Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: urban heat island, United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (COP28)
Mains level: susceptibility to climate change impacts on health
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NALSA Judgment
Mains level: Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act (2019)

Central idea
The central idea revolves around advocating for the gradual and thoughtful inclusion of transgender individuals in the armed forces. By drawing parallels with successful women integration, proposing protected roles initially, and emphasizing social awareness, the approach aims for a balanced, transparent, and inclusive transformation within the military, recognizing and addressing historical discrimination.
Key Highlights:
- Growing Acceptance: People are becoming more accepting of transgender folks, which is a positive change. Society is starting to understand the importance of including everyone, regardless of their gender identity.
- Recognizing Challenges: We’re acknowledging that transgender individuals have faced a tough time with discrimination, stigma, and fewer opportunities. This recognition is crucial in addressing historical disadvantages.
- Legal Steps in India: India has taken legal steps, like the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act in 2019, to protect transgender rights. This shows a commitment to making things better since a significant judgment in 2014.
- Armed Forces Proposal: There’s a suggestion to include transgender individuals in the armed forces. This proposal comes from the realization that they’ve been at a disadvantage and need proactive help to be part of every aspect of life.
- Stepwise Integration Approach: The idea is to include transgender individuals gradually, just like how women’s roles in the armed forces expanded step by step. This way, we can be sure that we’re ready and set up for their inclusion.
- Learning from Women’s Inclusion: We’re learning from how women were included in the armed forces. By doing this, we hope to avoid problems and make the integration process smooth and successful.
- Roles for Transgender Personnel: Transgender individuals might start with roles in medical services and staff positions. Initially, these roles will be more protected to ensure they feel comfortable and respected.
- Social Awareness Emphasis: There’s a suggestion to make the armed forces more aware of societal justice and the discrimination faced by transgender individuals. This change in mindset is vital for a successful integration.
Key Challenges:
- Societal Prejudices: A challenge is dealing with society’s biases within the armed forces. Overcoming these biases is crucial for creating an inclusive environment.
- Balancing Inclusion with Discipline: We need to be careful about how inclusion might affect the strong discipline and camaraderie in the armed forces. Balancing inclusion with maintaining teamwork is a tricky but necessary challenge.
- Infrastructure Support: Developing the needed support for transgender individuals is important. This includes making sure the armed forces are ready and equipped for their inclusion.
- Dignity Concerns: We’re aware of concerns about respecting the dignity and self-respect of transgender individuals. To address this, there’s a proposal for more protected roles initially.
Key Terms and Phrases:
- Camaraderie and Discipline: The armed forces have strong bonds based on trust and teamwork. Keeping these bonds intact while embracing diversity is a challenge.
- Sensitization Road Map: We’re planning a roadmap to sensitize the armed forces at all levels. This means we want everyone to understand and accept the realities of discrimination.
- Competence and Capabilities: Transgender individuals should be accepted based on their skills and abilities. Competency and capability are what matter most.
- Sheltered Appointments: Initially, there’s a proposal for more protected roles to make sure transgender individuals feel secure and respected.
- Aide-de-Camp: Imagining a capable transgender officer in a prestigious role shows the positive impact they can have on perceptions and acceptance.
- Gradual Integration: Just like how women were gradually included, we’re looking at a step-by-step approach for transgender integration.
Key Facts and Data:
- NALSA Judgment as a Legal Milestone: In 2014, there was a significant decision recognizing and protecting transgender rights. This decision set the stage for later legal measures.
- Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act (2019): In 2019, India took legislative steps to protect transgender rights. These measures show a commitment to making things better.
- Success of Women in Armed Forces: We’re looking at the achievements of women in the armed forces as a guide for including transgender individuals. Learning from past successes helps us avoid problems.
Critical Analysis:
- Acknowledging Historical Discrimination: We’re recognizing that a big change is needed in the armed forces’ way of thinking. This acknowledgment sets the stage for real change.
- Calibrated Approach to Integration: We’re emphasizing the importance of careful planning and a step-by-step approach. This ensures that inclusion happens smoothly.
- Learning from Women’s Inclusion: We’re learning from how women were included in the armed forces. This shows a readiness to apply lessons from one integration process to another.
- Impact on Discipline and Camaraderie: We’re considering how inclusion might affect the unique bonds within the armed forces. This balance is crucial for a successful integration.
- Recognizing Importance of Social Awareness: We’re identifying the need for the armed forces to understand societal justice. This change in mindset is vital for true and lasting change.
Way Forward:
- Advocating Wider Discussions: We’re suggesting more discussions and debates within the armed forces. This ensures that everyone’s perspective is considered.
- Gradual Expansion of Roles: We’re advocating for more roles based on abilities and merit. This ensures that everyone gets opportunities based on their skills.
- Involvement of Transgender Community: We’re suggesting that the transgender community should be part of decision-making. This makes sure their views are central to the integration process.
- Establishing Social Awareness Strategy: We’re emphasizing the need for a strategy to make the armed forces more aware. This ensures that everyone understands and accepts the need for change.
- Transparent and Just Process: We’re highlighting the importance of openness and fairness in the integration process. This ensures that the process is respectful and just for everyone involved.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: governor topic
Mains level: accountability and balance to the role of governors

Central idea
The article delves into the persistent constitutional challenges posed by the role of governors in India, emphasizing historical debates, predicting issues realized over time, and proposing judicial and constitutional solutions for effective governance and accountability.
Key Highlights:
- Governor’s Constitutional Role: The article highlights the constitutional concerns regarding the role of governors in Indian states, emphasizing their appointed nature and potential overreach in state matters.
- Recent Instances in Tamil Nadu: Specific instances in Tamil Nadu, where Governor R N Ravi returned bills for assent and delayed decisions, serve as examples of the ongoing issues related to gubernatorial powers.
- Constitutional Design Critique: The piece delves into the historical debates in the Constituent Assembly, expressing concerns raised by members like Dakshayani Velayudhan about the replication of colonial structures and the centralized nature of power.
- Unaddressed Predictions: The article points out that predictions made during the Constituent Assembly debates about potential misuse of gubernatorial powers have materialized, with governors often serving as agents of the Union government.
Challenges:
- Appointment and Removal Disparities: It highlights the disparities between the appointment and removal processes of the President and the Governor, suggesting a lack of checks and balances for governors’ actions.
- Perverse Incentives: The piece discusses the perverse incentives for governors, as they are secure in their positions as long as they align with the Union government, potentially leading to undue interference in state affairs.
Key Phrases:
- Colonial Legacy of Governors: The article stresses the continuation of the colonial institution of governors, raising questions about its relevance in an independent India.
- Powers and Accountability: It explores the imbalance in powers and accountability between the President and the Governor, pointing out the governor’s vulnerability to the Union government’s preferences.
Analysis:
- Judicial Intervention: The piece acknowledges the increasing judicial intervention to address governors’ conduct but questions the need for repeated court interventions and calls for a more sustainable solution.
- Constitutional Reform Proposal: While presenting a constitutional reform proposal from “Heads Held High,” the article suggests making governors accountable to state legislatures through election and impeachment, mirroring the President’s accountability to the Union Parliament.
Way Forward:
- Viable Alternatives: Instead of outright abolition, the article advocates for viable alternatives such as judicial scrutiny and comprehensive constitutional reforms to bring accountability and balance to the role of governors.
- State Legislature Accountability: Proposing a way forward, the article suggests a model where governors are made accountable to state legislatures through election and impeachment, akin to the President’s accountability at the national level.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: GSAT-7 and GSAT-7A
Mains level: emerging technologies in the military landscape

Central idea
The Indian military’s strategic embrace of emerging technologies, encompassing AI, cyber, and unmanned systems, reflects a forward-looking vision. While showcasing diverse initiatives, the article underscores the need for organizational shifts, jointness, and collaboration with civilians to effectively integrate these technologies
Key Highlights:
- Diverse Initiatives: Indian military strategically adopts AI, cyber, and unmanned systems, with each service branch leading initiatives.
- Strategic Vision: Reflects a forward-looking approach, leveraging technology for operational and strategic advantages.
- AIDef Showcases: Defence Ministry’s ‘AIDef’ presents Defence AI Council and Project Agency, showcasing a commitment to integrate AI across allied organizations.
- Indigenous Emphasis: Highlights a push for indigenization, aligning with national goals of self-reliance in defence.
Challenges:
- Organizational Shift Needed: Warns against viewing technology as a ‘plug and play,’ stressing the need for organizational and doctrinal changes.
- Data-sharing Imperative: Advocates for a cultural shift, urging military to share data with civilians for technology to reach its full potential.
- Crucial Interconnectedness: Identifies jointness and interoperability challenges, crucial for effective integration of emerging technologies.
- Need for Unified Commands: Stresses the urgency of joint theatre commands to streamline operations and enhance coordination.
Key Phrases:
- Civil-Military Partnerships: Emphasizes collaborative defence, necessitating partnerships with scientists, academics, and technologists.
- Shared Responsibility: Highlights the shared responsibility of the military and civilians in navigating the complexities of emerging technologies.
- Historical Challenge: Explores the perpetual military challenge of adapting to change, underlining the complexity of integrating emerging technologies.
- Strategic Evolution: Recognizes the need for a strategic evolution to effectively incorporate emerging technologies into military operations.

Analysis:
- Operational Synergy: Advocates for joint theatre commands to achieve operational synergy and seamless integration of emerging technologies.
- Unified Strategy: Stresses the importance of a unified strategy for joint operations, minimizing challenges related to technology integration.
- Specialization Advocacy: Urges a shift towards specialization in human resources practices, aligning officer expertise with the demands of emerging technologies.
- Intellectual Inclination: Recommends extended tenures for officers inclined towards technological domains, fostering intellectual capabilities.
| Value addition box from Civilsdaily
The U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) actively engages with private tech companies through initiatives like the Defense Innovation Unit (DIU) and In-Q-Tel to leverage cutting-edge technologies.
The U.S. prioritizes collaboration between defense agencies and civilian entities, exemplified by the establishment of the Defense Innovation Board, composed of experts from various industries.
The U.S. military emphasizes jointness through unified combatant commands, promoting interoperability in the application of emerging technologies across different branches. |
Key Data:
- ‘UDAAN’ Initiative: The Indian Air Force is utilizing AI, cyber, and virtual reality under ‘UDAAN’ to address operational, logistical, and training needs.
- Integrated Unmanned Roadmap: The Navy is progressing with emerging technologies, including an Integrated Unmanned Roadmap, as part of project ‘Swavlamban.’
- Defence Cyber Agency: Established in 2018, the Defence Cyber Agency addresses threats in the cyber domain.
- Defence Space Agency: Launched in 2018, it focuses on threats and capabilities related to space.
- Comprehensive Approach: Reveals the military’s comprehensive approach, identifying 45 niche technologies for diverse military applications.
- Strategic Preparedness: Illustrates a strategic preparedness to harness a spectrum of technologies for operational superiority.
- Communication Enhancements: Mentions GSAT-7 and GSAT-7A launches, highlighting advancements in military communication capabilities through satellite technology.
- Space for Defence: Showcases India’s utilization of space capabilities for defence purposes, marking a significant leap in technological applications.
Way Forward:
- Integrated Planning: Calls for integrated planning to address challenges in jointness and interoperability, laying the groundwork for successful technology integration.
- Cross-Service Collaboration: Advocates for cross-service collaboration, emphasizing the need for unified efforts to maximize the potential of emerging technologies.
- Private Sector Integration: Recommends openness to technocrats from the private sector, fostering innovation and expertise infusion for defence.
- Innovation Ecosystem: Calls for the creation of an innovation ecosystem, encouraging collaboration between defence and civilian talent for holistic technological advancements.
This transformative journey requires a multi-faceted approach, encompassing strategic vision, organizational adaptability, collaborative partnerships, and talent infusion to fully realize the potential of emerging technologies in the military landscape.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: freedom of speech
)
Central idea
The article critically examines the Government of Tamil Nadu’s establishment of a Fact Check Unit, highlighting constitutional concerns, the potential impact on freedom of speech, and the challenges posed by ambiguity and absence of due process.
What is fact check unit?
A Fact Check Unit is an entity or organization tasked with verifying the authenticity and accuracy of information, particularly in the context of news, announcements, policies, schemes, guidelines, and initiatives of a government or other institutions.
Key Highlights:
- Establishment of Tamil Nadu Fact Check Unit: The Government of Tamil Nadu issues an order to create a Fact Check Unit for verifying information related to the state government across diverse media platforms.
- Constitutional Concerns Raised: Assertions about the order violating fundamental rights and being constitutionally vague and arbitrary, particularly emphasizing the potential infringement on freedom of speech.
- Impact on Freedom of Speech: Examining the implications of the Fact Check Unit on freedom of speech and expression, highlighting the need for reasonable restrictions and challenging the authority of a Government Order in imposing such restrictions.
- Chilling Effect Analysis: A deeper analysis of the perceived chilling effect on freedom of speech, exploring the implications of the Government acting as the arbiter of information authenticity.

Challenges:
- Scope Ambiguity and Potential Misuse: Critiques the lack of specificity in defining “information related to the Government of Tamil Nadu,” raising concerns about ambiguity and the possibility of misuse.
- Due Process Absence: Points out the absence of due process, where the Fact Check Unit lacks a mechanism for the author’s hearing, positioning the government as the sole determinant of information authenticity.
- Legal Limitations on Government Orders: Discusses the legal limitations of Government Orders in imposing restrictions on freedom of speech, underscoring the need for a more nuanced and legislative approach.
- Global Challenges of Misinformation: Draws parallels with global challenges of misinformation, citing events like the U.S. presidential election, and underscores the necessity for effective measures in addressing this widespread issue.
Key Phrases for enhancing answer quality:
- “Chilling effect on freedom of speech”
- “Unconstitutionally vague and arbitrary”
- “Opportunity of hearing”
- “Mis/disinformation and fake news challenge”
- “Government as judge, jury, and executioner”
Analysis:
- Constitutional Implications Explored: In-depth analysis of the constitutional concerns, with a focus on how the Fact Check Unit might impact freedom of speech and questioning the legal standing of a Government Order.
- Interrogation of Scope Ambiguity: Scrutiny of the ambiguity surrounding the definition of “information related to the Government of Tamil Nadu,” delving into potential implications for various forms of expression.
Key Facts:
- US Election and Misinformation Parallel: Drawing parallels with global challenges of misinformation during events like the U.S. presidential election, emphasizing the need for effective measures.
Way Forward:
- Stakeholder Consultation Advocacy: Advocacy for comprehensive consultations with stakeholders, including the public and intermediaries, to develop effective measures against misinformation.
- Global Best Practices Exploration: Encouraging exploration of global best practices, such as the European Commission’s Code of Practice on Disinformation, for a more inclusive and well-informed approach.
- Media Literacy Promotion Recommendation: Recommending the promotion of media literacy and support for an independent network of fact-checkers as constructive measures to combat misinformation.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Hindu Kush region
Mains level: mineral wealth

Central idea
The article highlights India’s opportunity in the emerging critical minerals market in Afghanistan’s Hindu Kush, emphasizing responsible mining amidst environmental considerations. It connects this opportunity to the global shift towards electric mobility, with the potential for job creation.
Key Highlights:
- Afghanistan’s Riches: The Hindu Kush region in Afghanistan holds minerals worth a trillion dollars, a potential game-changer.
- Mobility Shift: Global movement from oil to electric vehicles is escalating demand for critical minerals.
- Indian Opportunity: Geological hints suggest the possibility of similar mineral wealth in the northern Indian side of the Hindu Kush range.
- Untapped Potential: India, with vast unexplored land and advancements in deep-sea mining, may have undiscovered mineral riches.
Challenges:
- Governance and Environmental Concerns: Past issues highlight the need for robust laws to balance environmental concerns with job creation.
- Political Tensions: Historical discord between the central government and Congress on mining needs resolution for cohesive policies.
- Legislative Balance: Striking a balance between ecological conservation and job creation requires nuanced legislation.
- Private Sector Role: Private sector involvement is crucial for capital-intensive mining, demanding careful governance.
Key Phrases for value addition:
- “Afghanistan: Saudi Arabia of lithium” emphasizes the potential of the Hindu Kush region.
- “Transition from oil to electric mobility” underlines the global shift and increasing demand for critical minerals.
- “New Middle East: Hindu Kush mountain range” positions the region as a significant player in the emerging critical minerals market.
- “Global critical minerals race” highlights the competitive dynamics in securing these resources worldwide.
Analysis:
- Global Shift: The global transition to electric mobility is a key driver behind the soaring demand for critical minerals.
- Indian Potential: India, with its untapped resources, is poised to benefit from the increasing global demand for minerals.
- Balancing Act: Striking a balance between environmental conservation and job creation is essential for sustainable mining practices.
- Private Sector Significance: In the capital-intensive mining sector, the private sector’s involvement is crucial for efficiency and technological advancements.
Key Data:
- Trillion-Dollar Potential: Afghanistan’s Hindu Kush region is estimated to hold minerals worth a trillion dollars.
- Geological Reports: Reports suggest the possibility of untapped mineral deposits in the northern Indian side of the Hindu Kush range.
- Exploration Status: Less than 10% of India’s landmass has been explored, with only 2% mined.
Way Forward:
- Legislation: Enforcing robust environmental, labor, and land laws is crucial for responsible and sustainable mining.
- Private Exploration: Encouraging large-scale private exploration for critical minerals is vital for efficiency and technological advancements.
- Deep-Sea Prospects: Leveraging emerging deep-sea mining technologies can open new avenues for resource exploration.
- Balance Priority: Striking a balance between environmental conservation and job creation should be a priority in future mining policies.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Odisha Adarsha Vidyalayas
Mains level: education quality in government schools

Central idea
Odisha revolutionizes public education with initiatives like Odisha Adarsha Vidyalayas, ‘Mo School’ Abhiyan, and 5T-High School Transformation, aiming to surpass private schools in quality. This results in a substantial shift, with 81% of students currently enrolled in government schools. The state’s commitment to inclusivity, alumni engagement, and technology integration drives equality and excellence in education.
Key Highlights:
- Revolutionary Reforms: Odisha’s education sector undergoes revolutionary changes through initiatives like Odisha Adarsha Vidyalayas, ‘Mo School’ Abhiyan, and 5T-High School Transformation Programme.
- Recognition and Ranking: OAVs receive accolades, with one ranked the fifth-best in government-run day schools, emphasizing qualitative English-medium education for rural and semi-urban areas.
- Inclusive Enrollment: OAVs ensure representation of marginalized groups, leading to a higher enrollment of female students. They also rescue and prepare vulnerable children for OAV entrance exams.
- Alumni Engagement: Mo School Abhiyan connects schools with alumni, promoting mentorship, collaboration, and financial contributions, creating a significant impact on infrastructure and engagement.
Key Phrases:
- Quality Education: Odisha’s focus on continuous teacher education, technology integration, and maintaining a favorable teacher-pupil ratio highlights its commitment to providing quality education.
- Alumni Community: Mo School Abhiyan leverages the alumni community to contribute to school development, creating a unique model of collaborative efforts for educational improvement.
- 5T-High School Transformation: The 5T concept drives the High School Transformation Programme, emphasizing transparency, technology, teamwork, and timeliness for comprehensive educational changes.

Analysis:
Odisha’s proactive approach to education, combining infrastructure development, alumni engagement, and technology integration, has led to a significant shift in enrollment patterns, with a majority of students now choosing government schools.
Key Data:
- Enrollment Shift: In 2019-20, private schools had 16,05,000 students; in 2021-22, this number reduced to 14,62,000, indicating a shift towards government schools.
- Financial Contributions: More than 5.5 lakh contributors, including ministers, MPs, and professionals, have contributed over ₹797 crore in 40,855 schools under the School Adoption Programme.
Key Terms:
- Odisha Adarsha Vidyalayas (OAV): A model aiming to bridge the rural-urban education gap by providing qualitative and affordable English-medium education.
- Mo School Abhiyan: An initiative connecting schools with alumni, promoting collaboration, contributions, and celebrating successes to improve government schools.
- 5T-High School Transformation Programme: Rooted in transparency, technology, teamwork, and timeliness, focusing on technological advancements and holistic development in high schools.
Challenges:
- Parental Trust: Historical perceptions of poor education quality in government schools challenge rebuilding parental trust.
- Affordability Concerns: Despite reforms, concerns persist regarding the economic accessibility of quality education in government schools.
- Perceived Quality Gap: Overcoming the perception gap regarding the quality of education in government schools compared to private counterparts.
- Economic Accessibility: Addressing financial barriers for families, ensuring that quality education remains economically accessible.
Way Forward:
- Continuous Alumni Engagement: Strengthen collaborations between schools and alumni to maintain a sustained focus on improvement. Explore mentorship programs and alumni-led initiatives for ongoing school development.
- Enhancing Perceived Value: Implement awareness campaigns highlighting the positive changes in government schools. Showcase success stories and academic achievements to alter perceptions.
- Financial Inclusivity: Introduce scholarship programs or financial aid to address economic barriers. Collaborate with governmental and non-governmental organizations to provide educational subsidies.
- Technology Integration: Expand technological resources in schools for interactive and enhanced learning experiences. Introduce digital literacy programs to prepare students for a technology-driven future.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Act, 2019
Mains level: road safety in India

Central idea
India’s road safety crisis, witnessing an estimated 300,000 annual fatalities, demands immediate interventions. Despite economic progress, road crashes cost 5-7% of the national GDP, emphasizing the need for strategic investments, political will, and a collective mindset shift. Urgent actions are crucial to curb this silent but deadly pandemic.
Key Highlights:
- India’s Annual Road Fatalities: Approximately 3,00,000 people lose their lives on Indian roads annually.
- Global Road Deaths: India contributes to 25% of the worldwide road fatalities.
- India’s Disproportionate Role: Despite global road safety concerns, one in four road deaths occurs in India.
- Economic Toll: Road crashes in India impose a substantial economic cost, ranging from 5-7% of the nation’s GDP.
Challenges:
- Urgent Intervention Needed: Over 34 deaths per hour underscore the critical need for immediate and coordinated action.
- Economic Impact: The economic toll of road crashes in India is substantial, affecting the nation’s GDP.
- Economic Toll: Road crashes in India impose a substantial economic cost, ranging from 5-7% of the nation’s GDP.
- State Disparities: The economic impact varies across states, impacting the quality of emergency care and after-care services.
Key Data:
- Annual Road Fatalities: Approximately 3,00,000 people are estimated to be killed on Indian roads every year. Equivalent to more than 34 people every hour of every day.
- Economic Toll: Road crashes in India are estimated to cost between 5% and 7% of the national GDP.
- Global Road Safety: Positions road safety as a global problem, with 1.3 million people killed in road crashes every year.
Key Phrases:
- Silent Pandemic: Describes road-related fatalities as a silent but deadly pandemic demanding attention.
- Whole-of-Society Effort: Emphasizes the need for a collaborative approach involving government, private sector, and citizens.
- World Day of Remembrance: Commemorates the World Day of Remembrance for Road Traffic Victims on November 19.
- Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Act, 2019: Indicates positive steps taken by the Indian government to enhance road safety measures.
Analysis:
- Pedestrians and Two-Wheelers: Emphasizes the vulnerability of pedestrians, cyclists, and two-wheeler riders, constituting 75% of road deaths in India.
- Policy Impact: Acknowledges positive steps like the Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Act, 2019, and improved data collection while emphasizing the need for a comprehensive safe-system approach.
- Legislative Impact: Acknowledges positive steps like the Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Act, 2019, and emphasizes the need for strategic investments in road safety measures.
- Data-Driven Approach: Highlights the importance of enhanced data collection to understand the causes and locations of road crashes better.
Way Forward:
- Seatbelt and Helmet Use: Prioritize the enforcement of seatbelt and helmet use for both drivers and passengers to significantly reduce fatalities.
- Behavioral Change: Emphasize the importance of public awareness campaigns like #MakeASafetyStatement to instigate behavioral changes and promote road safety.
- Large-Scale Initiatives: Launch campaigns on a national scale, such as #MakeASafetyStatement, involving international celebrities, to raise awareness and instigate behavioral changes.
- Collaborative Efforts: Encourage a whole-of-society effort involving the government, private sector, and citizens for effective road safety measures.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Sixth Schedule and PESA
Mains level: tribal politics

Central idea
The article explores the significant role of tribal votes in the 2023 Madhya Pradesh assembly election, focusing on the competition between Congress and BJP for tribal support. It traces the historical evolution of tribal politics in the region, highlighting key factors influencing tribal voting patterns. The central theme revolves around the ongoing battle for tribal empowerment, with promises and challenges shaping the political landscape in Madhya Pradesh.
Key Highlights:
- Tribal Electoral Battleground: The 2023 Madhya Pradesh assembly election is marked by a fierce struggle between Congress and BJP for the pivotal tribal vote, constituting 21% of the state’s population.
- Political Activism: Over decades, tribal communities have become politically active, influencing electoral outcomes and reshaping the state’s political dynamics.
- Historical Contestation: The political contest for tribal support intensified in the 1990s, with Congress historically dominant but facing challenges as the BJP strategically entered tribal areas.
- Fluid Voting Patterns: Tribal voting, historically with Congress, has witnessed shifts, creating a dynamic landscape for both major parties.
Challenges:
- Shifting Political Alliances: Historical Congress dominance faces challenges, with BJP making strategic inroads, making the tribal vote a pivotal factor.
- Unresolved Policy Demands: Tribals express concerns about autonomy, job creation, forest conservation, and access to government welfare schemes, posing challenges for effective electoral strategies.
- Dynamic Tribal Voting: The fluid nature of tribal voting patterns adds complexity to electoral strategies, requiring adaptable and responsive political approaches.
- Competing Electoral Narratives: The battle for tribal votes involves competing promises and narratives, with Congress emphasizing empowerment through policies like the Sixth Schedule and PESA, while BJP highlights welfare initiatives and cultural ties.
Key Phrases:
- Empowerment Pledges: Congress commits to implementing the Sixth Schedule, enacting PESA, and raising tendu patta rates. BJP emphasizes welfare initiatives and cultural connections.
- Political Mobilization: Grassroots efforts by Vanvasi Kalyan Parishad and RSS play a pivotal role in BJP’s success in tribal areas.
- Party Dynamics: The rise and decline of smaller parties like GGP and the emergence of JAYS signify the evolving political landscape in tribal-dominated regions.
- Historical Turnovers: Post-Independence, Congress dominance in tribal areas faced challenges, with a bi-polar contest emerging in the 2003 elections and subsequent turnovers.
Analysis:
- Political Dynamics: The historical shift from Congress to BJP dominance in tribal areas reflects evolving political strategies and grassroots mobilization.
- Voter Behavior: Grievances against the Shivraj Singh Chouhan-led BJP government and demands for autonomy, job creation, and forest rights significantly influenced tribal voting patterns in the 2018 elections.
- Historical Voting Trends: The 2003 elections marked the beginning of a bi-polar contest, with Congress gaining ground in 2008 and 2018, showcasing the dynamic nature of tribal votes.
- Influence of Grassroots Movements: The sustained efforts of organizations like Vanvasi Kalyan Parishad and RSS contributed to BJP’s success in entering tribal areas.
Key Data:
- Tribal Population Impact: Constitutes 21% of Madhya Pradesh, with 48 out of 230 assembly seats reserved for tribal communities.
- Voter Turnout Surge: Tribal voter turnout rises significantly, reaching 76.39% in the 2018 assembly elections, indicating increased political consciousness.
- Party Strength: Congress relies on tribal leaders like Umang Singhar, Bala Bachchan, and Kantilal Bhuria for securing seats in tribal-dominated areas.
- BJP Initiatives: BJP highlights the appointment of Droupadi Murmu as the first tribal woman president and announces a Rs 24,000 crore welfare program for tribal communities.
Key Facts:
- Prominent Figures: Congress relies on tribal leaders like Umang Singhar, Bala Bachchan, and Kantilal Bhuria to secure seats in tribal-dominated areas.
- BJP Initiatives: BJP highlights the appointment of Droupadi Murmu as the first tribal woman president and announces a Rs 24,000 crore welfare program for tribal communities.
- Shift in Voting Patterns: The 2018 elections witnessed a reversal, with Congress obtaining 32 seats and BJP 16, reflecting changing voter sentiments.
- Role of Grassroots Movements: Organizations like Vanvasi Kalyan Parishad and RSS played a crucial role in BJP’s success in entering tribal areas.
Way Forward:
- Inclusive Policies: Future success hinges on inclusive policies addressing tribal demands for autonomy, job opportunities, and access to welfare schemes.
- Collaborative Governance: A collaborative approach between mainstream parties and tribal communities is crucial to ensure effective representation and address long-standing grievances.
- Responsive Electoral Strategies: Adaptable and responsive political approaches are essential to navigate the dynamic nature of tribal voting patterns.
- Effective Policy Implementation: Resolving policy demands related to autonomy, job creation, forest conservation, and welfare schemes becomes pivotal in securing tribal votes.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Major Opium-Producing Districts
Mains level: cultural heritage, economic considerations, and global standards for opium farming

Central idea
The article explores the multifaceted challenges arising from the intersection of cultural pride and economic shifts in opium cultivation in India. It delves into concerns surrounding the government’s policy shift, addressing potential impacts on livelihoods, national security, and transparency.
Key Highlights
- Cultural Significance of Opium Cultivation: Opium farming is a source of cultural pride, termed “agriculture of dignity” in the Mewar region, linking social status to this traditional trade and reflecting generations’ engagement.
- Government Policy Shift in 2021: In 2021, the government allowed private players to produce Concentrate of Poppy Straw (CPS) alongside traditional opium gum, aiming to boost alkaloid yield and align India with global practices. However, this shift faces resistance from opium farmers.
- Concerns about Private Players: Opium farmers express worries about the entry of private companies, fearing threats to livelihood, profits, and national security. Farmers argue that private involvement may lead to misuse of opium, increased drug trafficking, and rising costs of life-saving medicines.
- Impact on Farmers and Traditional Practices: Opium farmers face economic challenges, citing stagnant procurement rates, increased input costs, and reduced poppy seed yield under the new system. The shift to CPS raises concerns about transparency, farmer consultation, and the potential decline in income for traditional opium cultivators.
Challenges
- Threat to Livelihood and National Security: Opium farmers fear that private entry may endanger their profession and lead to increased drug-related issues. There is a possibility of drug mafia influence and security threats if alkaloids fall into the wrong hands.
- Impact of Policy Shift on Farmers: Economic challenges for opium farmers, including reduced poppy seed yield and concerns about transparent practices under CPS. Farmers worry about income loss and express dissatisfaction with the lack of government consultation.
- Safety and Security of Alkaloids: Opium farmers question the safety and security of alkaloids under private production. Fears that private involvement may compromise the integrity of life-saving medicines made from opium.
- Division among Farmers and Lack of Transparency: Farmers express concerns about the government creating divisions with two production systems. Calls for transparent policies and farmer involvement, alleging a lack of transparency in the CPS mechanism.
Key Phrases and Terms for answer enrichment
- Swabhiman ki Kheti (Agriculture of Dignity): Opium cultivation holds cultural pride in the Mewar region, reflecting social status.
- Afeem and Aulat Barabar (Poppy Plants and Children Deserve Similar Treatment): Highlights the cultural significance of opium, equating it with the care given to children.
- Concentrate of Poppy Straw (CPS): New method introduced in 2021, allowing private players to extract alkaloids from poppy straw alongside traditional opium gum.
- Make in India: Farmers question the government’s commitment to “Make in India” while allowing imports of poppy seeds.
Analysis for mains answer
- Cultural Pride vs. Economic Realities: Opium farming holds cultural significance, but economic challenges, policy shifts, and private entry threaten traditional practices.
- Balancing Global Practices and Farmer Concerns: The government’s shift to CPS aligns with global norms but faces resistance from farmers concerned about income, transparency, and safety.
- Security Concerns and Misuse of Opium: Farmers express worries about the potential misuse of opium and security threats, emphasizing the need for strict controls.
- Need for Transparent Policies and Farmer Involvement: Farmers demand transparency, consultation, and the continuation of traditional practices, expressing dissatisfaction with the current policy.
Key Data and Facts
- Opium Farmers in India: About 1 lakh farmers across 22 districts in Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh have licenses to cultivate opium.
- Major Opium-Producing Districts: Mandsaur, Neemuch, and Chittorgarh contribute to 80% of India’s opium production.
- Change in Government Policy (2021): Government policy shift in 2021 allows private players to produce CPS, aiming to boost alkaloid yield.
- Economic Impact on Farmers: Opium farmers face economic challenges, citing stagnant procurement rates, increased input costs, and reduced poppy seed yield under the new system.
Way forward
- Policy Review and Farmer Consultation: Conduct a comprehensive review of the opium policy, ensuring active participation and consultation with opium farmers to address their concerns and incorporate their insights into the decision-making process.
- Transparency Measures: Implement transparent mechanisms in the Concentrate of Poppy Straw (CPS) system, providing clear information on pricing, procurement, and production processes. This ensures accountability and builds trust among farmers.
- Public-Private Collaboration: Establish a structured collaboration between the government and private entities to leverage expertise and resources. This collaboration should prioritize safeguarding national security, ensuring the integrity of medicinal opium production, and preventing misuse.
- Diversification and Economic Support: Explore avenues for diversification in agriculture, providing support and incentives for opium farmers to engage in alternative crops. This can mitigate economic challenges and reduce dependency on a single agricultural practice.
As the government’s 2021 policy allows private entry, concerns about livelihoods, security, and transparency emerge. Navigating the way forward requires a delicate balance, harmonizing cultural heritage, economic considerations, and global standards for a sustainable future.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Projected GDP Growth
Mains level: economic success after the COVID-19 pandemic

Central idea
The article highlights India’s economic challenges, including concerns about post-COVID recovery sustainability, vulnerabilities to geopolitical shifts, a growing dependency on Chinese imports, and a decline in industrial growth rates. The central idea revolves around acknowledging these challenges and the imperative for strategic interventions to ensure long-term economic resilience and growth
Key Highlights
- GDP Growth and Recovery: India’s GDP projected to grow by 6.3% in 2023-24, showcasing post-COVID recovery. Positive signs of resilience, but concerns persist about employment quality and inflation.
- Geopolitical Shifts and Vulnerabilities: Globalization ended in 2022-23, exposing India to geopolitical vulnerabilities. Calls for a reevaluation of economic strategies to navigate changing global dynamics.
- Trade Deficit with China: India grapples with a soaring trade deficit with China. Strategic threat due to dependency on Chinese imports; calls for diversification.
- Industrial Woes and Growth Rates: Industrial growth rates, especially in capital goods, have regressed. Decline in key sectors signals a threat to overall economic stability.
- Public Sector Investment: Public sector investment appears stagnant despite reported growth. Doubts about credibility underscore the need for transparent reporting.
- Social Development Challenges: India’s Human Development Index (HDI) ranking has slipped. Recognition of challenges in social development, prompting a need for improved strategies.
Challenges
- Sustainability Concerns Post-COVID Recovery: Quality and sustainability of post-COVID recovery raise concerns, necessitating comprehensive strategies.
- Vulnerabilities to Geopolitical Shifts: Geopolitical vulnerabilities impact India’s economic stability, demanding adaptation of economic policies.
- Dependency on Chinese Imports: Rising trade deficit with China poses economic frailty, urging the urgent need to diversify imports.
- Decline in Industrial Growth: Regression in industrial growth rates, especially in capital goods, requiring targeted interventions for revitalization.
Key Phrases and Terms for making mains answer value added
- Post-COVID Resilience: Short-term economic success after the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Geopolitical Realignment: Recognition of shifts in global dynamics impacting India’s economic strategies.
- Trade Deficit Dynamics: China’s influence on India’s economic vulnerabilities due to a soaring trade deficit.
- Industrial Regression: Decline in growth rates, especially in capital goods, signaling industrial challenges.
- Credibility of Public Sector Investment: Doubts raised about the accuracy of reported public sector investment growth..
Analysis of the article in balanced way for mains score improvement
- Short-Term Success vs. Long-Term Resilience: Balancing short-term GDP growth with the need for sustainable and inclusive recovery.
- Adapting to Geopolitical Realities: Necessity to adapt economic policies to navigate geopolitical shifts and ensure stability.
- Diversification for Economic Stability: Addressing the trade deficit challenge by diversifying imports and promoting self-reliance.
- Revitalizing Key Sectors for Growth: Targeted interventions required to revitalize industrial growth, especially in crucial sectors.
Key Data and Facts
- Projected GDP Growth (2023-24):3%
- Trade Deficit with China: Strategic Threat
- Industrial Growth Decline: Capital Goods
- HDI Ranking (2021): Decline
The Way Forward
- Sustainable and Inclusive Growth: Develop comprehensive strategies for sustained and inclusive growth post-COVID.
- Adaptive Economic Policies: Adapt economic policies to navigate evolving global dynamics and ensure stability.
- Diversification and Self-Reliance: Diversify imports and boost domestic production for economic self-reliance.
- Targeted Interventions for Industrial Revitalization: Implement targeted interventions to revitalize key industrial sectors and stimulate overall economic growth.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Family Health Survey 5
Mains level: domestic violence
Central idea
The article talks about how women facing domestic violence in India struggle to get justice due to biases in the legal system. It mentions challenges like police not taking complaints seriously and judges making unfair comments. To make things better, it suggests that judges should be fair, and the media should report responsibly to help women get the justice they deserve.
Key Highlights:
- Systemic Flaws in Legal Process: The study of 4 lakh FIRs in Haryana exposes inherent biases against women, revealing flaws from the filing of complaints to the conviction process.
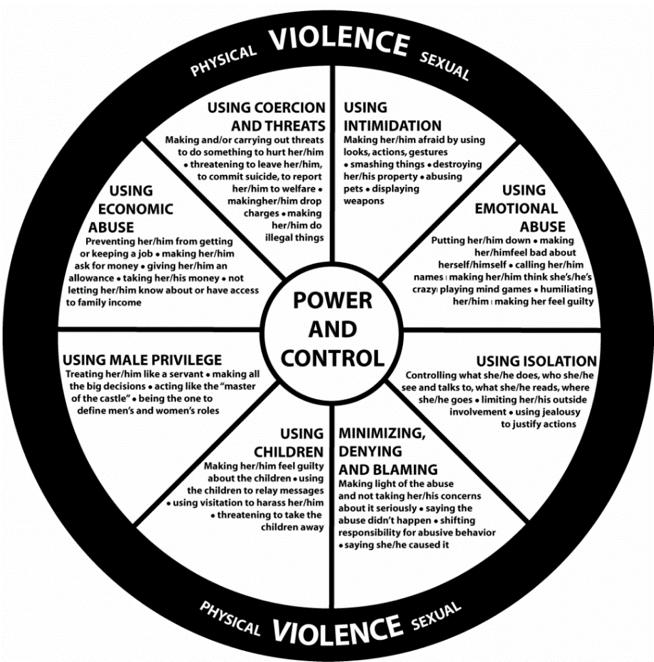
- NGO’s Testimony on Domestic Violence: Majlis, an NGO in Mumbai, provides a firsthand account of the grave domestic violence faced by women, spanning physical, economic, verbal, emotional, and sexual abuse.
- Alarming Crime Rates: India witnesses rising crimes against women, with 21 daily dowry-related deaths and 4 lakh cases under Section 498A of the IPC in 2019, emphasizing the urgent need for systemic change.
Challenges:
- Reluctance to File FIRs: Police reluctance persists despite legal provisions, steering victims towards counseling instead of criminal complaints, hindering justice for domestic violence victims.
- Patriarchal Mindset Impact: The police’s apathy is rooted in a patriarchal mindset, exacerbated by demeaning comments from the judiciary, contributing to the perception that women misuse legal provisions.
- Impact on Victim Hope: Women turned away by police often lose hope, leading to dire consequences, such as suicide or murder, highlighting the severity of the challenges in obtaining justice.
Analysis:
- Stereotype Reinforcement: Demeaning comments, accusing women of misusing Section 498A, perpetuate stereotypes and contribute to the reluctance of police in handling domestic violence cases.
- Judiciary’s Role in Victim Perception: Judicial comments play a significant role in shaping public perception, impacting the willingness of women to seek justice for domestic violence.
- Need for Judicial Sensitivity: Recognizing the need for sensitivity in judicial language and approach to avoid further victimization of women seeking legal recourse.
Key Data for mains value addition:
- Dowry-Related Deaths: NCRB reports highlight disturbing statistics, indicating 21 daily dowry-related deaths and 4 lakh cases under Section 498A in 2019, underscoring the urgency for intervention.
- Prevalence of Domestic Violence: National Family Health Survey 5 (2019-20) data reveals that 30% of women (over 20 crore) experience physical violence, emphasizing the widespread nature of the issue.
- Need for Data-Driven Interventions: Utilizing crime statistics to inform targeted interventions and policy measures is crucial for addressing the increasing rates of crimes against women.
Way Forward:
- Sensitization Programs: Implementing sensitization programs to eliminate the patriarchal mindset within the police force, fostering a more empathetic and proactive approach.
- Legal Procedure Adherence: Ensuring strict adherence to legal procedures in handling domestic violence cases to prevent police reluctance and promote efficient and unbiased investigations.
- Continuous Training: Continuous training programs for law enforcement officers to enhance their understanding of the complexities surrounding domestic violence cases.
- Unbiased Judgment Enforcement: Establishing mechanisms to hold the judiciary accountable for unbiased judgments, discouraging sweeping generalizations and ensuring fair treatment of domestic violence cases.
- Judicial Education Initiatives: Advocating for ongoing judicial education on domestic violence issues to keep judges informed and sensitive to the unique challenges faced by victims.
Conclusion:
The multifaceted challenges women face in obtaining justice for domestic violence necessitate a holistic approach involving legal reforms, sensitization programs for law enforcement, and responsible media reporting. Addressing systemic biases, legal loopholes, and societal perceptions is essential for meaningful change and ensuring justice for victims of domestic violence.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: The Hathi Committee
Mains level: Nexus between pharmaceutical companies and doctors
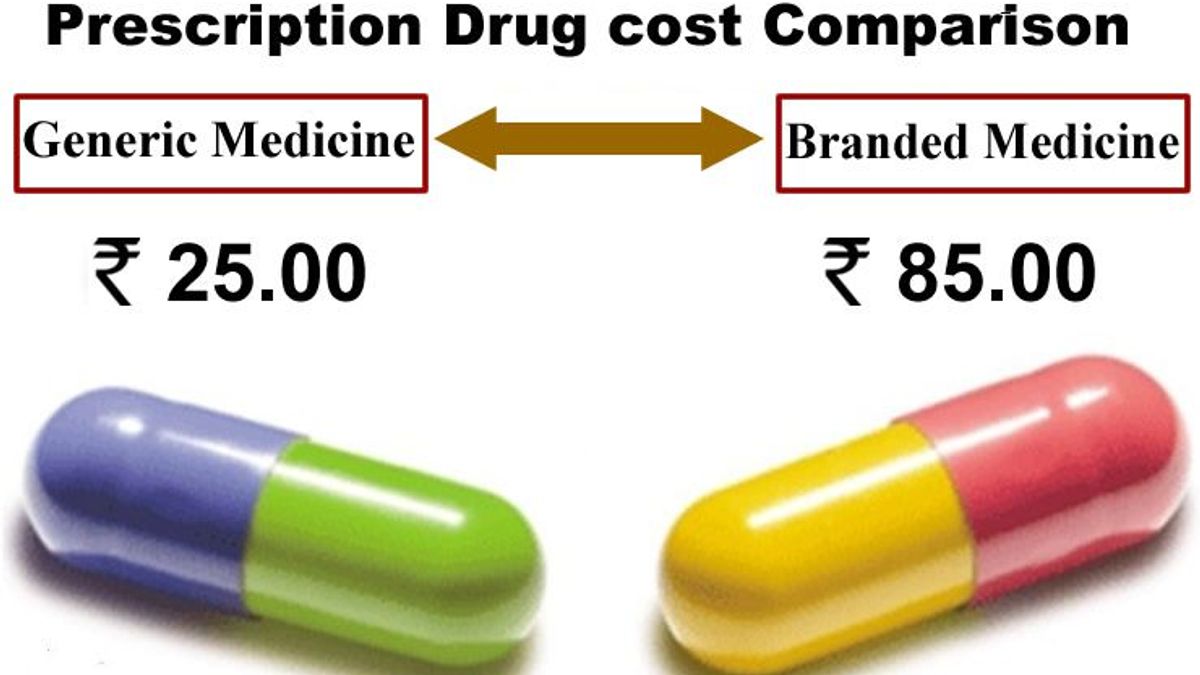
What is the news?
Following the Indian Medical Association’s protest, the NMC has withdrawn the order on ‘generic prescribing’ since August 23, 2023
Central idea
The article highlights challenges in India’s healthcare system, emphasizing the struggle between generic and brand prescriptions. It discusses the alleged nexus between pharmaceutical companies and doctors, quality assurance concerns, and the need for comprehensive measures to ensure affordable and reliable access to medicines. The withdrawal of the generic prescribing order reflects ongoing complexities in achieving universal healthcare goals.
Key Highlights:
- Over-the-Counter Medical Sales in India: Patients often seek second opinions from non-qualified individuals in medical shops, with queries ranging from medicine strength to potential side effects.
- Generic vs. Brand Names: The National Medical Council (NMC) directed doctors to prescribe generic names over brand names, emphasizing the cost factor and the affordability of generic names. The Hathi Committee in 1975 supported the gradual phasing out of brand names.
- Alleged Nexus and Ethical Commitment: An alleged nexus between pharmaceutical companies and doctors exists, but medical associations stress their ethical commitment to improving access to affordable medicines.
- Quality Assurance Concerns: Concerns about the quality of medicines persist, with a prevalence rate of 4.5% for spurious and 3.4% for “not standard quality” medicines. The need for 100% quality-tested drugs is crucial for patient safety.
- Government’s Role: The government is urged to ensure quality through Universal Health Coverage and private healthcare networks, with calls for periodic sampling, banning batches that fail quality tests, and taking punitive actions against manufacturers.
Challenges:
- Quality Assurance Implementation: Existing mechanisms for quality assurance are not earnestly implemented, raising concerns about the reliability of the system.
- Enforcement of Generic Prescription: The moral dilemma in enforcing generic prescription without concrete evidence of standard quality poses a challenge in the healthcare system.
- Availability of Essential Medicines: The low availability rate of essential medicines, especially pediatric medicines, hampers the effective treatment of patients.
- Unscientific Combinations: The presence of unscientific combinations of medicines in the retail market adds complexity to the pharmaceutical landscape.
Analysis:
- Role of the Chemist: Concerns revolve around the chemist or less knowledgeable salesperson determining the brand, potentially based on profit motives, impacting the choice of medicines.
- Withdrawal of Generic Prescription Order: The withdrawal of the NMC order on generic prescribing, following the Indian Medical Association’s protest, reflects the ongoing challenges in healthcare policy.
| Case study to improve answer quality
The Tamil Nadu Medical Services Corporation Limited’s practice, where all supplied medicines are kept under quarantine stock till double blinded samples are cleared in quality testing by government and private sector laboratories, is worth replicating. |
Key Data:
- Prevalence of Spurious and NSQ Medicines: National drug surveys in the last 10 years indicate prevalence rates of 4.5% for spurious and 3.4% for “not standard quality” medicines, highlighting the need for stricter quality control.
- Availability of Essential Pediatric Medicines: A study in Chhattisgarh in 2010 found only a 17% availability rate of essential pediatric medicines, indicating a significant gap in accessibility.
Way Forward:
- Government Assurance and Evidence: The government should provide concrete evidence of the standard quality of medicines before enforcing generic prescriptions, ensuring patient safety.
- Comprehensive Measures: Implementing comprehensive measures, such as limiting profit margins for wholesale and retail agents, is crucial for creating a transparent and fair pharmaceutical ecosystem.
- Janaushadhi Kendras Expansion: Expanding the network of Janaushadhi kendras is essential to improve accessibility to affordable medicines and promote their widespread availability.
- Monitoring Implementation: Ensuring proper implementation and monitoring of policies for free medicines and diagnostics under Universal Health Care is vital for the success of healthcare initiatives.
- Addressing Profit Motives: Addressing profit motives influencing the choice of medicines by chemists and salespersons is essential for a patient-centric healthcare system.
Conclusion:
The withdrawal of the generic prescribing order is seen as a step back in achieving universal access to affordable generic medicines. Addressing quality concerns, ensuring availability, and monitoring implementation are crucial for a successful healthcare system.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Electoral Trusts Scheme Electoral Bond Scheme
Mains level: Opacity and anonymity in corporate donations.

Key Highlights:
- Tradition of Secrecy: Indian political parties, historically resistant to public scrutiny, operate in a culture of secrecy regarding their funding sources and applications.
- Corporate Dependency: The exorbitant funds required for political processes and operations often come from Big Business entities, creating a financial reliance on these corporations.
- Quid Pro Quo: Political parties, in return for financial support from corporations, are often expected to reciprocate with political favors, creating a symbiotic relationship between the two.
- Voter Empowerment: Civil society campaigns, notably through Public Interest Litigation (PIL), seek to empower voters by improving access to background information on electoral candidates.
- Challenging Legislative Opacity: PIL serves as a tool to challenge legislative attempts to obscure the identities of corporate donors, promoting transparency in political funding.
- Democratic Right to Information: The campaign is grounded in the citizen’s democratic right to information, an integral aspect of the fundamental right to speech and expression under the Constitution.
- Countering Legislative Maneuvers: PIL acts as a countermeasure against legislative maneuvers designed to undermine transparency in political funding.
Challenges:
- Hiding Corporate Donors: Political establishments employ legislative tactics to conceal the identities of corporate donors, preventing public awareness of the financial backers of political parties.
- Electoral Trusts and Bond Schemes: The introduction of schemes like the Electoral Trusts Scheme (2013) and the Electoral Bond Scheme (EBS) creates barriers that obscure the direct link between political parties and their corporate donors.
- Transparency Concerns: Legislative changes raise concerns about jeopardizing transparency, incentivizing corrupt practices, and limiting the accountability of political parties.
- Nexus Between Politics and Business: The legislative landscape contributes to a growing perception of a nexus between political entities and big business, raising questions about ethical governance.
Key Phrases for value addition:
- Amendments Under Scrutiny: Recent amendments in the legal framework of corporate donations face scrutiny and constitutional challenges.
- ‘Right to Know’ Infringement: Allegations arise that these amendments infringe upon the citizen’s fundamental ‘Right to know’ under Article 19(1)(a) of the Constitution.
- Transparency Need: The importance of transparency in political funding is emphasized as a cornerstone of a healthy and accountable democratic process.
- Autonomy Compromise: Concerns are raised about the compromise of the country’s autonomy, with potential negative impacts on governance and democratic values.
Analysis
- Undermining Transparency: Legislative changes are criticized for undermining transparency, creating a more opaque environment in political funding.
- Electoral Bond Scheme Critique: The Electoral Bond Scheme (EBS) faces critique for introducing opacity in political funding, limiting citizens’ access to vital information concerning electoral financing.
- Opacity in Politics and Business: The intertwining opacity in political and business spheres is identified as a growing trend with potential repercussions for democratic processes.
- Influence of Special Interest Groups: Critics argue that legislative changes enable special interest groups, corporate lobbyists, and foreign entities to exert undue influence on the electoral process.
Key Data for mains value addition:
- Favored Donation Mode: Electoral bonds have become the favored mode of political donation due to their anonymity features.
- ₹13,791 Crore Sales: Until July 2023, electoral bonds amounting to ₹13,791 crore have been sold in 27 tranches.
- 55.9% Donation Share: Electoral bonds contribute significantly, accounting for 55.9% of political donations received by 31 parties.
- BJP’s Leading Redemption: The BJP leads in the redemption of electoral bonds, with 74.5% of the total until 2020-2021.
Key Facts:
- Opacity and Corruption Concerns: Critics express concerns about the opacity introduced by legislative changes, potentially incentivizing corrupt practices in political funding.
- Majority Cash Dealings: Despite the availability of formal options like electoral bonds, the majority of political dealings continue to be in cash.
- Electoral Bond Impact: Receipts from electoral bonds enable political parties to engage in formal economy transactions, covering infrastructure, equipment, and media publicity costs.
- Ongoing Legislative Scrutiny: Legislative changes continue to undergo scrutiny, impacting transparency and accountability in political funding.
Key Terms:
- Electoral Trusts Scheme
- Electoral Bond Scheme
- Right to Know
- Corporate Donations
- Transparency
- Corruption
- Political Funding
- Constitutional Challenges
Way Forward:
- Hopes for a Level Playing Field: Expectations are pinned on judicial intervention to ensure a more level playing field in future elections.
- Upholding Freedom of Speech: The judiciary is anticipated to play a crucial role in upholding the right to freedom of speech and expression, empowering voters with information.
- Addressing Transparency Concerns: Recognizing the critical need for transparency, steps are expected to be taken to address concerns related to opacity and anonymity in corporate donations.
- Judicial Scrutiny Importance: The importance of judicial scrutiny in ensuring the preservation of democratic values and principles is emphasized.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Introduction of Basmati rice cultivation in Dehradun by Dost Mohammad Khan.
Mains level: cultural tourism

Central idea
Dehradun’s historical ties with Afghanistan, spanning from Ahmad Shah Durrani to Yakub Khan, shape the city’s cultural landscape. The legacy includes agricultural influences, introduction of music like the rubab, and specific locations favored by Afghan royals. Safeguarding this historical tapestry is essential for cultural preservation and promoting tourism.
Key Highlights:
- Founder of Afghanistan: Ahmad Shah Durrani’s role in unifying Afghan tribes, shaping modern Afghanistan.
- Anglo-Afghan War: Events leading to the war and its impact on the region’s political landscape.
- Legacy of Dost Mohammad Khan: His settlement in Dehradun and influence on local culture.
- Basmati Rice Cultivation: Introduction of Basmati rice cultivation in Dehradun by Dost Mohammad Khan.
- Cultural Impact: How Afghan royals influenced local practices, including hunting and food habits.
- Cultural Patrons: Contribution to music, introduction of the rubab instrument, and planting fruit trees.

Challenges:
- Political Turmoil: Challenges faced by rulers like Shah Shuja in maintaining stability.
- British Influence: Impact of British involvement and the power struggles during different dynasties.
- Impact on Stability: How political unrest affected the region’s stability and governance.
- Yakub Khan’s Abdication: Circumstances leading to Yakub Khan’s abdication and exile in British India.
- Adjustment Challenges: The challenges faced by exiled rulers in adapting to a new cultural and political environment.
- Shift in Power Dynamics: Impact of rebellion and power shifts on the political landscape.

Key Phrases:
- Great Game:
- Geopolitical Rivalry: Explanation of the geopolitical rivalry between British and Russian Empires.
- Buffer State Significance: Afghanistan’s role as a crucial buffer state during the Great Game.
- Anglo-Afghan War Context: How the war unfolded amid the larger geopolitical scenario.
- Treaty of Gandamak:
- Limited Autonomy: Understanding the terms of the treaty and its implications for Afghanistan.
- Internal Unrest: Discussion on how the treaty caused internal unrest in Afghanistan.
- Abdication of Yakub Khan: Consequences leading to Yakub Khan’s abdication.
Key data for mains answer enrichment
- Historical Roots: Dehradun’s connection with Afghanistan dates back to Ahmad Shah Durrani’s rule in 1747, shaping the city’s history and cultural influences.
- Anglo-Afghan War Impact: The Anglo-Afghan War (1838-1842) led to Dost Mohammad Khan’s exile to Dehradun, where he settled and influenced the local culture.
- Yakub Khan’s Legacy: Yakub Khan, a descendent of Dost Mohammad Khan, acquired Kabul House in Dehradun and contributed to the region’s cultural and horticultural landscape.
- Cultural Contributions: Afghan royals introduced the rubab instrument, planted fruit trees, and patronized music, leaving a lasting impact on Dehradun’s cultural heritage.
Analysis:
- Cultural Imprint: Examining the lasting cultural impact of Afghan royals on Dehradun.
- Local Practices: Influence on local practices, including music, agriculture, and hunting.
- Preservation Efforts: Highlighting the importance of preserving this cultural heritage.
- Shaping Historical Narrative: Understanding how political shifts and conflicts shaped the region’s historical narrative.
- Long-term Impact: Examining the long-term consequences of the Anglo-Afghan War on political dynamics.
- Local Identity: Discussing how historical events contribute to shaping the local identity.
Key Data:
- Construction Year of Radha Bhawan:
- 1871: Establishing Radha Bhawan’s historical significance and contribution to the region.
- Architectural Heritage: The role of Radha Bhawan as one of the earliest and expansive estates.
- Yakub Khan’s Death Year:
- 1924: Understanding the timeline of events related to Yakub Khan’s death and its impact.
Way Forward:
- Community Involvement: Involving the local community in preserving and celebrating cultural contributions.
- Heritage Awareness: Promoting awareness about the historical ties and cultural heritage in educational programs.
- Tourism Promotion: Leveraging historical awareness for cultural tourism and local pride.
- Educational Initiatives: Incorporating historical narratives into educational curricula to foster a sense of identity.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now

Central idea
Claudia Goldin’s Nobel Prize win highlights the belated acknowledgment of gender dynamics in labor markets, prompting a reevaluation of entrenched biases in economics. Feminist economists stress the imperative to dismantle androcentric biases, advocating for a more inclusive economic theory that reflects diverse experiences.
Key Terms for quality answers:
- Androcentric biases
- Economic man
- Gender inequalities
- Unpaid work
- Masculinity in economics
- Empirical findings
- Feminist economists
- Social mechanisms
Key Phrases for improving mains score:
- Androcentric Biases: Are gender-based prejudices or preferences that favor male perspectives, often manifested in economic theories that reflect traditional gender roles and reinforce a male-centric viewpoint.
- Economic Man: Is a theoretical construct representing a rational, self-interested individual in economic models. It simplifies human behavior for analytical purposes but is critiqued for its failure to capture the complexities of real-life decision-making.
- Humanizing Economics: Involves infusing empathy, emotions, and a more realistic understanding of human behavior into economic analyses, recognizing that individuals are not solely motivated by rational self-interest.
Key Highlights:
- Claudia Goldin wins Nobel Prize in Economic Sciences for gender dynamics research in labor markets.
- Recognition prompts reflection on the delayed acknowledgment of gender-focused economic research.
- Economics traditionally male-dominated, leading to the marginalization of gender inequality issues.
Challenges:
- Under-representation of women in economics.
- Androcentric biases in economic theories, perpetuating gender hierarchies.
- Economic models ignoring gendered experiences and unpaid work, especially by women.
- Limited understanding of non-market spaces like households, hindering accurate economic analysis.
- Economic man assumptions perpetuate gender stereotypes and fail to question existing hierarchies.
- Masculinity in economics detaches the discipline from gendered experiences, particularly of women.
Analysis:
- Feminist economists call for an economic theory free of androcentric biases to address gender inequalities.
- Economic models fail to account for the contributions of women as unpaid workers, impacting the accuracy of empirical findings.
- Biases in economic theory can affect statistical methods and interpretation of empirical results.
- Economic rationality may overlook social mechanisms, leading to misinterpretation of empirical findings.
Way Forward:
- Educational Initiatives: Propose educational programs to sensitize economists to gender biases and promote inclusivity.
- Policy Changes: Advocate for policy changes within academic institutions to encourage diverse perspectives in economic research.
- Recognizing Diverse Contributions: Encourage acknowledgment of the work of economists from diverse backgrounds.
- Inclusive Policies: Advocate for policies that actively promote diversity and inclusivity within economics departments.
- Training Economists: Suggest incorporating training on mixed methods in economics education.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Promote collaboration with sociologists, anthropologists, and other disciplines to enrich economic research
Conclusion:
Claudia Goldin’s Nobel Prize win serves as a catalyst for a much-needed evolution in economic thinking. By addressing historical biases, overcoming gender-based challenges, and embracing a more inclusive and nuanced approach, the discipline can truly reflect the complexities of reality.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: na
Mains level: criminal justice system

Central idea
The article highlights gender-based challenges in India’s criminal justice system, citing delays and discrimination against women complainants. Despite increased representation and specialized stations, the study in Haryana indicates persistent issues. The central idea emphasizes the need for reforms, gender sensitivity, and equal treatment within the justice system.
Key Highlights:
- Justice System Accessibility: Citizens face challenges accessing the criminal justice system in India due to police station unapproachability, court delays, and outdated forensic equipment.
- Gender Disparities: The study reveals “multi-dimensional discrimination” against women in the justice system, with differential treatment at all stages and levels.
- All-Women Police Stations: Despite efforts, the study, focused on Haryana, suggests that women face delays, dismissals, and lower conviction rates in cases where they are complainants.
- Limited Representation: While more women are joining the justice system, the study emphasizes the need for increased sensitivity and recruitment drives for female officers.
Challenges:
- Police Station Atmosphere: Unfriendly police stations, especially for women, contribute to delays and hinder justice delivery.
- Legal System Inefficiencies: Overworked prosecutors, court delays, and overcrowded prisons impact the overall efficiency of the justice system.
- Gender Bias: Discrimination against women at various stages, including delayed investigations and dismissals, poses a significant challenge.
- Recruitment Delays: Achieving the 33% reservation target for women in police stations may take another decade, delaying the improvement of gender sensitivity.
Key Phrases:
- Multi-dimensional Discrimination: The study identifies pervasive gender-based discrimination throughout the justice system.
- All-Women Police Stations: Initially created to address women’s concerns, the study questions the effectiveness of this approach.
- Delayed Investigations: Cases with women complainants experience longer waiting times and fewer registrations.
- Lower Conviction Rates: Women complainants have a lower chance of seeing the accused being sent to prison.
Analysis:
- Insufficient Gender Sensitivity: Despite efforts to increase women’s representation, the study suggests that sensitivity and fair treatment are lacking in investigations and trials.
- Systemic Inequalities: The research highlights systemic issues leading to dismissals, delays, and lower conviction rates for cases with women complainants.
- Need for Effective Monitoring: Effective monitoring systems are essential to ensure equal treatment for all genders throughout the justice process.
- Research Limitations: While the study raises crucial issues, the lack of validation from police or judicial officers in Haryana raises questions about the data’s accuracy.
Key Data for answer enrichment:
- Representation: Women constitute only around 12% of the police force, emphasizing the need for increased recruitment.
- Conviction Rate: India struggles with less than a 60% conviction rate, reflecting inefficiencies in the justice system.
- Reservation Target: Achieving the 33% reservation target for women in police stations may take another decade.
- Haryana Sample: The study focuses on Haryana, providing insights into the state-specific challenges faced by women in the justice system.
Way Forward:
- Increased Recruitment: Urgent recruitment drives are needed to enhance gender diversity in police stations and improve sensitivity.
- Efficient Justice System: Addressing inefficiencies, overhauling procedures, and providing adequate resources are essential for an accessible and fair justice system.
- Effective Monitoring: Implementing robust monitoring systems ensures consistent and unbiased treatment for all genders.
- Research Validation: Future research should involve direct interactions with police and judicial officers for accurate data validation and a comprehensive understanding of the issues.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Digital Public Infrastructure
Mains level: digital public goods in shaping international development frameworks
Central idea
India’s digital journey, marked by Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), exemplifies a commitment to inclusivity. The article underscores global collaboration, with MOSIP impacting millions, and highlights Norway’s role, advocating for the 50-in-5 campaign. It emphasizes the balance between openness and security in navigating the digital domain.
Key Highlights:
- DPI Transforming India: Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) has transformed India, providing digital identities and access to services for its vast population.
- Global Recognition and Frameworks: India’s G-20 presidency gained global recognition for DPI, setting frameworks for digital public goods and highlighting its development benefits.
- Digital Inclusion Success Stories: MOSIP, developed in Bengaluru, serves as a global blueprint, benefiting over 97 million citizens in diverse countries, showcasing achievements in digital inclusion.
- Comprehensive Development Framework: DPI is a comprehensive framework aligning with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), emphasizing development, inclusion, innovation, trust, and global competition.
Challenges:
- South-South Cooperation Dynamics: The article explores the dynamics of South-South cooperation, especially in the context of MOSIP, showcasing organic global organization.
- Financial Considerations and Privacy: Financial challenges in developing digital protocols and concerns about data privacy are highlighted as critical challenges for the future.
- Safeguarding Digital Sovereignty: Governments and businesses must navigate challenges, ensuring digital sovereignty without compromising an open, free, and secure Internet.
- Balancing Openness and Security: Balancing openness and security is crucial, emphasizing the importance of DPGA’s compass in certifying and pooling digital public goods.
Key Phrases:
- “Leaving no one behind” – Emphasizes the commitment to inclusivity and the challenge in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- “Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)” – Highlights the transformative role of DPI in providing digital identities and access to services.
- “South-South cooperation” – Signifies the collaborative efforts among countries in the global South, exemplified by MOSIP’s impact.
- “Global development architecture” – Describes the role of digital public goods in shaping international development frameworks.
Analysis:
- Global Recognition of DPI: The article analyzes India’s G-20 presidency and its impact on recognizing DPI as part of the international development architecture.
- Challenges in Digital Domain: The challenges of financial considerations, data privacy, and safeguarding digital sovereignty are critically examined.
- Norway’s Digital Contributions: The analysis delves into Norway’s contributions to the digital domain, showcasing its commitment to the 50-in-5 campaign.
- Balancing Openness and Security: The article emphasizes the need to balance openness and security, considering the complexities of the digital domain.
Key Data:
- MOSIP’s Global Reach: Over 97 million people in various countries, including Morocco, Togo, Sri Lanka, and the Philippines, have received IDs through MOSIP.
- Norwegian Digital Goods: Examples include weather services (Yr), health information systems (DHIS2), and contributions targeting SDG2 on ending food hunger.
- 50-in-5 Campaign: Norway pledges to make at least one national digital good available globally in the next five years as part of the 50-in-5 campaign.
- Digital Public Goods Alliance (DPGA): The article highlights the DPGA’s role as a registry of certified digital public goods, shaping the global digital landscape.
Key Facts:
- Digital Inclusion in India: DPI has played a pivotal role in providing digital identities to almost all of India’s 1.4 billion citizens.
- G-20 Framework for DPI: India’s achievement in getting all G-20 countries to agree to the G-20 Framework for Systems of Digital Public Infrastructure is emphasized.
- Norway’s Role in DPGA: Norway is a co-founder and member of the DPGA, contributing to the certification and pooling of digital public goods.
- Digital Goods Addressing Global Challenges: Digital goods like VIPS and DHIS2 contribute to addressing global challenges such as food insecurity and health management.
Key Terms for enriching answer quality:
- Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)
- South-South Cooperation
- MOSIP (Modular Open Source Identity Platform)
- G-20 Framework for Systems of Digital Public Infrastructure
- 50-in-5 Campaign
- Digital Public Goods Alliance (DPGA)
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The Way Forward:
- Collaborative Frameworks with India: Encouraging closer collaboration with India within DPGA frameworks is seen as a positive step for advancing global digital initiatives.
- Learning from India’s Digital Journey: Leveraging lessons from India’s digital journey is crucial for inclusive global development, offering insights into effective transformation strategies.
- Balancing Sovereignty and Collaboration: Collaborating with India within the DPGA framework requires a delicate balance, ensuring digital sovereignty while fostering successful global digital initiatives.
- Certification and Pooling for Global Good: Certification and pooling of digital public goods under DPGA’s global leadership provide a compass for future collaborations, emphasizing global cooperation for mutual benefit.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: social justice agenda
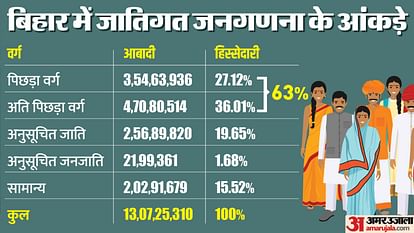
Central idea
Bihar’s caste census is a significant step, yet modernizing caste politics faces hurdles with global economic changes, an authoritative government, and assertive Hindutva ideology. To lead in this complexity, Bihar can pioneer a nuanced, coalition-based approach, reshaping caste politics for the 21st century.
Key Highlights:
- Historic Steps: Bihar takes significant strides in social justice by conducting a caste census and revealing socio-economic data associated with different castes.
- Leadership Challenge: The RJD-JD(U) coalition faces a critical juncture in utilizing caste survey data for an effective social justice agenda, beyond mere reservation expansions.
- Global Economic Situation: Neoliberal policies demand innovative approaches for mass employment (decent work).
- Authoritarian Regime: India experiences an authoritarian shift impacting constitutional norms and federal structures.
- Upper-Caste Hegemony: A visible rise of aggressive north-Indian Hindu upper-caste dominance through Hindutva ideology.
- Internal Differentiations: Complex internal variations within major caste groups challenge traditional one-dimensional caste politics.
Key Data for enhancing answer quality:
- “Formal Sector Jobs”: Despite market-friendly policies, the formal sector of the Indian economy offers less than 8% of all jobs.
- “Reservation Expansion”: Bihar Chief Minister Nitish Kumar’s announcement of expanding reservations to 65%.
- “Resistance Against Hindutva”: Bihar’s historical role in resisting Hindutva politics, along with other states like Karnataka, Kerala, and Rajasthan.
- “Erosion of Indian Federalism”: The resistance against the erosion of Indian federalism, with Bihar contributing to the assertion of State rights.
Key Terms for value addition:
- Caste Census,
- Neoliberal Policies,
- Authoritarian Regime,
- Hindutva Ideology,
- Internal Caste Differentiations,
- Portrait vs. Proxy Model,
- Evolution of Caste Politics,
- State Rights Assertion,
Challenges:
- Neoliberal Constraints: Limited formal sector jobs despite market-friendly policies pose a challenge for reducing caste inequalities.
- Authoritarian Shift: Constitutional norms, checks and balances eroded by an authoritarian regime, altering the Indian state’s shape.
- Hindutva Ideology: Overt and aggressive upper-caste dominance through Hindutva challenges secularism, creating a one-dimensional Hindu identity.
- Internal Caste Differentiations: Diverse class interests within castes require a coalitional approach, potentially leading to unpredictable consequences.
Analysis:
- Changing Caste Politics: The article highlights the need for evolving caste politics beyond automatic association with social justice, considering the complexities of the present context.
- Role of Lower Castes: Lower caste politics can counter Hindutva, even when focused on community interests, offering resistance to the dominance of upper-caste neo-elites.
- State Rights Assertion: Bihar’s resistance against Hindutva and the act of conducting a caste census assert State rights, contributing to the fight against the erosion of Indian federalism.
- Portrait vs. Proxy Model: The caste survey raises questions about representation—whether elected representatives should resemble the population (portrait model) or act on their behalf (proxy model).
The Way Forward:
- Innovative Social Justice: Bihar has the opportunity to pioneer a new form of caste politics, adapting to the present context, breaking from past habits while upholding the core of the social justice agenda.
- Political Representation: The article questions the idea that sharing the same identity is sufficient for representation, emphasizing the need for effective action on behalf of the represented.
- Balancing Identities: Despite the census favoring larger numbers, Bihar can demonstrate that shared identity is a necessary but not sufficient condition for political representation.
- Championing Federalism: Bihar, along with other states, can lead the resistance against the erosion of Indian federalism, emphasizing the importance of locally-relevant policies.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: counter-terrorism strategy

Central idea
The article explores India’s strategic decision-making in response to terrorism, highlighting the delicate nature of counter-terrorism efforts, the economic consequences of potential military actions, and the significance of thoughtful strategies in shaping international relations. It emphasizes the importance of strategic wisdom over impulsive actions, showcasing India’s nuanced approach to navigating complex geopolitical challenges.
Thomas Friedman’s Praise:
- Columnist’s Perspective: Thomas Friedman commends former PM Manmohan Singh for exercising notable restraint in a recent column.
- Outrage on Social Media: The article triggers heated debates on social platforms, with users expressing strong opinions on India’s past actions.
- Criticizing Past Inaction: Some perceive India’s historical restraint, post-Mumbai attacks, as an act of cowardice, sparking passionate discussions.
Understanding the Context:
- Social Media Dynamics: Vibrant discussions on the Israel-Hamas conflict unfold on social media platforms, reflecting global interest.
- Traumatic Memory: India’s emotional connection to the conflict emerges from the haunting memories of the 2008 Mumbai attacks.
- Opinion Amplification: Thomas Friedman’s praise triggers intense reactions, amplifying opinions on India’s historical decisions.
- National Pride: The ongoing discourse is influenced by national pride, especially in the context of India’s military actions, like the Balakot airstrikes.
Navigating Counter-Terrorism Challenges:
- Delicate Counter-Terrorism: The article underscores the need for nuanced counter-terrorism strategies, cautioning against impulsive actions.
- Hypothetical Scenario: Imagining India’s response post-26/11 prompts consideration of potential nuclear risks and their implications.
- Global Economic Impact: The hypothetical bombing scenario in Pakistan during a global financial crisis raises concerns about broader economic consequences.
- War Consequences: Evaluating the economic aftermath if Pakistan faced aggressive military action underscores the potential disastrous outcomes.
Strategic Thinking and Framing Issues:
- Strategic Counter-Terrorism: Emphasizing the importance of well-thought-out counter-terrorism strategies for effective outcomes.
- International Response: Crafting responses to terrorism globally requires strategic thinking aligned with prevailing economic conditions.
- Alignment with ‘War on Terror’: The consequences of aligning with the global ‘war on terror’ shape international relations and diplomatic considerations.
- Responses Based on Global Conditions: Shaping actions based on economic circumstances highlights the strategic importance of thoughtful decision-making.
Data, Facts, and Economic Consequences:
- Market Crash: The impact of the global financial crisis on India’s stock market and the potential economic fallout from a war.
- Increased U.S. Aid: Rise in U.S. military aid to Pakistan during the ‘war on terror’ and its effects on geopolitical dynamics.
- Pakistan’s Economic Fallout: Examining Pakistan’s economic decline post-2008-09, indicating repercussions of global narratives.
- Investment Decline: The substantial drop in Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan and its significant implications for the nation’s economy.
Emphasizing Key Phrases:
- Delicate Counter-Terrorism Actions: Stressing the importance of sensitive responses in counter-terrorism efforts, emphasizing caution and precision.
- Strategic International Response: Highlighting the significance of thoughtful and planned approaches on the global stage for impactful outcomes.
- Strength in Deliberation: Recognizing the power and effectiveness in well-thought-out actions and decisions for lasting impacts.
Analysis and International Relations:
- Narrative Shift: Changing perceptions of Pakistan as America’s most dangerous ally and the consequential shifts in global narratives.
- Praise for Responsibility: Recognition of India as a responsible nuclear power with global consequences, influencing diplomatic relations.
- Operationalizing Agreements: Timing of the India-U.S. Civil Nuclear agreement and its significance in shaping geopolitical dynamics.
- Economic Consequences: Analyzing the impact on Pakistan’s economic fortunes and India’s sustained growth in the long term.
The Way Forward:
- Importance of Strategy: Emphasizing the critical role of a thoughtful counter-terrorism strategy for effectively addressing future challenges.
- Diplomacy in Action: Acknowledging the instrumental role of diplomatic responses in shaping international outcomes and fostering stability.
- Air Strikes Significance: Recognizing the strategic significance of well-executed airstrikes as a crucial element in diplomatic and military strategies.
- Avoiding ‘Boots on the Ground’: Underlining the strategic approach of avoiding ground invasions, emphasizing the importance of wit and strategic maneuvering in conflict resolution.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now






)