ₹150 crore), and ₹30 crore to Seychelles (up from ₹10 crore).
Reasons for reduced focus on Bhutan
- Bhutan, the largest recipient of MEA’s annual allocation, saw a dip in funding by ₹332.02 crore to ₹2,068.56 crore.
- However, this slight reduction does not indicate a decrease in funding for projects in Bhutan, as India and Bhutan recently cleared 61 projects amounting to ₹4,958 crore.
Importance of Bhutan for India:
-
-
- Bhutan shares borders with India and China, acting as a buffer state between the two. Its strategic location is crucial for India’s security interests.
- India has provided assistance to Bhutan in areas like defence, infrastructure, and communication to maintain its sovereignty and territorial integrity.
- During the 2017 Doklam standoff between India and China, Bhutan allowed Indian troops to enter its territory to resist Chinese incursions.
-
-
- India is Bhutan’s largest trading partner, accounting for 98% of its exports and 90% of its imports.
- Bhutan’s hydropower potential is a significant source of revenue, and India has been instrumental in assisting Bhutan in developing these projects.
- India provides substantial economic support to Bhutan. In 2015-16, India’s budgetary support to Bhutan stood at ₹61.60 billion, making it the largest recipient of India’s foreign aid.
- Cultural Ties: Bhutan and India share strong cultural ties, as both countries are predominantly Buddhist
Future scope for India’s Neighbourhood Policy (Way forward)
- Strengthening Bilateral Ties: Need to negotiate free trade agreements, promote investments, and collaborate on infrastructure projects to boost economic ties.
- For example, India and Bangladesh have made significant progress in recent years, with the inauguration of the Maitri Setu bridge connecting Tripura to Bangladesh. The two countries are also working on the Akhaura-Agartala rail link to enhance connectivity.
- Promoting Regional Cooperation: Need to collaborate on regional initiatives such as the BBIN (Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal) Motor Vehicles Agreement for seamless movement of goods and people.
- For instance, India has been actively involved in the BIMSTEC Coastal Shipping Agreement and the BIMSTEC Grid Interconnection project to enhance regional connectivity and energy cooperation.
Mains PYQ:
Q Evaluate the economic and strategic dimensions of India’s Look East Policy in the context of the post-Cold War international scenario. (UPSC IAS/2016)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Trend in Defence budgeting;
Mains level: Significance of indigenisation in defence sector ;
Why in the News?
Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman has allocated ₹6.22 lakh crore for the Defence Ministry for 2024-25, matching the amount presented in the interim Budget in February.
Budgetary allocation for different sectors
- Border Roads Organisation (BRO): The BRO received a significant increase in funding, with an allocation of ₹6,500 crore, aimed at improving border infrastructure and promoting socio-economic development in border areas.
- Indian Coast Guard: The allocation for the Indian Coast Guard is ₹7,651.8 crore, which is 6% lower than the revised estimates for FY24. Of this, ₹3,500 crore is designated for capital expenditure to enhance maritime capabilities.
- Innovation in Defence: An additional ₹400 crore has been allocated for innovation in defence through the Acing Development of Innovative Technologies with iDEX (ADITI) scheme, aimed at engaging startups and MSMEs in developing indigenous defence technologies.
- Overall Allocation Breakdown: The allocation for the Defence Ministry includes 27.66% for capital expenditure, 14.82% for revenue expenditure, 30.66% for pay and allowances, 22.7% for defence pensions, and 4.17% for civil organizations under the Defence Ministry.
Marginal Capex Push
- Slight increase in capital expenditure: The budget reflects a marginal increase in capital expenditure, focusing on strengthening the capabilities of the armed forces and enhancing domestic procurement.
- Strategic infrastructure development: The increased allocation to the BRO and the Coast Guard indicates a strategic push towards improving infrastructure in border areas and maritime security, though the overall capital push remains modest.
- Focus on Indigenous solutions: The emphasis on domestic capital procurement and innovation through the iDEX scheme aims to bolster self-reliance in defence technology, fostering a more robust Indigenous defence industry.
- Long-term strategic goals: The allocations are aligned with long-term strategic goals, including enhancing operational preparedness and infrastructure development in sensitive regions, although the overall growth in capital expenditure may be viewed as conservative.
- Balancing defence needs with budget constraints: While the budget seeks to address critical defence needs, the slight reduction in the overall percentage of the budget allocated to defence suggests a balancing act between defence priorities and other pressing social and economic needs.
Way forward:
- Enhance Focus on Indigenous Production: The government should further promote indigenous production capabilities by increasing investments in research and development, and by providing incentives for domestic manufacturers to produce advanced defence technologies.
- Strengthen Infrastructure Development: The need for continued emphasis on infrastructure projects, particularly in border areas, should be prioritized to enhance national security and socio-economic development, ensuring that allocations are effectively utilized for maximum impact.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Constitutional background of Reservation
Why in the News?
The Karnataka State Employment Bill, 2024, proposing private sector reservations for Kannadigas, is on hold after backlash from business and industry leaders.
What Does the Constitution Say?
- Equality of Opportunity (Article 16):
- Article 16(1): Guarantees equality of opportunity in public employment and prohibits discrimination based on race, religion, caste, sex, descent, place of birth, or residence.
- Article 16(3): Allows Parliament to prescribe residence requirements for public office in a specific state or Union Territory, but this power does not extend to state legislatures.
- Freedom of Movement and Residence (Article 19):
- Article 19(1)(d): Ensures the freedom of movement throughout India.
- Article 19(1)(e): Grants the right to reside and settle in any part of India.
- Article 19(1)(g): Protects the right to practice any profession or carry on any occupation, trade, or business.
- Legislative Powers (Article 35):
- Article 35(a): Designates Parliament as the sole authority to make laws concerning residence requirements for employment or appointments to public offices, thereby restricting state legislatures from enacting such laws.
|
Why Is the constitutionality of the Karnataka State Employment of local candidates in the Industries, factories and Other Establishments Bill, 2024, being doubted?
- Absence of Provision for Private Sector Reservation: The Constitution does not provide for reservation in the private sector, leading to concerns about the legality of such mandates at the state level.
- Legislative limits on residential criteria: State Assemblies lack the power to prescribe residential criteria for private sector employment, as such powers are reserved for Parliament under Article 35(a).
- Impact on Fundamental Rights:
- The Bill may infringe on citizens’ rights under Article 19(1)(d) and (e), restricting their freedom of movement and right to reside or settle in different states.
- The quota system might violate Article 19(1)(g), impinging on individuals’ freedom to pursue occupations of their choice.
What Is the Status of Similar Laws in Other States Such as Haryana?
- Haryana State Employment of Local Candidates Act, 2020: Mandated 75% reservation in the private sector for jobs with salaries up to ₹30,000. This Act was struck down by the Punjab and Haryana High Court, and the matter is pending before the Supreme Court.
- Andhra Pradesh Employment of Local Candidates in Industries/Factories Act, 2019: Proposed 75% reservation for local candidates and allowed a three-year period for training and engagement. This Act has faced legal challenges and has not been zealously implemented by the government.
- Jharkhand Definition of Local Persons Bill: Initially faced resistance from the Governor over its constitutionality, especially regarding 100% reservation for locals in certain job categories. The bill was re-enacted in December 2023 despite concerns about its constitutionality.
Way forward:
- Inclusive Dialogue: The Karnataka government should engage in comprehensive consultations with all stakeholders, including industry representatives, legal experts, and civil society, to understand their concerns and suggestions.
- Impact Analysis: Need to conduct a detailed socio-economic impact assessment of the proposed reservation policy can provide insights into its potential benefits and drawbacks.
Mains PYQ:
Q The reservation of seats for women in the institutions of local self-government has had a limited impact on the patriarchal character of the Indian Political Process.” Comment. (2019)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bordering states of India with Bangladesh
Mains level: Initiatives related to 'Strengthening Ties and Empowering Governance'
Why in the News?
At least 130 people have died in clashes during student protests over government job quotas in Bangladesh.
Why have students in Bangladesh taken to the streets?
- Opposition to Quota System: Students are protesting against the quota system for government jobs, specifically the 30% reserved for freedom fighters and their descendants, which they believe limits merit-based opportunities.
- Reversal of Quota Reforms: The protests intensified after the Supreme Court restored the quota system, reversing the previous decision to abolish it. Students demand a more balanced and inclusive quota system.
Why Is the 30% quota for Freedom fighters and their descendants an emotive matter for the Awami League?
- Legacy of Sheikh Mujib: The quota system was introduced by Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, and continuing it is seen as fulfilling his legacy and honouring the sacrifices of freedom fighters.
- Political Significance: The Awami League views the quota as a means to reinforce support within the bureaucracy and maintain political loyalty, linking it closely to the party’s historical and ideological narrative.
How did the protests turn violent?
- The violence escalated when Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina labeled protesters as “razakars” or traitors, which enraged students and led to violent clashes with the police and Rapid Action Battalion (RAB).
- The situation deteriorated to the point where the military had to be deployed to control the unrest, further intensifying the violence and confrontation between protesters and authorities.
Have the Quotas Been Misused?
- Allegations of Abuse: There have been claims that the quota system has been misused, with reservations extended to party operatives and not just deserving freedom fighters’ descendants.
- Dilution and Extension: The quota system, initially meant for freedom fighters and war survivors, has been criticized for being extended to broader categories over time, leading to concerns about fairness and effective utilization.
India’s recent Initiatives – ‘Strengthening Ties and Empowering Governance’
- Economic Cooperation: India and Bangladesh agreed to strengthen trade and investment linkages, including the early commencement of negotiations for a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA).
- Capacity Building for Civil Servants: India has been providing training and capacity-building programs for Bangladeshi civil servants through the National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG).
- Development Assistance: India is the largest development partner for Bangladesh, having extended approximately $8 billion in Lines of Credit (LOC) over the past eight years for infrastructure development in sectors such as roads, railways, and shipping.
|
Way forward:
- Balanced Approach: The Bangladesh government should consider a transparent and balanced quota reform that addresses both merit-based and reservation needs.
- Monitoring and Accountability: Establishing mechanisms to monitor the implementation of quotas and prevent misuse is crucial.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: About UNSC, BRICS and QUAD
Mains level: Importance of BRICS
Why in the News?
Recently, the Quad Foreign Ministers’ meeting in Japan highlighted the UNSC’s paralysis, ongoing violations of international law, and the growing influence of China and an axis of Russia, China, North Korea, and Iran.
Present State of the UNSC:
- Paralysis and Ineffectiveness: The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is currently paralyzed, unable to effectively address or resolve significant global conflicts. Efforts to reform the UNSC have stalled, leaving it incapable of adapting to contemporary geopolitical realities.
- Impunity in Violations of International Law: International law is being violated with impunity in conflicts such as the Ukraine war and the assault on Gaza by Israel.
- The UNSC’s inability to act decisively has contributed to a growing disregard for its authority and mandates.
Role of India in QUAD:
- Strategic Partnership: India’s involvement in QUAD enhances its strategic partnerships with the other member nations, allowing for collaborative efforts in maritime security, humanitarian assistance, and disaster relief operations.
- Building Indo-In Pacific Policy: One of the primary objectives of QUAD is to mitigate China’s assertive actions in Indo Pacific region.
- India is positioned to take on a leadership role in regional security.
- Economic Collaboration: The QUAD nations are working towards strengthening economic ties, including infrastructure development at ‘Strait of Malacca’ and alternative financing options for Indo-Pacific countries.
- Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief: India has actively engaged in humanitarian efforts, exemplified by its Operation Sanjeevani, which provided medical assistance to several Indo-Pacific nations during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Silverlining on BRICS
- Promoting South-South Cooperation: BRICS represents a significant non-Western global initiative in the post-Cold War era. It can bring together major emerging economies from different parts of the world.
- Amplifying Voices in Global Governance: The BRICS Population is around 40% of the world so the BRICS nations can amplify their voices in global governance and expand their choices of international partners through this grouping.
- Fostering Economic Resilience: Despite the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, BRICS has emerged as a more effective and efficient institution in fostering economic resilience among its member nations.
- Exploring Alternative Financial Mechanisms: BRICS has taken steps to establish alternative financial mechanisms, such as the New Development Bank (NDB) and the Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA).
-
- Role BRICS group in G20: The BRICS group has consistently pushed for the inclusion of development issues in the G20 agenda. They argue that the G20 should prioritize the needs of developing countries, particularly in terms of infrastructure investment and social sector support
- Promoting Sustainable Development: The BRICS nations have emphasized the importance of responsible financing for green and sustainable development.
- Initiatives like the NDB’s focus on sustainable infrastructure projects which would help in achieving of SDG Goal 9.
Conclusion: Need to support and advocate for comprehensive reforms of the UNSC to address its paralysis and enhance its effectiveness. This includes expanding permanent membership to better represent contemporary global dynamics and improving decision-making processes to tackle conflicts with greater agility.
Mains PYQ:
Q Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad) is transforming itself into a trade bloc from a military alliance, in present times Discuss. (2020)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: World Economic Forum (WEF) report;
Mains level: Gender-based issues in India;
Why in the news?
The 2024 World Economic Forum (WEF) report on global gender gaps has ranked India at 129 out of 146 economies, marking a decline of two positions from the previous year.
Key Highlights by WEF Report:
- Gender Parity Regression: India’s gender parity levels in educational attainment dipped in the 18th edition of the report, with a score of 0.964, down from a perfect 1.000 in the 17th edition.
- This decline is attributed to a 17.2 percentage point gap between men’s and women’s literacy rates, causing India to rank 124th on this indicator.
- Data Update and Period Variation: WEF’s Insight and Data Lead, Ricky Li, explained that the regression is due to updated data from UNESCO for the 2022 and 2023 periods, contrasting with the data from 2018, 2021, and 2022 used in the previous edition.
- This emphasizes the impact of periodic updates and corresponding periods on the gender parity score.
|
What do figures from the Unified District Information System for Education and the All India Survey on Higher Education indicate?
- Overall Enrolment and Gender Ratio: UDISE+ (2021-22) shows that girls constitute 48% of the school population, with enrolment increasing from 46.8% in preschool/kindergarten to 48.3% in higher secondary education.
- Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) in Higher Education: AISHE (2021-22) reports that the GER for women in higher education is 28.5%, slightly higher than the male GER of 28.3%, indicating a positive trend in female participation in higher education.
- Trends in Female Enrolment: Female enrolment has seen a 32% increase since 2014-15, demonstrating significant progress in higher education, despite challenges such as lower enrolment in STEM fields and regional disparities in secondary education access.
Are girls more likely to complete secondary education when they have access to it?
- Yes, girls are more likely to complete secondary education when they have access to it. The data from UDISE+ (2021-22) shows that while there is a slight drop in the percentage of girls enrolled in secondary education (47.9%), those who do have access to secondary education are more likely to continue to higher secondary education, where the gender gap narrows again to 48.3%.
- This trend indicates that providing access to secondary education facilities helps girls stay in school and complete their education.
What needs to be done to ensure girls and boys, don’t drop out? (Way forward)
- Addressing Socio-Cultural Barriers: Raising awareness about social issues such as early marriage, which disproportionately affects girls, is essential. Collaborating with local authorities and community leaders to advocate for girls’ education can help mitigate these challenges
- Community Involvement: Engaging parents and the community in the educational process can foster a supportive environment for students. This can include parent workshops, support groups, and regular communication about student progress.
- Flexible Learning Options: Offering flexible learning arrangements, such as part-time schooling or distance education, can accommodate students facing economic or personal challenges. This flexibility can help students balance their responsibilities while continuing their education.
- Vocational Training and Skill Development: Incorporating vocational training programs into the school curriculum can equip students with practical skills that increase their employability. This can motivate students to stay in school as they see a direct link between education and future job opportunities
Mains PYQ:
Q Can the vicious cycle of gender inequality, poverty and malnutrition be broken through microfinancing of women SHGs? Explain with examples. (2021)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: How will iCAL work?
Mains level: How are local bodies audited in India?
Why in the news?
On July 18, CAG Girish Chandra Murmu inaugurated the International Centre for Audit of Local Governance (iCAL) in Rajkot, marking India’s first institute to set global standards for auditing local governance.
How will iCAL work?
- iCAL will serve as a platform for policymakers, administrators, and auditors connected with local governments to enhance collaboration and share best practices.
- Objective: It aims to improve the independence and effectiveness of local government auditors through training, leadership development, and capacity-building initiatives.
- Significance: iCAL will act as a think tank for addressing governance issues at the grassroots level through interactive workshops, knowledge-sharing sessions, and peer exchanges.
How are local bodies audited in India?
- India has a three-tier system consisting of the Union government, state governments, and local bodies (both urban and rural).
- Local bodies like Panchayats and Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) are audited by various entities:
- State-level offices like the Examiner of Local Fund Accounts (ELFA)/Director of Local Fund Accounts (DLFA) audit the utilisation of state funds by local bodies.
- CAG conducts audits of all funds at the central and state levels, including those of local bodies. The CAG also advises and supports ELFA/DLFA.
Why was a need felt for it?
- Increased Funding and Need for Proper Auditing: With significant funds flowing to local bodies, there is a pressing need for improved auditing practices to ensure proper utilisation and financial management.
- Global Practices and Collaboration: There is a need to promote global good practices and institutionalised collaboration among supreme audit institutions (SAIs) to enhance local government audit practices and share best practices.
- Addressing Inefficiencies: Concerns have been raised about inefficiencies in local body financial management and reporting, as highlighted by the Reserve Bank of India’s 2022 report. iCAL aims to address these inefficiencies through better auditing practices and capacity building.
Way forward:
- Expand Capacity Building and Training Programs: Enhance iCAL’s focus on training and capacity-building for auditors and local government officials.
- Foster International Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing: Strengthen partnerships with global audit institutions and engage in knowledge exchange initiatives.
Mains PYQ:
Q In the absence of well – educated and organised local-level government systems, Panchayats and Samitis have remained mainly political institutions and not effective instruments of governance. Critically Discuss. (UPSC IAS/2015)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Indemnity-based Insurance Products and Parametric insurance
Mains level: Limitation of Parametric insurance
Why in the news?
In 2023, natural disaster losses hit $280 billion, with only $100 billion insured, highlighting a need for innovative insurance solutions amid rising extreme weather events.
Present Method of Disaster Risk Reduction
- Indemnity-based Insurance Products: Indemnity-based insurance products require a physical assessment of damage after a disaster to determine the payout amount. For example Health Insurance, Motor Insurance and Travel Insurance.
Challenges:
- Verification Issues: When large-scale calamities strike, especially in economically disadvantaged areas, it is difficult to verify losses due to the lack of records and widespread destruction.
- Delays in Payouts: The need for physical assessment can cause delays in providing financial assistance to the affected individuals and communities.
- Insurance Gap: There is a significant gap in insurance coverage between developed and developing economies, leaving many vulnerable populations without adequate protection.
Changing course and the associated limitations:
- Parametric insurance: Payments are made based on predefined parameters of weather events (e.g., rainfall exceeding 100 mm per day for two consecutive days, specific flood levels, wind speed).The payouts are made without the need for physical assessment of losses, enabling quicker disbursements.
Examples:
- Disaster-prone Island Countries: Many have adopted parametric insurance for climate adaptation, moving away from risk retention models. For example, Fiji launched its first parametric insurance product in 2021
- Morocco received $275 million in parametric insurance after a 6.8 magnitude earthquake, arranged with the help of the World Bank.
- India has initiated crop insurance (e.g., Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana and the Restructured Weather Based Crop Insurance Scheme).
Associated Limitations
- Current Focus: Primarily used for low-frequency, high-impact disasters like earthquakes, cyclones, and hurricanes.
- Data and Infrastructure Requirements: There is challenges related to developing and maintaining the necessary infrastructure for data collection and monitoring can be challenging, especially in developing regions.
- Affordability and Accessibility issues: It demands high premiums can still be a barrier for economically disadvantaged communities.
Case Study of Nagaland:
- Nagaland was the first state in India to buy parametric cover for extreme precipitation in 2021.
- Based on lessons learned, it improved the product by fixing an absolute annual premium, duration, and rate online, allowing bidders to compete over lower threshold limits and maximized payouts.
|
What can be done to ensure effectiveness? (Way Forward)
- Precise Thresholds and Robust Monitoring: Establish clear, accurate parameters for insurance triggers and implement reliable monitoring systems to track these parameters effectively.
- Transparent Bidding and Experience Sharing: Follow a transparent bidding process for price discovery and facilitate the exchange of best practices and lessons learned between governments.
- Widespread Payout Systems and Household Premium Support: Develop comprehensive systems for distributing payouts and promote long-term premium payment by households, leveraging tools like Aadhaar-based payment dissemination.
Mains PYQ:
Q Describe various measures taken in India for Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) before and after signing ‘Sendai Framework for DRR (2015-2030)’. How is this framework different from ‘Hyogo Framework for Action, 2005’? (UPSC IAS/2018)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Green Revolution
Mains level: Present India’s Maize Production
Why in the news?
Over the past two decades, India’s maize production has more than tripled, emerging as a private sector-driven green revolution success story. Maize has transitioned from being primarily a feed crop to also serving as a fuel crop.
What was the Green Revolution?
- Began in 1968 with the introduction of high-yielding variety (HYV) seeds, especially for wheat and rice, developed by agronomist Norman Borlaug
- Institutions like CIMMYT (International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center) and IARI (Indian Agricultural Research Institute), led by scientists like Norman Borlaug and M S Swaminathan, played a crucial role.
- The Green Revolution is credited to M.S. Swaminathan, known as the “Father of the Indian Green Revolution”, who introduced Borlaug’s wheat varieties and other technologies.
- The initiative focused on increasing agricultural productivity through advanced breeding techniques, fertilizers, and irrigation methods.
- Wheat production increased from 12 million tons in 1964-65 to 20 million tons in 1970-71.India became self-sufficient in food grain production and a major exporter
Present India’s Maize Production called as a Green Revolution in Maize
- Significant Production Increase: Over the last two decades, India’s maize production has surged from 11.5 million tonnes in 1999-2000 to over 35 million tonnes in 2023-24, showcasing a remarkable increase in both yield and output.
- Private Sector Leadership: This growth has been largely driven by the private sector, with more than 80% of the maize area planted with high-yielding hybrids developed by private seed companies, indicating a successful private sector-led green revolution.
- Diverse Utilization: Maize in India has evolved from being primarily a feed crop for poultry and livestock to also being a vital industrial crop used for starch and ethanol production, reflecting its expanded role in the economy.
On Starch and Ethanol Production
- Maize contains 68-72% starch, with significant industrial applications in textiles, paper, pharmaceuticals, food, and beverages.
- Maize is emerging as a key feedstock for ethanol production, especially for blending with petrol.
- IARI has developed a waxy maize hybrid with high amylopectin content, enhancing its suitability for ethanol production.
- The new Pusa Waxy Maize Hybrid-1 has 71-72% starch with 68-70% recoverable, increasing ethanol yield per tonne.
Can India adopt new strategies? (Way forward)
- India can adopt new strategies through innovative breeding techniques like the doubled haploid (DH) technology used by CIMMYT.
- The DH facility in Karnataka speeds up the development of genetically pure inbred lines, enhancing the efficiency of maize breeding.
- IARI’s waxy maize hybrid is ready for field trials and commercial release, potentially boosting ethanol production.
- Collaboration between public sector institutions and private seed companies can drive the adoption of high-yielding, disease-resistant maize varieties.
- Private sector-bred hybrids account for over 80% of India’s maize area, indicating strong potential for further growth and innovation in maize production.
Mains PYQ:
Q Explain various types of revolutions, that took place in Agriculture after Independence in India. How these revolutions have helped in poverty alleviation and food security in India? (UPSC IAS/2017)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Paris Agreement
Mains level: Bilateral Ties between India and Japan related to climate change
Why in the news?
India is set to establish a Joint Crediting Mechanism (JCM) with Japan for carbon trading and emission-reduction credits.
Memorandum of Cooperation for Setting Up a Joint Crediting Mechanism (JCM)
- Objective and Framework: India and Japan plan to sign a Memorandum of Cooperation to establish a Joint Crediting Mechanism (JCM) for sharing emission-reduction credits. The JCM will involve a structured allocation of carbon credits and maintain a registry to track these credits, with projects needing clearance from a Joint Committee.
- Implementation and Oversight: The mechanism will be governed under Article 6.2 of the Paris Agreement, adhering to relevant domestic laws and regulations of both countries. A Joint Committee will develop rules, manage project cycles, and oversee monitoring and issuance of credits.
Emission Cuts
- Credit Allocation: Credits issued under the JCM will contribute to both Japan’s and India’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement. The JCM will avoid double counting of credits and may authorize some credits for international mitigation purposes.
- Technology Transfer and Capacity Building: Japan will support technology transfer, finance, and capacity building to enhance the effectiveness of the JCM and facilitate the adoption of new technologies.
Significance of JCM:
- Increased Access to Clean Technologies: The JCM will facilitate the transfer of advanced decarbonizing technologies from Japan to India, such as renewable energy systems, energy-efficient appliances, and waste management solutions.
- Job Creation and Skill Development: The implementation of JCM projects will create new employment opportunities in sectors like renewable energy, energy efficiency, and waste management
Bilateral ties between India and Japan
- Strategic Partnership: The JCM will strengthen bilateral ties between India and Japan by fostering collaboration on low-carbon technologies and climate action, aimed at boosting job creation and investments in clean technologies.
- Clean Energy Partnership: It was launched in March 2022, the India-Japan Clean Energy Partnership (CEP) aims to enhance cooperation in sustainable energy transitions to achieve net-zero emissions by 2070.
- Investment Commitments: During the 14th India-Japan Annual Summit in March 2022, both nations agreed on a target of $42 billion (JPY 5 trillion) in public and private investment from Japan to India over the next five years
- Low Carbon Emission Strategies: A $600 million fund was established to focus on environmental sustainability and low carbon emission strategies. This initiative is part of a broader effort to enhance Japanese investments in India while addressing climate change.
|
Way forward:
- Prioritize the adoption of cutting-edge decarbonizing technologies: Japan should prioritize the transfer of its most advanced low-carbon technologies to India, such as renewable energy systems, energy-efficient appliances, and carbon capture and storage solutions.
- Expand the scope of the JCM to include other areas of climate cooperation: While the initial focus of the JCM should be on emission reduction projects, India and Japan could explore expanding its scope to include other areas of climate cooperation, such as adaptation measures, climate finance, and capacity building.
Mains PYQ:
Q Clean energy is the order of the day.’ Describe briefly India’s changing policy towards climate change in various international fora in the context of geopolitics. (UPSC IAS/2022)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Tobacoo industry in India
Mains level: CRISPR can reduce the impact of Tobacoo
Why in the news?
On July 8th, 1497, Vasco da Gama’s historic voyage began, reshaping global maritime routes and leaving a lasting impact on trade and culture. This era of exploration introduced and disseminated tobacco, profoundly affecting societies in numerous ways.
Cultivation and Production of Tobacco
- Historical Introduction: Tobacco was originally cultivated by Native Americans and brought to Europe in the 16th century. It was introduced to South Asia by European traders and colonizers, notably the Portuguese, Dutch, and British.
- Economic Significance: Tobacco is a drought-tolerant crop providing livelihoods to many. It accounts for about 2% of India’s agricultural exports and employs over 45 million people.
- Revenue Generation: The tobacco industry is a major source of revenue through taxation and exports, generating over ₹22,000 crores annually.
Implications on Human Health
- Health Issues: Tobacco use contributes to various cancers (lung, mouth, throat, oesophagus, pancreas, and bladder), respiratory diseases (COPD, emphysema, chronic bronchitis), cardiovascular problems (heart disease, stroke, hypertension), and other conditions like diabetes, infertility, weakened immune system, and complications in pregnancy.
- Addiction: Nicotine, a highly addictive substance in tobacco, alters brain function leading to severe addiction.
- Health Crisis: In India, tobacco use causes over 1.2 million deaths annually. It is responsible for 27% of all cancers and adds significant costs to healthcare and productivity losses, totaling approximately ₹1.82 trillion annually.
Ethical and Revenue Considerations
- Economic Benefits vs. Health Costs: While tobacco provides economic benefits and employment, it comes with tremendous human and financial costs due to tobacco-related illnesses.
- Constitutional Provisions: Under Article 21 of the Indian Constitution guarantees the right to life and health. The Directive Principles of State Policy mandate the state to improve public health and living standards.So,Govt. has responsibility to prevent tobacoo consumption.
Indian needs to Stack Up Its Priorities
- Institutional Conflict: The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) focuses on eliminating tobacco to mitigate health impacts, while the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) aims to increase tobacco crop yields.
- Policy and Ethical Dilemma: The conflicting priorities between ICMR and ICAR create significant policy challenges. The constitutional mandate to prioritize public health should guide policy decisions.
Will CRISPR make a difference?
- Gene Editing Potential: CRISPR technology offers potential solutions by developing genetically modified tobacco plants with reduced nicotine content.
- Research Developments: Studies have shown promise in using CRISPR to significantly lower nicotine levels in tobacco plants. However, further characterization is needed to ensure these modifications do not negatively impact other important traits.
- Collaborative Efforts: Collaboration between ICMR and ICAR is crucial to align scientific advancements with public health goals and agricultural sustainability.
The Tobacco Lobby and Surrogate Advertising
- Circumventing Regulations: The tobacco industry employs surrogate advertising to promote its products despite stringent advertising bans. These tactics perpetuate tobacco consumption, especially among youth, undermining public health efforts.
- Aggressive Lobbying: The tobacco industry has a large network of 1,027 registered lobbyists at the state level in 2024, many of whom are former government employees. They engage in extensive lobbying to weaken, delay or block life-saving tobacco control measures.
Way forward:
- Implement Stricter Regulations: Enforce stringent regulations on tobacco advertising, including surrogate advertising, and ensure compliance through regular monitoring and penalties.
- Ban on Public Smoking: Implement and strictly enforce smoking bans in public places to reduce exposure to second-hand smoke.
Mains PYQ:
Q What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of the society? (UPSC IAS/2021)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: About Foreigners Tribunals
Mains level: Decision-Making Process of Foreigners Tribunals
Why in the news?
On July 5, the Assam government instructed the Border wing of the State police not to refer cases of non-Muslims who entered India illegally before 2014 to the Foreigners Tribunals (FTs).
About Foreigners Tribunals:
- Foreigners Tribunals are quasi-judicial bodies established to determine if a person staying illegally in India is a “foreigner” or not.
- They were set up under the Foreigners (Tribunals) Order, 1964, enacted by the central government under the Foreigners Act, 1946.
- Initially, only the central government could set up these tribunals. But a 2019 amendment empowered district magistrates in all states and UTs to establish Foreigners Tribunals.
- The tribunals have the powers of a civil court to summon witnesses, require document production, and examine evidence.
Decision-Making Process of Foreigners Tribunals:
- Referral: Individuals suspected of being foreigners are referred to FTs by local authorities or border police. This referral can be based on various factors, including lack of documentation or doubtful voter status.
- Notice Issuance: Upon receiving a reference, the FT issues a notice to the person alleged to be a foreigner. This notice is served in English or the state’s official language.The person has 10 days to respond to the notice and an additional 10 days to submit evidence supporting their claim of citizenship.
- Submission of Evidence: The individual must present evidence to prove their Indian citizenship. This may include documents like birth certificates, school certificates, land records, or other official records.
- Verification: The tribunal examines the documents and evidence provided, and may call witnesses or seek additional information if necessary.
- Hearing: The FT has the authority to summon and examine the individual on oath, and to require the production of additional documents. The tribunal operates with certain powers of a civil court.
- Judgment: If the evidence provided is deemed insufficient to prove citizenship, the individual may be declared a foreigner. If evidence is adequate, the person is recognized as an Indian citizen.
- Detention and Deportation: If declared a foreigner and unable to appeal successfully, the person may be sent to a detention center (transit camp) for deportation.
Role of Border Police:
- Detection and Referral: The Assam Police Border Organisation is responsible for detecting illegal foreigners and referring suspicious cases to FTs.
- Patrolling and Defence: They patrol the India-Bangladesh border, work with the Border Security Force, and maintain a second line of defense.
- Monitoring: They monitor people settled in riverine and char (sandbar) areas.
- Cases of ‘D’ Voters: They refer cases of ‘D’ (doubtful) voters to FTs as directed by the Election Commission of India.
- NRC Appeals: People excluded from the NRC can appeal to the FTs through this wing to prove their citizenship.
Challenges and Criticisms:
- Supreme Court Rulings: The Supreme Court has overturned FT orders citing grave miscarriages of justice, such as the wrongful declaration of a deceased farmer, Rahim Ali, as a foreigner.
- Corruption and Malpractice: Observations have been made about corruption within the system, with allegations of notices being improperly served.
Conclusion: Need to Implement stricter oversight and auditing of Foreigners Tribunals to ensure fairness and adherence to legal procedures. Regular reviews and monitoring can help prevent corruption and malpractice, ensuring that notices are properly served and tribunal processes are transparent.
Mains PYQ:
Q How far are India’s internal security challenges linked with border management particularly in view of the long porous borders with most countries of South Asia and Myanmar? (UPSC IAS/2013)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Initiative related to Tree plantation
Mains level: India's accountability and challenges toward environmental Goals
Why in the news?
India’s tree planting schemes have garnered attention as part of the country’s efforts to combat climate change and restore degraded ecosystems. However, these initiatives face several challenges and criticisms.
Recent Trends of Special Conservation Drives:
- Increased Initiatives: There has been a surge in global and national tree planting drives, such as the “One Trillion Project” by the World Economic Forum, Pakistan’s “10 Billion Tree Tsunami,” China’s “Great Green Wall,” and the “Bonn Challenge” to restore degraded landscapes.
- High Media Attention: These drives often feature catchy slogans and glamorous campaigns that attract substantial media attention and public involvement.
- Annual Events: India celebrates Van Mahotsava annually in July, aiming to promote tree planting and environmental conservation.
Issues Associated with These Drives:
- Limited Community Participation: Many programs lack significant involvement from local communities, affecting their effectiveness and sustainability.
- Post-Planting Measures: Insufficient focus on post-planting care and monitoring hinders the success of tree planting efforts.
- Monoculture Risks: Some drives promote monoculture, which can be detrimental to biodiversity and carbon sequestration.
- Ecological Impact: Inappropriate tree planting in non-deforested areas like grasslands or animal habitats can damage ecosystems, increase wildfire risk, and exacerbate global warming.
India’s Accountability and Challenges Toward Environmental Goals:
- Achievements: India claims to have fulfilled its Paris Agreement commitments and achieved an additional carbon sink of 1.97 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent.
- Encroachment and Loss: Approximately 10 million hectares of Indian forests are under encroachment, and about 5.7 million hectares have been lost for non-forestry purposes.
- Dependence on Forests: Nearly 27.5 crore people rely on forests for subsistence, highlighting the importance of sustainable management.
- Restoration Goals: India aims to restore 26 million hectares of degraded forests by 2030, but faces challenges such as encroachment and the need for effective tree planting strategies.
Way forward:
- Community Involvement: Need to foster local participation in tree planting drives by involving communities in planning, execution, and ongoing maintenance.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Try to implement robust post-planting monitoring and care systems to ensure the survival and growth of planted trees.
- Policy and Strategy Improvements: To address criticism of mass planting drives, India needs to prioritize adequate financing, active community participation, and technical considerations in forestry and restoration strategies.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: About NSSO
Mains level: Key highlight of recent survey by NSSO
Why in the news?
The NSSO’s 2021-22 and 2022-23 survey outcomes reveal effects of significant economic shocks due to demonetisation, GST implementation, and the COVID-19 pandemic on India’s economy.
About NSSO:
- The NSSO is India’s premier agency for conducting large-scale nationwide sample surveys on socio-economic aspects that collects data on employment, consumption, health, education, and other areas to provide essential inputs for policy and planning.
- The NSSO was merged with the Central Statistical Office in 2019 to form the National Statistical Office.
Key highlight as per the recent survey by NSSO
- Impact of Economic Shocks: The surveys reflect the aftermath of major economic events such as demonetisation (November 2016), the rollout of GST (July 2017), and the COVID-19 pandemic (starting March 2020).
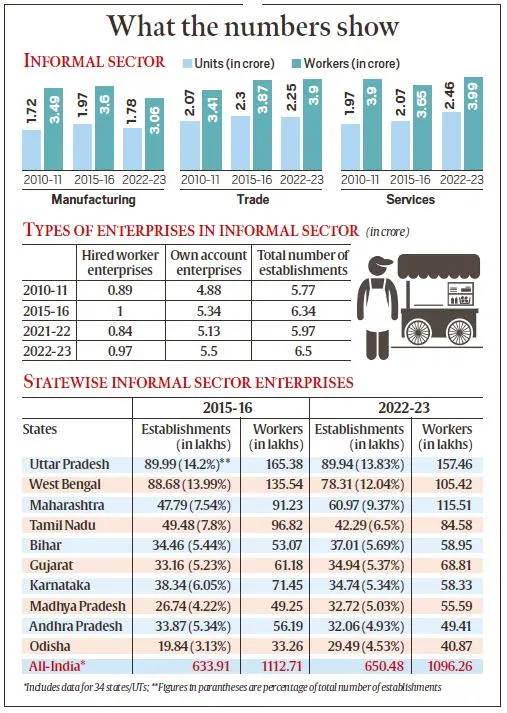
- Employment Trends: There has been a noticeable decline in employment within the informal sector over the past seven years, with around 16.45 lakh jobs lost.
- Sectoral Dynamics: The unincorporated manufacturing sector saw a significant contraction, with the number of enterprises declining by 9.3% from 19.7 million in 2015-16 to 17.82 million in 2022-23.
|
What are unincorporated enterprises?
- Unincorporated enterprises are informal businesses not legally registered as companies.
- They include MSMEs, household units, own-account enterprises, and partnerships, operating outside formal regulatory frameworks but contributing significantly to employment and economic activity.
Why are these survey results important and what do they represent?
- Timely Insights: These survey results offer current data crucial for understanding the evolving role of the informal sector in job creation, particularly during economic slowdowns when formal sector employment may decline.
- Impact Assessment: They provide a detailed analysis of how significant economic events like demonetisation, GST implementation, and the COVID-19 lockdowns have affected the informal sector, highlighting vulnerabilities and resilience.
- Policy Relevance: The findings inform policymaking aimed at supporting and regulating the informal sector, ensuring that measures address its unique challenges and contributions to overall economic stability and inclusivity.
What has been the pattern of ‘Informal Employment’ across states?
- The data shows a mixed pattern across states, with 16 out of 34 states/UTs recording a decline in informal sector workers in 2022-23 compared to 2015-16.
- Around 63 lakh informal enterprises shut down due to GST between 2015-16 and 2022-23, resulting in a loss of about 1.6 crore jobs.
- The number of informal enterprises plunged from 50.32 lakh with 85.6 lakh workers in April-June 2021 at the peak of the COVID-19 second wave, to 1.91 crore firms with 3.12 crore employees in January-March 2022.
Way Forward:
- The government should provide targeted support and incentives to help informal enterprises adapt to the post-GST and post-pandemic environment.
- Policymakers should aim to facilitate a gradual transition of informal enterprises to the formal sector.
Mains PYQ:
Q How globalization has led to the reduction of employment in the formal sector of the Indian economy? Is increased informalization detrimental to the development of the country? (UPSC IAS/2016)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: About 106th Amendment Act
Mains level: Quota should be provided in political parties for women
Why in the News?
In the recently concluded general elections in the U.K., a record 263 women MPs, making up 40% of the total, have been elected to the House of Commons.
Political representation of Women in the world:
Have women been fairly represented in Parliament in independent India?
Women were granted the right to vote from the First General Elections in 1952, yet their representation in the Lok Sabha has been low.
- Statistics about women’s representation: The women’s representation in Lok sabha in between of 1952 and 2004 was about ranged from 5% to 10%.
- The percentage women’s representation had increased to 12% in 2014 and stands at 13.6% in the 18th Lok Sabha while in the Rajya Sabha (upper house), the figure is 13%.
- Constitutional Amendments: The 73rd and 74th amendments in 1992/1993 provided one-third reservation for women in panchayats and municipalities, but similar reservations for the Lok Sabha and State assemblies have not been successful until recently.
Note: The global average of 26.9% of women in National parliaments.
Women’s Representation in State Legislatures:
- No state has more than 20% women representation in its legislative assembly.
- Chhattisgarh has the highest representation with 18% women MLAs.
- Himachal Pradesh has just one woman MLA and Mizoram has none.
|
Should political parties provide internal reservations to increase women’s political participation?
- Globally, higher representation for women is achieved through voluntary or legislated compulsory quotas for candidates within political parties or reserved seats in parliament.
- So, quotas within political parties offer more democratic choices to voters and flexibility in candidate selection. It means quota in Political parties could be the most important step to increase women’s representation in Parliament.
- Some parties, like Naam Tamilar Katchi in Tamil Nadu, have adopted voluntary quotas (50% for women candidates), but such measures alone have not significantly improved overall representation.
When will the 106th constitutional amendment be implemented?
- The 106th Amendment Act provides for 33% reservation for women in the Lok Sabha and state legislative assemblies, including the Delhi Legislative Assembly.
- The reservation will come into effect after an exercise of delimitation is undertaken following the first census conducted after the commencement of the 106th Amendment Act.
- The women’s reservation will be in operation for a period of 15 years from its commencement.
Way Forward:
- Public Awareness and Advocacy: Need to conduct widespread awareness campaigns to highlight the importance of gender equality in political representation.
- Capacity Building and Support Mechanisms: Need to implement comprehensive capacity-building programs aimed at empowering women politically. For example,provide training in leadership skills, campaign management, and legislative processes.
Mains PYQ:
Q The reservation of seats for women in the institutions of local self-government has had a limited impact on the patriarchal character of the Indian Political Process.” Comment. (UPSC IAS/2019)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Agronomy; Food production;
Mains level: Challenges in Farm Sector; Value Chains;
Why in the News?
India holds the position of the second-largest agricultural producer globally however, it only accounts for 2.4% of global agricultural exports, ranking eighth worldwide due to the post-harvest loss.
A closer look at India’s post-harvest loss:
- Economic Impact: India faces annual post-harvest losses amounting to approximately ₹1,52,790 crore, significantly impacting farmer incomes and the agricultural economy.
- Perishable Commodities: The biggest losses occur in perishable commodities like livestock produce (22%), fruits (19%), and vegetables (18%). Export processes further add to these losses, particularly at the import-country stage.
- Supply Chain Inefficiencies: There is Inefficiencies in storage, transportation, and marketing, alongside a lack of assured market connectivity, contribute to significant post-harvest losses. Small and marginal farmers, who make up 86% of the farming community, struggle with economies of scale and market access.
Initiatives taken by the Railways Department:
- Truck-on-Train Service: Indian Railways introduced the truck-on-train service, allowing loaded trucks to be transported on railway wagons. This service has been expanded following successful trials with commodities like milk and cattle feed.
- Parcel Special Trains: During the COVID-19 pandemic, the Railways introduced parcel special trains to transport perishables and seeds between producers and markets, ensuring timely delivery and reducing post-harvest losses.
- The DFI (Doubling farmers’ income) committee recommends streamlining loading and unloading processes to minimize transit times and address staffing shortages through recruitment and training initiatives.
- Kisan Rail Scheme: It was launched to connect production surplus regions with consumption regions. This scheme facilitates the transportation of perishables (including milk, meat, and fish) more efficiently.
- Specialized Wagons and Facilities: Investment in specialized wagons for temperature-controlled transport and establishing rail-side facilities for safe cargo handling are essential steps taken by the Railways.
Way for Untapped Opportunities:
- Enhanced Environmental Benefits: Rail transport generates up to 80% less carbon dioxide for freight traffic compared to road transport.
- Public-Private Partnerships: The private sector can play a crucial role in enhancing operational efficiency and strengthening rail infrastructure through public-private partnerships, thereby improving the overall logistics ecosystem for agricultural produce.
- Budgetary Support and Infrastructure Development: The budgetary allocation for agriculture in 2024 aims to bridge the farm-to-market gap with modern infrastructure and value-addition support.
- Technology Integration: Incorporating advanced technologies like real-time tracking, temperature monitoring, and automated loading/unloading systems.
Way forward:
- Expand climate-controlled storage facilities and cold storage capacity to accommodate a larger share of agricultural produce.
- Provide small and marginal farmers access to storage facilities through cooperatives or subsidies.
- Invest in specialized rail wagons for temperature-controlled transport and establish rail-side cargo handling facilities.
Mains PYQ:
Q How do subsidies affect the cropping pattern, crop diversity and economy of farmers? What is the significance of crop insurance, minimum support price and food processing for small and marginal farmers? (UPSC IAS/2017)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Population of SC and ST in India
Mains level: Objective of reservation
Why in the News?
The Supreme Court has reserved its decision on sub-caste reservations for SC/STs. Any ruling on this matter must be substantiated not only legally but also academically.
What is the Sub-categorization of castes?
It refers to the practice of further dividing larger caste categories into smaller groups or sub-groups based on specific criteria such as socio-economic status, geographical location, historical background, or specific needs for policy implementation.
Background of the Case:
- The case involves the validity of sub-classification within the SC and ST categories for providing reservations in government jobs and education.
- In 2004 Supreme Court strikes down Andhra Pradesh Scheduled Castes (Rationalisation of Reservations) Act, 2000, citing violation of the right to equality in the E.V. Chinnaiah v State of Andhra Pradesh case and emphasised that the SC list should be treated as a single, homogeneous group
- Only Parliament has the power to sub-classify SCs and STs for reservations
- The Supreme Court is now considering whether states have the power to create sub-classifications within these reserved categories.
- The case stems from a 1975 Punjab government notification that divided its 25% reservation for SCs into two categories: half for Balmikis (Valmikis) and Mazhabi Sikhs, and the other half for the remaining groups within the SC category.
|
Objectives behind the implementation of reservations and present SC scenario:
- Objective of Reservations: The primary objective of reservations, as advocated by Dr. B.R. Ambedkar, is to ensure equitable representation and opportunities for historically marginalized communities, particularly Scheduled Castes (SCs).
- Present SC scenario: Despite reservations, certain sub-castes within SCs continue to face challenges in securing adequate representation in jobs and education. This under-representation is often attributed to factors such as inadequate educational opportunities, economic disparities, and historical discrimination.
The policy of economic empowerment in India and its associated challenges:
- Policies for Economic Empowerment: These policies complement reservations by focusing on enhancing the ownership of capital assets (like land and businesses) and improving educational attainment among SC individuals
- For example, Self-Employment Scheme for Rehabilitation of Manual Scavengers (SRMS), National Scheduled Castes Finance & Development Corporation (NSFDC) and National Safai Karamcharis Finance & Development Corporation (NSKFDC).
- These policies are aimed at building capabilities and enabling greater participation in economic activities.
- Challenges: There are challenges in implementing economic empowerment policies including inadequate access to credit and financial resources, lack of skill development initiatives, and persistent socio-economic barriers that hinder the upward mobility of SC communities.
- Intersection with Reservations: Integrating economic empowerment with reservations is crucial to ensure that individuals from SC backgrounds not only secure reserved positions but also have the necessary skills and resources to thrive in competitive environments.
What must be our focus? (Way Forward)
- Holistic Approach: There is a need for a holistic approach that combines reservations with targeted economic and educational interventions. This approach should address both systemic discrimination and socio-economic barriers faced by SC communities.
- Capacity Building: There should be emphasis on enhancing the educational infrastructure and skill development programs tailored to the needs of SC individuals.
- Data-Driven Policy: The policy decisions related to sub-caste reservations should be informed by empirical data that assesses the actual impact of discrimination versus socio-economic factors on under-representation.
Mains PYQ:
Q Whether National Commission for Scheduled Castes (NCSC) can enforce the implementation of constitutional reservation for the Scheduled Castes in the religious minority institutions? Examine (UPSC IAS/2018)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Burnt Memory of EVM
Mains level: Process to be followed for the verification of EVMs and VVPATs
Why in the News?
The ECI released a technical Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) on July 16 for verifying burnt memory in EVMs and VVPATs, following an April Supreme Court verdict.
What is the Burnt Memory of EVM?
- “Burnt memory” in Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs) refers to the firmware or software program permanently written onto the microcontroller’s memory during the manufacturing process.
- This memory controls the EVM’s operations, and “burnt” implies it is fixed and cannot be altered or reprogrammed easily.
|
What was the case before the Supreme Court, and what did it order?
Case Before the Supreme Court:
- The Supreme Court was hearing a challenge to the reliability of Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs). The judgment was delivered on April 26, 2024, during the Lok Sabha election.
- The Supreme Court upheld the EVM-VVPAT system and rejected the plea for a return to paper ballots and for 100% counting of VVPAT slips.
- The court directed the Election Commission of India (ECI) to allow second and third-placed candidates to seek verification of burnt memories of EVMs and VVPATs of up to 5% of machines in an Assembly constituency or an Assembly segment of a Lok Sabha constituency.
Court’s Orders:
- The burnt memory/microcontroller in 5% of the EVMs (control unit, ballot unit, and VVPAT) per assembly constituency/assembly segment of a parliamentary constituency shall be checked and verified for tampering or modification.
- Candidates who are at Sl. No. 2 or Sl. No. 3 behind the highest polled candidate can request verification in writing.
- Candidates or their representatives have the option to be present during the verification process. Requests for verification must be made within seven days of the declaration of the result.
- The actual cost or expenses for the verification will be notified by the ECI, and the candidate requesting the verification will bear the expenses. These expenses will be refunded if tampering is found.
What is the process to be followed for the verification of EVMs and VVPATs?
Technical SOP by ECI:
- Mock Poll: A mock poll of up to 1,400 votes per machine will be conducted in the presence of candidates or their representatives.
- Result Comparison: If the results of the machines and VVPAT slips match, it will be concluded that the burnt memory or microcontrollers have not been tampered with.
- Selection of Machines: Candidates can select the polling stations, EVMs, BUs, CUs, and VVPATs they want checked.
- Verification Team: Trained engineers from the EVM manufacturers, Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL) and Electronics Corporation of India Ltd (ECIL) will perform the checks.
- Technical Methods: Various technical methods will be used to verify the fidelity of firmware burnt into a microcontroller through a public process.
When will this process of checking start?
- Preliminary Step: Verification will commence after it is confirmed by the High Courts of the respective states that no Election Petitions have been filed regarding the constituencies in question.
- Election Petitions: Petitions challenging the election outcome can be filed within 45 days of the results being declared. Since the results were announced on June 4, petitions can be filed until July 19.
- Applications Received: Eleven applications cover 118 polling stations or sets of EVMs and VVPATs. Applications have been received from candidates from BJP, Congress, DMDK, and YSRCP.
Way forward:
- Enhanced Transparency and Confidence: Conduct regular and public verification processes of EVMs and VVPATs with involvement from political parties and independent observers to build public trust and confidence in the electoral system.
- Technological Upgradation and Training: Invest in upgrading EVM technology and provide comprehensive training for election officials and engineers to ensure efficient and accurate verification and operation of voting machines.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Staus of digital Infrastructure of India
Mains level: Digital Infrastructure;
Why in the News?
The telecom industry has proposed several policy recommendations to the Ministry of Communications that are essential to realize the Government’s vision of promoting digital empowerment and inclusivity.
Present global status of the Indian market:
- Digital Connectivity Advancements: India has made significant strides in digital connectivity, positioning itself as the third-largest digitized country globally, following the USA and China.
- Telecommunications Infrastructure: The telecommunications infrastructure in India serves as a cornerstone for digital transformation, facilitating connectivity across various devices and applications, thereby contributing to higher standards of living and economic growth.
- Policy Reforms: Ambitious policy reforms have been implemented to elevate India’s status as a leading digital economy. These reforms aim at fostering digital empowerment and inclusivity, crucial for sustaining growth and competitiveness in the global market.
|
Recommendations submitted by the telecom industry
- Reduction in Levy and Tax Burden:
- Abolishment of the USOF (Universal Service Obligation Fund) levy because of imposes a burden on telecom service providers (TSPs), diverting resources that could be invested in newer technologies such as 5G and network upgrades
- USOF is the pool of funds generated by 5% Universal Service Levy that is charged upon all the telecom fund operators on their Adjusted Gross Revenue (AGR).
- Reduction of the license fee from 3% to 1%.
- Clarity in the definition of Gross Revenue (GR) to exclude non-telecom activities from tax calculations.
- Exemption and Duty Reductions:
- Exemption of Service Tax on additional Adjusted Gross Revenue (AGR) liabilities is demanded because it is crucial for the recovery of the industry’s financial health and ensuring efficient 5G rollout.
- AGR has resulted in massive dues of over ₹1.5 lakh crore that telecom companies like Bharti Airtel, Vodafone Idea, and others have to pay.
- Reduction of Customs Duty to zero for telecom manufacturing, with gradual increases for 4G and 5G products.
- Urgency in renewing Customs Duty exemptions for submarine cable vessels to prevent future cost increases.
- Spectrum Allocation:
- Prioritization of 6 GHz spectrum for 5G deployment in India.
- Strategic planning of 6 GHz spectrum for future 6G technologies, aiming at enhancing network quality, coverage, and supporting a range of advanced applications like telemedicine and smart cities.
- Telecommunications Act 2023:
- Introduction of the Telecommunications Act 2023, addressing critical issues such as Right of Way (RoW) for telecom infrastructure.
- Standardization of RoW rules across states, simplification of licensing processes, and delinking telecom infrastructure from property taxes to facilitate faster deployment of 5G services.
- Implementation of Reforms:
- Emphasis on the swift implementation of regulatory reforms to minimize bureaucratic delays and operational hurdles.
- Creation of a conducive environment for telecom investments by ensuring clarity and uniformity in RoW regulations, thereby improving the Ease of Doing Business (EoDB) in the sector.
Conclusion: The Government should prioritize the swift implementation of proposed policy reforms, including the reduction of levies and taxes, clarity in revenue definitions, and spectrum allocation for 5G and future 6G technologies. Timely execution will bolster investor confidence, accelerate infrastructure development, and enhance digital connectivity nationwide.
Mains PYQ:
Q Cyber warfare is considered by some defence analysts to be a larger threat than even Al Qaeda or terrorism. What do you understand by Cyberwarfare? Outline the cyber threats which India is vulnerable to and bring out the state of the country’s preparedness to deal with the same. (2013)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now

