Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Willingness to pay mechanism
Mains level: Air pollution in Delhi

Air pollution claimed approximately 54,000 lives in Delhi in 2020, according to a Greenpeace Southeast Asia analysis of the cost to the economy due to air pollution.
Try this question from CS Mains 2015:
Q.Mumbai, Delhi and Kolkata are the three megacities of the country but the air pollution is a much more serious problem in Delhi as compared to the other two. Why is this so?
Deaths due to Air Pollution
- Globally, approximately 1,60,000 deaths have been attributed to PM 2.5 air pollution in the five most populous cities — Delhi, Mexico City, Sao Paulo, Shanghai and Tokyo.
- Six Indian cities — Delhi, Mumbai, Bengaluru, Chennai, Hyderabad and Lucknow — feature in the global analysis.
- An estimated 25,000 avoidable deaths in Mumbai in 2020 have been attributed to air pollution.
- Bengaluru, Chennai and Hyderabad estimated an approximate 12,000, 11,000, and 11,000 avoidable deaths respectively due to polluted air.
The ‘Cost Estimator’
- The ‘Cost Estimator’, an online tool that estimates the real-time health impact and economic cost from fine particulate matter (PM 2.5) air pollution in major world cities.
- It was deployed in collaboration between Greenpeace Southeast Asia, IQAir and the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air (CREA).
- Using real-time ground-level PM 2.5 measurements collated in IQAir’s database, the algorithm applies scientific risk models in combination with population and public health data.
Computing the “Lost Years”
- To show the impact of air pollution-related deaths on the economy, the approach used by Greenpeace is called ‘willingness-to-pay.
- It refers to a lost life year or a year lived with a disability is converted to money by the amount that people are willing to pay in order to avoid this negative outcome.
- The cost estimator also sustained the estimated air pollution-related economic losses of ₹1,23,65,15,40,000.
Greenpeace recommends-
- Despite a temporary reprieve in air quality owing to the lockdown, the latest figures from the report underscore the need to act immediately.
- The need of the hour is to rapidly scale up renewable energy, bring an end to fossil fuel emissions and boost sustainable and accessible transport systems.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Tree Cities of the World
Mains level: Urban forestry
Hyderabad city has received another feather in its cap by being chosen as one among the ‘Tree Cities of the World’.
Tree Cities of the World
- The Tree Cities of the World programme is an international effort to recognize cities and towns committed to ensuring that their urban forests and trees are properly maintained, sustainably managed, and duly celebrated.
- This status is accorded by the Arbor Day Foundation jointly with the Food and Agriculture Organisation of the UN.
- To receive recognition, a town or city must meet five core standards:
- Establish Responsibility
- Set the Rules
- Know What You Have
- Allocate the Resources and
- Celebrate the Achievements
Try this question:
Q.The Miyawaki Forests technique has to potential to revolutionize the concept of urban afforestation in India. Discuss.
Why it is a great achievement?
- Hyderabad is the only city in the country to have been selected for this recognition in response to its commitment to growing and maintaining urban forestry.
- The recognition stands Hyderabad alongside 120 cities from 23 countries, including developed nations such as USA, UK, Canada, Australia and others.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: New York Convention
Mains level: Not Much
Cairn Energy has filed a case in a U.S. district court to enforce a $1.2 billion arbitration award it won in a tax dispute against India. Cairn aims to enforce the award under international arbitration rules, commonly called the New York Convention.
New York Convention
- The Convention on the Recognition and Enforcement of Foreign Arbitral Awards is commonly known as the New York Convention.
- It was adopted by a UN diplomatic conference on 10 June 1958 and entered into force on 7 June 1959.
- It requires courts of contracting states to give effect to private agreements to arbitrate and to recognize and enforce arbitration awards made in other contracting states.
- Widely considered the foundational instrument for international arbitration, it applies to arbitrations that are not considered domestic awards in the state where recognition and enforcement are sought.
What was the case?
- The Indian government has lost an international arbitration case to energy giant Cairn Plc over the retrospective levy of taxes and has been asked to pay damages worth $1.2 billion to the UK firm.
- The Permanent Court of Arbitration at The Hague has maintained that the Cairn tax issue is not a tax dispute but a tax-related investment dispute and, hence, it falls under its jurisdiction.
- India’s demand in past taxes, it said, was in breach of fair treatment under the UK-India Bilateral Investment Treaty.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: UN HRC
Mains level: US policies revision after regime change
The Biden administration is set to reengage with the much-maligned UN Human Rights Council that former Donald Trump withdrew from almost three years ago.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Consider the following:
- Right to education.
- Right to equal access to public service.
- Right to food.
Which of the above is/are Human Right/Human Rights under “Universal Declaration of Human Rights”?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) Only 1
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) Only 3
Why did the US pulled-out earlier?
- Trump pulled out of the world body’s main human rights agency in 2018 due to its disproportionate focus on Israel.
- Israel had received by far the largest number of critical council resolutions against any country.
- The Trump administration took issue with the body’s membership, which currently includes China, Cuba, Eritrea, Russia and Venezuela, all of which have been accused of human rights abuses.
About UN Human Rights Council
- The UNHRC describes itself as “an inter-governmental body within the UN system responsible for strengthening the promotion and protection of human rights around the globe.
- It addresses situations of human rights violations and make recommendations on them.
- The first session took place from June 19-30, 2006, three months after the Council was created by UN General Assembly Resolution 60/251 on March 15 that year.
- The UNHRC has the ability to discuss all thematic human rights issues and situations that require its attention throughout the year.
- The HRC replaced the former United Nations Commission on Human Rights (UNCHR).
HRC Meetings
- The Human Rights Council holds no fewer than three regular sessions a year, for a total of at least 10 weeks.
- The meetings take place for four weeks in March, for three weeks in June, and for another three weeks in September.
- The sessions are held at the UN Office in Geneva, Switzerland.
- If one-third of the Member States so request, the HRC can decide at any time to hold a special session to address human rights violations and emergencies.
Membership
- The Council is made up of 47 UN Member States, which are elected by the UNGA through a direct and secret ballot.
- The General Assembly takes into account the contribution of the candidate states to the promotion and protection of human rights, as well as their voluntary pledges and commitments in this regard.
- Members of the Council serve for a period of three years and are not eligible for immediate re-election after serving two consecutive terms.
- As of January 1, 2019, 114 UN Member States have served on the HRC. Both India and Pakistan are on this list.
- The HRC has a Bureau of one President and four Vice-Presidents, representing the five regional groups. They serve for a year, in accordance with the Council’s annual cycle.
Seat distribution
- African States: 13 seats
- Asia-Pacific States: 13 seats
- Latin American and Caribbean States: 8 seats
- Western European and other States: 7 seats
- Eastern European States: 6 seats
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CPI
Mains level: Prevalence of corruption in India
The Transparency International (TI)’s corruption perception index (CPI) was recently released for 2020.
Another set of useful data in news to be noted by aspirants. Such data are essential and need to be memorized. One must note here. Such data recur every year. So it is not a big task to deal with such numbers along with other critical indices.
About the Corruption Perception Index
- The index ranks 180 countries and territories by their perceived levels of public sector corruption.
- It uses a scale of 0 to 100, where 0 is highly corrupt and 100 is very clean.
Global prospects
- Denmark and New Zealand top the index, with 88 points. Syria, Somalia and South Sudan come last, with 14, 12 and 12 points, respectively.
- Nearly half of countries have been stagnant on the index for almost a decade, indicating stalled government efforts to tackle the root causes of corruption.
- More than two-thirds score below 50.
India’s performance
- The CPI score for India is constant this year as well as the previous year’s score.
- India’s rank is 86 out of 180 nations with a score of 40.
- It was ranked at 80th position out of 180 countries in 2019 with a score of 41.
A comparison with neighbours
- At 40, India’s score is below the average score of the Asia-Pacific region (31 countries) and global average, the CPI 2020 report stated.
- India’s overall score is also two points less than that of China, which docked at 78th position, with a score of 42.
- Pakistan, however, scored just 31 points, falling at the 144th position on the index.
What does it mean for India?
- India is still very low on corruption Index, the report said, noting that experts feel the CPI does not reflect the actual corruption level in any country.
- The integrity score determines the corruption situation of a country.
Recommendations made by TI
To reduce corruption and better respond to future crises, Transparency International recommends that all governments:
- Strengthen oversight institutions to ensure resources reach those most in need. Anti-corruption authorities and oversight institutions must have sufficient funds, resources and independence to perform their duties.
- Ensure open and transparent contracting to combat wrong-doing, identify conflicts of interest and ensure fair pricing.
- Defend democracy and promote civic space to create the enabling conditions to hold governments accountable.
- Publish relevant data and guarantee access to information to ensure the public receives easy, accessible, timely and meaningful information.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: EDISON alliance
Mains level: Global action against digital divide
The World Economic Forum (WEF) has announced the launch of an Essential Digital Infrastructure and Services Network (EDISON) Alliance.
The peculiarity of name ‘EDISON Alliance’ creates a hotspot here for prelims. UPSC may either crate confusion over purpose or parent organization. The alliance is yet to take shape completely; hence there is an ambiguity over its members.
EDISON Alliance
- Geneva-based World Economic Forum (WEF), which describes itself as an international organization for public-private partnership, will serve as the secretariat and platform for the EDISON Alliance.
- A wider group of ‘Champions Leaders’ will advise and support the Alliance, the WEF said while announcing the launch.
- Alliance aims to work towards ensuring global and equitable access to the digital economy.
- Its prime goal is to ensure an unprecedented level of cross-sectoral collaboration between the technology industry and other critical sectors of the economy, according to the WEF.
Why need such an alliance?
- Access to digital technologies has enabled many to work, learn and live during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- However, the pandemic has exposed and exacerbated existing gaps and inequalities in almost half of the global population.
- Some 3.6 billion people, remain offline and broadband services are too expensive for 50 percent of the population in developed countries, the WEF said.
- This hampers access to health, education, and economic inclusion.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: OST, INF Treaty, New START policy
Mains level: US-Russia power tussle
The Russian lower house of Parliament, the Duma has ratified a new START nuclear treaty with the US. Both countries had “agreed in principle” to extend the arms treaty by five years with Joe Biden swearing-in.
The New START, INF and the Open Skies …. Be clear about the differences of these treaties. For example- to check if their inception was during cold war era etc.
New START Treaty
- The New Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty (New START) pact limits the number of deployed nuclear warheads, missiles and bombers and is due to expire in 2021 unless renewed.
- The treaty limits the US and Russia to a maximum of 1,550 deployed nuclear warheads and 700 deployed missiles and bombers, well below Cold War caps.
- It was signed in 2010 by former US President Barack Obama and then-Russian President Dmitry Medvedev.
- It is one of the key controls on the superpower deployment of nuclear weapons.
A reset to Trumps policies
- In February 2020, the US withdrew from the 1987 Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty (INF), accusing Moscow of violating the agreement.
- Russian then had proposed a one-year extension without conditions of the last major nuclear arms reduction accord, the New START Treaty between Russia and the U.S.
- If it had fallen, it could have been the second nuclear weapons treaty to collapse under the leadership of Trump.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: 'The Inequality Virus' Report
Mains level: Economic implications of COVID
The ‘Inequality Virus Report’ was recently released on the opening day of the World Economic Forum in Davos.
About the report
- The Inequality Virus Report was released by Oxfam.
- It inquired into different forms of inequities, including educational, gender and health during the pandemic.
Highlights of the report
‘Rise’ in wealth
- Indian billionaires increased their wealth by 35% during the lockdown to ₹ 3 trillion, ranking India after the U.S., China, Germany, Russia and France.
- The wealth of just the top 11 billionaires during the pandemic could easily sustain the MGNREGS or the Health Ministry for the next 10 years, stated the report.
- A person (no citation needed!) who emerged as the richest man in India and Asia, earned ₹90 crores an hour during the pandemic when around 24% of the people in the country were earning under ₹ 3,000 a month during the lockdown.
- The increase in his wealth alone could keep 40 crores, informal workers, out of poverty for at least five months, said the report.
Observations made
Health: Only 6% of the poorest 20% have access to non-shared sources of improved sanitation, compared to 93.4 % of the top 20 %.
Education: Till October, 32 crores students were hit by the closure of schools, of whom 84 % resided in rural areas and 70 %attended government schools. Dalits, Adivasis and Muslims were likely to see a higher rate of dropout. Girls were also most vulnerable as they were at risk of early and forced marriage, violence and early pregnancies, it noted.
Gender: Unemployment of women rose by 15% from a pre-lockdown level of 18 %, which could result in a loss of India’s GDP of about 8 % or ₹15 trillion. Women who were employed before the lockdown were also 23.5 percentage points less likely to be re-employed compared to men in the post lockdown phase.
Recommendations
- It recommended reintroducing the wealth tax and affecting a one-time COVID-19 cess of 4% on taxable income of over ₹10 lakh to help the economy recover from the lockdown.
- According to its estimate, a wealth tax on the nation’s 954 richest families could raise the equivalent of 1% of the GDP.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: IGN, UNSC
Mains level: India's agenda at UNSC
Seeking urgent reform of the United Nations Security Council (UNSC), India has highlighted the failure of the Intergovernmental Negotiations (IGN) since 13 years of its establishment.
Note various countries in the various groups.
What is the news?
- India, along with Brazil, Japan and Germany are pressing for urgent reform of the UNSC and for a permanent seat in the reformed 15-member top organ of the world body.
- India has said that the UNSC is finding itself unable to act effectively to address increasingly complex issues of international peace and security.
- The UNSC lacks inclusivity of those who need to be members of the powerful organ of the world body.
What is IGN?
- The Intergovernmental Negotiations framework or IGN is a group of nation-states working within the United Nations to further reform of the UNSC.
- The IGN is composed of several different international organizations, namely:
- African Union (55 member states)
- G4 nations (Brazil, Germany, India and Japan)
- Uniting for Consensus Group (UfC), also known as the “Coffee Club” (it aims to counter the bids for permanent seats proposed by G4 nations, includes Pakistan, Turkey, Canada, Spain and Italy)
- L69 Group of Developing Countries ( it includes developing countries from Africa, Latin America and the Caribbean, Asia and the Pacific)
- Arab League (six members: Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Lebanon, Saudi Arabia, and Syria) and
- Caribbean Community ( a group of 15 member countries called CARICOM)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: WEF
Mains level: The Great Reset

This news card is an excerpt from the original article published in The Indian Express and is articulated by C. Raja Mohan.
The Great Reset
- The Great Reset is a proposal by the World Economic Forum (WEF) to rebuild the economy sustainably following the COVID-19 pandemic.
- It was unveiled in May 2020 by the United Kingdom’s Prince Charles and WEF director Klaus Schwab.
The basis for the said reset
- It is based on the assessment that the world economy is in deep trouble.
- Schwab has argued that the situation has been made a lot worse by many factors, including the pandemic’s devastating effects on global society, the un- folding technological revolution, and the consequences of climate change.
- He demands that the world must act jointly and swiftly to revamp all aspects of our societies and economies, from education to social contracts and working conditions.
- Every country must participate, and every industry, from oil and gas to tech, must be transformed.

Agenda behind
The agenda of The Great Reset touches on many key issues facing the world a/c to C Raja Mohan. Three of them stand out as:
First is the question of reforming capitalism
- The WEF has been at the forefront of calling for “stakeholder capitalism” that looks beyond the traditional corporate focus on maximizing profit for shareholders.
Second, it is certainly right to focus on the deepening climate crisis
- Climate skeptics have been ousted from Washington and President Biden has rejoined the 2015 Paris accord on mitigating climate change.
The third is the growing difficulty of global cooperation
- The era of great power harmony that accompanied the liberalization of the global economy at the turn of the 1990s has yielded place to intense contestation. The contestation is not just political but increasingly economic and technological.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Global Climate Risk Index 2021
Mains level: Climate change vulnerability and the economics behind
India was ranked the seventh worst-hit country in 2019 in the Global Climate Risk Index 2021.
The report holds much significance for prelims as well as mains. Just for the sake of information, we must be aware of India’s performance.
Global Climate Risk Index
- The GCRI is released annually by the environmental think tank and sustainable development lobbyist Germanwatch.
- It analyses to what extent countries have been affected by the impacts of weather-related loss events (storms, floods, heat waves etc.).
- It pushes for the need to support developing countries in coping with the effects of climate change.
Highlights of the 2020 year
Global prospects
- Mozambique, Zimbabwe and The Bahamas were the worst-affected countries in 2019.
- While hurricane Dorian ravaged The Bahamas; Mozambique, Zimbabwe and Malawi were affected by the single extreme weather event of cyclone Idai.
- Japan and Afghanistan were the other countries that fared worse than India on the Index, while South Sudan, Niger and Bolivia fared better in comparison but still made it to the top 10 worst-affected countries.
The burden of development
- Eight of the 10 countries most affected between 2000 and 2019 were developing countries with low or lower middle income per capita.
- Vulnerable people in developing countries suffered most from extreme weather events like storms, floods and heatwaves, whereas the impact of climate change was visible around the globe.
- Poorer countries are hit hardest because they are more vulnerable to the damaging effects of a hazard and have the lower coping capacity.
Data about India
- According to the Index floods caused by heavy rain in 2019 took 1,800 lives across 14 states in India and displaced 1.8 million people.
- Overall, the intense monsoon season affected 11.8 million people, with the economic damage estimated to be $10 billion (Rs.72,900 crore at $1=INR 72.9).
- A total of eight tropical cyclones meant that 2019 was one of the most active Northern Indian Ocean cyclone seasons on record. Six of them intensified to become “very severe”.
- The worst was Cyclone Fani in May 2019 which affected a total of 28 million people, killing nearly 90 people in India and Bangladesh, and causing economic losses of $8.1 billion (Rs.59,066 crore).
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: G7. G8, G20
Mains level: G7 and its significance for India
The United Kingdom has invited PM Modi to attend the G7 summit that is scheduled to be held in June.
Note the members of G7 and G20. UPSC may puzzle you asking which G20 nation isn’t a member of G7. 
G7 Countries
- The G-7 or ‘Group of Seven’ includes Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
- It is an intergovernmental organisation that was formed in 1975 by the top economies of the time as an informal forum to discuss pressing world issues.
- Initially, it was formed as an effort by the US and its allies to discuss economic issues.
- The G-7 forum now discusses several challenges such as oil prices and many pressing issues such as financial crises, terrorism, arms control, and drug trafficking.
- It does not have a formal constitution or a fixed headquarters. The decisions taken by leaders during annual summits are non-binding.
- Canada joined the group in 1976, and the European Union began attending in 1977.
Evolution of the G-7
- When it started in 1975—with six members, Canada joining a year later—it represented about 70% of the world economy.
- And it was a cozy club for tackling issues such as the response to oil shocks.
- Now it accounts for about 40% of global GDP.
- Since the global financial crisis of 2007-09, it has sometimes been overshadowed by the broader g20.
- The G-7 became the G-8 in 1997 when Russia was invited to join.
- In 2014, Russia was debarred after it took over Crimea.
Significance of G7 for India
- India will get more voice, more influence, and more power by entering the G7.
- After the UN Security Council (UNSC), this is the most influential grouping.
- If the group is expanded it will collectively address the humongous issues created by the Wuhan virus,
- Diplomatically, a seat at the high table could help India further its security and foreign policy interests, especially at the nuclear club and UN Security Council reform as well as protecting its interests in the Indian Ocean.
Back2Basics: The G-20
- The G-20 is a larger group of countries, which also includes G7 members.
- The G-20 was formed in 1999, in response to a felt need to bring more countries on board to address global economic concerns.
- Apart from the G-7 countries, the G-20 comprises Argentina, Australia, Brazil, China, India, Indonesia, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, South Korea, and Turkey.
- Together, the G-20 countries make up around 80% of the world’s economy.
- As opposed to the G-7, which discusses a broad range of issues, deliberations at the G-20 are confined to those concerning the global economy and financial markets.
- India is slated to host a G-20 summit in 2022.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Adaptation Cost
Mains level: Progress of global climate action

The United Nations Adaptation Gap Report, 2020 was recently released by the UNEP.
Must read edition: Five years of Paris Agreement
UN Adaptation Gap Report
- UN Environment Programme (UNEP) has managed the production of UN Environment’s Adaptation Gap Report series since its first edition in 2014.
- The aim of the reports is to inform national and international efforts to advance climate change adaptation.
Behind the concept: Adaptation Cost
- Adaptation Cost includes costs of planning, preparing for, facilitating and implementing the climate change adaptation measures.
- It thus derives benefits as the avoided damage costs or the accrued benefits following the adoption and implementation of adaptation measures.
Highlights of the 2020 report
- The annual cost of adaptation to the effects of climate change for developing countries is estimated to at least quadruple by 2050, according to the United Nations Adaptation Gap Report, 2020.
- The current cost for developing countries is in the range of $70 billion (Rs 5.1 lakh crore) and may rise to $140-300 billion in 2030 and $280-500 billion in 2050.
Funding gaps
- The ever-increasing adaptation cost has also outpaced the growth in adaptation finance that refers to the flow of funds to developing countries to help them tide over the damages caused by climate change.
- This, in turn, has kept the adaptation finance gap from closing with the current efforts, although the fund flow has increased, the report said.
- Adaptation costs, in actual terms, are higher in developed countries but the burden of adaptation is greater for developing countries in relation to their gross domestic product.
- These countries, especially in Africa and Asia, which are least equipped to tackle climate change will also, be the most impacted by it, the report noted.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not Much
Mains level: Global perception of India's image
A UK think-tank ‘Royal Institute of International Affairs’ has listed India in ‘Difficult 4’; clubs India with China, Saudi Arabia, and Turkey.
This newscard helps analyse the Western esp. that of the EU’s perception of India and its global image under the present regime.
What is the news?
- A report called ‘Global Britain, Global Broker’ has warned the UK government to consider India as more of a rival that a cooperative partner.
- It accepts the fact that India is set to be the largest country in the world by population very soon and will have the third-largest economy and defence budget at some point in this decade.
- But it cautions that gaining direct national benefit from the relationship, whether economically or diplomatically, will be difficult for the UK government.
- The report also accepts India’s importance to the UK as being “inescapable”.
The ‘Difficult Four’
- Clubbing India with China, Saudi Arabia and Turkey as the “difficult four”, the report says the Johnson government should be more realistic about developing deeper ties with India.
- They may be important to the UK’s commercial interests, but they will be rivals or, at best, awkward counterparts on many of its global goals, the report warns.
- India is now classed as a country, destined to count among the UK’s “rivals” or “awkward counterparts” as it pursues its global goals.
India has had bitter (colonial) past
- The think-tank strikes a note of caution over the two countries’ shared colonial history proving a stumbling block to the promise of a deeper relationship.
- India has a long and consistent record of resisting being corralled into a ‘Western’ camp.
- As a result, India is always on the list of countries with which a new UK government commits to engage.
- But it should be obvious by now that the idea of a deeper relationship with India always promises more than it can deliver.
- The legacy of British colonial rule consistently curdles the relationship.
Indian flaws
- The report points to India’s “complex, fragmented domestic politics”, which make it one of the countries resistant to open trade and foreign investment.
- It highlights concerns raised by domestic groups as well as the UN over a “crackdown on human rights activists and civil society groups” not being actively challenged by the judiciary.
- It raises concern over India’s pursuance of extreme right-winged policies. Indian domestic politics also has entered a more ethnic-nationalist phase, the report argues.
- Against this backdrop, the report reflects on the prospect of including India within any new Democratic 10 or D10 coalition of 10 leading democracies.
Try this question from 2019 CS Mains:
Q.What are the challenges to our cultural practices in the name of secularism? (150W)
UK’s resentment
- In a critique of India’s diplomatic behaviour, the report points out that despite border clashes with China, “India did not join the group of countries that criticized China at the UN in July 2019 over HR violations in Xinjiang.
- India has also been muted in its criticism of the passage of the new national security law in Hong Kong.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not Much
Mains level: Persecution of minorities in neighbouring countries

Pakistan’s Hazaras finally ended a protest and agreed to bury the bodies of 11 coal miners from the community killed by the IS.
Genocide and Pakistan are the two inseparable metaphors. Pakistan’s treatment of its minorities is the least highlighted global violation of Human Rights. Hindus, Sikhs and Christians are the most persecuted communities.
Who are the Hazaras?
- Around 1773, the mountainous region of Hazarajat in modern-day central Afghanistan was annexed and made a part of the territories of the Afghan Empire under Pashtun ruler Ahmad Shah Durrani.
- The Sunni Muslim majority under the Pashtun ruler resulted in further marginalization of the Shiite Hazara community, to the extent that in the 18th and 19th century.
- They were forced to leave fertile lowlands in central Afghanistan and make the dry, arid mountainous landscape their new home.
Their persecution
- Persecution of the Shiite Hazaras is nothing new in Pakistan or neighbouring Afghanistan.
- They have been frequently targeted by Taliban and IS militants and other militant groups in both countries.
Causes of persecution: Ethnicity and Religion
- Their unique identity, ethnicity and religion always made the Hazaras stand out among the other communities.
- Hazaras speak Hazaragi, which is close to Dari Persian, the official language of modern-day Afghanistan.
- The community also shares physical similarities with the Mongols and their speech, specific terms and phrases, reflect strong Central Asian Turkic influences.
- This sets them apart from their neighbours in Pakistan and other communities within Afghanistan.
An attempted ethnic cleansing
- In the 19th century, the Hazara community constituted approximately 67 per cent of Afghanistan’s total population.
- Since then, primarily due to violence, oppression and targeted massacres, that number has come down to a little as 10 to 20 per cent of the population now.
- The attacks reached a crescendo in 2013 when three separate bombings killed more than 200 people in Hazara neighbourhoods of Quetta.
- In the aftermath of this incident, the Shia community in Pakistan had erupted in anger over the Pakistani government’s lack of protection of its minorities.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: UNSC
Mains level: India's agenda at UNSC

India is back as a non-permanent member on the United Nations Security Council.
Q.What objective India should pursue in its stint at the UNSC? What challenges India will face in achieving these objectives?
India at the UNSC
Take a look at its seven previous terms, and what its agenda will be amid events concerning China, Pakistan and the US:
- In 1950-51, India, as President of UNSC, presided over the adoption of resolutions calling for the cessation of hostilities during the Korean War and for assistance to the Republic of Korea.
- In 1967-68, India co-sponsored Resolution 238 extending mandate of UN mission in Cyprus.
- In 1972-73, India pushed strongly for admission of Bangladesh into the UN. The resolution was not adopted because of a veto by a permanent member.
- In 1977-78, India was a strong voice for Africa in the UNSC and spoke against apartheid. Then External Affairs Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee spoke in UNSC for Namibia’s independence in 1978.
- In 1984-85, India was a leading voice in UNSC for resolution of conflicts in the Middle East, especially Palestine and Lebanon.
- In 1991-92, PM P V Narasimha Rao participated in the first-ever summit-level meeting of the UNSC and spoke on its role in the maintenance of peace and security.
- In 2011-2012, India was a strong voice for developing world, peacekeeping, counter-terrorism and Africa. The first statement on Syria was during India’s Presidency at the UNSC.
India’s diverse role-play
- India played an active role in discussions on all issues related to international peace and security.
- It included several new challenges which the UNSC was called upon to deal with in Afghanistan, Cote d’Ivoire, Iraq, Libya, South Sudan, Syria and Yemen.
- In view of the threat posed to international trade and security by piracy off the coast of Somalia, India promoted international cooperation against the pirates.
- At India’s initiative, the UNSC mandated international cooperation for release of hostages taken by pirates as well as for prosecution of those taking hostages and those aiding and abetting these acts.
- India also worked for enhancing international cooperation in counter-terrorism, prevention of the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction to non-state actors, and the strengthening of UN peacekeeping efforts.
Issues at UNSC: The politics within
- The seven previous terms have given Indian diplomats the experience of how diplomacy is conducted at the multilateral setting.
- There have been instances where permanent members would like the non-permanent members to be “cooperative”, and no stand in the way of major resolutions.
- Most non-permanent members get influenced by the P-5 members. They did not wish to irritate the permanent members and were keen to be perceived by them as ‘cooperative’.
- This was precisely how the permanent members would like the non-permanent members to behave.
Walk-alone moves by India
- The Indians took P5 work more seriously and consequently had to fight a lonely battle.
- This was the time when the Gulf War erupted and India voted in favour of the US-sponsored resolution in April 1991.
- India’s vote was dictated by pragmatic considerations.
- The US had made it clear to India that failure to support the resolution would make it very difficult for them to help India in the World Bank and the IMF.
- Back then, India was going through a severe balance-of-payment crisis and needed funds from these organisations.
- Also, India needed the US on its side, if and when the Kashmir issue came up.
Twenty years later, when India again became a non-permanent member at the UNSC, it was stronger economically but still had to negotiate politics within the Council.
Ugly faces of the council
- Most professional diplomats shed their innocence before they arrive at the horse-shoe table around which the Security Council meets.
- In the real world of foreign and security policy, decision-makers are invariably confronted by cruel choices that are equally problematic and come in various shades.
- Practitioners are acutely conscious that it is only diplomacy’s outward packaging that dwells in a commitment to a higher moral purpose.
- The shameless pursuit of narrowly defined interests is most often the motivation and seldom raises eyebrows in the world of multilateral diplomacy.
Issues before India
(A) Long slated UN reforms
- New Delhi has said it is essential that the Security Council is expanded in both the permanent and non-permanent categories.
- It says India is eminently suited for permanent UNSC membership by any objective criteria, such as population, territorial size, GDP, economic potential and ongoing contributions to UN activities.
(B) Terrorism
- The international effort against terrorism is a key priority for India in the UN.
- With the objective of providing a comprehensive legal framework to combat terrorism, India took the initiative to pilot a draft Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism (CCIT) in 1996.
- A text of the Convention is being negotiated in the 6th Committee of the UN General Assembly.
- India worked closely to ensure the listing of Pakistan-based terrorist Masood Azhar under the UNSC’s 1267 Sanctions Committee (May 2019) concerning al-Qaida and ISIS terrorists.
(C) China challenge
- India is entering the UNSC at a time when Beijing is asserting itself at the global stage much more vigorously than ever.
- It heads at least six UN organisations — and has challenged the global rules.
- China’s aggressive behaviour in the Indo-Pacific, as well as the India-China border, has been visible in all of 2020, and New Delhi will have to think on its feet to counter Beijing.
- At Pakistan’s behest, China has tried to raise the issue of Kashmir at the UNSC — but has not found much support.
- There is some discussion among the strategic community in New Delhi on raising the issues of Taiwan, Hong Kong and Tibet at the UNSC.
Conclusion
- India will weigh the pros and cons with partners on what steps to take in this direction.
- But, the polarizing politics inside India gives a window of opportunity to its rivals and opens up the possibility of criticism — especially on human rights issues.
Back2Basics: United Nations Security Council
- The UNSC is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations and is charged with the maintenance of international peace and security.
- Its powers include the establishment of peacekeeping operations, the establishment of international sanctions, and the authorization of military action through Security Council resolutions.
- It is the only UN body with the authority to issue binding resolutions to member states.
- The Security Council consists of fifteen members. Russia, the United Kingdom, France, China, and the United States—serve as the body’s five permanent members.
- These permanent members can veto any substantive Security Council resolution, including those on the admission of new member states or candidates for Secretary-General.
- The Security Council also has 10 non-permanent members, elected on a regional basis to serve two-year terms. The body’s presidency rotates monthly among its members.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Global Burden of Disease (GBD) Report
Mains level: Not Much

According to the Global Burden of Disease, nearly a quarter (24.8 per cent) of all deaths in India is due to cardiovascular diseases (CVDs).
The fastest-growing economy has some perils. In this newscard, you will get to see how CVDs are a legacy of economic growth.
Global Burden of Disease (GBD) Report
- The GBD is a comprehensive regional and global research program of disease burden that assesses mortality and disability from major diseases, injuries, and risk factors.
- GBD is a collaboration of over 3600 researchers from 145 countries.
- It is based out of the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington and funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
Indian burden of CVDs
- About a third of the senior citizens have been diagnosed with hypertension, 5.2% with chronic heart disease and 2.7% with stroke
- Even an analysis of the medical certification of cause of death (MCCD) reports points to an increase in the proportion of deaths due to CVD. It went from 20.4 per cent in 1990 to 27.1 per cent in 2004.
- According to MCCD report, 2018, CVDs accounted for more than half (57%) of the total deaths in the age group of 25–69 years.
- Case fatality due to CVD in low-income countries, including India, appears to be much higher than in middle and high-income countries.
- In India, for example, the mean age at which people get the first myocardial infarction is 53 years, which is about 10 years earlier than their counterparts in developed countries.
- About a third (32 per cent) of the senior citizens have been diagnosed with hypertension, 5.2 per cent were diagnosed with chronic heart disease and 2.7 per cent with stroke.
Women are more vulnerable
- Numerous studies have also pointed out that CVD remains the number-one threat to women’s health as more women than men die annually due to these diseases.
- A Harvard study shows low high-density lipoproteins and high triglycerides appear are the main factors that increase the chances of death from cardiovascular disease in women over age 65.
- As per the LASI report, gender differences were evident in cross-state variations.
- CVD among men was higher in Kerala (45 per cent), Goa (44 per cent), Andaman and Nicobar (41 per cent) and lower in Chhattisgarh (15 per cent), Meghalaya (16 per cent), Nagaland (17 per cent).
Why CVDs are prevalent in India?
- Epidemiological evidence suggests that CVD is associated with behavioural factors such as smoking, alcohol use, low physical activity, and insufficient vegetable and fruit intake.
- In the Indian context, poverty, maternal malnutrition, and early life changes enhance an individual’s risk of CVDs.
- Rural to urban migration that happens in distress leads to over-crowded and unclean environments in urban slums.
- Problems of inadequate housing, indoor pollution, infectious diseases, inappropriate diet, stress and smoking crop up as a result.
Need of the hour
- CVD-risk prevention is one of the important priorities among India’s sustainable development goals.
- In an earlier estimate, WHO had said with India’s present CVD burden, the country would lose $237 billion from the loss of productivity and spending on healthcare over 10 years (2005–2015).
- This is because the diseases affect the country’s working population.
Way ahead
- The government should devise an approach that can improve the efficiency of care and health system preparedness to curb the CVD epidemic currently sweeping India.
- Attempts in direction to preserve the traditional lifestyle are also necessary.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: FAO Food Price Index
Mains level: Poverty and Hunger
World food prices rose for a seventh consecutive month in December 2020, with all the major categories, barring sugar, said the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (UN-FAO).
Try this PYQ:
Q.Which one of the following is not a sub-index of the World Bank’s ‘Ease of Doing Business Index’? (CSP 2019)
(a) Maintenance of law and order
(b) Paying taxes
(c) Registering property
(d) Dealing with construction permits
World Food Price Index
- The FAO Food Price Index is a measure of the monthly change in international prices of a basket of food commodities.
- It consists of the average of five commodity group price indices [cereal, vegetable, dairy, meat and sugar], weighted with the average export shares.
- The index has become a critical and timely monthly indicator of the state of international food markets, gauging the change in food commodity prices over time in nominal and real terms.
Why it matters?
- High food prices have contributed to a surge in inflation
- There are social and economic advantages from high food prices for example higher prices are an opportunity to improve farmers’ incomes and to stimulate investments in farming.
- For developing countries that are major exporters of food, the rise in world prices helped to bring about an improvement in the terms of trade and a strong balance of payments.
Concerns raised
- That said higher food prices for domestic consumers created fresh problems of poverty and hunger.
- Lower-income families spend a higher proportion of their budgets on food.
- Higher prices hit them hardest causing a fall in real living standards.
- This means that food price inflation can act as a tax on the poor and have a regressive effect on the distribution of income.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Trade Policy Review (TPR)
Mains level: WTO and India
India’s seventh Trade Policy Review (TPR) has begun at the World Trade Organization in Geneva.
Q.In the wake of the global economic fallout of the COVID-19 pandemic, discuss the challenges ahead of WTO.
Trade Policy Review (TPR)
- The TPR is an important mechanism under the WTO’s monitoring function and involves a comprehensive peer-review of the Member’s national trade policies.
- India’s last TPR took place in 2015.
Why need a TPR?
- To increase the transparency and understanding of countries’ trade policies and practices, through regular monitoring
- To improve the quality of public and intergovernmental debate on the issues
- To enable a multilateral assessment of the effects of policies on the world trading system
India’s progress
- Since previous TPR, India has worked diligently to reform and transform the entire economic eco-system to meet the socio-economic aspirations of a billion-plus Indians.
- The introduction of the GST, the IBC, labour sector reforms, an enabling and investor-friendly FDI Policy, and various national programmes like Make in India, Digital India, Startup India and Skill were the path-breakers.
- The improvement in the economic and business environment, on account of the wide-ranging reforms, has enabled India to better its position in the World Bank’s Doing Business ranking from 142 in 2015 to 63 in 2019.
- This improvement is also endorsed by investors who continue to view India as a desirable investment destination even during the testing time of the pandemic.
- In 2019-20, India received highest ever FDI inflow of USD 74.39 billion.
A note of caution
- India’s trade policy remained largely unchanged since the previous review.
- India continues to rely on trade policy instruments such as the tariff, export taxes, minimum import prices, import and export restrictions, and licensing, WTO said.
- These are used to manage domestic demand and supply requirements, protect the economy from wide domestic price fluctuations, and ensure conservation and proper utilization of natural resources.
- As a result, frequent changes are made to tariff rates and other trade policy instruments, which create uncertainty for traders.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: OECD , various parameters mentioned
Mains level: Concerns of farmers other than MSP
The OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) has provided five sets of data on the issue of agriculture support and India trails on most counts:
The ongoing debate about farmers protest has brought to light some of the key support mechanisms for agriculture in India. And it is being argued that the government has preferred the welfare of Indian consumers over the Indian farmers.
Lets’ have a look at various OECD’s parameters:
(1) Producer Support Estimates (PSE)

- These are transfers to agricultural producers and are measured at the farm gate level.
- They comprise market price support, budgetary payments and the cost of revenue foregone.
(2) Consumer Support Estimates (CSE)

- These refer to transfers from consumers of agricultural commodities. They are measured at the farm gate level.
- If negative, the CSE measures the burden (implicit tax) on consumers through market price support (higher prices), that more than offsets consumer subsidies that lower prices to consumers.
(3) General Services Support Estimates (GSSE)

- GSSE transfers are linked to measures creating enabling conditions for the primary agricultural sector through the development of private or public services, institutions and infrastructure.
- GSSE includes policies where primary agriculture is the main beneficiary but does not include any payments to individual producers.
- GSSE transfers do not directly alter producer receipts or costs or consumption expenditure.
(4) Total Support Estimate (TSE)
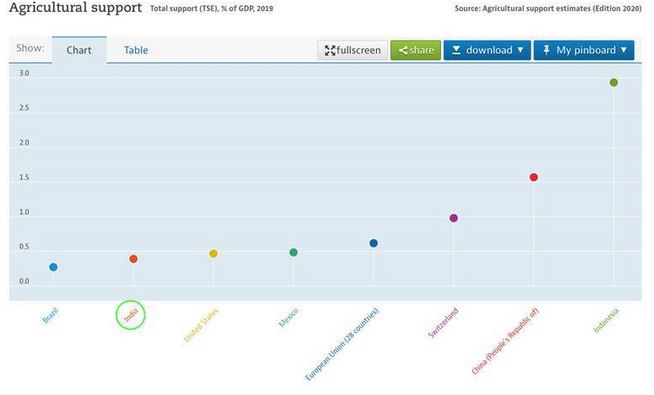
- The TSE transfers represent the total support granted to the agricultural sector, and consist of producer support (PSE), consumer support (CSE) and general services support (GSSE).
(5) Producer protection

- Lastly, the OECD also provides data on “producer protection”.
- The PP is the ratio between the average price received by producers (measured at the farm gate), including net payments per unit of current output, and the border price (measured at the farm gate).
- For instance, a coefficient of 1.10, which China has, suggests that farmers, overall, received prices that were 10% above international market levels.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now













