Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Madhuca diplostemon
Mains level: Not Much

A tree species, long believed extinct, has been rediscovered after a gap of more than 180 years from a sacred grove in Kollam district.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Consider the following statements:
- Biodiversity hotspots are located only in tropical regions.
- India has four biodiversity hotspots i.e., Eastern Himalayas, Western Himalayas, Western Ghats and Andaman and the Nicobar Islands.
Which of the above statements is/ are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Madhuca diplostemon
- Scientists have identified the tree as Madhuca diplostemon (family Sapotaceae), a threatened species of the Western Ghats whose specimen was first collected in 1835.
- In 1835, Robert Wight, a surgeon-botanist with the East India Company, had collected three specimens of the species.
- Only one mature tree has been found so far, which makes this remarkable rediscovery extremely valuable from a scientific, environmental and conservation point of view.
- Since the species is represented only by one specimen in a single locality, it is eligible to be categorised ‘Critically Endangered’ by the IUCN.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Kaling frog and its habitat
Mains level: Western Ghats and its biodiversity richness

Indian scientists have reported a first-of-its-kind discovery of morphological phenotypic plasticity (MPP) in the Kalinga cricket frog.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Consider the following statements:
- Biodiversity hotspots are located only in tropical regions.
- India has four biodiversity hotspots i.e., Eastern Himalayas, Western Himalayas, Western Ghats and Andaman and the Nicobar Islands.
Which of the above statements is/ are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Kalinga Frog
- The Kalinga Frog (Fejervarya Kalinga) was recently identified species which was documented in 2018.
- The species was encountered several times during field expeditions in the Western Ghats. However, the physical characteristics vary entirely from the known species of Eastern Ghats.
- However, it has been reported from the central Western Ghats, with the evidence of considerable MPP.
- It was the only genetic analysis that helped prove that physically different-looking frogs from eastern and western ghats were the same.
What is MPP?
- The morphological phenotypic plasticity (MPP) is the ability of an organism to show drastic morphological (physical features) variations in response to natural environmental variations or stimuli.
- The term “phenotype” refers to the observable physical properties of an organism, which include the organism’s appearance, development, and behaviour.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Project Dolphin
Mains level: NA

In his Independence Day Speech this year, PM has announced the government’s plan to launch a Project Dolphin. The proposed project is aimed at saving both river and marine dolphins.
Project Dolphin
- The Project will be on the lines of Project Tiger, which has helped increase the tiger population.
- So far, the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG), which implements the government’s flagship scheme Namami Gange, has been taking some initiatives for saving dolphins.
- Now, Project Dolphin is expected to be implemented by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
About Gangetic Dolphin
- The Gangetic river system is home to a vast variety of aquatic life, including the Gangetic dolphin (Platanista gangetica).
- It is one of five species of river dolphin found around the world.
- It is found mainly in the Indian subcontinent, particularly in Ganga-Brahmaputra-Meghna and Karnaphuli-Sangu river systems.
- An adult dolphin could weigh between 70 kg and 90 kg. The breeding season of the Gangetic dolphin extends from January to June.
- They feed on several species of fishes, invertebrates etc.
Why is it important to save dolphins?
- The construction of dams and barrages and increasing pollution has led to a decline in the population of aquatic animals in the rivers in general and of dolphins in particular.
- Aquatic life is an indicator of the health of river ecosystems.
- As the Gangetic dolphin is at the top of the food chain, protecting the species and its habitat will ensure
Aquatic life as an indicator of the health of a river system
- Globally, there have been such examples. For instance, the Rhine Action Plan (1987) of the International Commission for the Protection of the Rhine (ICPR) brought back the salmon.
- The return of the migratory fish is taken as an indicator of the river’s improved health.
- Salmon used to migrate from the North Sea to the Rhine every year and reproduce, but this stopped when pollution increased in the river.
- After a chemical accident in 1986 that caused the death of fish and microorganisms, the Action Plan was launched.
- This led to an improvement in the quality of the river water, and the salmons began to return.
What has been done to save Gangetic dolphins so far?
- Although efforts to save them were started in the mid-1980s, the estimates suggest the numbers have not risen as a result.
- The Gangetic dolphin remains listed as Endangered by the IUCN.
- After the launch of Ganga Action Plan in 1985, the government on November 24, 1986, included Gangetic dolphins in the First Schedule of the Indian Wildlife (Protection), Act 1972.
- This was aimed at checking hunting and providing conservation facilities such as wildlife sanctuaries. For instance, Vikramshila Ganges Dolphin Sanctuary was established in Bihar under this Act.
Conservation so far
- The government has prepared The Conservation Action Plan for the Ganges River Dolphin 2010-2020.
- It identified threats to Gangetic Dolphins and impact of river traffic, irrigation canals and depletion of prey-base on Dolphins populations.
- On October 5, 2009, the then PM declared the Gangetic river dolphin as the national aquatic animal.
- A notification was issued by the MoEFCC the following year. Now, the National Mission for Clean Ganga celebrates October 5 as National Ganga River Dolphin Day.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Barn Owl
Mains level: Not Much

With a thriving rat population playing havoc with its coconut yield, the UT of Lakshadweep hires barn owls for help.
Try this PYQ:
Q.The Red Data Books published by the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) contains lists of:
- Endemic plant and animal species present in the biodiversity hotspots.
- Threatened plant and animal species.
- Protected sites for conservation of nature and natural resources in various countries.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 3
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 only
Barn Owl
IUCN status: Least Concerned
- The barn owl is the most widely distributed species of owl in the world and one of the most widespread of all species of birds.
- It is found almost everywhere in the world except for the polar and desert regions, Asia north of the Himalayas, most of Indonesia, and some Pacific islands.
What is Barn?
- A barn is an agricultural building usually on farms and used for various purposes.
- It refers to structures that house livestock, including cattle and horses, as well as equipment and fodder, and often grain.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Indian Peafowl
Mains level: Wildlife conservation and various policy efforts

This newscard is an excerpt from the original article published in the D2E.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Which one of the following is the national aquatic animal of India? (CSP 2015)
(a) Saltwater crocodile
(b) Olive ridley turtle
(c) Gangetic dolphin
(d) Gharial
Indian Peafowl
- The Indian peafowl is a native of India and some parts of Pakistan and Sri Lanka.
- The Arakan hills prevented their spread further east while the Himalayas and the Karakoram did so northwards.
- As our national bird, the peacock has the utmost level of legal protection.
Peacock vs. Peafowl
- Only the males of the species are peacocks.
- The females are properly called peahens, while young birds less than a year old are known as peachicks.
- Collectively they are known as peafowl, regardless of age or gender.
- Peacocks are male Indian peafowl (Pavo cristatus) belonging to the Phasianidae family
Various protections
- It comes under Section 51 (1-A) of Schedule I of the Wild (Life) (Protection) Act, 1972, with imprisonment that may be extended up to seven years, along with a fine that shall not be less than Rs 10,000.
- Since 2014, Indian Peafowl has been protected under Appendix III of the CITES.
- They are listed under the ‘Least Concern’ (LC) category of the IUCN Red Data List.
Threats
- Despite this, these birds experienced dwindling populations for many decades due to habitat loss, poaching and contamination of their food sources.
- In 1991, the peafowl population census conducted by the WWF revealed that 50 per cent of the species had declined, compared to their number at the time of independence.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Dhole and thier significance
Mains level: Wildlife conservation and various policy efforts

Karnataka, Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh rank high in the conservation of dhole in India, according to a new study.
Dhole
- The dhole is a canid native to Central, South, East Asia, and Southeast Asia.
- India perhaps supports the largest number of dholes, with key populations found in three landscapes — Western Ghats, Central India and Northeast India.
- It is a highly social animal, living in large clans without rigid dominance hierarchies and containing multiple breeding females.
- It is listed as ‘Endangered’ by the IUCN as populations are decreasing and are estimated at fewer than 2,500 adults.
- Factors contributing to this decline include habitat loss, loss of prey, competition with other species, persecution due to livestock predation and disease transfer from domestic dogs.
Their significance
- Dholes play an important role as apex predators in forest ecosystems.
- Besides the tiger, the dhole is the only large carnivore in India that is under IUCN’s ‘endangered’ category.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Hoolock Gibbons
Mains level: Wildlife conservation and various policy efforts

Hoolock Gibbons, the only species of apes found in India, are threatened with extinction in the Ukhrul and Kamjong districts of Manipur, a report has claimed.
Try this PYQ from CSP2013:
Q.Consider the following pairs:
Protected area:: Well-known for
- Bhitarkanika, Orissa:: Salt Water Crocodile
- Desert National Park, Rajasthan:: Great Indian Bustard
- Eravikulam, Kerala:: Hoolock Gibbon
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Hoolock Gibbons
- The two districts used to be covered with dense, tropical rainforests, which provided ideal tree canopies for the arboreal, brachiating ape species.
- Rampant deforestation for timber, forest fires and indiscriminate hunting had led to the decline in their population.
- Without the tree canopies, the gibbons cannot swing from branch to branch and stake out their territories.
- They also cannot adapt to living on the ground and cannot bear the high temperatures brought about by the loss of green cover.
Conservation status (a/c to WWF India)
- The gibbon has a much wider range, as it is found in all the states of the north-east, restricted between the south of the Brahmaputra River and east of the Dibang River.
- Outside India, it is found in eastern Bangladesh and north-west Myanmar.
- The eastern hoolock gibbon inhabits specific pockets of Arunachal Pradesh and Assam in India, and southern China and north-east Myanmar.
- Of the two, the western hoolock is listed as Endangered in the IUCN Redlist, while the eastern hoolock is listed as Vulnerable.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bats and thier natural role
Mains level: Illict wildlife trade and its prevention
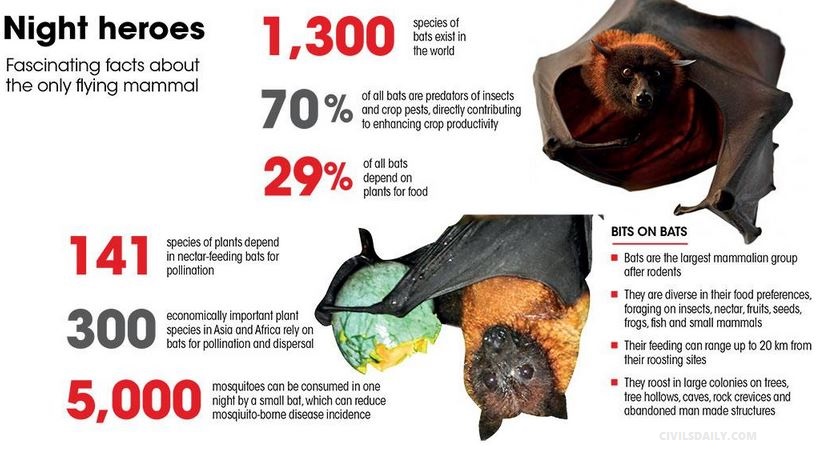
The COVID pandemic has magnified our fear of bats, but their conservation is crucial to prevent such events from arising again.
Try this PYQ from CSP 2014:
Q.Consider the following:
- Bats
- Bears
- Rodents
The phenomenon of hibernation can be observed in which of the above kinds of animals?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) Hibernation cannot be observed in any of the above
Bats
- Bats are the largest mammalian group after rodents, with over 1,300 species making up a quarter of all mammals.
- They occur on all continents except Antarctica and are particularly diverse in South Asia, with 114 species of insect-eating bats and 14 fruit bats, also known as “flying foxes”, occurring in India.
- They roost in large colonies on trees, tree hollows, caves, rock crevices and abandoned manmade structures.
- They play a unique role in maintaining ecosystem structure, making a singular contribution to our food production, economy and well-being.
- They are the only mammals capable of true flight and have a unique sonar-based echolocation mechanism to capture prey at night.
Their significance
1) Seed dispersal
- About 29 per cent of all bats depend upon plants for food.
- The diet of fruit-eating bats consists largely of flowers and fruits such as mangoes, bananas, guavas, custard apples, figs, tamarind and many species of forest trees.
- Therefore, bats play a vital role in seed dispersal and forest regeneration. Studies have shown that seedlings raised from bat dispersed seeds show higher germination and vigorous growth.
2) Pollination
- Studies have found that bats play a vital role in pollination, mainly of large-flowered plants, and in crop protection.
- Fruit bats (Megachiroptera) being large, require big flowers with copious amounts of nectar.
- Bats are major pollinators for many species of mangroves which are important for coastal ecosystems and local livelihoods.
3) Production boost
- Insects are a major problem for agriculture, destroying up to 26 per cent of the annual production of crops worldwide every year, roughly amounting to $470 billion.
- Insectivorous bats, which make up 70 per cent of all bat species, are voracious predators of nocturnal insects and crop pests.
- Some large insectivorous bats are also reported to feed on small rodents. Thus they contribute directly to enhancing the crop productivity with tremendous economic impact.
4) Soil fertility
- Bats contribute significantly to soil fertility and nutrient distribution due to their large numbers, high mobility and varied habitats for roosting and foraging.
- Bat droppings provide organic input to soil and facilitate nutrient transfer, contributing to soil fertility and agricultural productivity. The practice is harmless vis-a-vis human health.
5) Health benefits
- Several species of bats, in fact, contribute to human health by reducing populations of mosquitoes and other insect vectors that spread malaria, dengue, chikungunya and other diseases.
- It is reported that a small bat may feed on almost 5,000 mosquitoes each and every feeding night far more than other measures adopted to eliminate them.
Their conservation
- According to the IUCN, about 5 per cent of bats are categorised as endangered and another 11 per cent are data deficient.
- Further, some species of fruit bats are categorised under Schedule 5 of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1973, along with other vermin species like rats, making it difficult to legally conserve them.
Conclusion
- The pandemic has demonstrated that conservation of biodiversity and natural habitats is absolutely essential to prevent such events from arising again.
- Understanding the role played by bats helps us appreciate how their absence can greatly affect all facets of our lives.
- Viruses don’t jump directly from bats or other animals to humans.
- Rather, illicit trade in wildlife, high levels of hunting for the consumption of wild meat, and destruction of natural habitats are responsible for this.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bathynomus Raksasa
Mains level: NA

A team of researchers has discovered a supergiant cockroach when they explored waters of the Indian Ocean in Bantan, off the southern coast of West Java in Indonesia.
Try this MCQ:
Q.The ‘Bathynomus Raksasa’, a species recently discovered is basically a:
a) Mollusc
b) Annelid
c) Arthropod
d) Flagella
Bathynomus Raksasa
- The Bathynomus raksasa is a giant isopod (phylum: Arthropoda) in the genus Bathynomus.
- It is described as the “cockroach of the sea”. The epithet is the Indonesian word “raksasa” for giant, alluding to its enormous size.
- The giant isopods are distantly related to crabs, lobsters, and shrimps (which belong to the order of decapods), and are found in the cold depths of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans.
- It has 14 legs but uses these only to crawl along the bed of oceans in search of food.
- As a scavenger, Bathynomus raksasa eats the remains of dead marine animals, such as whales and fish, but can also go for long periods without food, a trait that it shares with the cockroach.
Why this cockroach matters?
- Bathynomus raksasa is the sixth ‘supergiant’ species from the Indo-West Pacific and is one of the largest known members of the genus.
- The discovery takes the number of known giant isopods to 20.
- As the Bathynomus raksasa reveals its secrets, it will contribute towards increasing knowledge about the deep.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Migration of Pied Cuckoo and its association with Indian monsoon onset
Mains level: NA

A new project by a number of agencies is using advancements in nanotechnology to study migratory patterns of the Pied Cuckoo.
This specie carries an unusual importance compared to other IUCN species. Go through this newscard to read more about it.
Pied Cuckoo
- There are basically three subspecies of the Pied Cuckoo of which one is resident in Africa while another is resident in South.
- The third is a migrant moving between India and Africa.
- The Pied Cuckoo is famous in North Indian folklore as ‘chatak’, a bird that quenches its thirst only with raindrops.
- From Southern Africa, it comes to the Himalayan foothills stretching from Jammu to Assam to breed every year. The birds come to the same localities every year.
- It is also a brood parasite in that it does not make its own nest and instead lays its egg in the nest of other birds, particularly the Jungle Babbler.
About the Study
- The project is a joint effort by the Wildlife Institute of India, Dehradun and the Indian Institute of Remote Sensing (IIRS), which comes under the Indian Space Research Organisation or ISRO.
- The Pied Cuckoo migration study is part of a larger project — Indian Bioresource Information portal (IBIN) funded by the Department of Biotechnology under the Union Ministry of Science and Technology.
- It aims to deliver relevant bioresources (plant, animal and other biological organisms) information of India through a web portal.
- The project aims to assess the likely impacts of projected climate change on the potential distribution of Pied Cuckoo in the altered climate change scenarios.
Why study Pied Cuckoo?
- It is closely linked with the arrival of the south-west monsoon in India.
- It moves to India during the summer.
- Being a small, terrestrial bird, a sea crossing holds a lot of risk for this cuckoo.
- Before it migrates back to its home in the southern African region, by flying over the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean, it must be stopping somewhere.
- It is these stopovers that researchers want to find out about.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Cestrum nocturnum
Mains level: Invasive alien species

Nilgiris forest officials are restoring native Shola habitats in places overrun by the invasive species ‘Cestrum nocturnum’.
Try this PYQ from CSP 2018:
Q.Why is a plant called Prosopis juliflora often mentioned in the news?
(a) Its extract is widely used in cosmetics.
(b) It tends to reduce the biodiversity in the area in which it grows
(c) Its extract is used in the pesticides.
(d) None of the above
Cestrum nocturnum
- Cestrum nocturnum is commonly known by the names night-blooming jasmine and raatrani.
- It is native to the West Indies but naturalized in South Asia.
- Its spread is a threat to all Shola and grassland habitats as it does not allow any native flora to thrive.
- The plants unless completely removed with their roots, keep sprouting and keep taking over Shola and native grasslands.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Golden Birdwing
Mains level: NA

A Himalayan butterfly named golden birdwing is now India’s largest recorded butterfly.
Try this MCQ:
Q.The Himalayan Golden Birdwing recently seen in news is a:
a)Biggest butterfly
b)Smallest avian specie
c)Biggest freshwater fish
d)Honeybee
Golden Birdwing
- A Himalayan butterfly named golden birdwing is now India’s largest, a record the southern birdwing held for 88 years.
- The male golden birdwing is much smaller at 106 mm.
- With a wingspan of 194 mm, the female of the species is marginally larger than the southern birdwing (190 mm) that Brigadier William Harry Evans, a British military officer and lepidopterist, recorded in 1932.
- It was an individual of the southern birdwing which was then treated as a subspecies of the common birdwing.
Other butterflies in news
- The Malabar Banded Peacock or the Buddha Mayoori which was recently declared the ‘State Butterfly’ of Kerala will have a dedicated butterfly park in Kochi.
- Tamil Nadu has also recently declared Tamil Yeoman (Cirrochroa Thais)as its state butterfly to symbolise its rich natural and cultural heritage, in a move aimed at boosting the conservation efforts of the attractive insects.
- Other states to have state butterflies are Maharashtra (Blue Mormon), Uttarakhand (Common peacock), Karnataka (Southern birdwings).
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Species in news: Globba Andersonii Plant
Mains level: NA

A team of researchers have “rediscovered” a rare species called Globba andersonii from the Sikkim Himalayas near the Teesta River valley region after a gap of nearly 136 years.
Try this question from CSP 2016:
Q.With reference to ‘Red Sanders’, sometimes seen in the news, consider the following statements:
- It is a tree species found in a part of South India.
- It is one of the most important trees in the tropical rain forest areas of South India.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Globba Andersonii
IUCN status: Critically Endangered
- Globba andersonii is characterised by white flowers, non-appendaged anthers (the part of a stamen that contains the pollen) and a “yellowish lip”.
- The plant, known commonly as ‘dancing ladies’ or ‘swan flowers’ was thought to have been extinct until its “re-collection”, for the first time since 1875.
- The earliest records of the collection of this plant were dated between the period 1862-70 when it was collected by Scottish botanist Thomas Anderson from Sikkim and Darjeeling.
- Then, in 1875, the British botanist Sir George King, had collected this taxon from the Sikkim Himalayas.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Golden Langur
Mains level: NA

Primatologists have observed that the Gee’s golden langur (Trachypithecus geei) induce stillbirth of babies killed inside the womb of females, besides practising infanticide.
Try this question from CSP 2013:
Q. In which of the following States is lion-tailed macaque found in its natural habitat?
- Tamil Nadu
- Kerala
- Karnataka
- Andhra Pradesh
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
a) 1, 2 and 3 only
b) 2 only
c) 1, 3 and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Golden Langurs
IUCN status: Endangered
- It is an Old World monkey found in a small region of western Assam, and in the neighbouring foothills of the Black Mountains of Bhutan.
- Long considered sacred by many Himalayan people, the golden langur was first brought to the attention of the western world by the naturalist E. P. Gee in the 1950s.
- Their habitat lies in the region, south of the Brahmaputra River, on the east by the Manas River, on the west by the Sankosh River, all in Assam, India, and on the north by the Black Mountains of Bhutan
- Chakrashila WLS in Assam is India’s first wildlife sanctuary with golden langur as the primary species.
- They are listed in Appendix I of CITES and Schedule I of Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Horseshoe Crab
Mains level: NA

Horseshoe crabs face an uncertain future in Odisha, their largest habitat in India, even as the world gets ready to celebrate the first-ever ‘International Horseshoe Crab Day’ on June 20, 2020.
Try this question from CSP 2012:
Q. Which one of the following groups of animals belongs to the category of endangered species?
(a) Great Indian Bustard, Musk Deer, Red Panda and Asiatic Wild Ass
(b) Kashmir Stag, Cheetal, Blue Bull and Great Indian Bustard
(c) Snow Leopard, Swamp Deer, Rhesus Monkey and Saras (Crane)
(d) Lion-tailed Macaque, Blue Bull, Hanuman Langur and Cheetal
Horseshoe Crabs
IUCN status: (Data insufficient for the Indian variant)
- Horseshoe crabs are marine and brackish water arthropods. They are not true crabs, which are crustaceans.
- The crabs are represented by four extant species in the world. Out of the four, two species are distributed along the northeast coast of India.
- Only T gigas species of the horseshoe crab is found along Balasore coast of Odisha.
- The crab was included on September 9, 2009, in the Schedule IV of the Wild (Life) Protection Act, 1972, under which, the catching and killing of a horseshoe crab is an offence.
Their significance
- The horseshoe crab is one of the oldest marine living fossils whose origin date back to 445 million years before the dinosaurs existed.
- One of their ecological functions is to lay millions of eggs on beaches to feed shorebirds, fish and other wildlife.
Threats
- Poachers kill them for their meat that is popularly believed to have aphrodisiac qualities.
- The blood of horseshoe crabs, which is blue in colour, is used for detection of bacterial endotoxins in medical applications.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Hilsa Fish`
Mains level: NA

Fishermen in West Bengal are in for a pleasant surprise amid the COVID-19 gloom as they have exuded hope of a bumper yield of Hilsa, known as “maacher rani” (queen of fish).
Try this question from CSP 2019:
Q. Consider the following pairs:
| Wildlife |
Naturally found in |
| 1. Blue-finned Mahseer |
Cauvery River |
| 2. Irrawaddy Dolphin |
Chambal River |
| 3. Rusty-spotted Cat |
Eastern Ghats |
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Hilsa Fish
IUCN status: Least Concerned
- The Hilsa is a species of fish related to the herring, in the family Clupeidae.
- It is a very popular and sought-after food fish in the Indian Subcontinent.
- It is the national fish of Bangladesh and state symbol in the Indian states of West Bengal and Tripura.
- The fish contributes about 12% of the total fish production and about 1.15% of GDP in Bangladesh.
What’s so special about Hilsa?
- Hilsa has a history of migrating to Allahabad in the Ganga river system from Bangladesh.
- Though it’s a saltwater fish, it migrates to sweet waters of the Ganges from the Bay of Bengal.
- It travels upstream of the river during the mating seasons and returns to its natural abode after spawning.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Poonam Awalokan
Mains level: Man-Animal conflict

Asiatic lions have now significantly risen in number at an estimated population of 674 in the Gir forest region of Gujarat. Unlike in previous years, this count was estimated not from a Census, but from a population “observation” exercise called Poonam Avlokan.
Try this question from CSP 2017:
Q. The term ‘M-STrIPES’ is sometimes seen in the news in the context of
(a) Captive breeding of Wild Fauna
(b) Maintenance of Tiger Reserves
(c) Indigenous Satellite Navigation System
(d) Security of National Highways
Asiatic Lion
- Indian Lion (Panthera Leo Persica) is listed as Endangered and exists as a single population in Gujarat.
- It is one of five big cat species found in India and Gir National Park and Wildlife Sanctuary is the only habitat for Asiatic lions.
- Historically, it inhabited much of Western Asia and the Middle East up to northern India.
- On the IUCN Red List, it is listed under its former scientific name Panthera leo persica as Endangered because of its small population size and area of occupancy.
- More than two dozen lions died last year in an outbreak of canine distemper virus (CDV) and Babesiosis.
What is Poonam Avlokan?
It includes two methods:
- Block counting method — in which census enumerators remain stationed at water points in a given block and estimate abundance of lions in that block, based on the direct sighting of lions who need to drink water at least once in 24 hours during the summer.
- Other teams keep moving in their respective territories and make their estimates based on inputs provided by lion trackers and on chance sightings.
Back2Basics: Lion Census in India
- The first Lion Census was conducted by the Nawab of Junagadh in 1936; since 1965, the Forest Department has been regularly conducting the Lion Census every five years.
- The 6th, 8th and 11th Censuses were each delayed by a year, for various reasons.
- This year it was postponed after the lockdown was announced.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Pashmina Goats
Mains level: NA

The Chinese Army’s intrusion in Chumur and Demchok has left Ladakh’s nomadic herding Changpa community cut off from large parts of summer pastures.
Pashmina shawl is a landmark product of the Kashmir Valley. But make a note here. It carries only a BIS certification and not a Geographical Indicator.
Also try this PYQ from CSP 2014:
Q. With reference to ‘Changpa’ community of India, consider the following statement:
1. They live mainly in the State of Uttarakhand.
2. They rear the Pashmina goats that yield fine wool.
3. They are kept in the category of Scheduled Tribes.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Changpa Tribes
- The Changpa of Ladakh is high altitude pastoralists, raising mainly yaks and goats.
- Among the Ladakh Changpa, those who are still nomadic are known as Phalpa, and they take their herds from in the Hanley Valley to the village of Lato.
- Hanley is home to six isolated settlements, where the sedentary Changpa, the Fangpa reside.
- Despite their different lifestyles, both these groups intermarry.
- The Changpa speak Changskhat, a dialect of Tibetan, and practice Tibetan Buddhism.
What is the issue?
- The Chinese Army has taken over 16 kanals (two acres) of cultivable land in Chumur and advanced around 15 km inside Demchok, taking over traditional grazing pastures and cultivable lowlands.
- In a cascading effect, this has resulted in a sharp rise in deaths of young Pashmina goats this year in the Korzok-Chumur belt of Changthang plateau in Ladakh.
- This incursion has destabilized the annual seasonal migration of livestocks, including yaks and Pashmina goats.
Back2Basics: Pashmina
- The Changthangi or Ladakh Pashmina is a breed of Cashmere goat native to the high plateau of Ladakh.
- The much-valued wool from the Ladakh herds is essential for the prized Pashmina shawls woven in Kashmir and famous for their intricate handwork.
- They survive on the grass in Ladakh, where temperatures plunge to as low as −20 °C.
- These goats provide the wool for Kashmir’s famous pashmina shawls. Shawls made from Pashmina wool are considered very fine and are exported worldwide.
- Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) has recently published an Indian Standard for identification, marking and labelling of Pashmina products to certify its purity.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Cordyceps militaris
Mains level: NA

A university in Assam has developed a fungal powder to help people boost their immunity to disease.
Try this question from CSP 2019:
Q.) Recently, there was a growing awareness in our country about the importance of Himalayan nettle (Girardinia diversifolia) because it is found to be a sustainable source of
(a) anti-malarial drug
(b) bio-diesel
(c) pulp for paper industry
(d) textile fibre
A similar question related to Cordyceps militaris can be asked. UPSC may ask whether it is a Fungi, Algae, a Moss or a Lichen.
Cordyceps militaris
- The powder is from a parasitic but rare “super mushroom” called Cordyceps militaris.
- The militaris underwent powdering through lyophilisation or freeze-drying at –80°C.
- The earth has more than 400 species of Cordyceps, a fungus parasitic on insects as well as other fungi.
- Often referred to as a super mushroom, Cordyceps known for its anti-ageing, anti-viral, energy and immunity-boosting effect.
- Natural Cordyceps is hard to get and if dried, costs at least ₹8 lakh per kg.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Charru mussel
Mains level: NA

An invasive mussel native to the South and Central American coasts is spreading quickly in the backwaters of Kerala.
Try this PYQ from CSP 2018:
Q. Why is a plant called Prosopis juliflora often mentioned in news?
(a) Its extract is widely used in cosmetics.
(b) It tends to reduce the biodiversity in the area in which it grows
(c) Its extract is used in the pesticides.
(d) None of the above
Charru mussel
- The rapid spread of the Charru mussel (Mytella strigata) may have been triggered by Cyclone Ockhi which struck the region in 2017.
- With a population as high as 11,384 per sq metre here, it has replaced the Asian green mussel (Perna Viridis) and the edible oyster Magallana bilineata (known locally as muringa).
- Externally, the Charru mussel resembles the green and brown mussels (kallummekka in Malayalam) but is much smaller in size. Its colour varies from black to brown, purple or dark green.
- Surveys show the presence of the Charru mussel in the Kadinamkulam, Paravur, Edava-Nadayara, Ashtamudi, Kayamkulam, Vembanad, Chettuva and Ponnani estuaries/backwaters.
- Ashtamudi Lake, a Ramsar site in Kollam district, remains the worst-hit.
Threats posed
- Though this smaller mussel is edible, the overall economic loss and impact on biodiversity are much bigger, it is pointed out.
- It is throwing out other mussel and clam species and threatening the livelihoods of fishermen engaged in shrimp fisheries.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now




















