Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Commission for Women (NCW): Powers and Functions
Mains level: NA
What is the news-
NCW-RPF MoU: Key Objectives
- Prevention and Rescue: The MoU aims to prevent human trafficking and facilitate the rescue of trafficked women through joint efforts.
- Role of RPF Personnel: RPF personnel stationed at railway stations are crucial in preventing trafficking and addressing crimes against women.
- Expanding Collaboration: NCW, which established an Anti-Human Trafficking Cell on April 2, 2022, has already been working with the Central Industrial Security Force (CISF) to combat the trafficking of women.
|
About National Commission for Women (NCW)
- The NCW is the Statutory Body generally concerned with advising the government on all policy matters affecting women.
- It was established on 31 January 1992 under the provisions of the Indian Constitution as defined in the National Commission for Women Act, 1990.
- The first head of the commission was Jayanti Patnaik.
- The Indian Constitution doesn’t contain any provision specifically made to favor women intrinsically.
- Article 15 (3), Article 14 and Article 21 protect and safeguard women. They are more gender-neutral.
Objectives
- The objective of the NCW is to represent the rights of women in India and to provide a voice for their issues and concerns.
- The subjects of their campaigns have included dowry, politics, religion, equal representation for women in jobs, and the exploitation of women for labor.
- They have also discussed police abuses against women.
Composition of the NCW
The Commission shall consist of:
- Chairperson: To be nominated by the Central Government.
- Five Members: To be nominated by the Central Government from amongst persons of ability, integrity and standing who have had experience in law or legislation, trade unionism, management of an industry potential of women, women’s voluntary organizations (including women activists), administration, economic development, health, education or social welfare;
- Special Representations: At least one Member each shall be from amongst persons belonging to the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes respectively;
Powers of NCW
- Provide consultation on all major policy matters that affect women.
- Issuing summons for the examination of documents and the witnesses.
- Requisitioning any public record or copy thereof from any court or office.
- Receiving evidence on affidavits
- Discovery and production of documents
- Summoning and enforcement
Functions of the NCW
- Submission of Annual Reports: Table reports should be submitted to the Central Government every year, when deemed appropriate by the commission. These reports focus on the functioning and working of the safeguards.
- Investigation and Examination: Proper investigation and examination are conducted under the Constitution and other laws, primarily aimed at protecting the rights of women.
- Review and Scrutiny of Laws: Constant review and scrutiny of all laws are undertaken, with necessary amendments and alterations made to meet the needs of the current world.
- Prevention of Violations: Ensuring there is no violation against women and taking due care of such cases to protect their rights.
- Handling Complaints and Suo Motu Matters: Handling complaints and addressing suo motu matters about the deprivation of rights of women, with a focus on implementing laws favoring women’s welfare.
- Assessment of Development and Progress: Assessing the development and progress of the women community at both the Center and State levels.
- Identification and Mitigation of Systemic Limitations: Understanding the limitations in the system and devising strategic plans and mechanisms to address them effectively.
Issues faced by NCW
- Limited Enforcement Power: The NCW is only recommendatory and lacks the power to enforce its decisions, often taking action only when issues are brought to light.
- Lack of Constitutional Status: The Commission lacks constitutional status, resulting in no legal powers to summon police officers or witnesses.
- Dependency on Grants: NCW’s functions are heavily dependent on grants offered by the central government, with insufficient financial assistance to cater to its needs.
- Limited Autonomy in Member Selection: The Commission does not have the power to choose its own members, impacting its autonomy and effectiveness.
PYQ:
Q.Is the National Commission for Women able to strategize and tackle the problems that women face at both public and private spheres? Give reasons in support of your answer. (2017)
Q.According to the Constitution of India, it is the duty of the President of India to cause to be laid before the Parliament which of the following?
- The Recommendations of the Union Finance Commission
- The Report of the Public Accounts Committee
- The Report of the Comptroller and Auditor General
- The Report of the National Commission for the Scheduled Castes
Select the correct answer the using the codes given below:
- 1 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Practice MCQ:
Which of the following does not constitute to the powers of National Commission for Women (NCW)?
- Issuing summons
- To make any record public
- Receiving evidence on affidavits
- Enforcing legal action against individuals
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA)
Mains level: NA
In the news
- The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister, has approved the establishment of the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) with headquarters in India.
About the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA)
- Objective: The IBCA aims to spearhead efforts towards the protection and conservation of the 7 major big cats: tiger, lion, leopard, snow leopard, puma, jaguar, and cheetah.
- Funding: The Government of India has pledged an initial support of Rs. 150 crore for the first five years. Additionally, the alliance will explore contributions from bilateral and multilateral agencies, financial institutions, and donor agencies to augment its corpus.
- Membership: Membership to the alliance will be open to 96 “range” countries, which are nations containing the natural habitat of the seven big cats.
- Activities: The alliance’s activities will include advocacy, partnership building, knowledge dissemination through an e-portal, capacity building, eco-tourism promotion, and financial resource mobilization.
Governance Structure
- Composition: The governance structure of IBCA includes a General Assembly comprising all member countries, a Council of elected member countries, and a Secretariat.
- Appointment: The General Assembly appoints the Secretary General of IBCA upon the recommendation of the Council.
- Framework: The alliance’s governance framework, drafted on the lines of the International Solar Alliance (ISA), will be finalised by the International Steering Committee (ISC).
India’s Role in Big Cat Conservation
- Big Cat Diversity: India is home to five of the seven major big cats: tiger, lion, leopard, snow leopard, and cheetah.
- Conservation Efforts: India has undertaken significant conservation efforts, as reflected in the increase in tiger and lion populations. For instance, India now hosts about 70% of the world’s tiger population, and the Asiatic lion population in Gir National Park has shown steady growth.
- Cheetah Reintroduction: Cheetahs, once extinct in India since 1952, have been reintroduced into the wild. Eight cheetahs were imported from Namibia and released into the Kuno National Park in Madhya Pradesh in November 2022.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Sangam: Digital Twin Initiative
Mains level: Digital Twin Technology

Introduction
- Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has introduced the ‘Sangam: Digital Twin’ initiative, inviting Expressions of Interest (EoI) from industry pioneers, startups, MSMEs, academia, innovators, and forward-thinkers.
What is Digital Twin Technology?
- A digital twin is a digital representation of a physical object, person, or process, contextualized in a digital version of its environment.
- Digital twins can help an organization simulate real situations and their outcomes, ultimately allowing it to make better decisions.
About Sangam: Digital Twin Initiative
- Context: The initiative aligns with the technological advancements of the past decade in communication, computation, and sensing, in line with the vision for 2047.
- Proof of Concept (PoC) in Two Stages: The initiative will be distributed in two stages, conducted in one of India’s major cities.
- First Stage: An exploratory phase focusing on clarifying horizons and creative exploration to unleash potential.
- Second Stage: A practical demonstration of specific use cases, generating a future blueprint for collaboration and scaling successful strategies in future infrastructure projects.
- Objectives:
- Demonstrate practical implementation of innovative infrastructure planning solutions.
- Develop a model framework for facilitating faster and more effective collaboration.
- Provide a future blueprint for scaling and replicating successful strategies in future infrastructure projects.
Features
- Sangam: Digital Twin represents a collaborative leap towards reshaping infrastructure planning and design.
- It integrates 5G, IoT, AI, AR/VR, AI native 6G, Digital Twin, and next-gen computational technologies, fostering collaboration among public entities, infrastructure planners, tech giants, startups, and academia.
- Sangam brings all stakeholders together, aiming to translate innovative ideas into tangible solutions, bridging the gap between conceptualization and realization, and paving the way for groundbreaking infrastructure advancements.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: GPAI
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- The Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit began in New Delhi on December 12, inaugurated by Prime Minister.
- India, along with 28 member countries, is working towards a consensus on a declaration document focusing on the proper use of AI, establishing guardrails for the technology, and its democratization.
GPAI and India
- Founding Member: India joined GPAI as a founding member in June 2020, aiming to bridge the gap between AI theory and practice.
- International Collaboration: The initiative fosters collaboration among scientists, industry professionals, civil society, governments, international organizations, and academia.
- Previous Summits: Prior GPAI summits were held in Montreal, Paris, and Tokyo.
- India’s Stance: IT Minister highlighted India’s focus on sustainable agriculture and collaborative AI, building on the Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) approach used in Aadhaar and UPI systems.
Content of the Proposed Declaration
- Themes and Focus: The declaration is expected to cover AI’s use in sustainable agriculture, healthcare, climate action, and building resilient societies.
- Regulatory Aspects: It will align with past agreements and global ideas on AI regulation.
- India’s Contribution: India’s emphasis is on evaluating AI in sustainable agriculture and promoting collaborative AI.
Global Conversation on AI Regulation
- EU’s AI Act: The European Union passed the AI Act, introducing safeguards and guardrails for AI use, especially in law enforcement, and setting up mechanisms for complaints against violations. It imposes strong restrictions on facial recognition and AI’s potential to manipulate human behavior.
- AI Safety Summit in the UK: Major countries agreed on a declaration for global action to address AI risks, acknowledging the dangers of misuse, cybersecurity threats, biotechnology, and disinformation risks.
- US Executive Order: The Biden Administration issued an order to safeguard against AI threats and oversee safety benchmarks for generative AI bots like ChatGPT and Google Bard.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- The inclusion of the Sanskrit term “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam” (The world is one family) in the G-20 logo has sparked diplomatic discussions between India and China.
- Reports surfaced suggesting that China objected to the use of non-UN languages like Sanskrit in G-20 texts being negotiated.
Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam
- The ancient Sanskrit phrase “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam” encapsulates the idea of the world as one interconnected family.
- Rooted in religious texts, this concept reverberates through history and has found resonance in modern times, impacting diplomatic exchanges and global events.
अयं निजः परो वेति गणना लघुचेतसाम्।
उदारचरितानां तु वसुधैव कुटुम्बकम्॥
Meaning: Considerations like “he is mine or he is another’s” occur only to the narrow minded person. To the broad-minded person the whole world is a family.
Origin and Meaning:
- Sanskrit Phrase: “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam” is composed of three words: Vasudha (Earth), Eva (Thus), and Kutumbakam (Family).
- Moral Value: It is considered a profound moral value, reflecting interconnectedness and universal harmony.
Historical Context:
- Maha Upanishad Verse: The original verse appears in Maha Upanishad stressing unity among all beings and the world.
- Engraved Symbolism: The verse is inscribed in the entrance hall of the Parliament of India, reflecting its importance in Indian society.
- Embrace of Unity: The verse advocates embracing the world as a family, urging magnanimity and detachment.
Interpretations and Influences
- Spiritual Progress: Subsequent shlokas expand on the idea, stating that detachment leads to attaining the Brahman (Universal Spirit).
- Influence in Hindu Literature: The Bhagavad Gita refers to “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam” as the “Loftiest Vedantic Thought,” demonstrating its influence in Hindu philosophy.
- Gandhian Connection: Dr. N. Radhakrishnan relates the concept to Gandhi’s holistic development vision and nonviolent conflict resolution.
Modern Relevance
- PM’s Reference: Prime Minister Modi invoked the phrase, highlighting its values of unity and cultural richness.
- International Earth Science Olympiad: The phrase was used in the logo of the 7th International Earth Science Olympiad, emphasizing Earth’s interconnected systems.
- India’s G20 Presidency: The theme and logo of India’s G20 Presidency included “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam,” representing global unity.
Diplomatic Controversy
- China’s Opposition: China objected to the use of Sanskrit in G20 documents, asserting that it’s not an official UN language.
- Logo Exclusion: Despite its significance, the phrase did not appear in official G20 documents due to China’s objections.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Multidimensional Poverty Index, 2023
Mains level: Not Much
Central Idea
- NITI Aayog released the report ‘National Multidimensional Poverty Index: A Progress Review 2023’.
- The report highlighted a record 13.5 crore people have moved out of multidimensional poverty in India between 2015-16 and 2019-21.
What is National Multidimensional Poverty Index (NMPI)?
- NITI Aayog serves as the nodal ministry for the MPI.
- It engages with publishing agencies such as Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative (OPHI) and the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
- It uses the Alkire-Foster (AF) methodology.
- The Baseline Report of MPI is based on the National Family Health Survey (NFHS) 4 conducted during 2015-16.
Indicators used
- The MPI considers three dimensions: health, education, and standard of living.
- It includes indicators such as nutrition, child and adolescent mortality, maternal care, years of schooling, school attendance, cooking fuel, sanitation, drinking water, electricity, housing, bank accounts, and assets.
Key findings of the report
- Decline in Poverty: India has witnessed a substantial decline in multidimensional poverty, with a decrease of 9.89 percentage points from 24.85% in 2015-16 to 14.96% in 2019-21.
- Progressiveness in rural areas: Rural areas experienced the fastest decline, from 32.59% to 19.28%, while urban areas saw a reduction from 8.65% to 5.27%.
- Regional Progress: UP recorded the largest decline in the number of poor, with 3.43 crore people escaping multidimensional poverty. The states of UP, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, and Rajasthan showed the fastest reduction in the proportion of multidimensional poor.
- Path towards SDG Targets: The report indicates that India is on track to achieve SDG Target 1.2, which aims to reduce multidimensional poverty by at least half by 2030.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: VAIBHAV Program
Mains level: Various initiatives for Indian Diaspora

Central Idea: The Ministry of Science & Technology has launched the Vaishvik Bhartiya Vaigyanik (VAIBHAV) fellowships programme.
VAIBHAV Program
- The program aims to connect the Indian STEMM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics, and Medicine) diaspora with Indian academic and R&D institutions.
- It promotes collaborative research work, knowledge sharing, and the exchange of best practices in frontier areas of science and technology.
Implementation and Eligibility
- Implementing Agency: Department of Science and Technology (DST), Ministry of Science and Technology.
- Beneficiaries: outstanding scientists/technologists of Indian origin (NRI/OCI/PIO) engaged in research activities in their respective countries.
- Benefits: Grant of INR 4,00,000 per month, international and domestic travel expenses, accommodation, and contingencies
- Verticals identified: 75 fellows will be selected to work in 18 identified knowledge verticals, including quantum technology, health, pharma, electronics, agriculture, energy, computer sciences, and material sciences.
- Collaborations: The VAIBHAV Fellow will collaborate with Indian Higher Educational Institutions (HEIs), universities, and/or public-funded scientific institutions.
- R&D Activity: The fellow can spend up to 2 months per year, for a maximum of 3years, in an Indian institution.
VAIBHAV Summit and Participation
- The Government of India organized the VAIBHAV Summit to connect the Indian STEMM diaspora with Indian institutions.
- The summit was inaugurated by the Hon’ble Prime Minister and saw the participation of over 25,000 attendees.
- Indian STEMM diaspora from more than 70 countries took part in the deliberations.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Price Support Scheme (PSS)
Mains level: Read the attached story
Central Idea
- Procurement Ceilings for Pulses: The government has removed the procurement ceilings of 40% for tur, urad, and masur under the Price Support Scheme (PSS) operations for 2023-24.
What is Price Support Scheme (PSS)?
- Physical procurement: The Price Support Scheme (PSS) involves the physical procurement of pulses, oilseeds, and copra by Central Nodal Agencies.
- Nodal Agencies: The National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation of India (NAFED) and the Food Corporation of India (FCI) are the designated agencies responsible for procuring crops under the PSS.
- Implementation: The scheme is implemented in collaboration with state governments, who exempt the procured commodities from mandi tax and provide logistical support, including gunny bags and working capital.
Need for such scheme
- Balancing farmer and consumer interests: The PSS strikes a balance between the welfare of farmers and consumers, ensuring fair returns for farmers and affordable prices for consumers.
- Remunerative prices: The primary objectives of the PSS are to provide remunerative prices to farmers, encouraging increased investment and production, while ensuring affordable prices and availability for consumers.
- Encouraging production: By offering a guaranteed price, the PSS incentivizes farmers to invest in agricultural production, leading to increased output and self-sufficiency.
- Consumer welfare: The scheme aims to protect the interests of consumers by ensuring a stable supply of essential commodities at reasonable prices, reducing intermediation costs.
- Market intervention: The PSS acts as a market intervention measure, stabilizing prices, and mitigating the risks faced by farmers due to market fluctuations and unforeseen circumstances.
- Support for agricultural growth: The scheme is part of the government’s broader efforts to support agricultural growth, enhance farmer income, and promote food security in the country.
Why in news?
- Notified Essential commodities: On June 2, 2023, the government imposed stock limits on tur and urad by invoking the Essential Commodities Act, 1955.
- Prevent hoarding: The imposition aims to prevent hoarding and unscrupulous speculation, as well as improve affordability for consumers.
- Applicability and declaration: Stock limits are applicable to wholesalers, retailers, big chain retailers, millers, and importers, who are required to declare their stock position on the portal of the Department of Consumer Affairs.
Enforcement of Stock Limits by State Governments:
- Directives to state governments: The Department of Consumer Affairs has directed state governments to ensure strict enforcement of the stock limits in their respective states.
- Monitoring and verification: States have been asked to monitor prices and verify the stock position by coordinating with various warehouse operators.
- Cooperation from warehousing corporations: Central Warehousing Corporation (CWC) and State Warehousing Corporations (SWCs) have been requested to provide details of tur and urad stocks held in their warehouses.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NIXI
Mains level: Not Much
Two new Internet Exchange points (IXP) of NIXI were inaugurated at Durgapur and Bardhman.
What is NIXI?
- NIXI is a not for profit Organization under section 8 of the Companies Act 2013 and was registered on 19th June 2003.
- It’s an initiative under Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) vision 1000 days.
- It aims for spreading the internet infrastructure to the citizens of India through the following activities:
- Internet Exchanges through which the internet data is exchanged amongst Internet Service Protocols (ISPs), Data Centers and CDNs.
- .IN Registry, managing and operation of .IN country-code domain and .भारत IDN domain for India.
- Indian Registry for Internet Names and Numbers (IRINN), managing and operating Internet protocol (IPv4/IPv6).
Why NIXI?
- NIXI was set up for peering of Internet Service Protocols (ISPs) among themselves for the purpose of routing the domestic traffic within the country, instead of taking it all the way to US/Abroad.
- It is thereby resulting in better quality of service (reduced latency) and reduced bandwidth charges for ISPs by saving on International Bandwidth.
- NIXI is managed and operated on a Neutral basis, in line with the best practices for such initiatives globally.
Utility of NIXI
- The launch of these new NIXI internet exchanges will contribute to the enhancement and improvement of Internet and Broadband services at local level and in neighbouring regions.
- The internet service providers connecting at these points will benefit as their broadband services to their end users will improve, bringing about a change in the lives of the people of the region.
- It will benefit every sector of the state ranging from health, education, agriculture, startup, and ecosystem to MSMEs & other business verticals.
- Accessibility and convenience will increase for citizens in terms of availing government benefits and improving quality of life.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: IS 17693: 2022
Mains level: NA
Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), the National Standards Body of India, has developed an Indian Standard, IS 17693: 2022 for ‘non-electric cooling cabinet made of clay’.
IS 17693: 2022
- BIS standard specifies the construction and performance requirements of a cooling cabinet made out of clay, which operates on the principle of evaporative cooling.
- These cabinets may be used to store perishable foodstuff without the need of electricity.
- This standard helps BIS in fulfilling 6 out of 17 UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) like No poverty, Zero hunger, Gender equality, Affordable and clean energy, Industry, innovation, and infrastructure, and Responsible consumption and production.
Why such move?
- Named as ‘Mitticool refrigerator’, Mansukh Bhai Prajapati from Gujarat is the innovator behind the refrigerator which projects an eco-friendly technology.
- It is a natural refrigerator made primarily from clay to store vegetables, fruits, milk, and also for cooling water.
- It provides natural coolness to foodstuffs stored in it without requiring any electricity.
- Fruits, vegetables, and milk can be stored reasonably fresh without deteriorating their quality.
Back2Basics: Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS)
- BIS is the National Standards Body of India working under the aegis of the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution.
- It is established by the Bureau of Indian Standards Act, 1986 which came into effect on 23 December 1986.
- The organization was formerly the Indian Standards Institution (ISI), set up under the Resolution of the Department of Industries and Supplies in September 1946.
- The ISI was registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- A new Bureau of Indian standard (BIS) Act 2016 has been brought into force with effect from 12 October 2017.
- The Act establishes the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) as the National Standards Body of India.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Param Ananta Supercomputer
Mains level: National Supercomputing Mission
Param Ananta, a state-of the art Supercomputer was commissioned at IIT Gandhinagar.
Param Ananta
- Param Ananta is capable of offering peak performance of 838 teraflops.
- It is a joint initiative of Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) and Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- This facility is established under Phase 2 of the National Supercomputing Mission (NSM).
- The system is equipped with a mix of CPU nodes, GPU nodes, High Memory nodes, High throughput storage and high performance Infiniband.
- The supercomputer will rank behind C-DAC’s Param Siddhi-AI, which as of November 2021 was the 102nd most powerful supercomputer in the world — with peak performance capability of 3.3 petaflops.
What is a Supercomputer?
- A supercomputer is a computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer.
- The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) instead of million instructions per second (MIPS).
- Since 2017, there are supercomputers which can perform over a hundred quadrillion FLOPS (peta FLOPS).
- Since November 2017, all of the world’s fastest 500 supercomputers run Linux-based operating systems.
Specific features
- Param Ananta system is based on Direct Contact Liquid Cooling technology to obtain a high power usage effectiveness and thereby reducing the operational cost.
- Multiple applications from various scientific domains such as Weather and Climate, Bioinformatics, Computational Chemistry, Molecular Dynamics, Material Sciences, Computational Fluid Dynamics etc. have been installed on the system for the benefit of researchers.
- This high end computing system will be a great value addition for the research community.
Back2Basics: National Supercomputing Mission (NSM)
- NSM is a proposed plan by GoI to create a cluster of seventy supercomputers connecting various academic and research institutions across India.
- In April 2015 the government approved the NSM with a total outlay of Rs.4500 crore for a period of 7 years.
- The mission was set up to provide the country with supercomputing infrastructure to meet the increasing computational demands of academia, researchers, MSMEs, and startups by creating the capability design, manufacturing, of supercomputers indigenously in India.
- Currently there are four supercomputers from India in Top 500 list of supercomputers in the world.
Aims and objectives
- The target of the mission was set to establish a network of supercomputers ranging from a few Tera Flops (TF) to Hundreds of Tera Flops (TF) and three systems with greater than or equal to 3 Peta Flops (PF) in academic and research institutions of National importance across the country by 2022.
- This network of Supercomputers envisaging a total of 15-20 PF was approved in 2015 and was later revised to a total of 45 PF (45000 TFs), a jump of 6 times more compute power within the same cost and capable of solving large and complex computational problems.
When did India initiate its efforts to build supercomputers?
- India’s supercomputer program was initiated in the late 1980s, when the United States ceased the export of a Cray Supercomputer due to technology embargos.
- This resulted in India setting up C-DAC in 1988, which in 1991, unveiled the prototype of PARAM 800, benchmarked at 5 Gflops. This supercomputer was the second-fastest in the world at that time.
- Since June 2018, the USA’s Summit is the fastest supercomputer in the world, taking away this position from China.
- As of January 2018, Pratyush and Mihir are the fastest supercomputers in India with a maximum speed of Peta Flops.
What are the phases of the National Supercomputing Mission?
Phase I:
- In the first phase of the NSM, parts of the supercomputers are imported and assembled in India.
- A total of 6 supercomputers are to be installed in this phase.
- The first supercomputer that was assembled indigenously is called Param Shivay. It was installed in IIT (BHU) located in Varanasi.
- Similar systems, Param Shakti (IIT Kharagpur) and Param Brahma (IISER, Pune) were also later installed within the country.
- The rest will be installed at IIT Kanpur, IIT Hyderabad and Jawaharlal Nehru Institute of Advanced Studies (JNIAS).
Phase II:
- The supercomputers that are installed so far are about 60% indigenous.
- The 11 systems that are going to be installed in the next phase will have processors designed by the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) and will have a cumulative capacity of 10 petaflops.
- These new systems are to be constructed more cost-effectively than the previous ones.
- One of the 11 proposed supercomputers will be installed
- at C-DAC exclusively for small and medium enterprises so that they can train employees as well as work on supercomputers at a very low cost.
Phase III:
- The third phase aims to build fully indigenous supercomputers.
- The government had also approved a project to develop a cryogenic cooling system that rapidly dispels the heat generated by a computing chip. This will be jointly built together by IIT-Bombay and C-DAC.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Open Access Registry (NOAR)
Mains level: Not Much
National Open Access Registry (NOAR) has successfully gone live from 1st May 2022.
What is NOAR?
- NOAR is a centralized online platform through which the short-term open access to the inter-state transmission system is being managed in India.
- It is an integrated platform accessible to all stakeholders in the power sector, including open access customers (both sellers and buyers), power traders, power exchanges, National/Regional/State LDCs and others.
- The platform provides automation in the workflow to achieve shorter turnaround time for the transactions.
- NOAR platform also has a payment gateway integrated for making payments related to interstate short-term open access transactions.
- NOAR platform provides transparency and seamless flow of information among stakeholders of open access.
Key features
- Centralized System: Single point electronic platform for all the stakeholders
- Automated Process: Automated administration process of the short-term open access
- Common Interface: Interface with the RLDCs scheduling applications and Power Exchanges (s)
- Payment Gateway: Make payments related to STOA transactions
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Param Ganga, Petaflops
Mains level: National Supercomputing Mission

The National Supercomputing Mission (NSM) has now deployed “PARAM Ganga”, a supercomputer at IIT Roorkee, with a supercomputing capacity of 1.66 Petaflops.
What is a Supercomputer?
- A supercomputer is a computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer.
- The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) instead of million instructions per second (MIPS).
- Since 2017, there are supercomputers which can perform over a hundred quadrillion FLOPS (peta FLOPS).
- Since November 2017, all of the world’s fastest 500 supercomputers run Linux-based operating systems.
PARAM Ganga
- PARAM Ganga is designed and commissioned by C-DAC under Phase 2 of the build approach of the NSM.
- It is based on a heterogeneous and hybrid configuration of Intel Xeon Cascade lake processors, and NVIDIA Tesla V100.
- There are 312 (CPU+GPU+HM) nodes with a total peak computing capacity of 1.67 (CPU+GPU+HM) PFLOPS performance.
- The cluster consists of compute nodes connected with the Mellanox (HDR) InfiniBand interconnect network.
- The system uses the Lustre parallel file system and operating system is CentOS 7.x.
Back2Basics: National Supercomputing Mission (NSM)
- NSM is a proposed plan by GoI to create a cluster of seventy supercomputers connecting various academic and research institutions across India.
- In April 2015 the government approved the NSM with a total outlay of Rs.4500 crore for a period of 7 years.
- The mission was set up to provide the country with supercomputing infrastructure to meet the increasing computational demands of academia, researchers, MSMEs, and startups by creating the capability design, manufacturing, of supercomputers indigenously in India.
- Currently there are four supercomputers from India in Top 500 list of supercomputers in the world.
Aims and objectives
- The target of the mission was set to establish a network of supercomputers ranging from a few Tera Flops (TF) to Hundreds of Tera Flops (TF) and three systems with greater than or equal to 3 Peta Flops (PF) in academic and research institutions of National importance across the country by 2022.
- This network of Supercomputers envisaging a total of 15-20 PF was approved in 2015 and was later revised to a total of 45 PF (45000 TFs), a jump of 6 times more compute power within the same cost and capable of solving large and complex computational problems.
When did India initiate its efforts to build supercomputers?
- India’s supercomputer program was initiated in the late 1980s, when the United States ceased the export of a Cray Supercomputer due to technology embargos.
- This resulted in India setting up C-DAC in 1988, which in 1991, unveiled the prototype of PARAM 800, benchmarked at 5 Gflops. This supercomputer was the second-fastest in the world at that time.
- Since June 2018, the USA’s Summit is the fastest supercomputer in the world, taking away this position from China.
- As of January 2018, Pratyush and Mihir are the fastest supercomputers in India with a maximum speed of Peta Flops.
What are the phases of the National Supercomputing Mission?
Phase I:
- In the first phase of the NSM, parts of the supercomputers are imported and assembled in India.
- A total of 6 supercomputers are to be installed in this phase.
- The first supercomputer that was assembled indigenously is called Param Shivay. It was installed in IIT (BHU) located in Varanasi.
- Similar systems, Param Shakti (IIT Kharagpur) and Param Brahma (IISER, Pune) were also later installed within the country.
- The rest will be installed at IIT Kanpur, IIT Hyderabad and Jawaharlal Nehru Institute of Advanced Studies (JNIAS).
Phase II:
- The supercomputers that are installed so far are about 60% indigenous.
- The 11 systems that are going to be installed in the next phase will have processors designed by the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) and will have a cumulative capacity of 10 petaflops.
- These new systems are to be constructed more cost-effectively than the previous ones.
- One of the 11 proposed supercomputers will be installed
- at C-DAC exclusively for small and medium enterprises so that they can train employees as well as work on supercomputers at a very low cost.
Phase III:
- The third phase aims to build fully indigenous supercomputers.
- The government had also approved a project to develop a cryogenic cooling system that rapidly dispels the heat generated by a computing chip. This will be jointly built together by IIT-Bombay and C-DAC.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP)
Mains level: NA
National Logistics Portal (NLP) is set to be integrated with Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP) to make the multi-modal logistics ecosystem more efficient.
Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP)
- ULIP is designed to enhance efficiency and reduce the cost of logistics in India by creating a transparent, one window platform that can provide real-time information to all stakeholders.
- It was also emphasized that the solution should have the visibility of multi-modal transport, and all the existing systems of various ministries, governing bodies, and private stakeholders should be integrated with the ULIP system.
- This will create a National Single Window Logistics Portal which will help in reducing the logistics cost.
- ULIP will provide real-time monitoring of cargo movement while ensuring data confidentiality with end-to-end encryption, comprehensive reduction in logistic cost resulting in competitive costing.
There are three key components which are defining the ULIP platform:
- Integration with existing data sources of ministries: As authorization, compliance and clearance are some of the critical activities of Logistics; the integration with data points of ministries shall enable a holistic view and interlink the handshaking points.
- Data exchange with private players: To enable the private players, logistics service providers, and industries to utilize the data available with ULIP and at the same time share their data (transportation, dispatch, delivery, etc.) with ULIP, thereby streamlining the processes to bring better efficiency through data exchange.
- Unified document reference in the supply chain: To enable a single digitized document reference number for all the documentation processes in a single platform.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: QKD
Mains level: Secured Communications, QKD
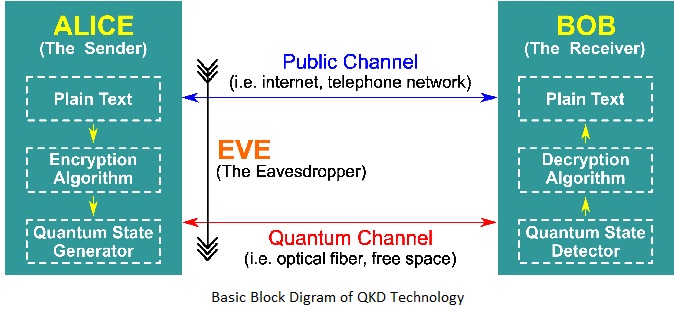
A joint team of scientists from DRDO and IIT Delhi, for the first time in the country successfully demonstrated Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) link between Prayagraj and Vindhyachal in Uttar Pradesh, a distance of more than 100 kilometers.
What is QKD Technology?
- Quantum key distribution (QKD) is a secure communication method that implements a cryptographic protocol involving components of quantum mechanics.
- It enables two parties to produce a shared random secret key known only to them, which can then be used to encrypt and decrypt messages.
- It gives the ability of the two communicating users to detect the presence of any third party trying to gain knowledge of the key.
- This is a result of a fundamental aspect of quantum mechanics: the process of measuring a quantum system, in general, disturbs the system.
- By using quantum superposition or quantum entanglement and transmitting information in quantum states, a communication system can be implemented that detects data leak.
How does it work?
- QKD works by transmitting many light particles, or photons, over fiber optic cables between parties.
- Each photon has a random quantum state, and collectively, the photons sent make up a stream of ones and zeros.
- This stream of quantum states that make up ones and zeros are called qubits — the equivalent of bits in a binary system.
- When a photon reaches its receiving end, it will travel through a beam splitter, which forces the photon to randomly take one path or another into a photon collector.
- The receiver will then respond to the original sender with data regarding the sequence of the photons sent, and the sender will then compare that with the emitter, which would have sent each photon.
Benefits offered
- It allows the detection of data leak or hacking because it can detect any such attempt.
- It also allows the process of setting the error level between the intercepted data in dependence.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: REWARD Program
Mains level: Not Much
The GoI, the State Governments of Karnataka and Odisha, and the World Bank have signed a $115 million for the REWARD Project.
What is REWARD Program?
- REWARD stands for Rejuvenating Watersheds for Agricultural Resilience through Innovative Development.
- The project aims to help national and state institutions adopt improved watershed management practices to help increase farmers’ resilience to climate change, promote higher productivity and better incomes.
- REWARD is being implemented in three to four Indian States.
- It is proposed as a 6 years Project.
Objectives of the project
- The outcomes are prevention of soil run-off, regeneration of natural vegetation, rainwater harvesting, and recharging of the groundwater table.
- This enables multi-cropping and the introduction of diverse agro-based activities, which help to provide sustainable livelihoods to the people residing in the watershed area.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Extended Producers Responsibility
Mains level: Need for plastic waste management
The Union Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change has notified the Guidelines on Extended Producers Responsibility on plastic packaging under Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016.
What is EPR?
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) means the responsibility of a producer for the environmentally sound management of the product (plastic packaging) until the end of its life.
- India had first introduced EPR in 2011 under the Plastic Waste (Management and Handling) Rules, 2011, and E-Waste Management and Handling Rules, 2011.
What are the new EPR rules for Plastic Waste?
(A) Plastic packaging
- The new EPR guidelines cover three categories of plastic packaging including:
- Rigid plastic
- Flexible plastic packaging of a single layer or multilayer (more than one layer with different types of plastic), plastic sheets and covers made of plastic sheet, carry bags (including carrying bags made of compostable plastics), plastic sachet or pouches
- Multi-layered plastic packaging has at least one layer of plastic and at least one layer of material other than plastic.
- It has also specified a system whereby makers and users of plastic packaging can collect certificates — called Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) certificates — and trade in them.
(B) Ineligible plastics for EPR
- Only a fraction of plastic that cannot be recycled will be eligible to be sent for end-of-life disposals such as road construction, waste to energy, waste to oil, and cement kilns.
- Only methods prescribed by the Central Pollution Control Board will be permitted for their disposal.
Targets for recycling
- In 2024, a minimum of 50% of their rigid plastic (category 1) will have to be recycled as will 30% of their category 2 and 3 plastic.
- Every year will see progressively higher targets and after 2026-27, 80% of their category 1 and 60% of the other two categories will need to be recycled.
- If entities cannot fulfill their obligations, they will on a “case by case basis” be permitted to buy certificates making up for their shortfall.
Effects on non-compliance
- Non-compliance, however, will not invite a traditional fine.
- Instead, an “environmental compensation” will be levied, though the rules do not specify how much this compensation will be.
Challenges in mandatory EPR
There are several challenges faced by both producers and bulk consumers that hinder proactive participation.
- Consumer awareness: Waste segregation has been the greatest challenge in India owing to the lack of consumer awareness.
- Lack of compliance: The plastic producers do not wish to engage in the process holistically and take the effort to build awareness.
- Large-scale involvement: The EPR doesn’t take into account the formalization of informal waste pickers, aggregators, and dismantlers.
- Lack of recycling infrastructure: These challenges range from lack of handling capacity to illegitimate facilities in the forms of multiple accounting of waste, selling to aggregators, and leakages.
Way forward
- Tracking mechanism: Develop tracking mechanisms and provide oversight of waste compliance, in order to ensure that the mechanism of waste disposal is streamlined.
- Strict enforcement: While enforcement strictness is of paramount importance, it is also vital to build an incentive structure around this to ensure better complicity by the producers.
- Innovation: The time is ripe for innovators to come up with an alternative for plastics and the strong will of the Government to rid the toxic waste in a sustainable and safe manner.
Try answering this PYQ:
Q.In India, ‘extended producer responsibility’ was introduced as an important feature in which of the following?
(a) The Bio-medical Waste (Management and Handling) Rules, 1998
(b) The Recycled Plastic (Manufacturing and Usage) Rules, 1999
(c) The e-Waste (Management and Handling) Rules, 2011
(d) The Food Safety and Standard Regulations, 2011
Post your answers here.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SEED Scheme, DNTs, Criminal Tribes Act
Mains level: Welfare of the Denotified and Nomadic Tribes
The Minister of Social Justice and Empowerment has launched the Scheme for Economic Empowerment of De-notified, Nomadic, and Semi Nomadic Communities (SEED).
Who are the DNTs?
- The term ‘De-notified Tribes’ stands for all those communities which were once notified under the Criminal Tribes Acts, enforced by the British Raj between l87l and I947.
- These Acts were repealed after Independence in l952, and these communities were “De-Notified”.
- The DNTs (of whom most are the medieval period Banjaras) are the most neglected, marginalized, and economically and socially deprived communities.
- Most of them have been living a life of destitution for generations and still continue to do so with an uncertain and gloomy future.
SEED Scheme
- Under the scheme, the government seeks to provide free coaching to students for civil services examinations, competitive exams for admission to professional courses; health insurance; livelihood support and housing.
- It has been formulated for families having income from all sources of Rs.2.50 lakh or less per annum and not availing any such benefits from similar Scheme of Centre Government or the State Government.
- The Scheme will be implemented through a portal, developed by the Department of Social Justice & Empowerment.
- Post verification, the funds will be transferred directly to the beneficiaries in their account.
- The other implementing agencies are Ministry of Rural Development, National Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM) and National Health Authority (NHA).
Components of the scheme
The Scheme will have the following four components:
[I] Free Coaching
- A component of free Coaching for DNT Students has been envisioned for the educational empowerment of these communities.
- The objective of this component is to enable them to appear in competitive examinations/ admission to professional courses like medicine, engineering, MBA, etc for obtaining an appropriate job in the Public/Private Sector.
- The selection of the candidates for each course will be based on system generated merit list through the portal.
- Approximately, 6250 students will be provided free coaching under this component in five years. The total funds spent in the five years will be Rs.50 crore.
[II] Health Insurance
- Members of these communities are likely to have little or no access to medical facilities and other benefits available under the mainstream health policies.
- The primary objective of the scheme is to provide financial assistance to National Health Authority (NHA) in association with State Health Agencies (SHAs).
- These agencies will provide a health insurance cover of Rs.5 lakhs per family per year for families as per norms of “Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana.
[III] Livelihood Initiatives
- The decline of traditional occupations of DNT/NT/SNT communities has exacerbated their poverty.
- A focus to support livelihood generation for these communities is required.
- The primary objective of the scheme is to provide financial assistance to National Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM).
- It would enhance productivity growth in key livelihood sectors for employment generation through investments in institutional support, technical assistance.
[IV] Financial support for Housing
- Considering the shortage of houses for DNTs, it has been proposed to earmark a separate outlay for PMAY to support specific importance in providing houses only for DNTs living in rural areas.
- It is for those who have not taken benefit of the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana as SC, ST, OBC and are living below the poverty line.
- The admissible support is Rs 1.20 lakhs in plains and 1.30 lakhs in hilly areas (per unit assistance).
Why need such a scheme?
- DNTs escaped the attention of our developmental framework and thus are deprived of the support unlike Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
- Historically, these communities never had access to private land or homeownership.
- These tribes used forests and grazing lands for their livelihood and residential use and had “strong ecological connections.
- Many of them are dependent upon various types of natural resources and carve out intricate ecological niches for their survival.
- The changes in ecology and environment seriously affect their livelihood options.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: New India Literacy Programme
Mains level: Basic literacy and numeracy amongs adults

The Union Government approved a new scheme “New India Literacy Programme (नव भारत साक्षरता कार्यक्रम) for the period FYs 2022-2027 to cover all the aspects of Adult Education to align with National Education Policy 2020.
New India Literacy Programme
- The scheme will cover non-literates of the age of 15 years and above in all states/UTs in the country.
- The target for Foundational Literacy and Numeracy for FYs 2022-27 is 5 (five) crore learners @ 1.00 crore per year by using “Online Teaching, Learning and Assessment System (OTLAS)”.
- A learner may register him/herself with essential information like name, date of birth, gender, Aadhaar number, mobile number, etc.
- The scheme will be implemented through volunteerism through online mode.
- The training, orientation, workshops of volunteers, maybe organized through face-to-face mode.
- All material and resources shall be provided digitally for easy access to registered volunteers.
Objectives of the scheme
The objectives of the scheme are:
- To impart foundational literacy and numeracy
- To cover other components which are necessary for a citizen of the 21st century such as critical life skills (including financial literacy, digital literacy, commercial skills, health care and awareness, child care and education, and family welfare)
- Vocational skills development (with a view towards obtaining local employment)
- Basic education (including preparatory, middle, and secondary stage equivalency)
- Continuing education (including engaging holistic adult education courses in arts, sciences, technology, culture, sports, recreation, etc.)
Salient features of the scheme
- The school will be a Unit for implementation of the scheme
- Schools to be used for conducting a survey of beneficiaries and Voluntary Teachers (VTs)
- Foundational Literacy and Numeracy will be imparted through Critical Life Skills to all non-literates in the age group of 15 years and above
- Performance Grading Index (PGI) for State/UT at the district level
- CSR/Philanthropic Support may be received by hosting ICT support, providing volunteer support
Need for this scheme
- As per Census 2011, the absolute number of non-literates of the country in 15 years and above age group is 25.76 crore (Male 9.08 crore, Female 16.68 crore).
- Even after the Saakshar Bharat program was implemented during 2009-10 to 2017-18, it is estimated that currently around 18.12 crore adults are still non-literate in India.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: TOP Scheme
Mains level: Not Much
The Union Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports (MYAS) has approved the inclusion of Alpine Skiing athlete Mohammad Arif Khan in the Target Olympic Podium Scheme (TOPS) Core group.
Target Olympic Podium Scheme
- In order to improve India’s performance at the Olympics and Paralympics, the MYAS started the Target Olympic Podium Scheme (TOPS) in September 2014.
- It includes foreign training, international competition, equipment, and coaching camp besides a monthly stipend of Rs. 50,000/- for each athlete.
- It was particularly launched for India’s Olympic medal dream, at the 2016 (Rio) and 2020 (Tokyo) Olympics.
How does it function?
- The Mission Olympic Cell is a dedicated body created to assist the athletes who are selected under the TOP Scheme.
- The MOC is under the Chairmanship of the Director-General, Sports Authority of India (DG, SAI).
- The idea of the MOC is to debate, discuss and decide the processes and methods so that the athlete receives the best assistance.
- The MOC also focuses on the selection, exclusion, and retention of athletes, coaches, training institutes that can receive TOPS assistance.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now







