Why in the News?
Kerala State Electricity Board (KSEB) has partnered with IIT Bombay to launch a pilot project on Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology, integrating electric vehicles into the power grid.

About V2G Technology:
- V2G enables Electric Vehicles (EVs) to send power back to the grid when not in use, turning EV batteries into decentralized energy storage devices.
- It involves two key functions:
- Grid-to-Vehicle (G2V): Power is transferred from the grid to charge the EV.
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G): Power is sent from the EV back to the grid, making the vehicle a distributed energy source.
- Smart charging strategies optimize charging based on grid demand and renewable energy availability, enhancing grid stability and enabling renewable energy integration.
About the KSEB-IIT Bombay V2G Pilot Project:
- This pilot aims to assess EVs’ role in supporting the power grid, especially during peak demand periods when solar energy is unavailable.
- Kerala’s growth in EV adoption and rooftop solar installations has raised concerns about increased electricity demand, particularly in the evenings.
- The project will explore the feasibility of using EVs to reduce grid strain and optimize the use of renewable energy.
|
Applications of V2G:
- Grid Support: EVs can supply power back to the grid during high-demand periods, improving grid stability.
- Solar Energy Integration: V2G encourages charging during the day when solar power is abundant, and storing excess energy to supply the grid at night.
- Emergency Power Source: EVs can act as backup power during crises or natural disasters, providing electricity to communities.
| [UPSC 2024] Which one of the following is the exhaust pipe emission from Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles powered by hydrogen?
(a) Hydrogen peroxide (b) Hydronium (c) Oxygen (d) Water vapour * |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
Scientists using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) have found signs of possible life on exoplanet K2-18 b by detecting gases usually produced by Earth’s biological processes.

Key findings of the Recent Study:
- Scientists detected significant biosignatures in the atmosphere of K2-18 b, including dimethyl sulphide (DMS) and dimethyl disulfide (DMDS).
- These gases, on Earth, are primarily produced by marine phytoplankton.
- High concentrations of these gases suggest the possibility of microbial life, particularly in the planet’s oceans.
- However, researchers caution that this is not definitive proof of life but a potential biosignature indicating biological processes.
- Further studies and observations are needed to confirm whether these gases are biologically produced or the result of other processes.
About James Webb Space Telescope (JWST):
- JWST is a joint venture between NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) launched in December 2021.
- It is an orbiting infrared observatory that will complement and extend the discoveries of the Hubble Space Telescope, with longer wavelength coverage and greatly improved sensitivity.
- Webb was formerly known as the “Next Generation Space Telescope” (NGST), and it was renamed in 2002 after a former NASA administrator, James Webb.
- It isa large infrared telescope with an approximately 6.5-meter primary mirror.
- JWST is positioned at the Earth-Sun L2 Lagrange point, 5 million km away.
- It consists of a mirror, spanning 6.5 meters in diameter compared to Hubble’s 2.4 meters, and its specialised instruments optimised for infrared observations.
- Key Objectives:
- JWST observes deeper into the universe than Hubble.
- Observes celestial objects from earlier epochs.
- Enables the detection of light from the universe’s earliest stars, dating back over 13.5 billion years.
| [UPSC 2020] The experiment will employ a trio of spacecraft flying in formation in the shape of an equilateral triangle that has sides one million kilometres long, with lasers shining between the craft.” The experiment in question refers to:
Options: (a) Voyager-2 (b) New Horizons (c) LISA Pathfinder (d) Evolved LISA* |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
The 6th edition of India-Uzbekistan Joint Military Exercise DUSTLIK-6 commenced at the Foreign Training Node at Aundh in Pune, Maharashtra.
About Exercise DUSTLIK
- Exercise DUSTLIK is an annual event alternating between India and Uzbekistan.
- It is named after Dustlik, a town in the Jizzakh region of Uzbekistan.
- The first edition of the exercise was held in 2019 near Tashkent.
- The 5th edition was held in Termez District, Uzbekistan.
- 4th edition held in Pithoragarh, India, in February 2023.
Objectives and Focus Areas:
- Focus on physical fitness, joint planning, and tactical drills.
- Emphasis on special arms skills and multi-domain operations.
- Tactical drills include establishing command posts, intelligence centers, heliborne operations, and room intervention.
Back2Basics: India’s bilateral exercises with Central Asian Countries
| Country |
Exercise |
| Kazakhstan |
Ex PRABAL DOSTYK, Ex KAZIND |
| Kyrgyzstan |
Ex KHANJAR |
| Mongolia |
Ex NOMADIC ELEPHANT |
| Tajikistan |
Ex Farkhor |
| [UPSC 2008] Hand-in-Hand 2007’, a joint anti-terrorism military training was held by the officers of the Indian Army and officers of the Army of which one of the following countries?
Options: (a) China * (b) Japan (c) Russia (d) USA |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Evolution of the Office of Governor
Why in the News?
The recent Supreme Court verdict on the powers of the President and Governors regarding assent to Bills under Articles 201 and 200 highlights the evolution of the office of the Governor and its changing role in India’s federal structure.
Evolution of the Office of Governor:
- Formal Establishment (1858): The office of the Governor was established under the Government of India Act of 1858, which transitioned administration from the East India Company to the British Crown. Governors acted as agents of the Crown and had significant powers in provincial administration.
- Montagu-Chelmsford Reforms (1919): The GoI Act of 1919, under the Montagu-Chelmsford Reforms, aimed to increase Indian participation but kept the Governor central to governance, including vetoing Bills passed by legislative councils.
- GoI Act of 1935: The GoI Act of 1935 gave provincial autonomy but retained the Governor’s discretionary powers, including vetoing Bills and withholding assent, signalling a transition toward more autonomy while maintaining significant Governor authority.
- Post-Independence Transition (1947): As India moved toward independence, the India (Provisional Constitution) Order of 1947 modified the 1935 Act. It removed the phrase “in his discretion,” reducing the Governor’s discretionary powers and signalling a shift to a more symbolic and constitutional role.
- Constituent Assembly Debates: It debated whether Governors should be elected or nominated. Concerns over separatism led to the decision that Governors would be nominated by the President to maintain unity and strengthen ties with the Centre, especially after the partition.
- Post-Independence Framework: Before Independence, various documents and political proposals, including the Commonwealth India Bill (1925) and the Nehru Report (1928), supported retaining the office of the Governor, inspired by the Westminster model of governance.
Constitutional Role of the Governor:
- Article 163: The Governor acts on the advice of the Council of Ministers headed by the Chief Minister, except in certain discretionary situations.
- Ambedkar’s Views: Dr. B.R. Ambedkar advocated for limited use of discretionary powers, ensuring the Governor’s actions align with the advice of the ministers.
- Article 200: The Governor must grant assent to Bills, but may withhold assent, reserve the Bill for the President, or return it for reconsideration. Ambedkar amended this in 1949 to ensure the Governor acts in alignment with the elected government.
- Symbolic and Impartial Role: The Governor is expected to represent the Union, support democratic functioning, and remain non-interfering in day-to-day state affairs.
- Discretionary Powers: The Governor’s discretion is limited to constitutional guidelines and should be used sparingly, ensuring the Governor’s role remains constitutional, not political.
| [UPSC 2017] In the context of Indian history, the-principle of ‘Dyarchy (diarchy)’ refers to:
(a) Division of the central legislature into two houses.
(b) Introduction of double government i.e., Central and State governments.
(c) Having two sets of rulers; one in London and another in Delhi.
(d) Division of the subjects delegated to the provinces into two categories. * |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
A 21-year-long study has resulted in the discovery of a new frog species, Leptobrachium aryatium, named after Arya Vidyapeeth College in Assam.

About the frog ‘Leptobrachium aryatium’
- Leptobrachium aryatium, a newly discovered species of frog, was found in the Garbhanga Reserve Forest, located on the southwestern edge of Guwahati, Assam, near the Meghalaya border.
- The species was identified through a re-analysis of past research and new studies on the Leptobrachium genus.
- Key Features:
- Distinctive Eyes: The frog has fiery orange-and-black eyes, setting it apart from other species in the genus.
- Reticulated Throat Pattern: A unique reticulated pattern on its throat adds to its distinct appearance.
- Smooth, Rhythmic Call: Emits a smooth, rhythmic call at dusk, a feature unique to this species in the genus.
- Molecular and Morphological Distinctiveness: DNA analysis and physical studies confirmed it as a new species, distinguished by its unique call and appearance.
| [UPSC 2016] Recently, our scientists have discovered a new and distinct species of banana plant which attains a height of about 11 metres and has orange-coloured fruit pulp. In which part of India has it been discovered?
(a) Andaman Islands* (b) Anaimalai Forests (c) Maikala Hills (d) Tropical rain forests of northeast |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
On April 16, 2025, the Ecological Restoration Alliance-India (ERA-I) has released a first-of-its-kind seed germination database aimed at enhancing the success of growing native plants for ecological restoration.
About the Seed Germination Database:
- It was launched by the Ecological Restoration Alliance-India (ERA-I). ERA was formed in July 2021, as an informal collective between practitioners, ecologists and individuals.
- ERA-I collaborated with organizations like Auroville Botanical Gardens, NCF, and Wildlife Trust of India.
- It features over 1,000 germination techniques for 465 native plant species found across India.
- It aims to help restoration practitioners, nursery managers, and native plant enthusiasts improve success rates in growing plants for ecological restoration.
- It is a free-access database and offers valuable information on germinating native plants crucial for restoration projects.
- Native Plants Included:
- The database features a diverse array of native plant species. These species are key to restoring balance in degraded ecosystems.
- They are – Aegle marmelos (Wood apple), Bauhinia racemosa (Beedi leaf tree), Ficus benghalensis (Banyan), Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha), Ziziphus mauritiana (Indian jujube), Knema attenuata (Wild nutmeg), Lawsonia inermis (Henna), Madhuca longifolia (Mahua), Vachellia nilotica (Babool).
Significance:
- Native plants are essential for creating climate-resilient ecosystems.
- Such database plays a vital role in ecological restoration.
- It provides 1,000+ techniques for growing native plants, enhancing the success of restoration projects.
- The database supports India’s Bonn Challenge commitment to restore 26 million hectares of degraded land by 2030.
| [UPSC 2016] In the context of food and nutritional security of India, enhancing the ‘Seed Replacement Rates’ of various crops helps in achieving the food production targets of the future. But what is/are the constraint/constraints in its wider/greater implementation?
1. There is no National Seeds Policy in place.
2. There is no participation of private sector seed companies in the supply of quality seeds of vegetables and planting materials of horticultural crops.
3. There is a demand-supply gap regarding quality seeds in case of low value and high volume crops. Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Options: (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 3 only * (c) 2 and 3 only (d) None of the above |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
Recent studies reveal that the Indian Plate is splitting into two, with the lower part detaching and sinking into the Earth’s mantle, a process called delamination, as published by the American Geophysical Union.
About Delamination:
- Delamination in tectonic plates refers to the process where the lower part of a continental plate, including the lower crust and/or lithospheric mantle, splits and sinks into the Asthenosphere.
- This process is driven by density differences and can lead to rapid uplift, changes in stress regimes, and altered magmatism.
- It can occur in various tectonic settings, including compressional zones, subduction zones, and intraplate regions.
- The denser lower part of the plate, including the lower crust and/or lithospheric mantle, is less buoyant than the less dense asthenosphere, leading to sinking.
- High temperatures can also weaken the lithosphere and facilitate delamination.

Indian Plate and Its Splitting:
- The Indian Plate has been colliding with the Eurasian Plate for about 60 million years, causing the formation of the Himalayas and influencing regional seismic activity.
- It is shifting northward at a rate of approximately 5 cm per year..
- The lower, denser part of the Indian Plate is detaching and sinking into the Earth’s mantle.
- This may lead to increased seismic activity due to shifts in tectonic stress.
- In regions like the Himalayan collision zone, delamination results in fractures that increase stress in the Earth’s crust, raising the likelihood of seismic events.
| [UPSC 2004] Consider the following geological phenomena:
1. Development of a fault 2. Movement along a fault 3. Impact produced by a volcanic eruption 4. Folding of rocks Which of the above cause earthquakes?
Options:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 (b) 2 and 4 (c) 1, 3 and 4 (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
Recently Google introduced its seventh-generation TPU (Tensor Processing Unit), named Ironwood.
About Ironwood
- Ironwood is Google’s seventh-generation Tensor Processing Unit (TPU), designed to accelerate AI model training and inference with improved performance and efficiency.
- It builds on previous TPUs, enhancing speed and efficiency for AI workloads.
- It has been optimized for complex AI tasks, especially those requiring high-speed data processing for neural networks and deep learning models.
- Initially used internally, Ironwood is now available via Google Cloud Platform, allowing businesses to harness its power without investing in dedicated hardware.
What is a TPU?
- A TPU is a specialized processor developed by Google to accelerate machine learning tasks, particularly those involving TensorFlow.
- TPUs are optimized for tensor operations, crucial for training deep learning models, enabling faster data processing and high efficiency.
How is TPU Different from GPU and CPU?
|
CPU |
GPU |
TPU |
| What is it? |
Central Processing Unit – General-purpose processor for various computing tasks. |
Graphics Processing Unit – Specialized for parallel processing, initially for graphics rendering. |
Tensor Processing Unit – Specialized processor designed by Google for accelerating machine learning tasks, particularly for AI and deep learning. |
| Specialization |
General-purpose tasks (sequential processing) |
Parallel processing (graphics, machine learning) |
Specialized for AI tasks (tensor computations) |
| Performance |
Slower for AI tasks due to sequential processing |
Faster than CPU for parallel tasks |
Fastest for AI tasks like matrix multiplication |
| Efficiency |
Versatile but less efficient for AI operations |
Energy-efficient for parallel tasks |
Highly energy-efficient for machine learning |
| Best for |
Running applications, managing systems |
Graphics rendering, machine learning |
Deep learning, neural network training |
| [UPSC 2020] With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following?
(1) Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units (2) Create meaningful short stories and songs (3) Disease diagnosis (4) Text-to-Speech Conversion (5) Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Options: (a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only (b) 1, 3 and 4 only (c) 2, 4 and 5 only (d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
PM recently remembered Sir Chettur Sankaran Nair, a nationalist and jurist who famously fought a courtroom battle against British officials involved in the Jallianwala Bagh massacre of 1919.
Nair’s stand in the courtroom is now a subject of a forthcoming film, Kesari Chapter 2.

About Sir Sankaran Nair:
- Born in 1857 in Mankara village, Kerala, Nair came from an aristocratic family.
- He was educated at Presidency College in Madras and pursued a law degree.
- Nair began his legal career with Sir Horatio Shepherd, Chief Justice of Madras High Court.
- In 1897, Nair became the youngest president of the Indian National Congress (Amravati (Mh) Session) and was appointed as a permanent judge of the Madras High Court in 1908.
Role in the Jallianwala Bagh Case:
- Nair challenged Michael O’Dwyer, the Lieutenant Governor of Punjab, for his role in the Jallianwala Bagh massacre (1919), accusing him of following policies that led to the massacre.
- O’Dwyer sued Nair in England for defamation. Despite biased British courts, Nair refused to apologize, even when O’Dwyer offered to forgo the £500 penalty.
- The trial highlighted the bias in the British judicial system and fuelled Indian resentment against British rule.
Other Contributions:
- Nair made progressive rulings, like supporting inter-caste and inter-religious marriages and ruling against treating converts to Hinduism as outcasts.
- He supported India’s self-government and played a key role in expanding the Montagu-Chelmsford reforms (1919).
- In 1922, Nair critiqued Gandhi‘s methods in his work “Gandhi and Anarchy”.
- He helped draft the 1919 constitutional reforms, pointing out flaws in British rule, with many of his suggestions accepted.
| [UPSC 2007] Which one of the following aroused a wave of popular indignation that led to the massacre by the British at Jallianwala Bagh?
(a) The Arms Act (b) The Public Safety Act (c) The Rowlatt Act (d) The Vernacular Press Act |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
China has suspended exports of a wide range of critical minerals and magnets after US’s tariff embargo.
What Are Rare Earth Elements (REEs) and RE Magnets?
- REEs are a group of 17 elements in the periodic table, including Lanthanum (La), Neodymium (Nd), Europium (Eu), and Ytterbium (Yb).
- Though not rare, they are found in low concentrations, making extraction challenging and costly.
-
- Light REEs (LREEs): Elements 57-63, such as La, Ce, Nd, and Sm.
- Heavy REEs (HREEs): Elements 64-71, like Gd, Tb, Dy, and Er.
- Scandium and Yttrium: Classified with HREEs due to similar chemical properties.
- Rare Earth Magnets are powerful permanent magnets made from elements like Neodymium (Nd), Samarium (Sm), and Dysprosium (Dy).
- They are far stronger and more efficient than traditional magnets, crucial for high-tech electronic applications.
Global Supply Chain of REEs:
- REEs are abundant but difficult to extract economically.
- China alone dominates, producing 70% of the global supply and controlling 80% of the refining capacity. REEs are primarily mined from China’s Bayan Obo mine.
- Australia, USA, Brazil, and Russia also contribute, though less significantly.
- Refining also is largely controlled by China, though other nations are working to build their own refining capabilities to reduce dependency.
| [UPSC 2022] Consider the following statements:
1. Monazite is a source of rare earths. 2. Monazite contains thorium. 3. Monazite occurs naturally in the entire Indian coastal sands in India. 4. In India, Government bodies only can process or export monazite.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only (b) 1, 2 and 4 only* (c) 3 and 4 only (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
The Telangana government has officially implemented the sub-categorization of Scheduled Castes (SCs) into three groups, following a Supreme Court judgment in August 2024 that upheld the constitutionality of sub-classifying SCs and Scheduled Tribes (STs) to grant separate quotas for the most marginalized groups.

About Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Their Subcategorization:
- SCs are a historically marginalized group identified in India’s Constitution to receive preferential treatment in education, employment, and political representation.
- Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 341: Empowers the President to specify castes as SCs within states or UTs.
- Article 342: Allows Parliament to include/exclude castes from the SC list.
- While grouped for reservations, disparities exist within SCs, with some groups being more disadvantaged than others.
- Subcategorization involves dividing SCs into smaller groups based on social, economic, and educational backwardness, ensuring the most marginalized receive targeted benefits.
- Sub-classification of SCs and STs for reservations is subject to judicial review to prevent misuse.
Supreme Court Verdict on Sub-categorization: State of Punjab v. Davinder Singh (2020) Case
- In its August 2024 verdict, the Supreme Court allowed states to sub-classify SCs and STs, enabling separate quotas for the most marginalized groups.
- Key Points:
- Empirical Data: Subclassification must be based on data of systemic discrimination, not political motives.
- Creamy Layer: Excludes the more advanced members of SCs/STs, applying the creamy layer principle.
- Quota Limits: No sub-categorization can exceed the overall constitutional quota ceiling.
- First-Generation Benefit: Reservations are restricted to the first generation of a family that has not benefitted from previous reservations.
|
| [UPSC 2005] Which one of the following statements is correct regarding population?
(a) Bihar has the highest percentage of Scheduled Castes in its population.
(b) The decadal growth of population of India (1991-2001) has been below 20%.
(c) Mizoram is the Indian State with the least population.
(d) Pondicherry has the highest sex ratio among the Union Territories. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
The KATRIN (Karlsruhe Tritium Neutrino Experiment) has made a groundbreaking achievement by measuring neutrino mass with a new precision.
About the KATRIN Experiment:
- The KATRIN is located at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT), specifically on its Campus North site in Karlsruhe, Germany.
- It is aimed at measuring the mass of the electron antineutrino with sub-eV precision.
- It has measured the mass of neutrinos by studying the beta decay of tritium, a radioactive form of hydrogen.
- The mass was inferred by analyzing the energy of the emitted electrons.
- Technological Setup:
- A 70-meter-long beamline with a powerful tritium source.
- A 10-meter-wide spectrometer to measure the energy of emitted electrons with high precision.
- Key Findings:
- KATRIN has set a new upper limit for neutrino mass at less than 0.45 eV/c² (8 × 10⁻³⁷ kg), nearly twice as precise as previous measurements from 2022.
- Data Collection was based on five campaigns from 2019-2021, totalling 250 days of data.
Neutrinos and Their Properties
- Neutrinos are extremely light subatomic particles that rarely interact with matter, making them difficult to detect.
- They are found in cosmic rays and solar radiation.
- Properties:
- Mass: Their small mass influences cosmic structure formation, such as galaxies and clusters.
- Weak Interaction: They interact via the weak nuclear force, allowing them to pass through vast amounts of matter.
- They are essential in particle reactions and play a key role in galaxy formation and the study of dark matter.
|
| [UPSC 2010] India-based Neutrino Observatory is included by the planning commission as a mega-science project under the 11th Five-year plan. In this context, consider the following statements:
1.Neutrinos are chargeless elementary particles that travel close to the speed of light.
2.Neutrinos are created in nuclear reactions of beta decay.
3.Neutrinos have a negligible, but non-zero mass.
4.Trillions of Neutrinos pass through the human body every second.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only (b) 1, 2 and 3 only (c) 2, 3 and 4 (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Silicon Photonics
Why in the News?
In a major breakthrough, Indian researchers have developed a new type of laser that can be placed directly onto silicon chips, a key component of modern computers.
What is Silicon Photonics?
- Silicon photonics is a technology that uses light (photons) instead of electrical signals to transmit data inside computer systems.
- Light can carry more data at higher speeds with less energy than electricity, making it a promising technology for future computing and data transfer.
- Traditional silicon chips struggle to produce light, requiring external lasers, which were inefficient and costly.
- Silicon photonics can significantly enhance data transfer speed and efficiency, benefiting industries like data centers and telecommunications.
About the Miniaturized Laser Technology
- Indian researchers have successfully integrated a laser directly onto a silicon chip, eliminating the need for separate lasers.
- The laser is made using gallium arsenide (where 20% of gallium atoms had been replaced with indium to achieve optimal light emission), which helps silicon emit light, a crucial step since silicon alone cannot produce light efficiently.
- It uses minimal power, ideal for high-performance, energy-efficient computers.
- Direct integration reduces costs, making the technology scalable for mass production.
- This innovation boosts computing power, particularly in data centers where fast data transfer is critical.
- Efforts are underway to enhance its durability, especially at higher temperatures, for broader industrial use.
| [UPSC 2008] Which one of the following laser types is used in a laser printer?
(a) Dye laser (b) Gas laser (c) Semiconductor laser (d) Excimer laser |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully tested the Mk-II(A) Laser-Directed Energy Weapon (DEW) system, marking a major achievement in the country’s defense capabilities.
About Mk-II(A) Laser-Directed Energy Weapon (DEW) System
- The Mk-II(A) Laser-DEW system, also known as Sahastra Shakti, is an indigenously developed Laser weapon with an operational range of 5km.
- It is designed to neutralize threats like drones, missiles, and remotely piloted aircraft using a 30-kilowatt laser.
- It is developed by DRDO’s Centre for High Energy Systems and Sciences (CHESS), in collaboration with other DRDO labs, academic institutions, and Indian industries.
- It focuses primarily on neutralizing aerial threats such as drones and missiles, offering a cutting-edge solution against modern warfare tactics.
How does it work?
- It utilizes radar and Electro-Optic (EO) systems for target detection.
- The laser engages the target at the speed of light, causing structural failure or significant damage.
- It delivers rapid, precise strikes with lethal impact in seconds.
- The energy used for a few seconds of firing costs as little as a couple of litres of petrol, making it cost-efficient.
- The 30-kilowatt laser ensures quick target neutralization with minimal collateral damage.
Significance of the Mk-II(A) Laser-DEW System
- Cost-Effective: Far more affordable than traditional missile systems, providing sustainable defense options.
- Reduced Ammunition Dependence: Reduces reliance on expensive ammunition, offering a long-term sustainable defence solution.
- Precision & Speed: Engages targets almost instantaneously, minimizing collateral damage and ensuring high-value targets are neutralized quickly.
- Strategic Advantage: Enhances India’s defence capabilities, providing an advanced method for protecting infrastructure and addressing evolving aerial threats.
| [UPSC 2011] With reference to Indian defence, which one of the following statements is NOT correct?
(a) With the induction of Prithvi-II, the IAF is the only air force in the world with surface-to-surface ballistic missiles under its command.
(b) Sukhoi-30 MKI jet fighters can launch air-to-air and air-to-surface precision missiles
(c) Trishul is a supersonic surface-to-air missile with a range of 30 km
(d) The indigenously built INS Prabal can launch surface-to-surface missiles |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
A recent study published in Geophysical Research Letters revealed changes in both the amount and timing of rainfall using GSMaP Data between the decades 2001-2010 and 2011-2020.
About Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP)
- GSMaP is a specialized precipitation product developed through collaboration between ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation) and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency).
- It provides high-resolution precipitation data with a 0.1° x 0.1° grid and one-hour temporal resolution, focusing on the Indian subcontinent since March 2000.
- The data supports rainfall trend analysis, climate modelling, and water resource management.

Key Findings of the Study:
- Rainfall Trends:
- West-Central India: Increased daily rainfall (2 mm/day) from 2011-2020 compared to 2001-2010.
- Eastern India: A decrease of ~1 mm/day in rainfall during the same period.
- Regional Shifts: Northeastern and eastern India saw decreased rainfall, while the Indo-Gangetic Plain and southern India experienced increases.
- Vegetation & Soil Moisture:
- West-Central India saw an increase in vegetation (NDVI from 0.2 to 0.4) and soil moisture linked to increased rainfall.
- Eastern India had decreased soil moisture during the same period.
- Shifts in Peak Rainfall Timing:
- Indo-Gangetic Plain: Peak rainfall advanced by 2-4 hours.
- West-Central India: Peak rainfall delayed by 1-2 hours.
- Factors responsible for this Shift:
- Higher soil moisture supports rainfall, while reduced moisture, particularly in eastern India, decreases rainfall.
- Higher aerosol concentrations in polluted areas like the Indo-Gangetic Plain lead to earlier rainfall peaks.
- Changes in atmospheric circulation, topography, and coastal influences also affect rainfall distribution and timing.
| [UPSC 2012] Consider the following statements:
1. The duration of the monsoon decreases from southern India to northern India.
2. The amount of annual rainfall in the northern plains of India decreases from east to west.
Which of the statements given above is / are correct?
(a) 1 Only (b) 2 Only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
Researchers from Thiruvananthapuram have developed a cost-effective Real-Time LAMP (rt-LAMP) Assay for early Tuberculosis (TB) diagnosis.
About the rt-LAMP Assay
- The rt-LAMP assay (real-time Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification) is a molecular diagnostic test designed to detect TB DNA with high precision.
- It can detect TB DNA at concentrations as low as 10 copy numbers per microlitre, ensuring early detection even with low bacterial loads.
- Developed by SCTIMST, Thiruvananthapuram, the rt-LAMP assay uses Syto 16, a fluorescent dye, to monitor DNA amplification in real time, addressing the limitations of traditional LAMP tests.
- Working Principle:
- It uses six primers for DNA amplification (compared to two in RT-PCR), enhancing amplification speed.
- It operates at a single temperature, unlike RT-PCR, making it simpler and more cost-effective.
- It monitors the amplification process continuously, providing faster results.
Advantages Offered:
- High Sensitivity and Specificity: Ensures accurate detection of TB DNA due to the use of six primers.
- Cost-Effective: Uses affordable fluorescent dyes and primers, reducing diagnostic costs.
- Speed: Produces results in just 10-20 minutes, faster than traditional tests.
- Ease of Use: Compatible with existing RT-PCR machines, reducing the need for new infrastructure.
- High Throughput: Can process 96-384 tests in one run, making it ideal for high-volume settings.
| [UPSC 2007] Which of the following types is used by computed tomography employed for visualization of the internal structure of the human body?
(a) X-rays (b) Sound Waves (c) Magnetic Resonance (d) Radioisotopes |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
India and Italy have decided to enhance cooperation in trade, defence, clean energy, and high technology while working jointly on the India-Middle-East-Europe-Economic Corridor (IMEEC).
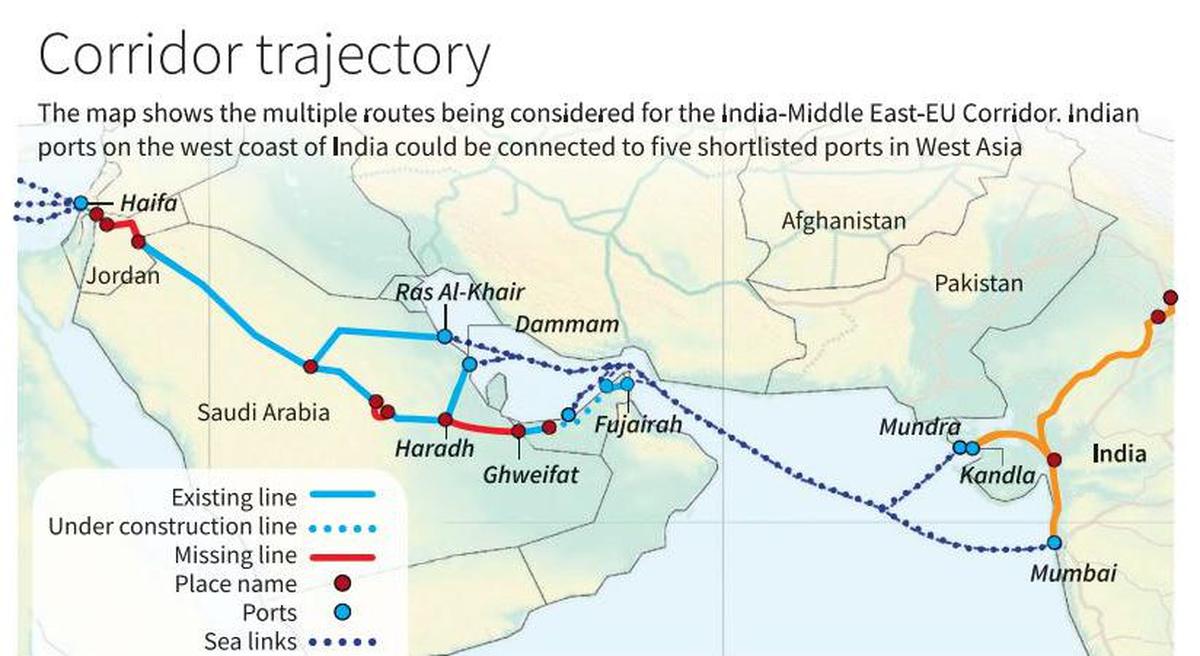
About IMEEC Project:
- IMEEC is a key initiative under the Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII), aimed at infrastructure development in developing regions.
- It was formally endorsed on September 10, 2023, during the 2023 G20 New Delhi summit.
- Signatories include: India, United States, UAE, Saudi Arabia, France, Germany, Italy, and the European Union.
- Objective: To integrate Asia, Europe, and the Middle East to boost economic cooperation, trade, and regional connectivity.
- IMEEC consists of two main corridors:
- East Corridor: Connecting India to the Arabian Gulf.
- Northern Corridor: Connecting the Gulf region to Europe.
- Key Ports to be Connected:
- India: Mundra, Kandla, Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust (Mumbai).
- Middle East: Fujairah (UAE), Jebel Ali (Dubai), Dammam (Saudi Arabia).
- Israel: Haifa Port.
- Europe: Piraeus (Greece), Messina (Italy), Marseille (France).
Significance of the Project:
- IMEEC will create a cost-efficient ship-to-rail transit network, enhancing existing transport links.
- The project will transform regional trade dynamics and foster sustainable economic growth.
| [UPSC 2023] With reference to India’s projects on connectivity, consider the following statements:
1. East-West Corridor under Golden Quadrilateral Project connects Dibrugarh and Surat.
2. Trilateral Highway connects Moreh in Manipur and Chiang Mai in Thailand via Myanmar.
3. Bangladesh-China -India -Myanmar Economic Corridor connects Varanasi in Uttar Pradesh with Kunming in China.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
Earlier this month, severe weather in the United States, including heavy rainfall, strong winds, and thunderstorms, was caused by an Atmospheric River.
What is an Atmospheric River?
- An atmospheric river is a narrow, fast-moving band of moisture and wind that transports large amounts of water vapor across vast distances.
- They form when large-scale weather patterns align, creating channels of moisture transport from tropical oceans, guided by low-level jet streams toward the coast.
- They typically span 402-606 km in width and can extend over 1600 km in length.
- The most powerful atmospheric rivers transport moisture equivalent to the Mississippi River’s flow.
- Example: The Pineapple Express, a well-known atmospheric river, transports moisture from Hawaii to the West Coasts of the U.S. and Canada.
- The intense rainfall from atmospheric rivers leads to flooding, mudslides, and infrastructure damage, with wind speeds comparable to hurricanes.

Impact and Climate Change:
- Rising global temperatures cause more water to evaporate, and warmer air can hold more moisture.
- For every 1°C increase, the atmosphere can hold 7% more moisture, leading to stronger storms.
- Research indicates such events will likely grow longer and more intense.
| [UPSC 2023] With reference to the Earth’s atmosphere, which one of the following statements is correct?
(a) The total amount of insolation received at the equator is roughly about 10 times of that received at the poles.
(b) Infrared waves are largely absorbed by carbon dioxide that is concentrated in the upper atmosphere.
(c) Infrared waves are largely absorbed by water vapour that is concentrated in the lower atmosphere.
(d) Ultraviolet rays are absorbed by the ozone layer lying in the ionosphere. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
On April 11, 2025, the Prime Minister paid tribute to Mahatma Jyotiba Phule on his 199th birth anniversary.

About Mahatma Phule
- Jyotirao Govindrao Phule, born on April 11, 1827, near Pune, was from the Mali caste.
- His father was a vegetable vendor, and his mother died when he was young.
- He pursued education at the Scottish Mission High School in Pune despite caste-based discrimination.
- He was inspired by Western thinkers like Thomas Paine and John Stuart Mill, fuelling his social justice dedication.
- At 13, he married Savitribai Phule, who became his partner in social reforms, particularly promoting education for women and marginalized communities.
His Contributions as a Social Reformer:
Educational Reforms:
- In 1848, Phule and his wife established India’s first girls’ school in Pune.
- He focused on educating Dalits and lower-caste groups, traditionally excluded from education.
- He founded night schools for working-class individuals, especially women.
Fighting Caste Discrimination:
- Phule criticized the caste system, calling it a means of oppression.
- In 1873, Phule’s book Gulamgiri condemned caste discrimination, comparing Dalits’ plight to slavery.
- Phule coined the term ‘Dalit’ to describe those outside the caste system.
Women’s Welfare and Empowerment:
- Phule advocated for widow remarriage and provided a dignified life for widows.
- In 1863, he opened homes to help pregnant widows.
- He co-founded an infanticide prevention center, tackling the killing of female infants.
Social Justice and Equality:
- Phule founded Satyashodhak Samaj in 1873 to promote social equality, rational thinking, and religious reform.
- The Samaj rejected idolatry and supported a more rational spiritual approach.
- He broke the social stigma of untouchability by opening his house and water-well to the oppressed.
Religious and Philosophical Contributions:
- Phule was an advocate for critical thinking of religion, rejecting superstition and blind faith.
- He believed in equality and justice across religions and cultures.
- He was influenced by Bhakti saints like Sant Kabir and Sant Tukaram in his fight against social oppression.
His Literary Contributions:
- Gulamgiri (Slavery) (1873): Critiqued the caste system and called for Dalit liberation.
- Shetkaryacha Asud (Farmer’s Whip) (1881): Addressed the exploitation of farmers and advocated for land reforms.
- Sarvajanik Satya Dharma Poostak: Promoted rationalist thought and social justice.
- Tritiya Ratna (1855): A significant work in advocating for social equality.
- Brahmananche Kasab (1869): Criticized the exploitation by the Brahmin class.
- Powada: Chatrapati Shivajiraje Bhosle Yancha (1869): A work celebrating the legacy of Shivaji Maharaj.
- Satsar Ank (1885): Another rationalist work addressing societal issues.
- Akhandadi Kavyarachana: A literary contribution reflecting Phule’s thoughts on social justice.
| [UPSC 2016] Satya Shodhak Samaj organized:
(a) a movement for the upliftment of tribals in Bihar’
(b) a temple-entry movement in Gujarat
(c) an anti-caste movement in Maharashtra
(d) a peasant movement in Punjab |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
A recent study conducted in Kolkata shows that the toxicity value of PM2.5 experiences a sudden jump when the pollution level reaches around 70 µg/m³.
About PM2.5
- PM2.5 refers to fine particulate matter with a diameter of 2.5 micrometers or smaller.
- It is a major air pollutant linked to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. Long-term exposure increases the risk of lung cancer, heart disease, asthma, and other health issues.
- Major sources include vehicle exhaust, industrial emissions, construction dust, biomass burning, and solid waste burning, contributing to both outdoor and indoor pollution.
- WHO recommends that the annual average PM2.5 concentration should NOT exceed 5 µg/m³, and the 24-hour average should not exceed 15 µg/m³ for more than 3-4 days per year.
PM2.5 on Govt. Focus: National Clean Air Program (NCAP)
- Launched in 2019 by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC), the NCAP aims to reduce particulate matter by 40% by 2026 compared to 2017 levels.
- It targets 131 non-attainment cities across India, focusing on improving air quality and addressing sources of pollution.
|
About the Notified Toxicity Standard for PM2.5
- A new toxicity standard for PM2.5 in Kolkata sets the critical threshold at 70 µg/m³.
- Below this level, toxicity remains stable, but it sharply increases once the concentration exceeds 70 µg/m³.
- It emphasizes reducing pollution sources, particularly biomass and solid waste burning, which contribute significantly to high PM2.5 levels and increased toxicity in Kolkata.
- Policy Recommendation: To reduce health risks, air quality control measures should aim to keep PM2.5 levels below 70 µg/m³.
| [UPSC 2022] In the context of WHO Air Quality Guidelines, consider the following statements:
1. The 24-hour mean of PM2.5 should not exceed 15 µg/m3 and annual mean of PM2.5 should not exceed 5 µg/m3.
2. In a year, the highest levels of ozone pollution occur during the periods of inclement weather.
3. PM10 can penetrate the lung barrier and enter the bloodstream.
4. Excessive ozone in the air can trigger asthma.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 3 and 4 (b) 1 and 4 only (c) 2, 3 and 4 (d) 1 and 2 only |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now










