Why in the News?
- The opposition party has demanded the immediate suspension of all clearances granted to NITI Aayog’s Great Nicobar Island (GNI) Project.
- It alleged violations of due process, legal and constitutional provisions protecting tribal communities.
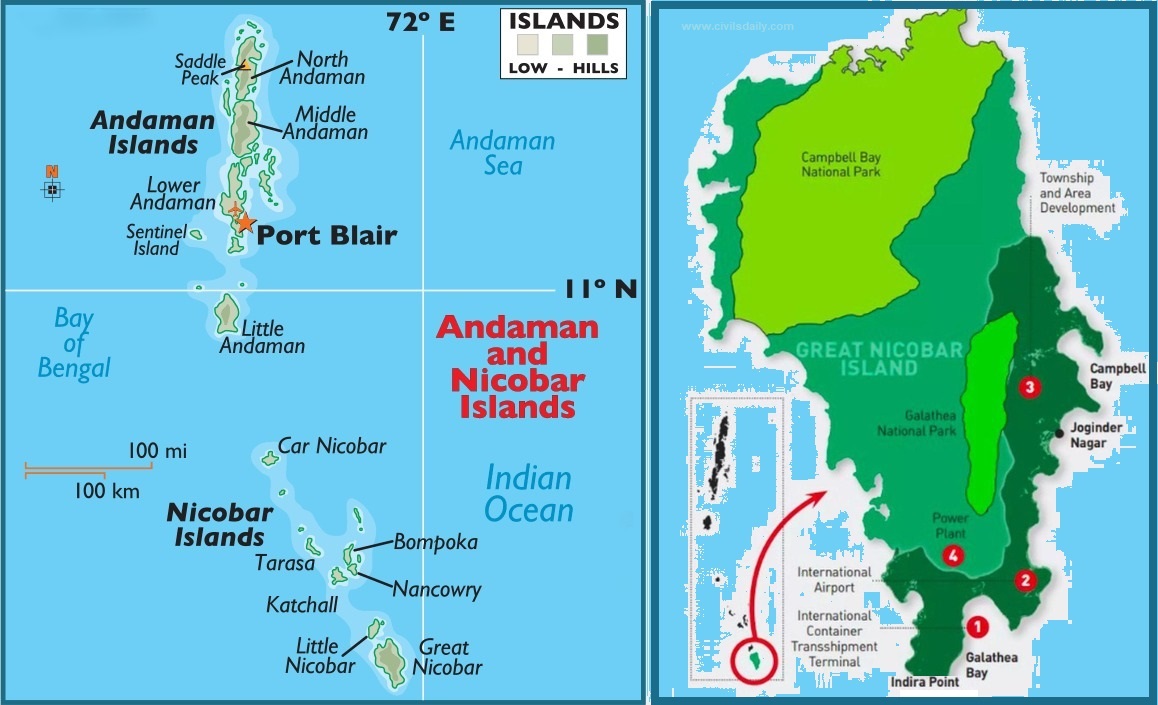
Great Nicobar Island: An Overview
- Geography and Ecology: Southernmost tip of India, part of the Andaman and Nicobar archipelago comprising 600-odd islands.
- Environment: Hilly, covered with lush rainforests, annual rainfall of around 3,500 mm.
- Biodiversity: Hosts numerous endangered and endemic species including the giant leatherback turtle, Nicobar megapode, Great Nicobar crake, Nicobar crab-eating macaque, and Nicobar tree shrew.
- Area: 910 sq km with mangroves and Pandan forests along the coast.
- Indigenous Communities:
- Shompen Tribe: Approximately 250 people live in interior forests, predominantly hunter-gatherers, classified as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group.
- Nicobarese Community: Two groups – Great Nicobarese and Little Nicobarese, practice farming and fishing.
- Resettlement: The Great Nicobarese were resettled in Campbell Bay after the 2004 tsunami.
- Administrative Hub: Campbell Bay serves as the administrative hub, housing local offices of the Andaman and Nicobar administration and the panchayat.
Back2Basics: “Nicobar Triangle”
It is named after the Nicobar Islands, which are located at the northern apex of this triangular area.
The islands within the Nicobar Triangle include:
- Nicobar Islands: This group of islands belongs to India and is situated to the south of the Andaman Islands. They are known for their diverse flora and fauna and are inhabited by indigenous tribes.
- Andaman Islands: Located to the north of the Nicobar Islands, the Andaman Islands are also part of India. They are well-known for their lush forests, coral reefs, and indigenous tribes.
- Indonesian Archipelago: To the south and southeast of the Nicobar Islands lies the Indonesian archipelago, which includes thousands of islands spanning a vast area between the Indian and Pacific Oceans.
|
|
What is GNI Project?
The GNI Project refers to the “Holistic Development of Great Nicobar Island,” a proposed mega project being piloted by NITI Aayog.
- Implementing Agency: The project is to be implemented by the Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation (ANIIDCO).
- Historical Context: Development plans for a port in Great Nicobar date back to the 1970s, aimed at leveraging its strategic location near the Malacca Strait.
- The project aims to develop the southern end of the Andaman and Nicobar group of Islands in the Bay of Bengal by constructing –
- Transshipment port
- Dual-use military-civil international airport
- Power plant (450 MVA gas and solar-based) and
- A township over a span of 30 years on more than 160 sq. km of land, of which 130 sq. km is primary forest
Features of the Project
- Transshipment hub of the East: The proposed port will allow Great Nicobar to participate in the regional and global maritime economy by becoming a major player in cargo transshipment.
- Naval control: The port will be controlled by the Indian Navy, while the airport will have dual military-civilian functions and will cater to tourism as well.
- Urban amenities: Roads, public transport, water supply and waste management facilities, and several hotels have been planned to cater to tourists.
Significance of the project
- Economic significance: The proposed port would allow GNI to become a significant player in cargo transhipment, as it is positioned equidistant from Colombo, Port Klang (Malaysia), and Singapore.
- Strategic significance: The proposal to develop GNI has been on the table since the 1970s, and it has been highlighted repeatedly as a crucial element for national security and consolidation of the Indian Ocean Region.
- In recent years, the escalating Chinese presence in the Indian Ocean has added greater urgency to this imperative.
Issues with the Project
- The project entails the deforestation of 130 sq km, and felling 10 lakh trees, threatens biodiversity at Galathea Bay, displaces indigenous tribes, lacks thorough impact assessments, and poses seismic risks to vulnerable communities.
Due-process Violations highlighted by the ‘Opposition’
(1) Did not recognise the grant ownership: The island administration did not recognise or grant ownership of any forest land to local tribespeople as per FRA, a requisite step under the Forest Conservation Rules, 2017, before Stage-I clearance is granted.
- This is despite the fact that Rule 6(3)(e) of Forest Conservation Rules-2017 (FCR) requires that any diversion of forest land first requires the District Collector to recognise and vest rights to locals under the FRA.
- The legislation allows forest communities the right to control and manage the use of the forest land over which they hold titles, and their consent is mandatory for diverting it.
(2) Inconsistencies with Stage-I Clearance: The Stage-I clearance for the project was granted in October 2022, two years after the application was received. Monthly progress reports show that the district administration did not process any claims over forest land under the FRA in the 26 months since project sanction.
(3) Withdrawal of Consent: Weeks after the Stage-I clearance was granted, the Tribal Council at Campbell Bay withdrew the consent granted by the Gram Sabha.