Why in the News?
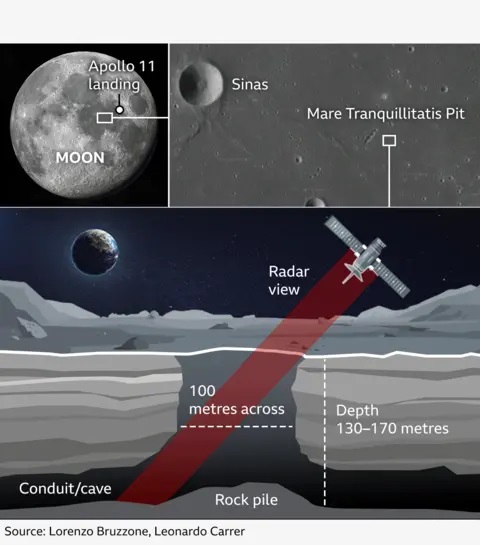
- Scientists have confirmed the presence of a cave on the Moon, near the site of the first lunar landing 55 years ago.
- This discovery could provide astronauts with a potential habitat on the Moon in the future.
About the Cave on Mare Tranquillitatis
- A study titled “Radar evidence of an accessible cave conduit on the Moon below the Mare Tranquillitatis pit” was published in the journal Nature Astronomy.
- The study established the presence of a moon cave at the Sea of Tranquillity, a large, dark, basaltic plain on the Moon’s surface.
- The cave is located 400 kilometers from where astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin landed in 1969.
- It is roughly 45 meters wide and up to 80 meters long, with an area equivalent to 14 tennis courts.
Research Method
- Researchers analyzed photos taken in 2010 by NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) spacecraft.
- They concluded that the pit was the entry point to a cave created by the collapse of a lava tube, a tunnel formed when molten lava flows beneath a field of cooled lava.
Back2Basics: Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO)
|
Characteristics of Lunar Caves
- Craters are bowl-shaped and result from asteroid or comet strikes.
- Pits, in contrast, appear as massive steep-walled depressions.
- At least 200 such pits have been discovered, with 16 believed to have formed from collapsed lava tubes due to volcanic activity over a billion years ago.
Benefits for Human Exploration
- The Moon is exposed to solar radiation 150 times stronger than Earth.
- The lunar surface heats to about 127 degrees Celsius during the day and cools to around -173 degrees Celsius at night.
- Caves, however, maintain stable average temperatures of around 17 degrees Celsius.
- They could shield human explorers from radiation and micrometeorites, making them viable for future lunar bases or emergency shelters.
Challenges and Further Research
- The depth of such caves could present challenges for accessibility.
- There are risks of potential avalanches and cave-ins.
Need for Further Research
- Further research is needed to understand and map the structural stability of the caves.
- This could be done using ground-penetrating radar, robots, or cameras.
- To become viable habitats, caves would need systems to monitor movement or seismic activity and safety zones for astronauts in case of a cave collapse.
PYQ:[2008] Selene-1, the lunar orbiter mission belongs to which one of the following? (a) China (b) European Union (c) Japan (d) USA |