Why in the News?
India’s National Security Council Secretariat recently hosted envoys from the US, UAE, Saudi Arabia, France, Italy, Germany, Israel, Jordan, and the EU to review progress on the India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC).
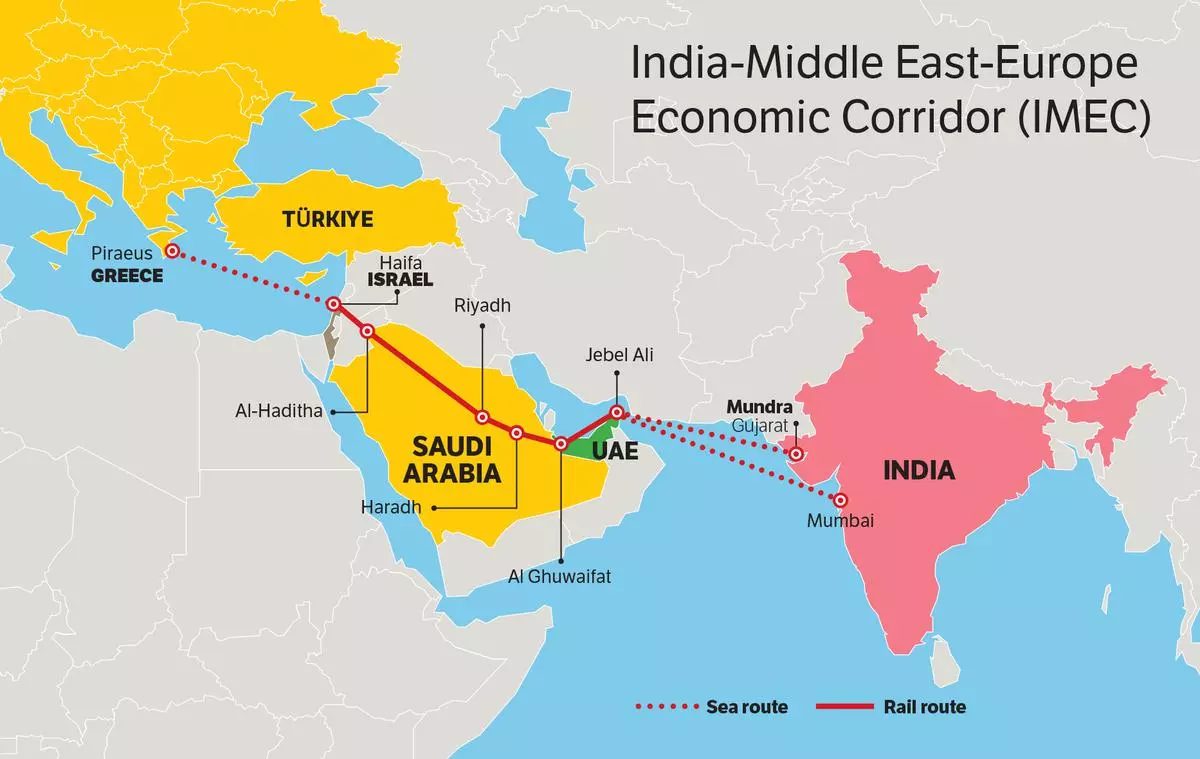
About IMEC Project:
- Part of the Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII) for developing connectivity in emerging regions.
- MoU signed on 10 September 2023 at the G20 New Delhi Summit.
- Members: India, US, UAE, Saudi Arabia, France, Germany, Italy, European Union.
- Aim: Integrate Asia, Middle East, and Europe to boost transport efficiency, reduce costs, create jobs, cut greenhouse gas emissions, and strengthen economic unity.
- Structure:
- East Corridor: India to Arabian Gulf.
- Northern Corridor: Gulf region to Europe.
- Key Ports:
- India – Mundra, Kandla, Jawaharlal Nehru Port (Mumbai).
- Middle East – Fujairah, Jebel Ali, Abu Dhabi, Dammam, Ras Al Khair.
- Israel – Haifa.
- Europe – Piraeus, Messina, Marseille.
- Infrastructure includes: Railway links, ship-to-rail hubs, roads, electricity cables, hydrogen pipelines, and high-speed data cables.
Impact of Gaza War:
- Derailed work: Conflict from late 2023 halted stakeholder meetings and derailed western leg (Middle East–Europe) progress.
- Jordan–Israel relations at historic low; Saudi–Israel normalisation stalled.
- Regional rivalries (e.g., Saudi–UAE trade competition) hinder unified operational planning.
Significance:
- Economic: EU is India’s largest trading partner; corridor promises faster, cheaper trade with reduced emissions.
- Strategic: Strengthens India’s role in West Asia and positions it as a connector between Europe and the Middle East.
- Energy & Technology: Potential for clean hydrogen pipelines, electricity and data cable links.
- Resilience: Provides alternative to Red Sea shipping routes vulnerable to disruptions.
| [UPSC 2025] India is one of the founding members of the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC), a multimodal transportation corridor, which will connect:
Options: (a) India to Central Asia to Europe via Iran* (b) India to Central Asia via China (c) India to South-East Asia through Bangladesh and Myanmar (d) India to Europe through Azerbaijan |