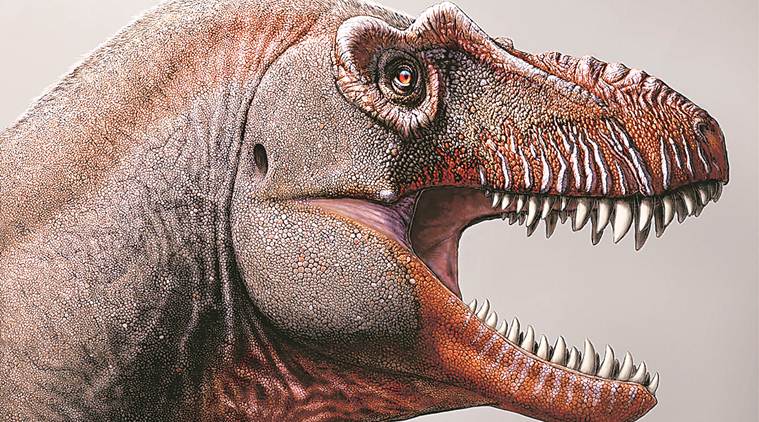Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Various species mentioned
Mains level: Western Ghats and its biodiversity richness
A team of scientists of the Botanical Survey of India (BSI) have reported the discovery of three new plant species from the evergreen forest patches of the southern end of the Western Ghats in Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
One may get carried away from the heavy botanical names. But UPSC is known for asking ruthless questions.
Q. Recently, our scientists have discovered new and distinct spices of banana plant which attains a height of about 11 meters and has orange – colored form of pulp. In which part of India has been discovered? (CSP 2016)
a) Andaman Islands
b) Anaimalai Forests
c) Maikala Hills
d) Tropical rainforest of North-East
Which are the new species?
The three new species found are:
1) Eugenia sphaerocarpa of the Myrtaceae or Rose apple family
- A good population of Eugenia sphaerocarpa is growing in the Kakkayam area of the Malabar wildlife sanctuary in Kerala above 800 m.
- The specific epithet ‘sphaerocarpa’ denotes to the large, showy lemon-yellow spherical fruit.
- The fruits of Eugenia species are known for their palatability and many of them are harvested from the wild with some under cultivation.
2) Goniothalamus sericeus of the Annonaceae family of custard apple
- A small number of Goniothalamus sericeus plants has been found in the Kanyakumari wildlife sanctuary in Tamil Nadu.
- Mature flowers with characteristic greenish-yellow to beige petals are fragrant while the fruits are very showy and an attractive golden yellow in colour.
- The specific epithet ‘sericeus’ refers to the presence of dense silky hair on the petals.
3) Memecylon nervosum of the Melastomataceae (Kayamboo or Kaasavu in local parlance) family
- A small population of Memecylon nervosum was also found at the same sanctuary at an altitude between 700-900 m with more that than 10 sub-populations located along the banks of a perennial rivulet.
- The species have showy purplish-blue flowers and mauve to purplish-red fruits.
- The specific epithet ‘nervosum’ alludes to the presence of prominently raised lateral and intramarginal veins on the lower surface of the lamina.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Pinanga Andamanensis
Mains level: NA

A rare palm endemic to the South Andaman Island is finding a second home at Thiruvananthapuram-based Jawaharlal Nehru Tropical Botanic Garden and Research Institute (JNTBGRI).
Last year one species from our newscard : Species in news: Hump-backed Mahseer made it into the CSP 2019. The ‘Abutilon ranadei’ flower in the newscard creates such a vibe yet again.
A stand-alone species being mentioned in the news for the first time often find their way into the prelims. Make a special note here.
Pinanga Andamanensis
- Pinanga andamanensis is an IUCN critically endangered species and one of the least known among the endemic palms of the Andaman Islands.
- The name is derived from ‘Penang’, the modern-day Malaysian state.
- Its entire population of some 600 specimens naturally occurs only in a tiny, evergreen forest pocket in South Andaman’s Mount Harriet National Park.
- It was originally described by the Italian botanist Odoardo Beccari in 1934.
- His description was based on an old herbarium specimen collected by E.H. Man, a late-19th century assistant superintendent in the Andaman administration.
- After that first identification, it was thought to be extinct till 1992.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Gharial, Mugger , Saltwater Crocodile
Mains level: Species reintroduction and various associated issues in news

Forty gharials (Gavialis gangeticus) were released in the Ghaghara River by the Bahraich forest division of Uttar Pradesh.
This year, we have seen many news focusing on species reintroduction into the wild. Can you recall them?? If not, Click Here.
And one may often get confused between the Mugger, Gharial and the Saltwater Crocodile. Note the differences about their IUCN status, habitat (freshwater/saltwater) etc..
Gharials
- The Gharial is a fish-eating crocodile is native to the Indian subcontinent. They are a crucial indicator of clean river water.
- Small released populations are present and increasing in the rivers of the National Chambal Sanctuary, Katarniaghat Wildlife Sanctuary, Son River Sanctuary.
- It is also found at the rainforest biome of Mahanadi in Satkosia Gorge Sanctuary, Orissa.
- Gharials are ‘Critically Endangered’ in the IUCN Red List of Species.
- The species is also listed under Schedule I of the Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972.
Into the wild
- A major chunk of gharials in India is found in the Chambal River, which has about 1,000 adults.
- The Ghaghara acts as an important aquatic corridor for gharials in Uttar Pradesh. The river is a major left-bank tributary of the Ganges.
- About 250 gharials have been released in the Ghaghara since 2014.
- However, there are satellite populations of less than 100 adults in the Girwa River (Katarniaghat Wildlife Sanctuary in Uttar Pradesh, the Ramganga River in Jim Corbett National Park and the Son River).
- Like Uttar Pradesh, Bihar too is releasing gharials in the Valmiki Tiger Reserve as part of restocking the wild population. Unlike crocodiles, gharials do not pose any danger to humans.
Back2Basics
Mugger
- The mugger is a marsh crocodile which is found throughout the Indian subcontinent.
- It is a freshwater species and found in lakes, rivers and marshes.
- IUCN Status: Vulnerable
Saltwater Crocodile
- It is the largest of all living reptiles.
- It is found along the eastern coast of India.
- IUCN Status: Least Concerned
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: HCQ, Quinine Nongladew
Mains level: NA
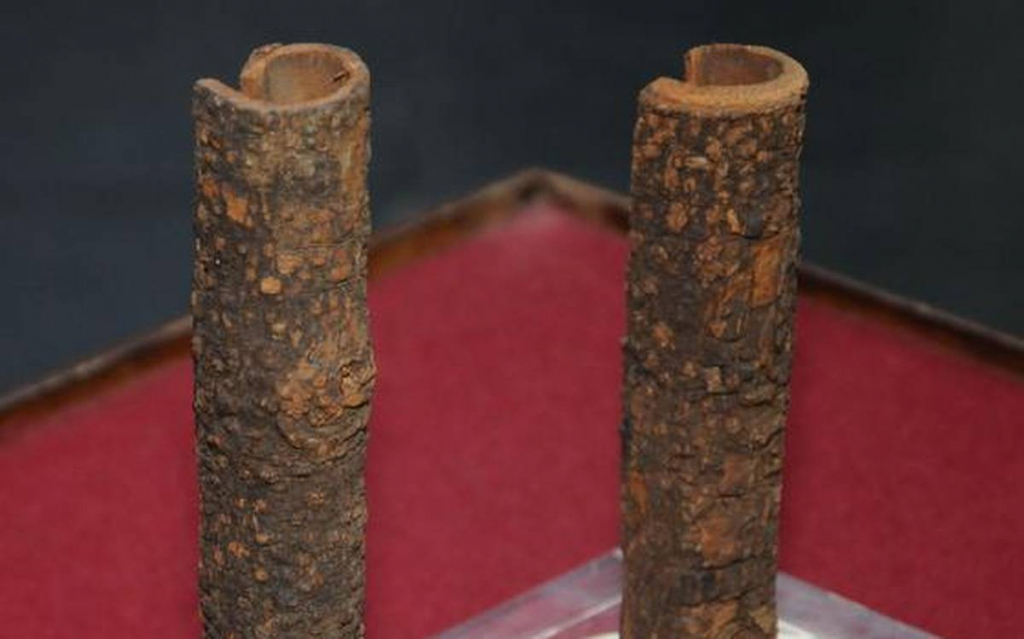

Quinine, the most primitive antimalarial avatar of Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), has made a village in Meghalaya latch on to its past for a curative future.
Relate Quinine Nongladew with the following question. Such peculiar names are very important.
Q. Recently, there was a growing awareness in our country about the importance of Himalayan nettle (Girardinia diversifolia) because it is found to be a sustainable source of (CSP 2019)
(a) anti-malarial drug
(b) bio-diesel
(c) pulp for paper industry
(d) textile fibre
Quinine Nongladew
- The herb Quinine Nongladew is the alkaloid quinine extracted from the bark of cinchona, a plant belonging to the Rubiaceae family and classified as either a large shrub or a small tree
- The tree is named after a village about 70 km south of Guwahati, on the highway to Meghalaya capital Shillong.
- The cinchona nursery was raised in the 19th century, probably around 1874, when Shillong became the British administrative headquarters for Assam Province.
- Large swathes of Meghalaya used to be, and still are, malaria-prone.
- The British had the foresight to start the plantation to combat malaria and other diseases caused by mosquitoes.
Back2Basics: Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ)
- HCQ is an oral tablet used as an anti-malarial drug. It is used to treat malaria, lupus erythematosus, and rheumatoid arthritis.
- It may be used as part of a combination therapy where it is taken with other drugs.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Trimeresurus Salazar
Mains level: Not Much

The new species, Trimeresurus Salazar is a snake been discovered in Arunachal Pradesh.
Another specie spotted with one more peculiarity, the name Salazar 🙂 Such species are most likely to be asked in prelims to match the columns with their habitat state.
Trimeresurus Salazar
- Salazar’s pit viper belongs to the genus Trimeresurus Lacépède comprising “charismatic venomous serpents with morphologically as well as ecologically diverse species”.
- Pit vipers are venomous snakes distinguished by their heat-sensing pit organs between the eye and the nostril.
- The name was inspired by Salazar Slytherin, the co-founder of J.K. Rowlings’ fictional Hogwarts School of Witchcraft and Wizardry.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Himalayan Ibex
Mains level: NA

A recent study by scientists of the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) has proved that Himalayan Ibex, distributed in the trans-Himalayan ranges of Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh and Himachal Pradesh, is a distinct species from the Siberian Ibex.
Himalayan Ibex
IUCN/WPA Status: Least Concern / Schedule I
- Himalayan Ibex (Capra ibex sibirica) is widely found in arid and rocky mountain of Karakoram, Hindukush and Himalayas of Gilgit-Baltistan.
- The males are characterized by heavy body, large horns, long bears while females have small body small horns.
- The threats that Himalayan ibex face are the illegal hunting, human disturbance, habitat loss and competition for forage with domestic livestock.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SAWEN, TRAFFIC, Red Panda
Mains level: Not Much
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/49388585/16071828377_85109fdee4_o.0.0.jpg)
According to a report by the TRAFFIC report, there has been a considerable reduction in the poaching of Red Panda (ailurus fulgens). The report also recommended trans-boundary law enforcement co-operation through the use of multi-government platforms like SAWEN (South Asia Wildlife Enforcement Network).
Red Panda
IUCN Red List Status: Endangered
- The red panda (Ailurus fulgens) is a mammal native to the eastern Himalayas and southwestern China.
- Its wild population is estimated at fewer than 10,000 mature individuals and continues to decline due to habitat loss and fragmentation, poaching, and inbreeding depression.
- Despite its name, it is not closely related to the giant panda
- The animal has been hunted for meat and fur, besides illegal capture for the pet trade.
- An estimated 14,500 animals are left in the wild across Nepal, Bhutan, India, China and Myanmar.
- About 5,000-6,000 red pandas are estimated to be present in four Indian states – Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, Sikkim and West Bengal.
- The diminishing habitat is a major threat to the species which is a very selective feeder and survives on selected species of bamboos.
About South Asia Wildlife Enforcement Network (SAWEN)
- SAWEN is a Regional network is comprised of eight countries in South Asia: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka.
- It aims at working as a strong regional intergovernmental body for combating wildlife crime by attempting common goals and approaches for combating illegal trade in the region.
- The South Asia region is very vulnerable to illegal traffic and wildlife crimes due to the presence of precious biodiversity and large markets as well as traffic routes for wildlife products in the south East Asian region.
- The collaboration in harmonizing as well as enforcing the wildlife protection in the region is considered very important for effective conservation of such precious biodiversity.
- India adopted the Statute of the SAWEN and became its formal member in 2016.
Back2Basics
TRAFFIC
- The TRAFFIC, the Wildlife Trade Monitoring Network, is a leading non-governmental organisation working on wildlife trade in the context of both biodiversity conservation and sustainable development.
- It is a joint program of World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and the IUCN.
- It aims to ensure that trade in wild plants and animals is not a threat to the conservation of nature.
- The TRAFFIC is governed by the TRAFFIC Committee, a steering group composed of members of TRAFFIC’s partner organizations, WWF and IUCN.
- TRAFFIC also works in close co-operation with the Secretariat of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES).
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Swamp Wallaby and its uniqueness
Mains level: NA

Researchers reported that the swamp wallaby, a marsupial related to the kangaroo, is pregnant throughout its adult life. It typically conceives a new embryo days before delivering the newborn from its previous pregnancy.
Swamp wallaby
IUCN Status: Least Concerned
- The swamp wallaby is a small macropod marsupial of eastern Australia. It is likely the only mammal pregnant and lactating all lifelong.
- Female wallabies and kangaroos have two uteri and two separate ovaries.
- At the end of a pregnancy in one uterus, a new embryo develops in the other uterus.
- Kangaroos and wallabies regularly have an embryo in the uterus, a young joey in the pouch, and a third semi-dependent young at foot, still drinking its mother’s milk.
How it is different from Kangaroo?
- In kangaroos, the new embryo is conceived a day or two after the previous birth.
- In the swamp wallaby (Wallabia bicolor), the new conception happens one or two days before the previous joey is delivered.
What happens after?
- As soon as the mature foetus is born and settles in the pouch, the swamp wallaby arrests the development of the new embryo.
- This is called embryonic diapause, which happens in many animals to pause reproduction until the conditions are right — season, climate, food availability.
- For wallabies, this is also to ensure that the new one is born only when the pouch is free again.
- If this did not happen, the swamp wallaby would be birthing new young every 30 days — it has a short gestation period — and its pouch could not support that.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Eurasian Otters
Mains level: NA
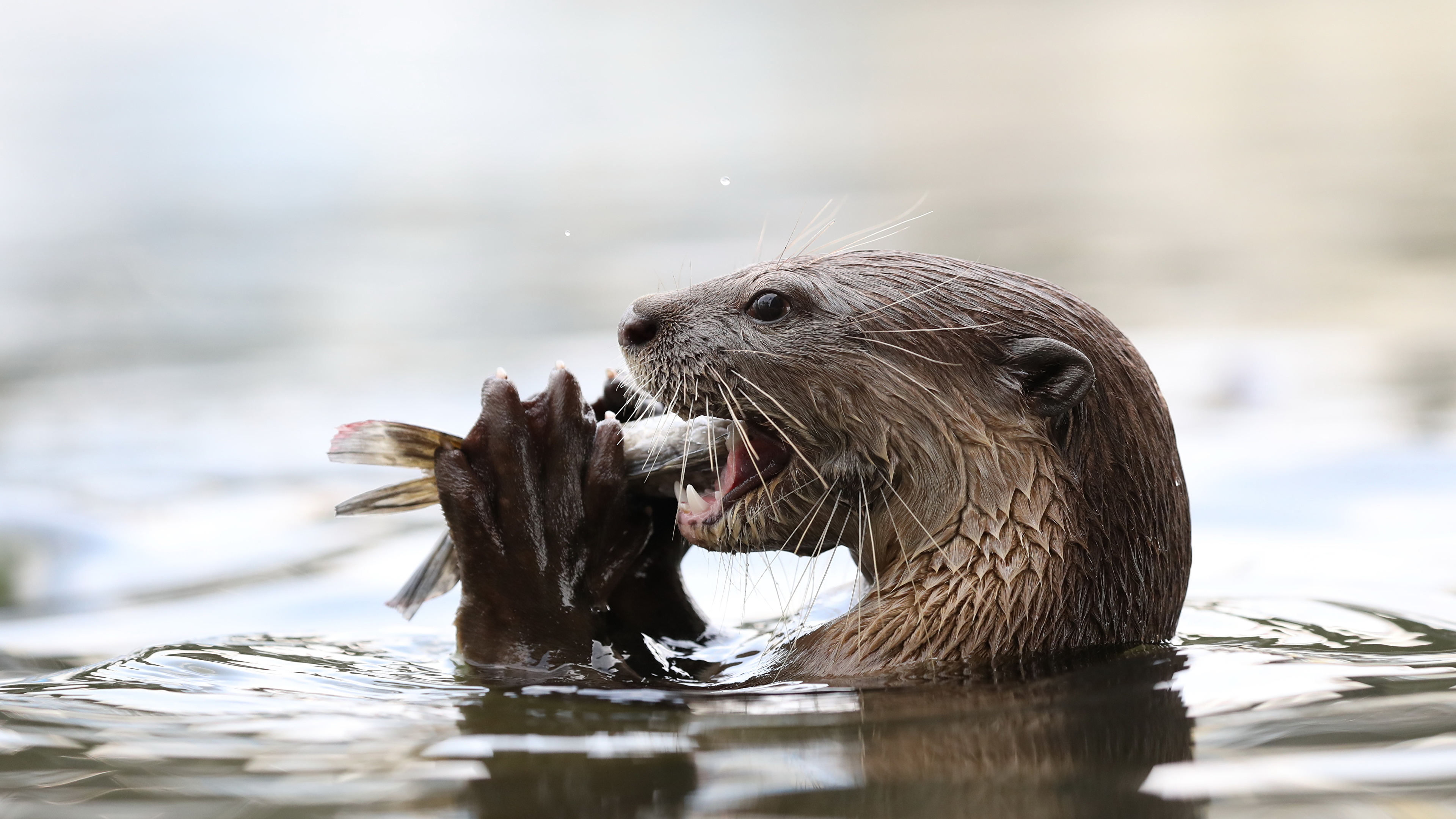

Researchers conducting a study in Odisha’s Chilika Lake have found the presence of a viable, breeding population of Eurasian Otters, a fishing cat in the brackish water lagoon.
Eurasian Otters
- IUCN Status: Near Threatened
- Species in India: Smooth-coated, Asian small-clawed and Eurasian Otters
- Habitat: Smooth-coated — all over India; Asian small-clawed — only in the Himalayan foothills, parts of the Eastern and southern Western Ghats; Eurasian — Western Ghats and Himalayas.
- Diet comprises several small animals, mainly crabs and small fishes.
- Lives in small packs, is mostly nocturnal, but can be diurnal in areas which are less disturbed.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Thanatotheristes
Mains level: Not Much
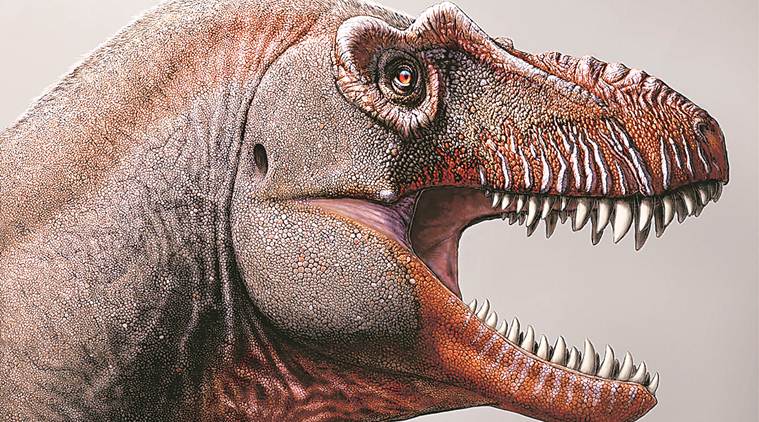
Scientists have found that a dinosaur fossil, found in Alberta in Canada in 2010, belongs to a new species of tyrannosaur. They have named it Thanatotheristes, which means “reaper of death”.
Thanatotheristes
- Tyrannosaurs were one of the largest meat-eating dinosaurs to have ever lived, with very large and high skulls, and the best known among them is the Tyrannosaurus rex, celebrated in the Jurassic Park series.
- The 79-million-year-old fossil that the researchers have found is the oldest tyrannosaur known from northern North America.
- Thanatotheristes preyed on large plant-eating dinosaurs such as the horned xenoceratops and the dome-headed colepiochephale.
- The research suggests that tyrannosaurs did not have one general body type; rather different tyrannosaur species evolved distinct body sizes, skull forms and other such physical features.
- The fossil specimen is important to understand the Late Cretaceous period, which is the period when tyrannosaurs roamed the Earth.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Flame-throated Bulbul
Mains level: NA

The flame-throated bulbul, also called the Rubigula, was chosen as the mascot of the 36th National Games to be held in Goa. It is the State bird of Goa.
Flame-throated Bulbul
IUCN status: Least Concern
- The Flame-throated Bulbul is endemic to southern peninsular India where it is locally distributed in southern Andhra Pradesh, eastern Karnataka, Goa, Orissa, eastern Kerala and northern Tamil Nadu.
- It prefer habitats like rocky, scrub-covered hills mostly in the Eastern Ghats and central peninsular India but also in some places in the Western Ghats.
- It is a Schedule – IV bird under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Natrialba Swarupiae, Sambhar Lake
Mains level: Not Much
- Scientists at the National Centre for Microbial Resource — National Centre for Cell Science (NCMR-NCCS) in Pune have reported a new archaeon (a kind of microorganism), which they discovered in Sambhar Salt Lake in Rajasthan.
- The new archaeon has been named Natrialba swarupiae, after Dr Renu Swarup, secretary, Department of Biotechnology, for her initiative in supporting microbial diversity studies in the country.
Archaea
- Archaea (singular archaeon) are a primitive group of microorganisms that thrive in extreme habitats such as hot springs, cold deserts and hypersaline lakes.
- These slow-growing organisms are also present in the human gut, and have a potential relationship with human health.
- They are known for producing antimicrobial molecules, and for anti-oxidant activity with applications in eco-friendly waste-water treatment.
- Archaea are extremely difficult to culture due to challenges in providing natural conditions in a laboratory setting.
- As archaea are relatively poorly studied, very little is known about how archaea behave in the human body.
- The organism has potential gene clusters that helps maintain the metabolism of the archaea to survive in extreme harsh conditions.
Search and discovery
- Sambhar Lake has been poorly studied for microbial ecology studies.
- With a salt production of 0.2 million tonnes per annum, it is also a hypersaline ecosystem which provides an opportunity for microbial ecologists to understand organisms that thrive in such concentrations.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Steppe Eagle
Mains level: Conservation of migratory birds in India

A lone endangered steppe eagle (Aquila nipalensis) has been sighted by a group of birdwatchers in a paddy field near Vijayawada.
Steppe Eagle
- The Steppe Eagle is a migratory raptor which has undergone extremely rapid population declines within all its range.
- It breeds in Russia, Kazakhstan, and Mongolia during the winter season.
- Steppe eagle is the second-largest migratory eagle species to India.
- IUCN Status: It has moved from ‘Least Concern’ to ‘Endangered’
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: In-vitro fertilization, White Rhinos
Mains level: Ethical issues surrounding IVF
Researchers had created another embryo — the third — of the nearly extinct northern white rhino. This is seen as a remarkable success in an ongoing global mission to keep the species from going extinct.
What is IVF?
- IVF is a type of assisted reproductive technology used for infertility treatment and gestational surrogacy.
- A fertilised egg may be implanted into a surrogate’s uterus, and the resulting child is genetically unrelated to the surrogate.
- Some countries have banned or otherwise regulate the availability of IVF treatment, giving rise to fertility tourism.
- Restrictions on the availability of IVF include costs and age, in order for a woman to carry a healthy pregnancy to term.
- IVF is generally not used until less invasive or expensive options have failed or been determined unlikely to work.
IVF process
- In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a process of fertilization where an egg is combined with sperm outside the body, in vitro (“in glass”).
- The process involves monitoring and stimulating a female ovulatory process, removing an ovum or ova (egg or eggs) from the female ovaries and letting sperm fertilise them in a liquid in a laboratory.
- After the fertilised egg (zygote) undergoes embryo culture for 2–6 days, it is implanted in the same or another female uterus, with the intention of establishing a successful pregnancy.
Types of Rhinos
- The northern white is one of the two subspecies of the white (or square-lipped) rhinoceros, which once roamed several African countries south of the Sahara.
- The other subspecies, the southern white is, by contrast, the most numerous subspecies of rhino, and is found primarily in South Africa.
- There is also the black (or hook-lipped) rhinoceros in Africa, which too, is fighting for survival, and at least three of whose subspecies are already extinct.
- The Indian rhinoceros is different from its African cousins, most prominently in that it has only one horn.
- There is also a Javan rhino, which too, has one horn, and a Sumatran rhino which, like the African rhinos, has two horns.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: IUCN , Red List, Chinese paddlefish
Mains level: IUCN mechanism of listing
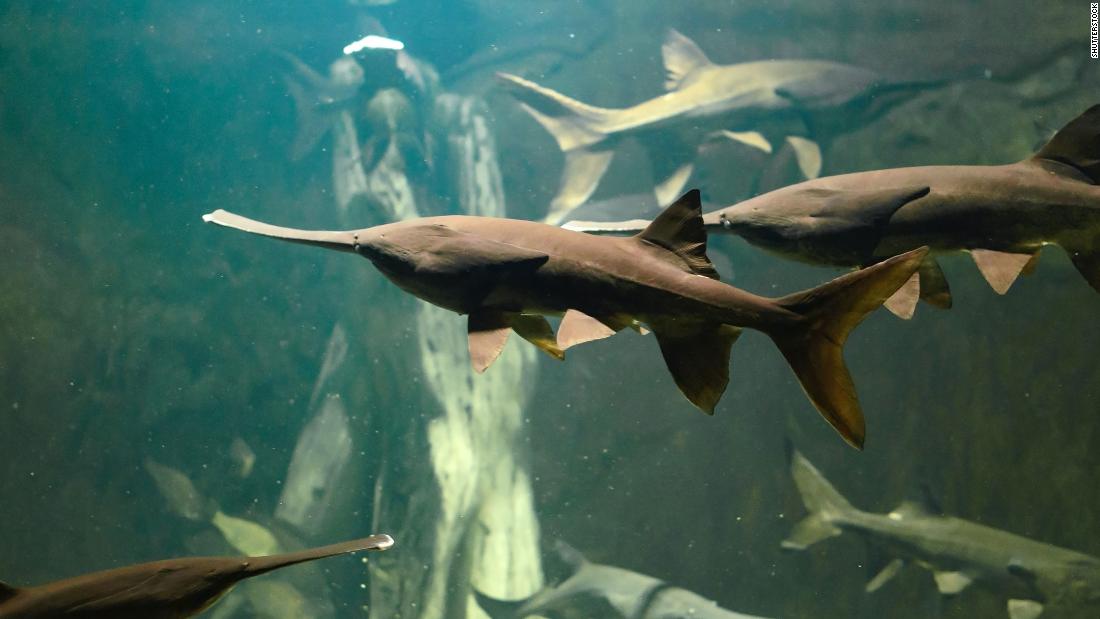

One of the largest freshwater species, Chinese paddlefish has been declared extinct.
Chinese paddlefish
- The Chinese paddlefish (Psephurus gladius) was an iconic species, measuring up to 7 m in length, dating back from 200 million years ago, and therefore swimming the rivers when dinosaurs ruled the Earth.
- Its ancestral home was the Yangtze River.
- It was once common in the Yangtze, before overfishing and habitat fragmentation — including dam building — caused its population to dwindle from the 1970s onwards.
- Between 1981 and 2003, there were just around 210 sightings of the fish. The researchers estimate that it became functionally extinct by 1993, and extinct sometime between 2005-2010.
How did the study determine that it has gone extinct?
- Chinese researchers made this conclusion based on the Red List criteria of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
- The Red List has several categories for extinction, or for how endangered a species is.
- For example, “extinct in the wild” means a species survives only in a captive environment while “locally extinct” means a species has ceased to exist in a particular area but may exist in other areas.
- Then there is “functionally extinct”, which means the species continues to exist but it has too few members to enable to reproduce meaningfully enough to ensure survival.
- To be “globally extinct”, it means a species has no surviving member anywhere. Such a conclusion is reached when there is no reasonable doubt left that its last member has died.
How does extinction status matters for conservation?
- Declaring a species extinct is an elaborate process.
- It involves a series of exhaustive surveys, which need to be taken at appropriate times, throughout the species’ historic range and over a time-frame that is appropriate to the species’ life cycle and form.
- When these surveys fail to record the existence of any individuals belonging to that species, a species may be presumed to be extinct.
- Once declared extinct, a species is not eligible for protective measures and conservation funding; therefore, the declaration has significant consequences.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Senna spectabilis
Mains level: Impacts of the invasive alien species

The Kerala Forest Department is planning to adopt steps to arrest the rampant growth of invasive plants, especially Senna spectabilis, in the forest areas of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve (NBR).
Senna spectabilis
- The Senna spectabilis species was planted as avenue trees in Wayanad. The vayal ecosystem (marshy land) of the forest area now has this plant in large numbers.
- The spread is posing a major threat to the forest areas of the reserve, owing to its quick growth and coppicing character.
- The tree species was found in nearly 10 sq km area of the 344.44 sq km sanctuary around five years ago.
- The plant has started to invade the adjacent Bandipur and Nagarhole tiger reserves in Karnataka and the Mudumalai tiger reserve in Tamil Nadu.
- Now, it had invaded to more than 50 sq km of the sanctuary Wayanad WLS.
- A recent study of the Ferns Nature Conservation Society recorded the presence of the plant in 78.91 sq km area of the sanctuary.
Impact
- An adult tree grows up to 15 to 20 metres in a short period of time and every year distributes thousands of seeds after gregarious flowering.
- The thick foliage arrests the growth of other indigenous tree and grass species and causes food shortage for the wildlife population, especially herbivores.
- Moreover, wildlife will not feed on the leaf of the treeas it is not palatable for them.
- The allelochemicals produced by this plant adversely affect the germination and growth of the native species.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now






/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/49388585/16071828377_85109fdee4_o.0.0.jpg)